AP Psych Lifespan Development
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
zygote
a fertilized egg
it enters a 2 week period of rapid cell division and develops into the embryo
Z-E-F
embryo
the developing human organism from about 2 weeks after fertilization through the second month.
Z-E-F
fetus
the developing organism from the end of the eighth week until birth
Z-E-F
teratogens
agents, such as chemicals and viruses, that can reach the embryo or fetus during prenatal development and cause harm
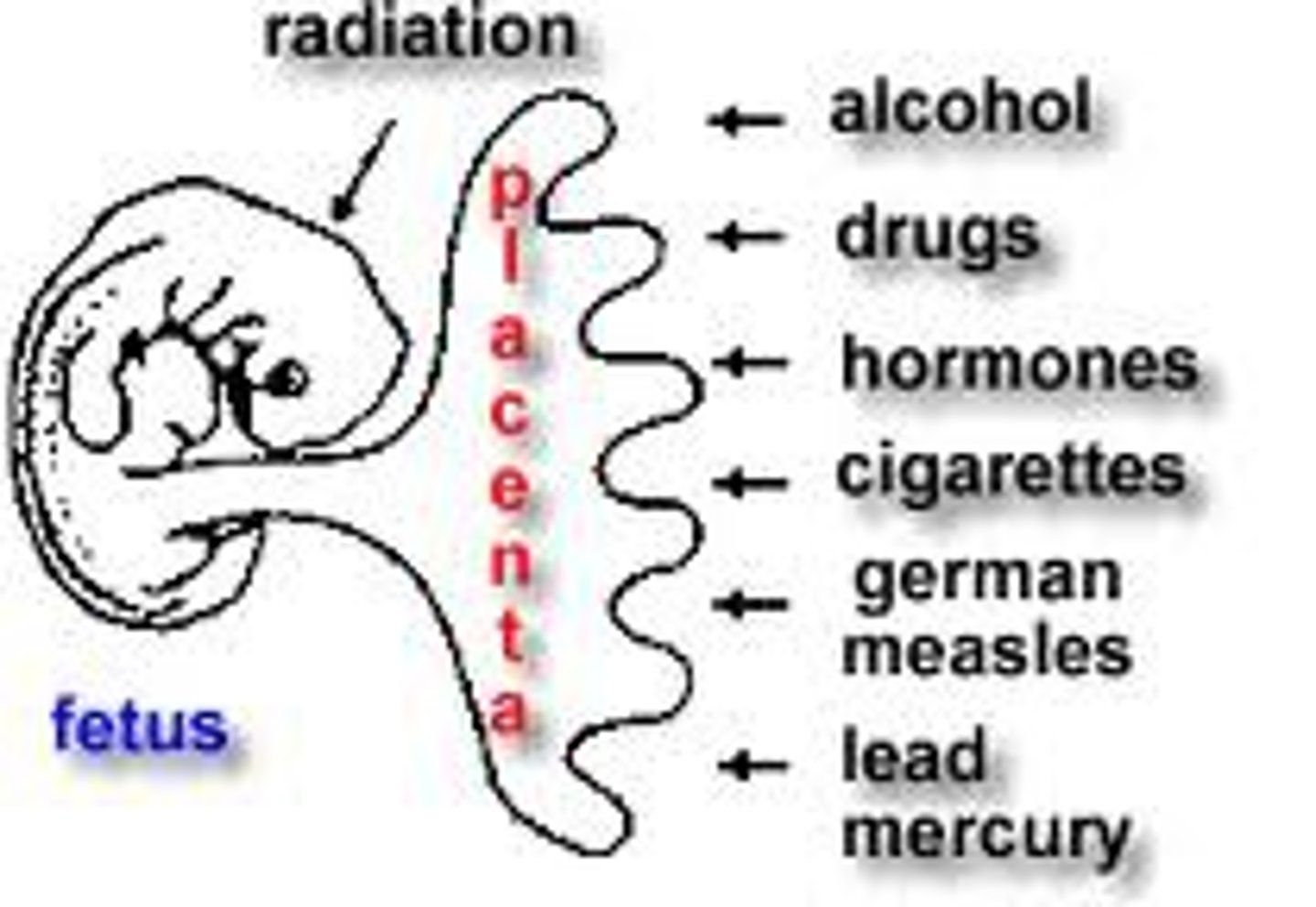
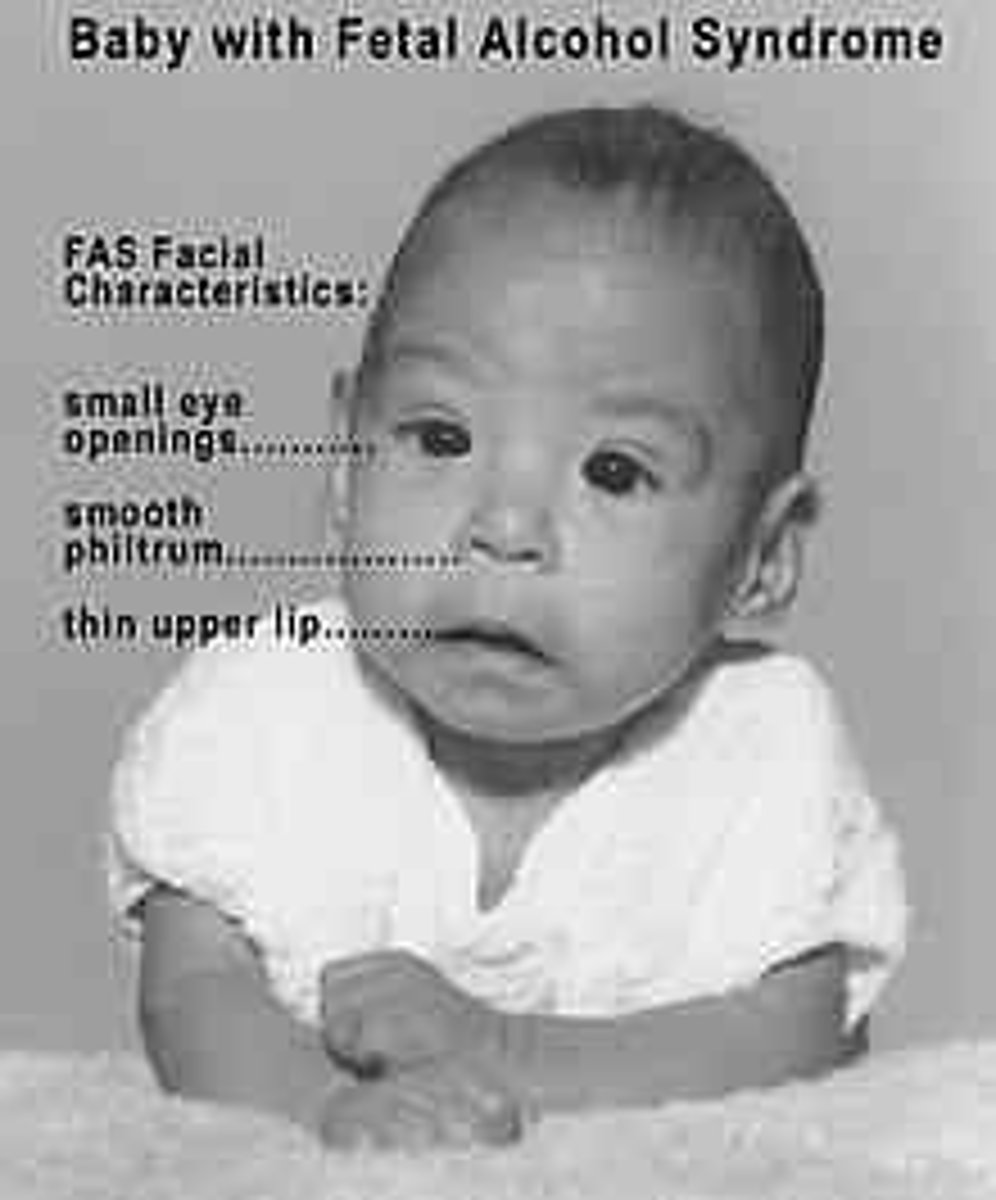
fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS)
Physical and cognitive abnormalities in children caused by a pregnant woman's heavy drinking.
