S2 AP HUMAN FINAL
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 1:18 PM on 5/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
1
New cards
Agriculture
\
modifying the environment to raise plants or animals for food or other uses’
modifying the environment to raise plants or animals for food or other uses’
2
New cards
Extensive agriculture
\
agriculture that uses small amounts of labor on a large area of land
agriculture that uses small amounts of labor on a large area of land
3
New cards
Intensive agriculture
\
agriculture that uses a lot of labor on a small area of land
agriculture that uses a lot of labor on a small area of land
4
New cards
Shifting cultivation
subsistence agriculture form used in tropical areas that cuts down vegetation for burning (__**Slash and Burn**__) which provides nourishment to the soil – every few years the farmer must move to a new location as the nutrients are gone and repeat
5
New cards
Ranching
commercial agriculture that allows livestock to wander a large area to feed using for meat or wool
6
New cards
Nomadic herding
raising animals and traveling from place to place with them to find pasture for their animals
7
New cards
Market gardening
Small scale food production (fruits/veggies) for sale at local markets.
8
New cards
Plantation agriculture
cash crops (cotton, sugar, coffee, tea) grown on large estates, usually for export
9
New cards
mixed crop/livestock systems:
combination of cash crops and livestock to complement land and labor demands across the year
10
New cards
Clustered
a pattern of rural settlement in which the houses and farm buildings of each family are situated close to each others' fields and surround the settlement
11
New cards
Disperse
settlement pattern with people living relatively far from each other on their farms
12
New cards
Linear settlement
a rural land use pattern that creates a long, narrow settlement around a river, coast, or road that looks like a line
13
New cards
\
Long lot
Long lot
a rural land use pattern that divides land into long, narrow lined up along a waterway or road
14
New cards
Metes and bounds:
\
a system of describing parcels of land where the metes are the lines (including angle and distance that surround the property) and bound describes features such as a river or public road
a system of describing parcels of land where the metes are the lines (including angle and distance that surround the property) and bound describes features such as a river or public road
15
New cards
Surveying
Examining and measuring the surface of the Earth for planning, preparing to build, or mapping
16
New cards
Township and range:
a system of dividing large parcels of where the townships describe how far north or south from the center point
17
New cards
Fertile Crescent
a crescent-shaped area in Southwest Asia where settled farming first began to emerge leading leading to the rise of cities
18
New cards
Columbian Exchange
a widespread exchange of animals, plants, culture, human populations, communicable diseases, and ideas between the American and Afro-Eurasian hemispheres that was launched by Columbus's voyages
19
New cards
First Agricultural Revolution
\
time when people first domesticate plants and animals which allows people to live in one place
time when people first domesticate plants and animals which allows people to live in one place
20
New cards
Domestication
the process of taming plants or animals for human use
21
New cards
Second Agricultural Revolution:
coincides with the Industrial Revolution; increasing yield and access through machines and transportation
Effects of the Second Agricultural Revolution: New technology, Led to increased food production, Better diet, longer life, and more people available for work in factories, Shifting demographics (moving to cities, less farmers)
Effects of the Second Agricultural Revolution: New technology, Led to increased food production, Better diet, longer life, and more people available for work in factories, Shifting demographics (moving to cities, less farmers)
22
New cards
Green Revolution
\
the spread of new technologies like high yield seeds and chemical fertilizers to the developing world in the 1960s and 1970s
the spread of new technologies like high yield seeds and chemical fertilizers to the developing world in the 1960s and 1970s
23
New cards
Positive of Green Revolution
\
* Able to grow more crops on same amount of land which decreases food prices
* More crops grown on same size land
* Improvement in variety
* Able to grow more crops on same amount of land which decreases food prices
* More crops grown on same size land
* Improvement in variety
24
New cards
Negative Green Revolution
\
* Destroying local land and traditional modes of agricultural production
* Decreasing biodiversity (hybrid seeds diminish local plant diversity)
* Impact of chemicals
* Destroying local land and traditional modes of agricultural production
* Decreasing biodiversity (hybrid seeds diminish local plant diversity)
* Impact of chemicals
25
New cards
subsistence agriculture:
form of farming in which nearly all of the crops or livestock raised are used to maintain the farmer and the farmer's family, leaving little, if any, surplus for sale or trade.
