BLD 324 Exam 3
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/114
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:38 PM on 11/12/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
1
New cards
What is the definition of Anemia?
Decrease in the oxygen-carrying capacity of blood.
2
New cards
What are the generic signs of anemia?
Pallor of skin and mucous membranes
Fatigue and dyspnea
neurologic symptoms (e.g. headache)
cardiac symptoms (e.g. palpitations)
if severe/prolonged - heart failure and death :(
Fatigue and dyspnea
neurologic symptoms (e.g. headache)
cardiac symptoms (e.g. palpitations)
if severe/prolonged - heart failure and death :(
3
New cards
What is the laboratory definition of anemia?
Decreased hemoglobin
4
New cards
What causes anemia in pregnant women?
Increase plasma volume while red cell mass is unchanged
5
New cards
What causes red blood cell production?
Production increases when Erythropoietin increases and it increases when kidneys detects hypoxia.
6
New cards
What causes increase of EPO?
Increases when kidneys detect hypoxia
7
New cards
What is the definition of Polycythemia?
Increased blood cells
8
New cards
What is the definition of Erythrocytosis?
Increased red cells
9
New cards
What is Absolute Erythrocytosis?
Increased red blood cell mass (truly an increase in red blood cell numbers in the vasculature)
10
New cards
What is PRIMARY Absolute Erythrocytosis?
-No underlying hypoxia and no increase in EPO, but RBCs increase dramatically
-Seen in polycythemia (rubra) vera
-leukemia
-NO INCREASE IN EPO
-Seen in polycythemia (rubra) vera
-leukemia
-NO INCREASE IN EPO
11
New cards
What is SECONDARY Absolute Erythrocytosis
-Increased red clood cell mass due to increased EPO
-Primary events are those that increase EPO
-Cause hypoxia
-INCREASE IN EPO
-Primary events are those that increase EPO
-Cause hypoxia
-INCREASE IN EPO
12
New cards
What are primary events that increase EPO?
-cigarette smoking
-living at high altitude
-increased HbF in newborns
-abnormal hemoglobins that don't carry oxygen well
-lung and cardiac diseases that impair oxygenation of blood
-living at high altitude
-increased HbF in newborns
-abnormal hemoglobins that don't carry oxygen well
-lung and cardiac diseases that impair oxygenation of blood
13
New cards
What is Relative Erythrocytosis?
-The red cells are unchanged in number, but the plasma component of blood changes
(Decrease in plasma volume creates false impression of erythrocytosis e.g elevated Hct)
-Lab results can be misleading
(Decrease in plasma volume creates false impression of erythrocytosis e.g elevated Hct)
-Lab results can be misleading
14
New cards
What laboratory testing is performed to distinguish relative and absolute polycythemia?
red cell mass measurement and measure plasma volume
15
New cards
What is the expected response to anemia?
Accelerated reticulocytosis
Requires: increase in reticulocytes and must be over 3% to adequately compensate for anemia
Requires: increase in reticulocytes and must be over 3% to adequately compensate for anemia
16
New cards
Microcytic ref range
17
New cards
Normocytic ref range
80-100 fL
18
New cards
Macrocytic ref range
>100 fL
19
New cards
What does cell color reflect?
Hemoglobin concentration in cells
20
New cards
Hypochromic ref range
21
New cards
Normochromic ref range
>32
22
New cards
Four major pathophysiological classifications
-Whole blood loss from the vascular system
-Increased destruction of red blood cells
-Mechanically by fragmentation - membrane rupture
-Increased destruction of red blood cells
-Mechanically by fragmentation - membrane rupture
23
New cards
What is the effect of fragmented red blood cells in the peripheral blood (shistocytes or schzocytes) on MCV and RDW?
MCV decreases; RDW increases
24
New cards
True or False. there is morphologic evidence in peripheral blood if the macrophage is fully successful in phagocytizing the red cell
False
25
New cards
What happens if the macrophage is partly successful in phagocytizing the red cell?
A sperocyte forms
26
New cards
What binds free heme in the plasma?
Hemopexin
27
New cards
What binds free hemoglobin?
Haptoglobin
28
New cards
What causes the anemia of pregnancy?
increase in plasma volume
29
New cards
What is the cause of Primary Absolute Erythrocytosis?
Increased EPO sensitivity
30
New cards
On Day 1 what distinguishes intravascular vs extravascular?
Plasma hemoglobin
31
New cards
What are pathophysiologic category of anemia?