type of teratogens
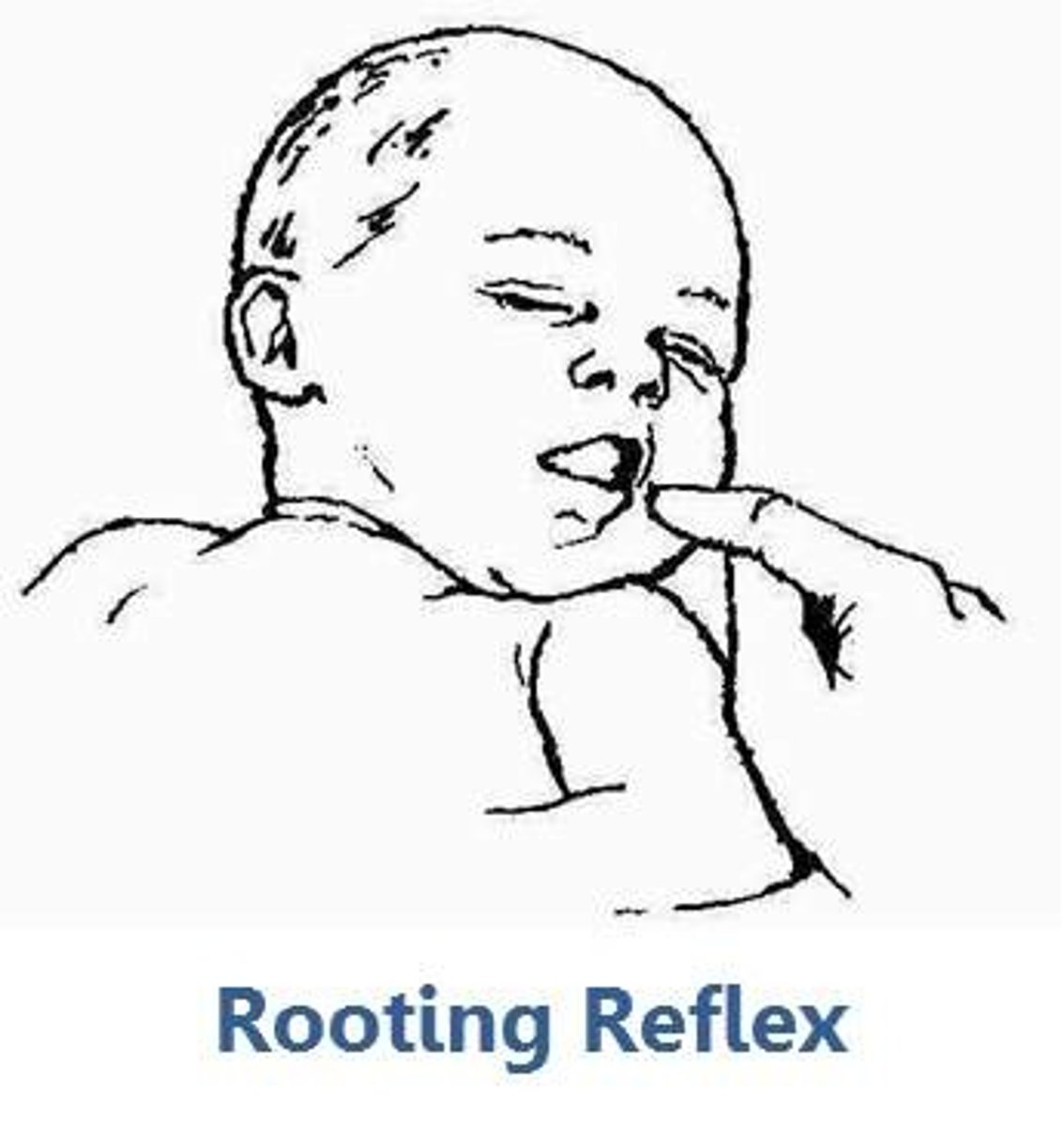
rooting reflex
a baby's tendency, when touched on the cheek, to turn toward the touch, open the mouth, and search for the nipple.
habituation
Decreasing responsiveness with repeated stimulation. As infants gain familiarity with repeated exposure to a visual stimulus, their interest wanes and they look away sooner.
ex: if you hang a toy in front of a baby's face for a short period of time, the baby will first be interested in the toy, but then lose interest because it's the same stimulus.