26
New cards
Commercial Agriculture
\
he production of crop for sale and profit
he production of crop for sale and profit
27
New cards
Monoculture
\
Growing one crop in a farm system at a given time
Growing one crop in a farm system at a given time
28
New cards
Mono-Cropping
\
Growing one crop in a farm system year after year.
Growing one crop in a farm system year after year.
29
New cards
Bid-rent theory
a geographic theory that states the price and demand for real estate change as the distance from the central business district (CBD) increases
30
New cards
Commodity Chain
\
activities involved in the creation of a product: design, production of raw materials, manufacturing and assembly, distribution
activities involved in the creation of a product: design, production of raw materials, manufacturing and assembly, distribution
31
New cards
Agribusiness
\
system of commercial agriculture that links various industries to the farm
system of commercial agriculture that links various industries to the farm
32
New cards
Economies of scale
\
cost advantages that come producing a large amount of an item
cost advantages that come producing a large amount of an item
33
New cards
Von Thünen’s model
helps to explain rural land use by emphasizing the importance of transportation costs associated with distance from the market. rings distribute various farming activities into concentric rings around a central market city.
\
* Dairy and gardening is close to the center because it is a perishable good, where the farmer can maximize the profit, intensive agriculture
* Forests are close to the market, because people need it for fuel and This needed to be close and is expensive to transport
* Extensive agriculture (grains, field crops) do not perish as quickly as vegetables and milk and need plenty space to grow
* Livestock and ranching further from the market for cheap land (need more of it and transportation is cheap)
\
* Dairy and gardening is close to the center because it is a perishable good, where the farmer can maximize the profit, intensive agriculture
* Forests are close to the market, because people need it for fuel and This needed to be close and is expensive to transport
* Extensive agriculture (grains, field crops) do not perish as quickly as vegetables and milk and need plenty space to grow
* Livestock and ranching further from the market for cheap land (need more of it and transportation is cheap)
34
New cards
Global Supply Chain
\
a worldwide network to maximize profits in production
a worldwide network to maximize profits in production
35
New cards
Export commodity
\
goods sent from one country to another for sale ( Some countries have become highly dependent on one or more export commodities including Haitian coffee, Sri Lankan Tea, and Cuban Sugar)
goods sent from one country to another for sale ( Some countries have become highly dependent on one or more export commodities including Haitian coffee, Sri Lankan Tea, and Cuban Sugar)
36
New cards
Land cover change
process by which agricultural areas are lost to development
37
New cards
Conservation
\
the protection of wildlife and natural resources
the protection of wildlife and natural resources
38
New cards
Deforestation
human-driven and natural loss of trees for not forest use
39
New cards
Desertification
the process of a dry area becoming drier and losing vegetation
40
New cards
**Irrigation**
\
moving water to where you need it
moving water to where you need it
41
New cards
Draining Wetlands
\
drainage for agricultural practices
drainage for agricultural practices
42
New cards
Pastoral nomadism
herding animals and migrating with them to find pasture areas without a permanent pasture area
43
New cards
Soil salinization
the slow build up of salt in soil, particularly in irrigated areas, that makes soil unable to grow plants
44
New cards
Terrace farming
method of growing crops on the sides of hills or mountains by planting on man-made steps (terraces)Agricultural Biotechnolog
45
New cards
Agricultural Biotechnology
\
the use of scientific tools and techniques to modify plants and animals (Pesticide resistant crops, Antibiotics, Biofuels)
the use of scientific tools and techniques to modify plants and animals (Pesticide resistant crops, Antibiotics, Biofuels)
46
New cards
GMO
\
plants or animals whose DNA has been genetically modified, often through a combination of DNA from similar plant or animal species for desired traits.
plants or animals whose DNA has been genetically modified, often through a combination of DNA from similar plant or animal species for desired traits.
