the role of oxygen and sulphur in drug molecules
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
lecture 4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
oxygen, its orbitals and characteristics?
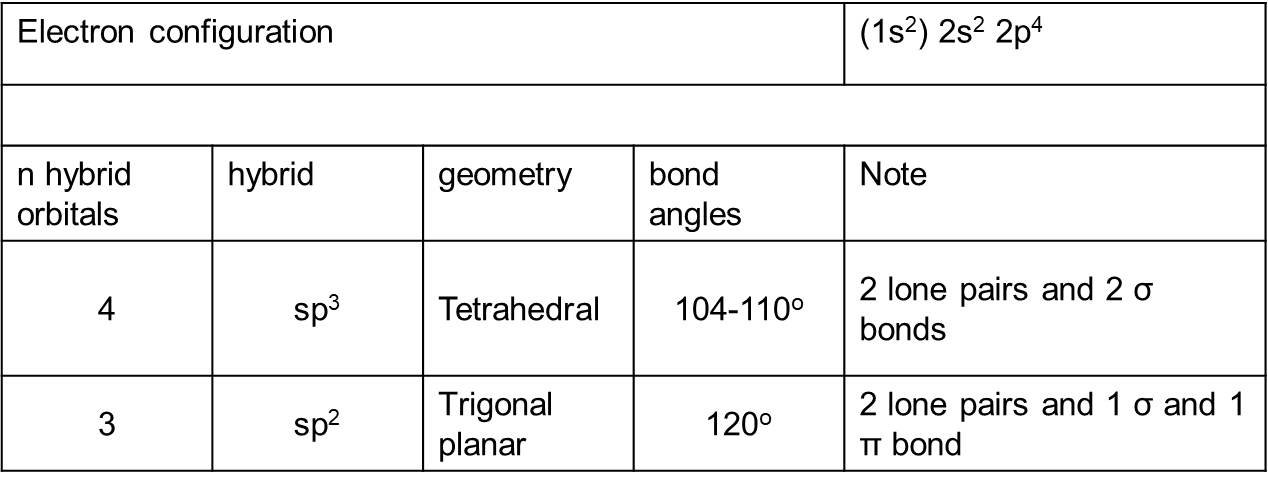


bond angles of oxygen vary with the size of what?
size of the substituents
due to higher electronegativity of the oxygen atom, the lone pair of electrons on oxygen atoms are generally less likely to be what compared to those on a nitrogen atom?
the lone pair of electrons on oxygen atoms less likely to be protonated than those on a nitrogen atom
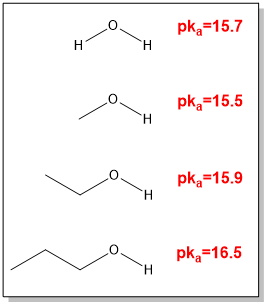
what are the pKa values of water and alcohols
MeOH
EtOH
nPrOH

MeOH is metabolised to what?
formaldehyde, which is an irritant
EtOH is an antimicrobial due to what?
due to its disruption of microbial membranes ( effective concentration is >70%)
nPrOH has stronger antimicrobials than EtOH but a higher what?
higher toxicity than EtOH
the loss of an alcohol function does not dictate biological activity whereas, in general, what is the effect of the loss of amino group?
results in loss of biological activity
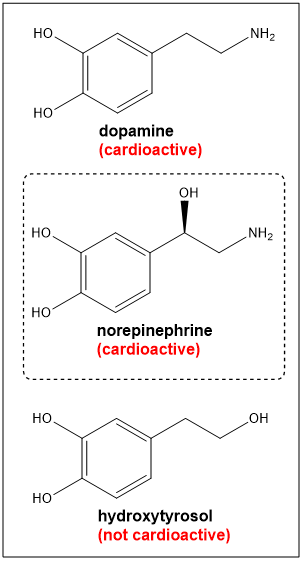
is dopamine, norepinephrine and hydroxytyrosol cardioactive or not?
no amine group on hydroxytyrosol- not cardioactive

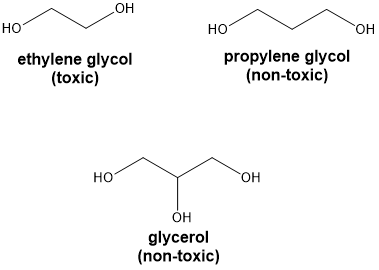
alcohols with 2 or 3 hydroxyl groups are known as what?
diols (glycols) and triols
-viscous, hygroscopic, water miscible, high boiling points

what kind of compounds are geminal diols?
hydrated carbonyl compounds
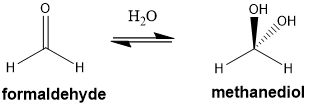

hydrocarbons with more than 3 hydroxyl groups are known as what?
polyols (e.g. carbohydrates)
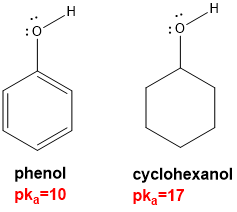
why are phenols are much stronger acids than alcohols?
due to delocalisation of the negative charge on the conjugate base (the phenoxide anion)
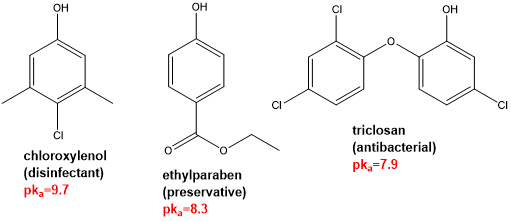
the more acidic phenols have which good properties?

