Trade Protection
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Trade Protection
Involves government intervention in international trade through the imposition of trade barriers to prevent the free entry of imports into a country. This is done to protect domestic firms and the domestic economy, from foreign competition
Tariffs
They are taxes on imported goods and are the most common form of trade restriction. They have 2 purposes: generating government revenue and protecting domestic firms.
Tariffs Graph
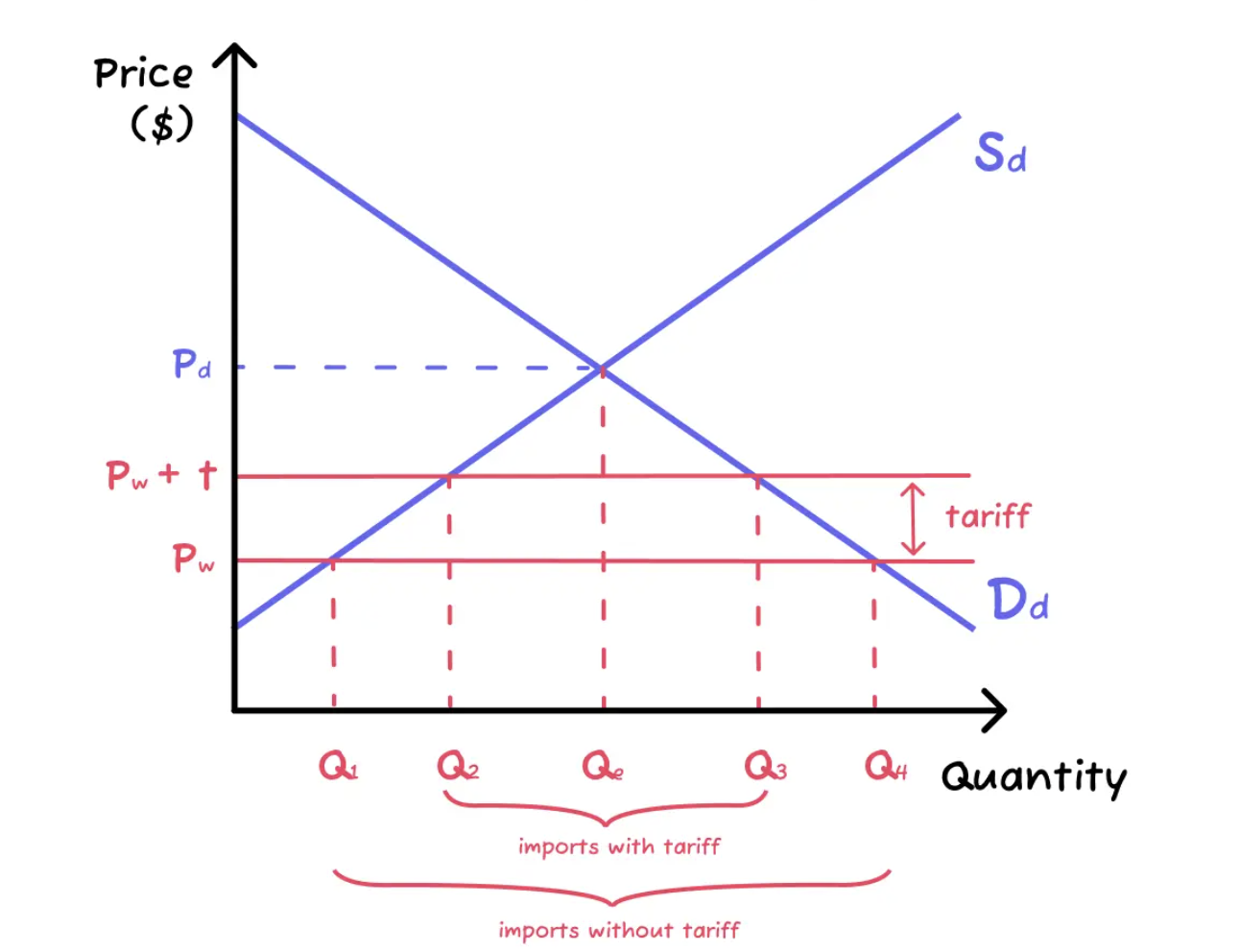
Tariffs Winners
Domestic producers: They are now supplying at a higher quantity and a higher price. Producer surplus increases
Workers: As producers now supply a larger quantity, this increases employment and protects the industry.
Government: Generating government revenue.