47
New cards
Aquaculture
raising of fish and shellfish in ponds and controlled saltwater hatcheries raising of fish and shellfish in ponds and controlled saltwater hatcheries
48
New cards
Value Added Foods
\
foods that have increased in value due to alterations in production, size, shape, appearance, location, and/or convenience
foods that have increased in value due to alterations in production, size, shape, appearance, location, and/or convenience
49
New cards
Organic Farming
\
crops produced without the use synthetic or industrially produced pesticides and fertilizers or genetically engineered seeds
crops produced without the use synthetic or industrially produced pesticides and fertilizers or genetically engineered seeds
50
New cards
Fair Trade
trade between MDC and LDC in which fair prices are paid to the producers
51
New cards
community-supported agriculture (CSA):
\
individuals who pledge support to a farm operation so that growers and consumers provide mutual support
individuals who pledge support to a farm operation so that growers and consumers provide mutual support
52
New cards
Urban farming
\
integrating growing crops or raising animals into an urban ecosystem
integrating growing crops or raising animals into an urban ecosystem
53
New cards
Dietary Shifts
movement from processed foods, meat, and sugars towards one more based in fruits and vegetables
54
New cards
Food Insecurity
the state of being without reliable access to a sufficient quantity of affordable, nutritious food
\
\
55
New cards
Food Desert
\
geographic area where large grocery stores are scarce or missing and residents have limited access to fresh nutritious foods. Typically found in urban, low-income neighborhoods
geographic area where large grocery stores are scarce or missing and residents have limited access to fresh nutritious foods. Typically found in urban, low-income neighborhoods
56
New cards
\
**Women in Agriculture**
**Women in Agriculture**
\
* Women are frequently denied loans or financial support, cannot afford tuition or fees; or rural communities lack funding to provide schools.
* Women may be unable to obtain or access inputs to improve productivity (e.g., land, animals, equipment, seeds, fertilizer, or infrastructure).
* Women practicing subsistence agriculture may not be able to generate a surplus.
* Impacts of exposure to environmental hazards (agricultural pollution, chemicals, groundwater pollution) that cause health problems for women and children which have an economic impact (household, local, or national scale).
* In many societies women hold agricultural knowledge and skills passed down to daughters.
* In many societies women represent a spiritual ideal of fertility that is tied to beliefs regarding agricultural productivity.
* Laws and government policies preventing women from acquiring land tenure, owning, or inheriting land.
* Women may lack access to political processes (voting), and institutions (representative government); or females lack political power to improve law and policy affecting women’s issues.
* Women are frequently denied loans or financial support, cannot afford tuition or fees; or rural communities lack funding to provide schools.
* Women may be unable to obtain or access inputs to improve productivity (e.g., land, animals, equipment, seeds, fertilizer, or infrastructure).
* Women practicing subsistence agriculture may not be able to generate a surplus.
* Impacts of exposure to environmental hazards (agricultural pollution, chemicals, groundwater pollution) that cause health problems for women and children which have an economic impact (household, local, or national scale).
* In many societies women hold agricultural knowledge and skills passed down to daughters.
* In many societies women represent a spiritual ideal of fertility that is tied to beliefs regarding agricultural productivity.
* Laws and government policies preventing women from acquiring land tenure, owning, or inheriting land.
* Women may lack access to political processes (voting), and institutions (representative government); or females lack political power to improve law and policy affecting women’s issues.