good antibacterial properties
(e.g. triclosan which is added to toothpaste and household detergents due to its antibacterial action)
electron withdrawing groups in o- and p- positions help to further stabilise the phenoxide anion, which increases what?
the acidity of such phenols
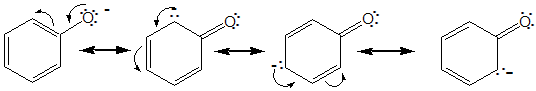

is the ionisation of phenols heterolytic or homolytic?
heterolytic
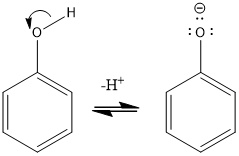

is the oxidation of phenols heterolytic or homolytic?
homolytic
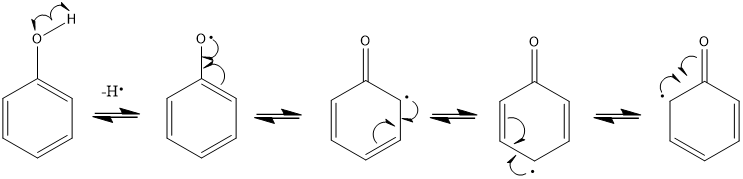

phenols are antioxidants, the phenoxy radical preferentially tends to dimerise and therefore terminate what?

the radical chain reaction
ethers are much less polar than what?
alcohols ( no hydrogen bond donor)
what were ethers formerly used in and describe their action?
•Formerly used in anaesthesia (e.g. diethyl ether), before non-flammable homologues were discovered to have the similar biological activity (halothane), by interacting with nerve cell membranes.
when are ethers liable to form potentially explosive epoxides?
in the presence of molecular oxygen and UV light
cyclic ethers are known as epoxides, describe this?
3 membered ring epoxides are highly reactive due to torsional strain
describe where ketones and aldehydes are commonly found?
Ketones are commonly found in the structure of drug molecules.
Aldehydes are less common. This is due to their higher reactivity towards nucleophiles.
Aldehydes are found in the open-chain form of reducing sugars.
the high reactivity of aldehydes results in what?
general cytotoxicity
the acidity of carboxylic acids is due to what?
the efficient resonance delocalisation of the negative charge of the carboxylate anions.
what can affect the acidity of carboxylic acids?
electronic effects (inductive and resonance)
in carboxylic acids, electron withdrawing groups can increase acidity by?
charge delocalisation
in carboxylic acids, electron donating groups can decrease acidity by?
charge localisation
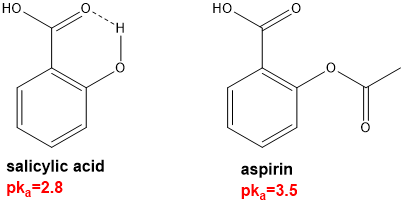
in carboxylic acids, H-bonding can affect acidity. describe how H-bonding affects acidity in the case of salicylic acid?

intramolecular H-bonding contributes to the charge delocalisation of the conjugate base of salicylic acid. Intramolecular H-bonding is not possible in the case of aspirin.
salts of carboxylic acids
formation of salts with alkali does what to solubility of drugs with carboxylic function?
increases the aqueous solubility of drugs with carboxylic functions
-this effect is limited by the size and lipophilicity of carboxylate anion
sulfur shares some of the same properties as oxygen, however describe the property differences?
sulfur has a larger atomic radius, lower electronegativity and empty 3d orbitals available for bonding
why are thiols more acidic than alcohols?
The larger sulphur atom is better at delocalising charge than oxygen
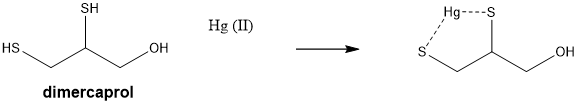
why can thiols be used to treat heavy metal poisoning ?
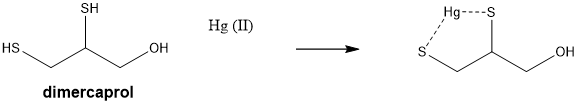
they have a larger binding affinity for heavy metals and therefore used to treat heavy metal poisoning by forming water soluble complexes that can be excreted
thiols are responsible for forming -S-S- by what?
by cysteine residues and for the detoxifying properties of glutathione (GSH)