maturation
biological growth processes that enable orderly changes in behavior, relatively uninfluenced by experience
motor development
schema
a concept or framework that organizes and interprets information

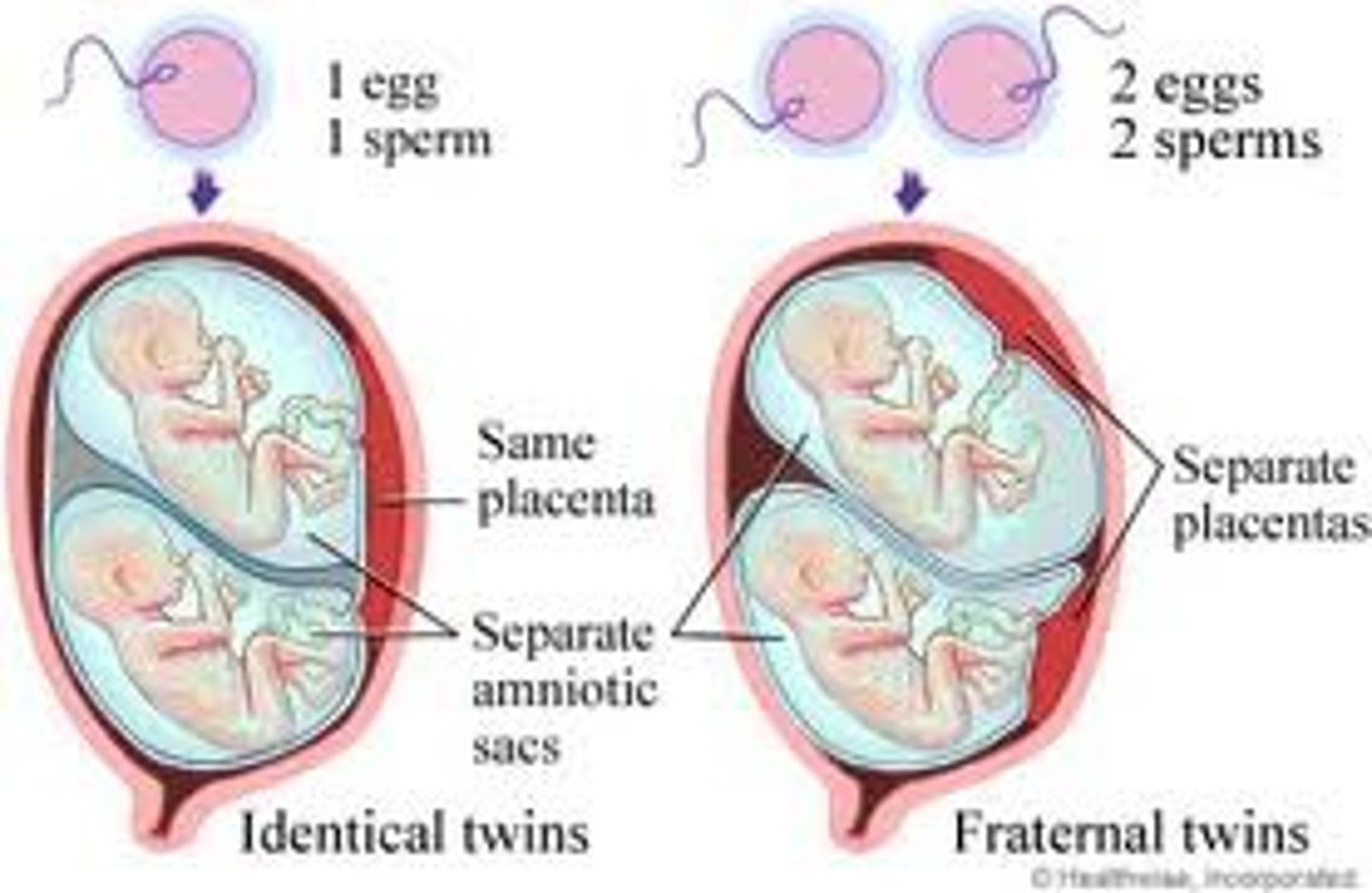
identical twins