57
New cards
urbanization:
refers to the movement of people to towns/cities and the resulting expansion of the rural countryside
* influences on urbanization: changes in transportation and communication, population growth, migration, economic development, and government policies
* influences on urbanization: changes in transportation and communication, population growth, migration, economic development, and government policies
58
New cards
site:
the actual physical qualities of the place that a city occupies which can influence origin, function, and growth e.g. coastal plain, valley, mountains
59
New cards
situation:
the relative location of a city (what is it near) which can influence origin, function, and growth e.g. located near shipping routes (Hong Kong, Singapore)
60
New cards
megacity:
a large city with over 10 million people and found increasingly in the periphery and semi-periphery e.g. LDCs: Mumbai, São Paulo, Jakarta, Lima, Shenzhen, MDC: Paris
61
New cards
meta-city:
a large city with over 20 million people and found increasingly in the periphery and semi-periphery e.g. LDCs: Delhi, Mexico City, Cairo, Beijing, Mumbai MDCs: Tokyo
62
New cards
suburbanization:
the transformation of large areas of rural land to urban uses
63
New cards
suburb:
a residential area located on the periphery of a city
64
New cards
suburban sprawl:
unrestricted suburban growth and development over large areas spreading out from a city in which cars provide primary source of transportation
65
New cards
edge city:
a concentration of residential and economic (business, shopping, entertainment) activity located in the suburbs
66
New cards
exurb:
a residential area beyond the suburbs, often in more rural areas
67
New cards
world city:
city that functions as a service center of the world economy driving globalization at the top of the urban hierarchy (hamlet, village, town, city, world city) e.g. New York City, London, Tokyo, Paris
68
New cards
network:
a system of interconnected people, goods, information, transportation, communication, finance
69
New cards
globalization:
the process of increased interconnectedness among countries most notably in the areas of economics, politics, and culture
70
New cards
urban hierarchy:
settlements ranked by population, number of services and sphere of influence e.g. hamlet, village, town, city
71
New cards
rank-size rule:
the idea that the population of a city or town will be inversely proportional to its rank in the urban hierarchy if the largest city in a country contained 1 million citizens then the: 2nd largest city would contain 500,00 (1 million/2) 3rd largest city would contain 333,333 (1 million/3) 4th largest city would contain 250,000 (1 million/4)
72
New cards
primate city:
a country's largest city, at least twice as large as the next largest city and more than twice as significant (usually the capital city) and represents national culture e.g. Paris, France and London, England
73
New cards
Christaller’s Central Place Theory (early 1933)
• explains the distribution, size, location, and interaction of settlements in an urban system • settlements provide a set of goods and services to their hinterland, which is the surrounding market area • larger settlements are fewer and farther apart and serve a large market area, providing low order goods as well as high-order goods • smaller centers serve smaller market areas generally providing low order goods • low-order goods: products that are replenished frequently such as food and other routine household items • high-order goods: specialized items such as cars, furniture, fine jewelry, and household appliances that are bought less often • threshold: the minimum number of people needed for a business to prosper • range: the maximum distance people
74
New cards
urban models
models that are useful for explaining internal structures of cities
75
New cards
Burgess Concentric Zone Model E.W. Burgess (1923)
a spatial model of the American city that suggests the existence of five concentric rings around a CBD (Central Business District) • center circle: the city grows outward beginning with the Central Business District • second ring: the zone in transition where industry and poorer-quality housing are located (usually new immigrants to the city in small quarters as well as single individuals in rooming houses) • third ring: zone of modest older homes typically for the working class • fourth ring: zone of better residences where more spacious houses for middle-class families • fifth ring: commuter zone made up of people who work in the center and choose to live in the suburbs