Tariffs Losers
Consumers: They are now paying a higher price for a lower quantity, which leads to a decrease in consumer surplus.
Income distribution: As the tax is on goods and services, it's regressive since it takes up a higher proportion of income from low-income individuals and households. This increases the disparity between incomes.
Inefficiency of production: The increase in domestic output represents an increase in production by relatively inefficient domestic producers, resulting in a waste of scarce resources
Foreign producers: They receive world price but export a smaller quantity since the quantity of imports decreases.
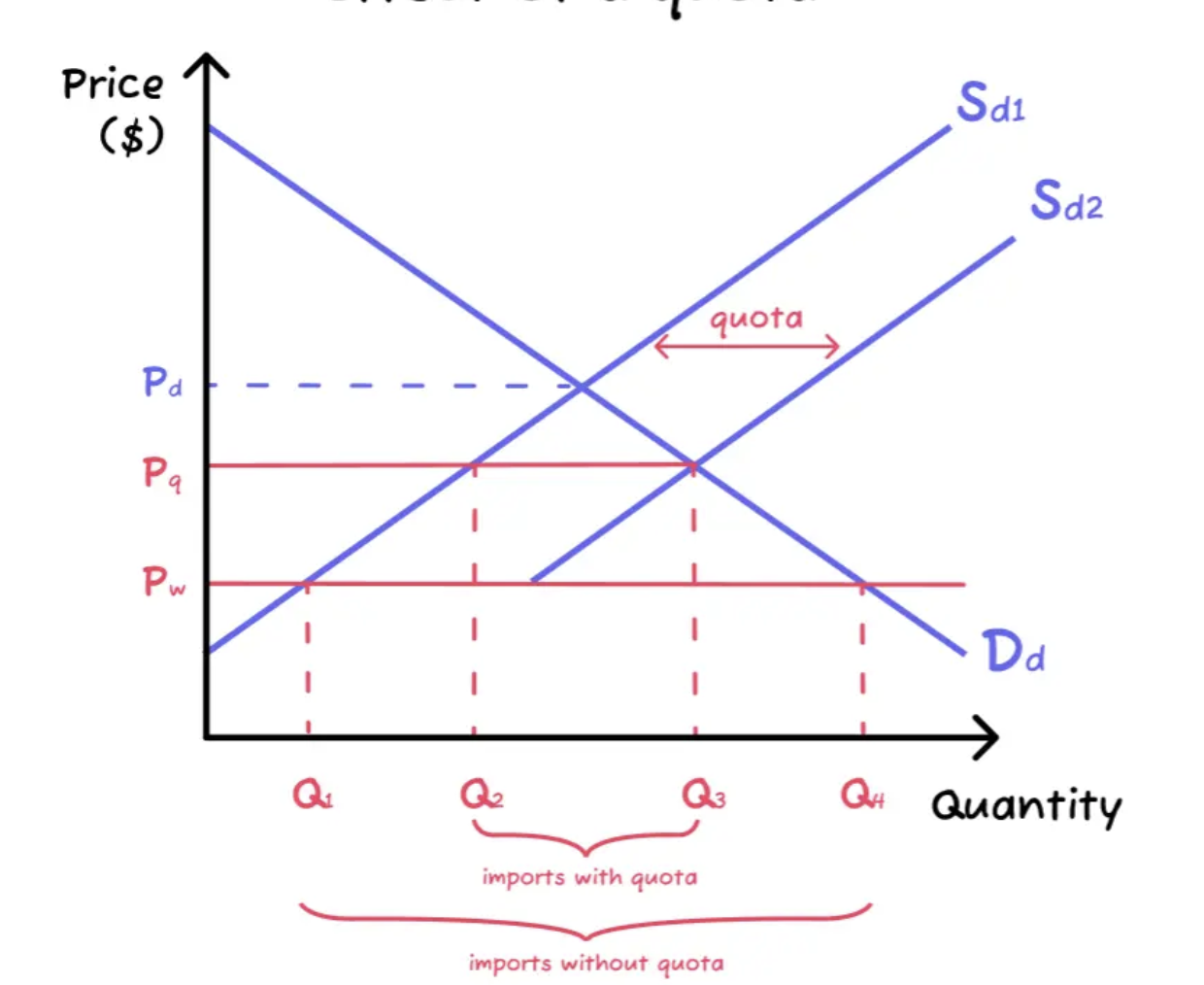
Import Quotas
A legal limit to the quantity of a good that can be imported over a particular period of time. Unlike tariffs, the do not generate government revenue.