Whole blood loss, Increased destruction, Decreased production
32
New cards
Where is conjugated bilirubin produced?
In the liver
33
New cards
Fragmentation Hemolysis (intravascular)
THINK OF GRAPH
THINK OF GRAPH
Decrease in serum haptoglobin as mega increase in plasma hemoglobin ( serum haptoglobin returns to normal when plasma hemoglobin decreases)
34
New cards
Macrophage-mediated Hemolysis (extravascular)
THINK OF GRAPH
THINK OF GRAPH
No plasma hemoglobin
No urinary hemoglobin
Normal serum haptoglobin
No urinary hemoglobin
Normal serum haptoglobin
35
New cards
Why does plasma volume in pregnant women increase?
They retain water in blood cells
36
New cards
Intravascular Hemolytic Anemia
decreased haptoglobin (binds Hb to try and save it), increased LDH and bilirubin
-INCREASED RETICS
-INCREASED RETICS
37
New cards
Macrophage mediated hemolytic anemia
-SPHEROCYTES
38
New cards
RDW in Hemolytic anemia
Elevated
39
New cards
Types of Anemias
-Sickle cell, chronic inflammation, sideroblastic, iron deficiency, intravascular hemolytic, extravascular hemolytic
40
New cards
Sickle Cell Anemia
-Normochromic, normocytic
-Defect in base pair : GAG - GTG
-Deoxygenated molecule is less soluble and it polymerizes (crystallization)
-Crystallization of hemoglobin leads to sickle shape
-Hemoglobinopathies
-RDW Increased
-Howell Jolly bodies and siderocytes
-thrombocytosis and leukocytosis
-Increased SI and total bilirubin
-Decreased haptoglobin
-Increased LD
-Increased Stool and Urine Urobilinogen
-Defect in base pair : GAG - GTG
-Deoxygenated molecule is less soluble and it polymerizes (crystallization)
-Crystallization of hemoglobin leads to sickle shape
-Hemoglobinopathies
-RDW Increased
-Howell Jolly bodies and siderocytes
-thrombocytosis and leukocytosis
-Increased SI and total bilirubin
-Decreased haptoglobin
-Increased LD
-Increased Stool and Urine Urobilinogen
41
New cards
Chronic Inflammation Anemia
Microcytic, Hypochromic
Serum Iron Decreased
FEP decreased due to decreased Iron
Serum Iron Decreased
FEP decreased due to decreased Iron
42
New cards
Sideroblastic Anemia
Microcytic, Hypochromic
43
New cards
Iron Deficiency Anemia
Microcytic, Hypochromic
LOW MCV HIGH RDW
RDW elevated
Ferritin Decreased
Total Serum Iron Decreased
Total iron Binding Capacity Increased
Percent Saturation Decreased
Protoporphyrin IX Increased
Zinc Protoporphyrin Increased
Serum transferrin receptor Increased
Stainable iron in bone marrow Decreased
LOW MCV HIGH RDW
RDW elevated
Ferritin Decreased
Total Serum Iron Decreased
Total iron Binding Capacity Increased
Percent Saturation Decreased
Protoporphyrin IX Increased
Zinc Protoporphyrin Increased
Serum transferrin receptor Increased
Stainable iron in bone marrow Decreased
44
New cards
Intravascular Anemia
Normocytic, Normochromic
45
New cards
Extravascular Anemia
Normocytic, Normochromic
46
New cards
What is a cause of Sideroblastic Anemia?
-Lead poisioning
47
New cards
What anemia are associated with anisocytosis?
iron deficiency anemia
48
New cards
What is the best test for iron deficiency anemia?
Hemoglobin content of reticulocytes
49
New cards
Is Ferritin a good test for iron deficiency?
No. It is sometimes unreliable
50
New cards
Percent Saturation
SI/ TIBC x 100%
51
New cards
What decreases first in development of iron deficiency anemia
Ferritin
52
New cards
Least likely to be seen in iron deficiency anemia
Macrocytosis
53
New cards
What does Ret-He assay measure?
Ret-He assay measures iron available for hematopoiesis
54
New cards
Increase Lymphocytes
Viral
55
New cards
Increase Neutrophils
Bacterial
56
New cards
Increase Eosinophils
allergies and parasites
57
New cards
How does Fe2+ enter cells?
Tf and TFR
58
New cards
Where does pain from sickle cell disease come from?
Due to blockage of blood vessels
59
New cards
What does sideroblastic anemia lead poisioning inhibit?