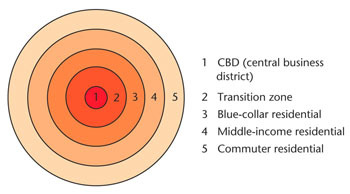
76
New cards
Hoyt Sector Model Homer Hoyt (1939)
a spatial model of the American city that suggests that land-use areas conform to a wedge-shaped pattern focused on the downtown core (CBD)
• focus is on residential patterns and where the wealthy choose to live • the city develops in a series of sectors • at the center: Central Business District • as the city grows, activities expands in a wedge, or sector, from the center • industrial and retailing activities develop outward from the CBD • once a district with "high-class" housing is established, the most expensive houses are built on the outer edge of that district further from the center • middle class residential sectors develop in proximity to high rent residential and then low-class residential nearest to industrial and transportation zones
• focus is on residential patterns and where the wealthy choose to live • the city develops in a series of sectors • at the center: Central Business District • as the city grows, activities expands in a wedge, or sector, from the center • industrial and retailing activities develop outward from the CBD • once a district with "high-class" housing is established, the most expensive houses are built on the outer edge of that district further from the center • middle class residential sectors develop in proximity to high rent residential and then low-class residential nearest to industrial and transportation zones
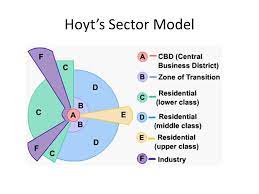
77
New cards
Multiple Nuclei Model Chauncey Harris and E.L. Ullman (1945)
a spatial model that shows the mid 20th century American city consisting of several land-use zones (nodes) arranged around a CBD (Central Business District)
• the CBD acts as the nucleus within the metropolitan area upon which activities revolve in various land-use zones or nodes • examples of these nodes include: ports, neighborhood business centers, universities, airport, and parks • some activities go with particular nodes while others do not, for example, a university node may attract well-educated residents, bookstores, and copy places, or, the airport may attract hotels and warehouses • incompatible land use activities will not be clustered together, for example, industries will not be placed near high-class housing
• the CBD acts as the nucleus within the metropolitan area upon which activities revolve in various land-use zones or nodes • examples of these nodes include: ports, neighborhood business centers, universities, airport, and parks • some activities go with particular nodes while others do not, for example, a university node may attract well-educated residents, bookstores, and copy places, or, the airport may attract hotels and warehouses • incompatible land use activities will not be clustered together, for example, industries will not be placed near high-class housing
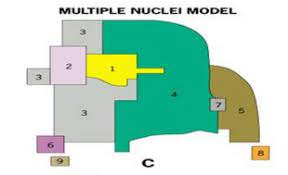
78
New cards
Galactic City Model (Peripheral Model)
a spatial model in which American urban areas consist of a central city surrounded by a large suburban area, shopping malls, office parks, industrial areas, and service complexes tied together by a beltway, or ring road
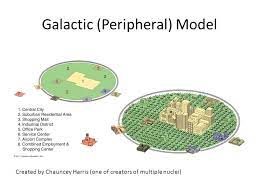
79
New cards
Latin American City Model
a spatial city model that includes a prestigious, commercial axis (spine) which emanates outward from the CBD and is surrounded by a peripheral area containing squatter settlements; the city structure can be attributed to colonialism, the rapid rise of industrialization, and rapid population increase
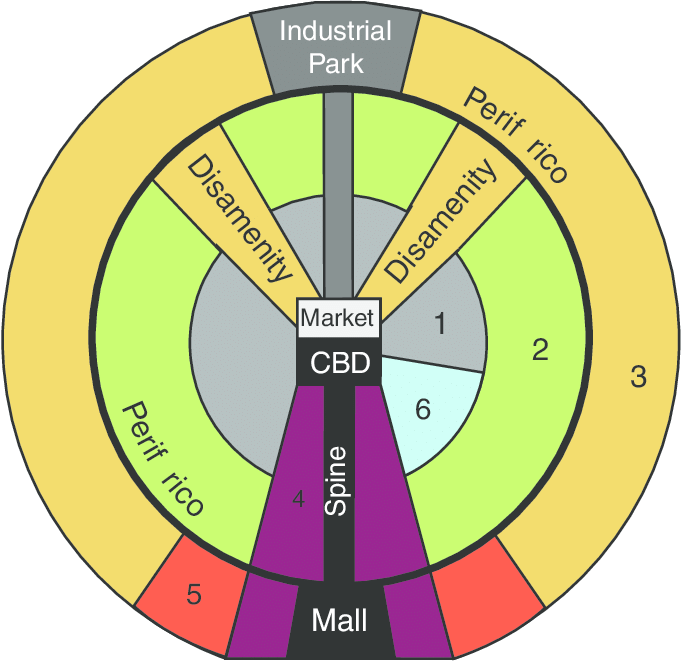
80
New cards
Southeast Asian City Model
a spatial city model that includes an old colonial port zone that is the focal point of the city reflecting a city oriented around exports, and radiating outward from the port zone are the Western commercial zone and Alien commercial zone
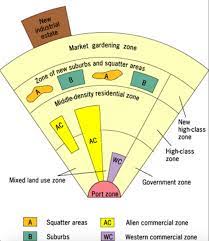
81
New cards
Sub-Saharan African City Model
a spatial city model that is difficult to formulate due to the imprint of European colonialism, but often consists of a colonial CBD as well as a traditional CBD, and a market zone that is surrounded by squatter settlements (informal satellite townships)
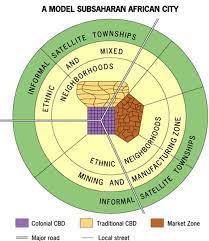
82
New cards