Quota Graph
Subsidy
Monetary help (direct or indirect payment) offered by the government to firms (sometimes households) to aid in lowering costs of production.
Production Subsidy
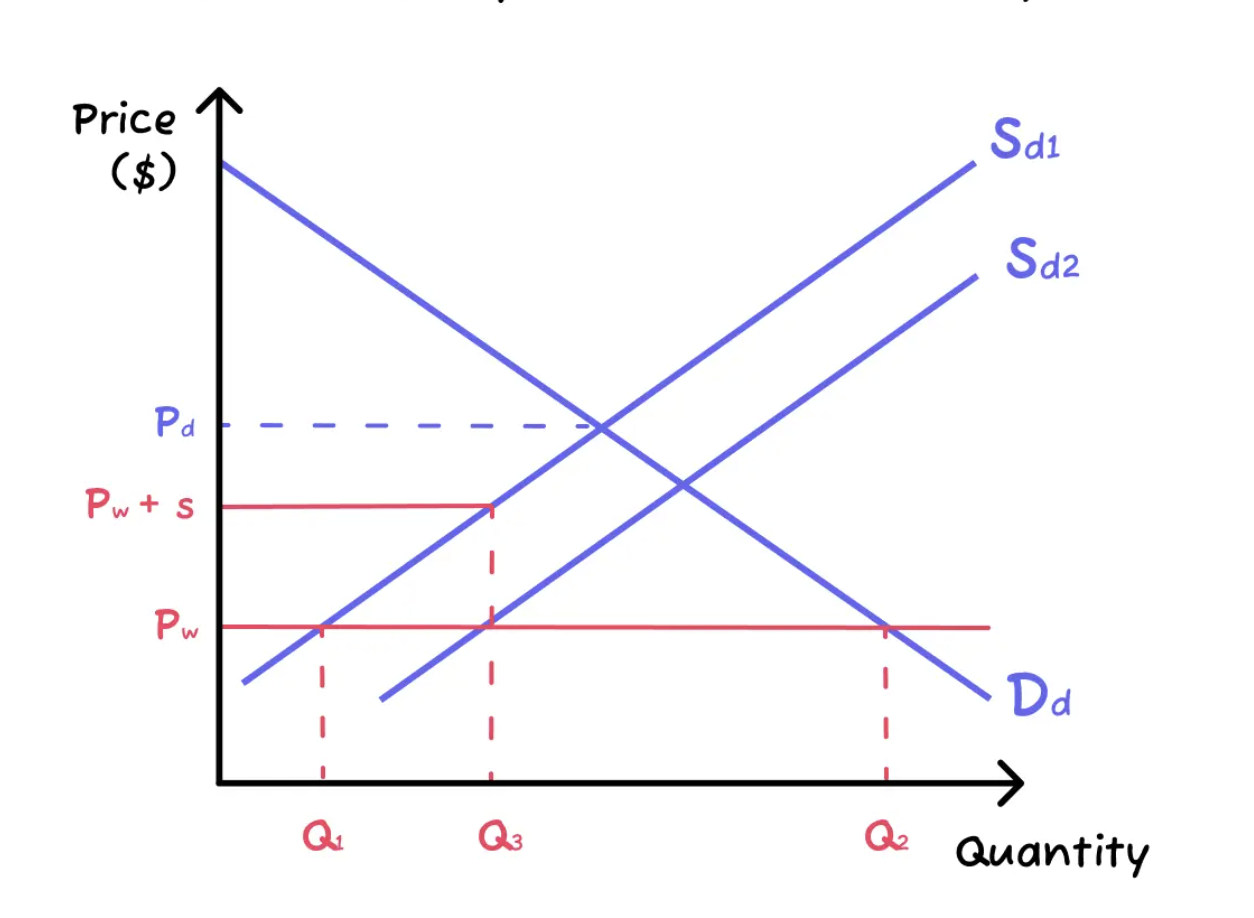
Subsidies where government gives payments to domestic firms competing with imports in order to encourage them to produce more and protect them.
Production subsidy graph
Production Subsidy Winners
Domestic producers are supplying more at a higher price, earning higher revenues. Producer surplus increases, indicating the gain from the new prices and trade restrictions.
Wokers: As domestic producers now produce and sell a larger quantity, the employment in the industry would be protected and increase as well.
Neutral: Consumers: Unlike the restrictions before, consumers don't face a higher price since they still purchase at Pw and the same quantity Q2.