twins who develop from a single fertilized egg that splits in two, creating two genetically identical organisms
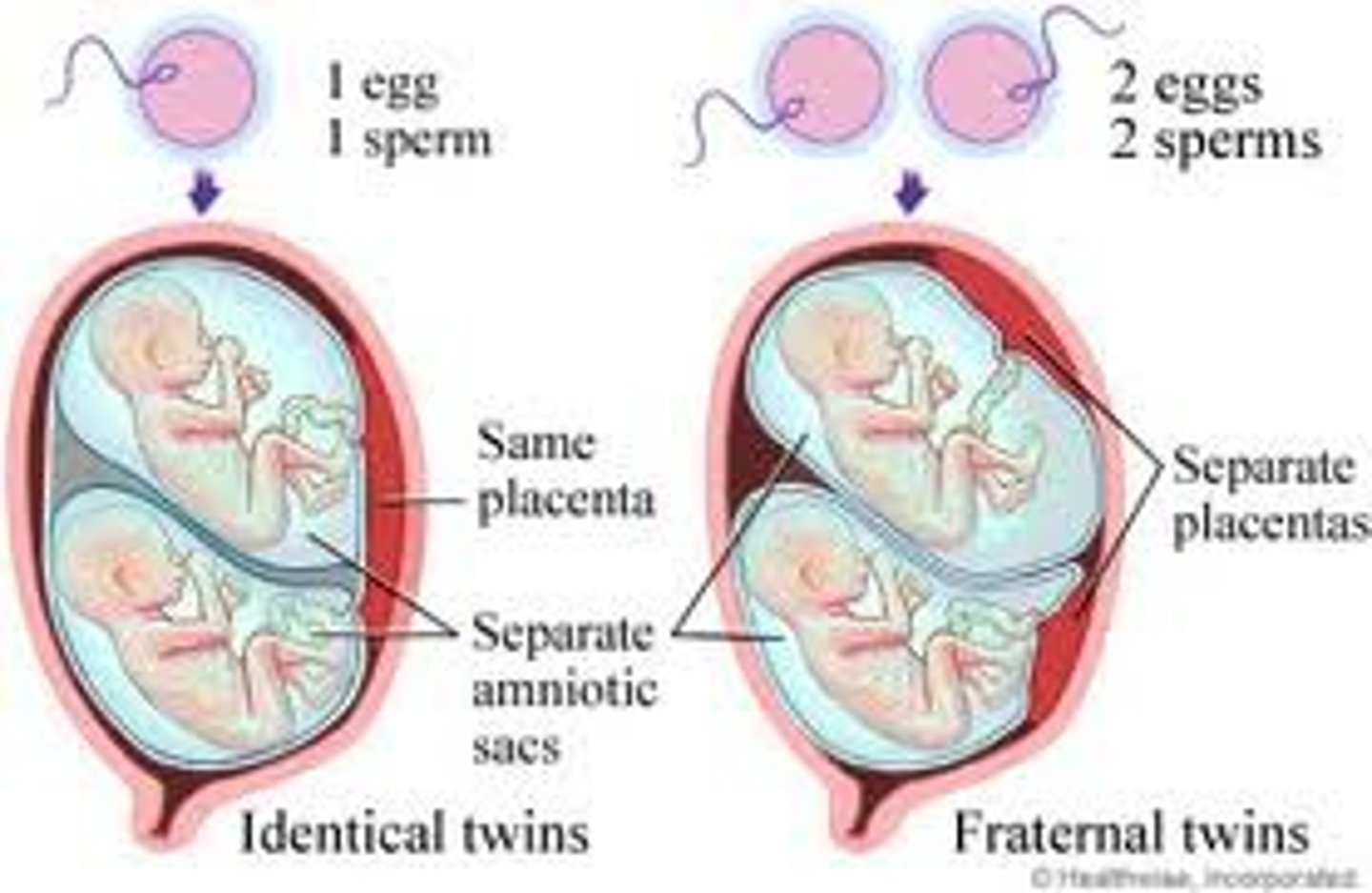
fraternal twins
twins who develop from separate fertilized eggs. They are genetically no closer than brothers and sisters, but they share a fetal environment.