Inhibition of Ferrochelatase
60
New cards
Cause of sideroblastic anemia
Failure to incorporate iron into protoporphyrin IX
61
New cards
What cells do not have ferroportin?
Erythroblasts
62
New cards
What distinguishes the anemia of chronic inflammation from other anemias?
Relative Retic count
63
New cards
Hemoglobinopathies
Hereditary qualitative and quantitative defects in globin chain production
-Sickle cell
-Sickle cell
64
New cards
Qualitative hemoglobinopathies
normocytic anemias of increased destruction
65
New cards
Sickle cell disease
Homozygous
Most severe
Almost all erythrocytes are sickled
Thrombosis -> organ damage
autosplenectomy
Most severe
Almost all erythrocytes are sickled
Thrombosis -> organ damage
autosplenectomy
66
New cards
Sickle cell trait
Heterozygous condition
one HbA allele and one HbS allele
some normal hemoglobin.
one HbA allele and one HbS allele
some normal hemoglobin.
67
New cards
Papenheimer bodies
Iron fragments
68
New cards
Screening for HbS
-Cells are lysed by saponin (soap)
- Released Hb is deoxygenated by sodium dithionite
RESULTS:
HbA stays clear
HbS crystallizes and forms cloudy solution
- Confirm with electrophoresis
- Released Hb is deoxygenated by sodium dithionite
RESULTS:
HbA stays clear
HbS crystallizes and forms cloudy solution
- Confirm with electrophoresis
69
New cards
Neutrophils
Develop from the HSC (hematopoietic stem cell) by way of the CMP and the GMP (granulocyte monocyte progenitor)
-Circulating and Marginated cells: equilibrium of neutrophils in the vessels (total # of WBCs in the vessels is unchanged but there are more of them circulating)
-Respond to chemical agents released during inflammation
-Move up concentration gradient
-Exit the blood vessel via diapedesis
-Receptor for Antibody and Complement
-Circulating and Marginated cells: equilibrium of neutrophils in the vessels (total # of WBCs in the vessels is unchanged but there are more of them circulating)
-Respond to chemical agents released during inflammation
-Move up concentration gradient
-Exit the blood vessel via diapedesis
-Receptor for Antibody and Complement
70
New cards
life span of a neutrophil
7 hours in tissues
4 hours in bloodstream
4 hours in bloodstream
71
New cards
Electrical impedance
# of pulses
size of cells and complexity of granules
size of cells and complexity of granules
72
New cards
Monocytes
Tuberculosis
73
New cards
What are the FEP levels in Chronic Inflammation
FEP increased due to Decreased iron availability
74
New cards
Viral
leukocytosis, absolute lymphocytosis, atypical lymphocytes
75
New cards
MCHC of spherocytes
Increased MCHC because they have less membrane
Same HGB, smaller size
Same HGB, smaller size
76
New cards
Sickle Cell Disease
S + A2
77
New cards
Neutrophil Extracellular Traps
Forms a web that traps and digests bacteria with digestive enzymes from release DNA
78
New cards
Important contents of neutrophil granules
-myeloperoxidase
-lactoferrin
-lysozyme
-collagenase
-lactoferrin