urban renewal:
the redevelopment of areas within an urban area, typically neighborhoods in economic decline
83
New cards
gentrification:
the restoration of deteriorated urban areas by wealthier (mostly middle-income) people who move into, renovate, and restore housing and sometimes businesses
84
New cards
industrialization:
process that occurs when countries evolve from primarily agricultural producing basic, primary goods to one based on mechanized mass manufacturing of goods (craftsmen are replaced by assembly lines)
85
New cards
spread of industrialization:
caused food supplies to increase and populations to grow created new industrial jobs in the cities changed social class structures caused investors in industry to seek out more raw materials and new markets contributed to the rise of colonialism and imperialism
86
New cards
primary sector:
economic activity that involves extracting (raw materials) or harvesting (food) products e.g. gathering industries (renewable resources): agriculture, forestry, hunting and gathering, fishing, grazing e.g. extractive industries (nonrenewable resources): mining, quarrying
87
New cards
secondary sector:
economic activity that processes raw materials and transforms them into finished goods e.g. manufacturing industries
88
New cards
tertiary sector:
economic activity that provides services e.g. health, legal, education, restaurants, stores
89
New cards
quaternary sector:
economic activity that involves collecting, processing & manipulation of information & capital e.g. finance, insurance, computer services
90
New cards
quinary sector:
economic activity consisting of high-level decision making and advancement of human capacities e.g. scientific research, higher education, government
91
New cards
core:
countries where economic power (wealth, innovation, technology) is concentrated that control and benefit from the global market on which periphery and semi-periphery countries depend e.g. U.S., Western European countries, Canada, Australia, Japan
92
New cards
semi-periphery:
countries that are industrializing that exert more power in the world economy than the periphery, but are dominated to some degree by the core
93
New cards
periphery:
countries with low levels of economic productivity and a disproportionately small share of the world’s wealth with weaker state institutions, lower standards of living and are often dependent on the core e.g. Sub-Saharan African countries (except South Africa), parts of South America and Asia
94
New cards
break of bulk point:
the transfer of transported cargo from one kind of carrier to another e.g. port: from ship to truck
95
New cards
Least Cost Theory:
Alfred Weber
• theory that describes the optimal location of an industry in relation to costs of transport, labor, and relative advantages of agglomeration
• an industry is located where it can minimize its costs, and therefore maximize its profits
• theory that describes the optimal location of an industry in relation to costs of transport, labor, and relative advantages of agglomeration
• an industry is located where it can minimize its costs, and therefore maximize its profits
96
New cards
agglomeration:
the clustering of businesses that can benefit from close proximity because they share skilled-labor e.g. auto industry in Michigan technology industry in northern California insurance industry in Connecticut
97
New cards
footloose industries:
industry in which the location is not impacted by the cost of transporting either raw materials or finished products e.g. software, insurance, semiconductors, computer chips, e-commerce
98
New cards
GDP (gross domestic product):
measurement of the total value of goods and services produced within the borders of a country during a specific time period, usually one year
99
New cards
GNP (gross national product):
measurement of the total value of goods and services produced within the borders of a country plus the net income from companies that are located outside the country and foreign investments during a specific time period, usually one year
100
New cards
GNI per capita (gross national income per capita):
measurement of the total value of goods and services produced within the borders of a country plus the net income from companies that are located outside the country and foreign investments, but minus dividend payments and indirect business taxes during a specific time period, usually one year, divided by the population