nature and nurture
whether the intelligence of children is influenced by their biology
or
by their home environments are most directly relevant to the debate regarding

continuity and stages
This focus looks at our development - to determine if it is gradual, a continuous process or a sequence of separate stages
stability and change
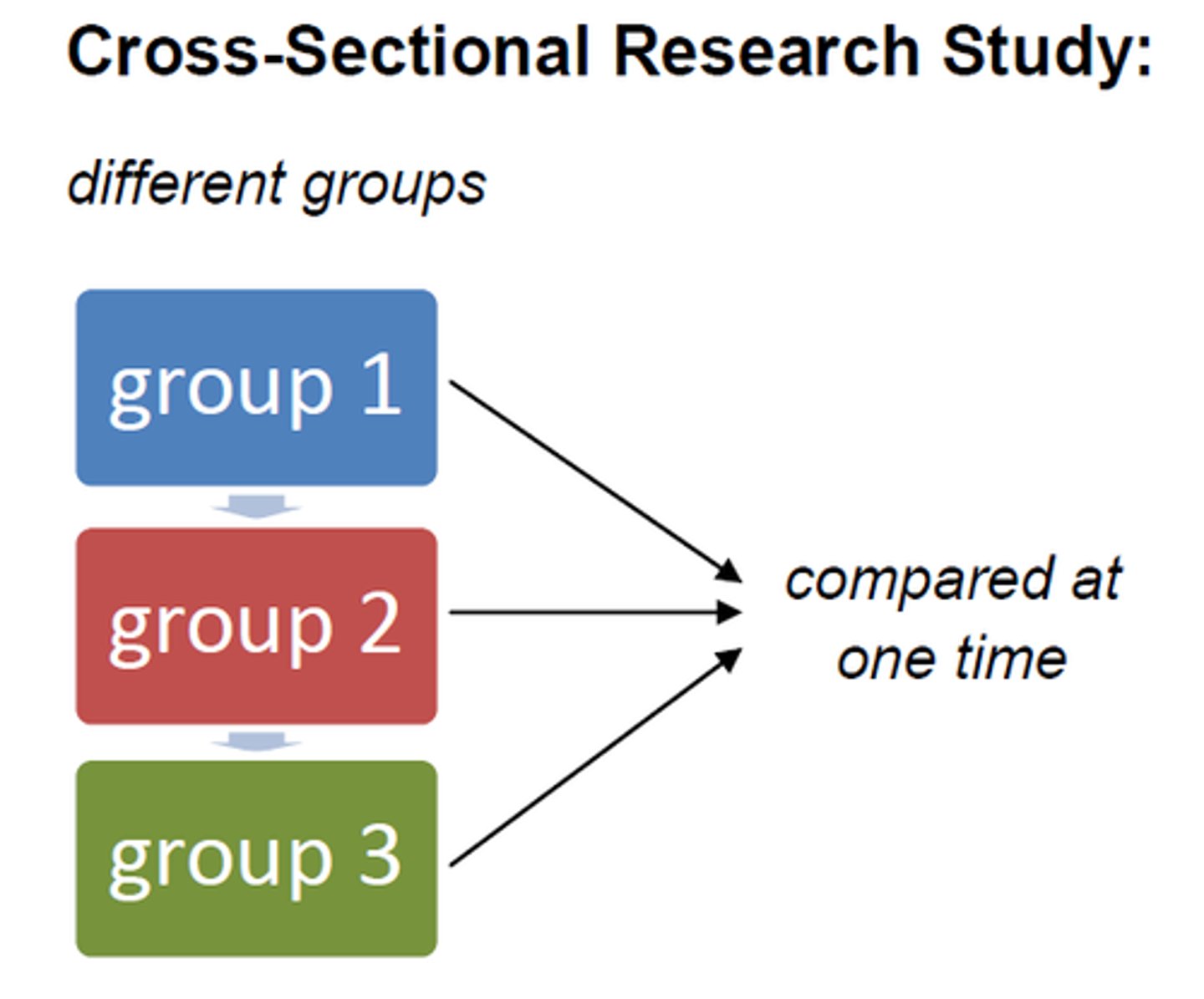
cross-sectional study
a study in which people of different ages are compared with one another
DIFFERENT AGES in study
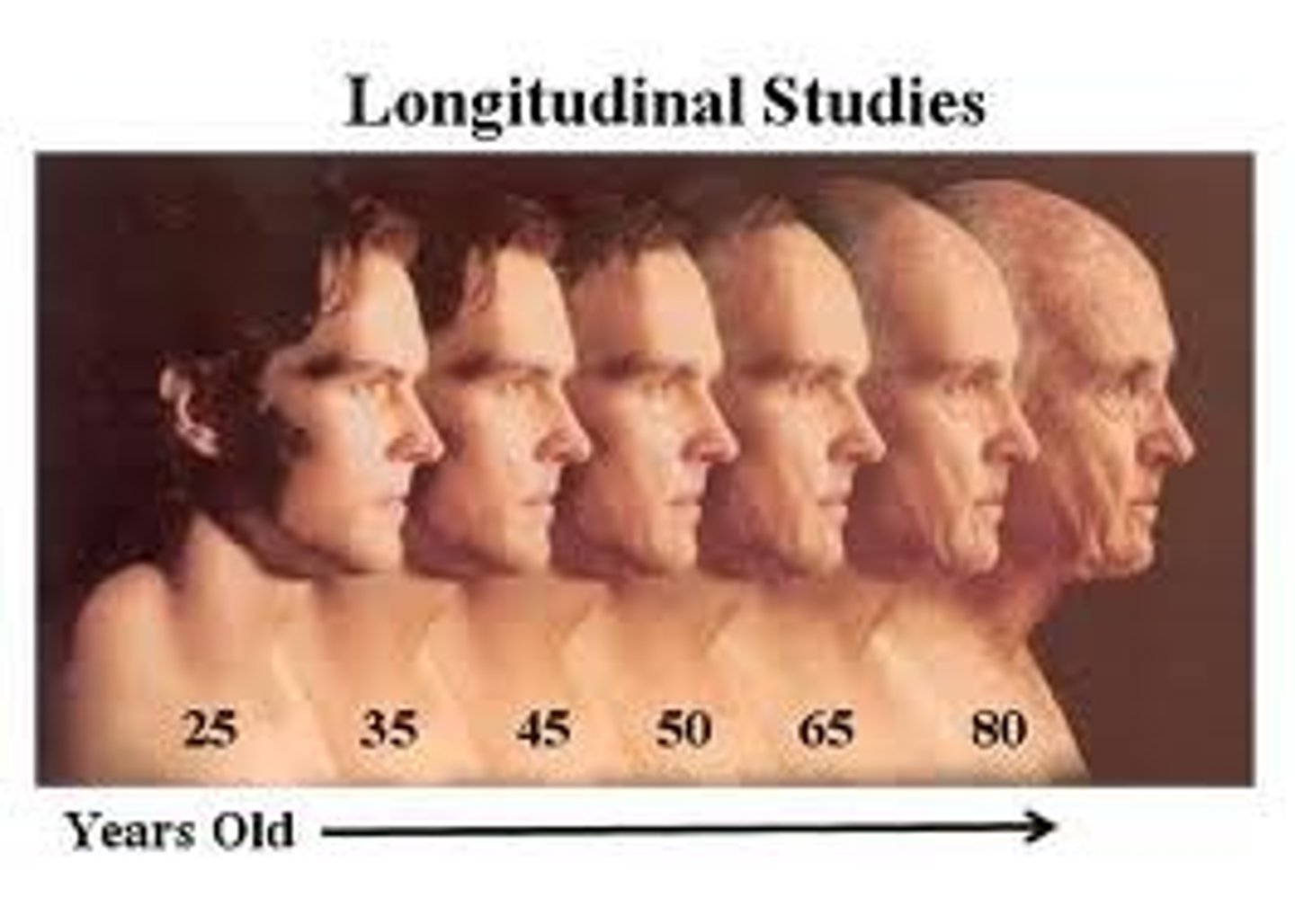
longitudinal study
study over a LONG time
A research approach that follows a group of people over time to determine change or stability in behavior.