-lysozyme
-collagenase
79
New cards
Eosinophils
CMP->GMP->EOP
Downregulate basophils
1-8 hours in blood, longer in tissues
High conc. in skin, GI tract, and respiratory tract
Downregulate basophils
1-8 hours in blood, longer in tissues
High conc. in skin, GI tract, and respiratory tract
80
New cards
Eosinophil granules contain:
major basic protein
eosinophil cationic protein
eosinophil cationic protein
81
New cards
Basophils
CMP->GMP-> unknown lol
Have an Fc receptor for IgE
Mediate hypersensitivity reactions
Life span: similar to eosinophils
Have an Fc receptor for IgE
Mediate hypersensitivity reactions
Life span: similar to eosinophils
82
New cards
Basophil granules contain
-compounds that recruit eosinophils
-Histamine
-Platelet and Endothelial cell activators (vaso active compounds)
-Histamine
-Platelet and Endothelial cell activators (vaso active compounds)
83
New cards
Myeloblast
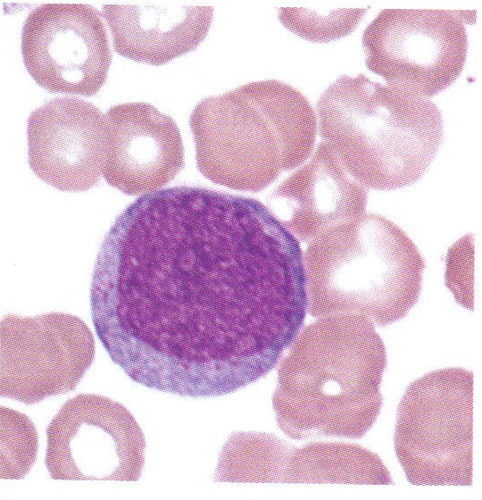
84
New cards
Promyelocyte
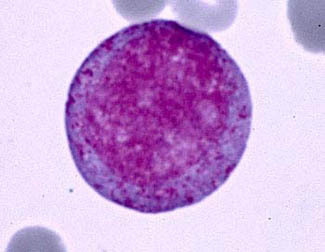
85
New cards
Myelocyte
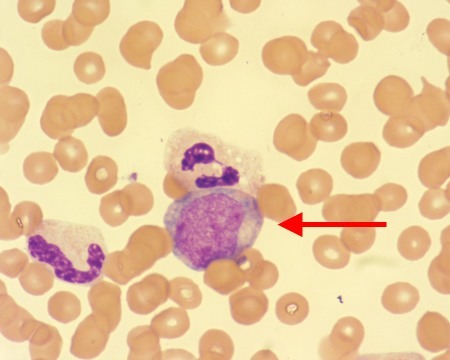
86
New cards
Metamyelocyte
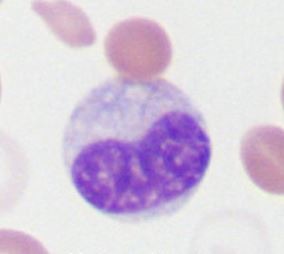
87
New cards
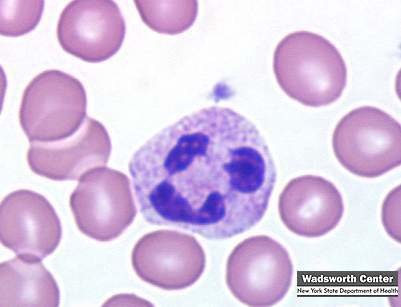
Band neutrophil
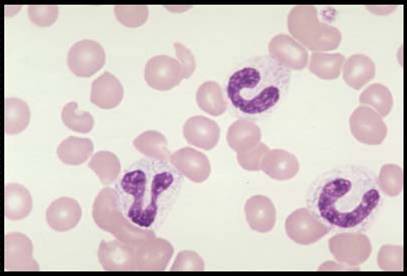
88
New cards
Neutrophil (PMN)
89
New cards
WBC in Adults vs Children
Healthy children have higher absolute numbers of lymphocytes than adults
90
New cards
How many lobes are in hypersegmentation of neutrophils
more than 5 lobes
Seen in megaloblastic anemia
Seen in megaloblastic anemia
91
New cards
How many lobes are in hyposegmentation of neutrophils
less than or equal to 2 lobes
genetic - inherited
Pelger-Huet anomaly
genetic - inherited
Pelger-Huet anomaly
92
New cards
Pelgeroid are seen when?
with infections and following chemotherapy
93
New cards
Toxic Triad
-Toxic granulation of neutrophils
-Dohle bodies in neutrophils
-Vaculoization of neutrophils
-Dohle bodies in neutrophils
-Vaculoization of neutrophils
94
New cards
Toxic granulation of neutrophils
Dark granules in cytoplasm
95
New cards
Dohle bodies in neutrophils
Areas of visible RNA in cytoplasm
Pale blue/gray round, oval, or rod shaped structures in cytoplasm
Pale blue/gray round, oval, or rod shaped structures in cytoplasm
96
New cards
Vacuolization of neutrophils
Foamy areas, bubbles, or open areas in the cytoplasm
Visible phagolysosomes
Associated with bacterial infections
Visible phagolysosomes
Associated with bacterial infections
97
New cards
Neutrophilia
Increase in neutrophils of any and all stages
Associated with inflammation but especially bacterial infections
Stimulated by G-CSF
Associated with inflammation but especially bacterial infections
Stimulated by G-CSF
98
New cards
Lymphocytosis
Increase in lymphocytes
99
New cards
Left Shift
Early release of neutrophilic cells
INCREASE bands
INCrease metamyelocytes
Increase myelocytes
INCREASE bands
INCrease metamyelocytes
Increase myelocytes
100
New cards
Monocytosis
Increase monocytes
TB
TB