ex: Genie
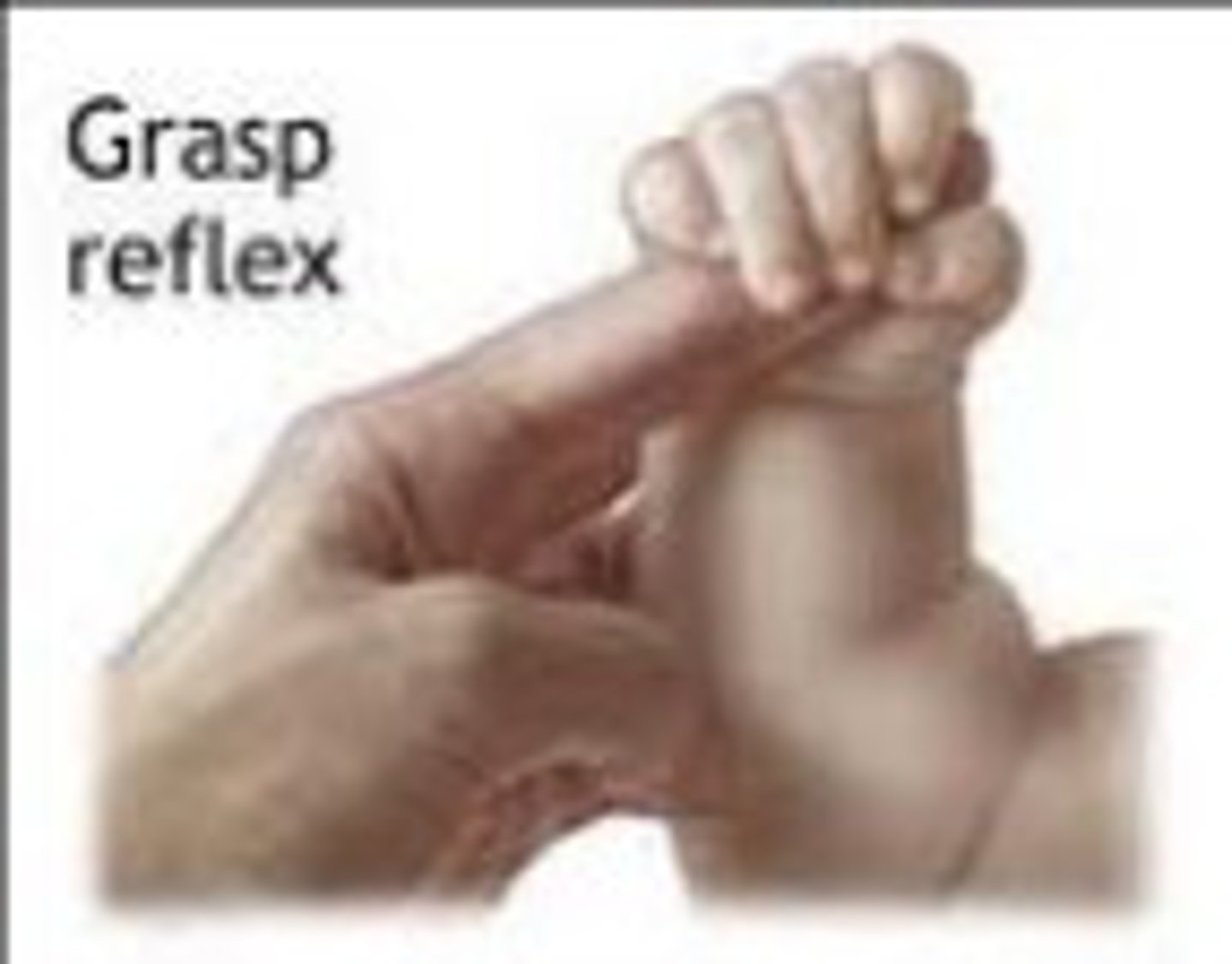
grasping reflex
an infant's clinging response to a touch on the palm of his or her hand
startle reflex
response that one makes after a sudden, unexpected loud noise or similar sudden stimulus
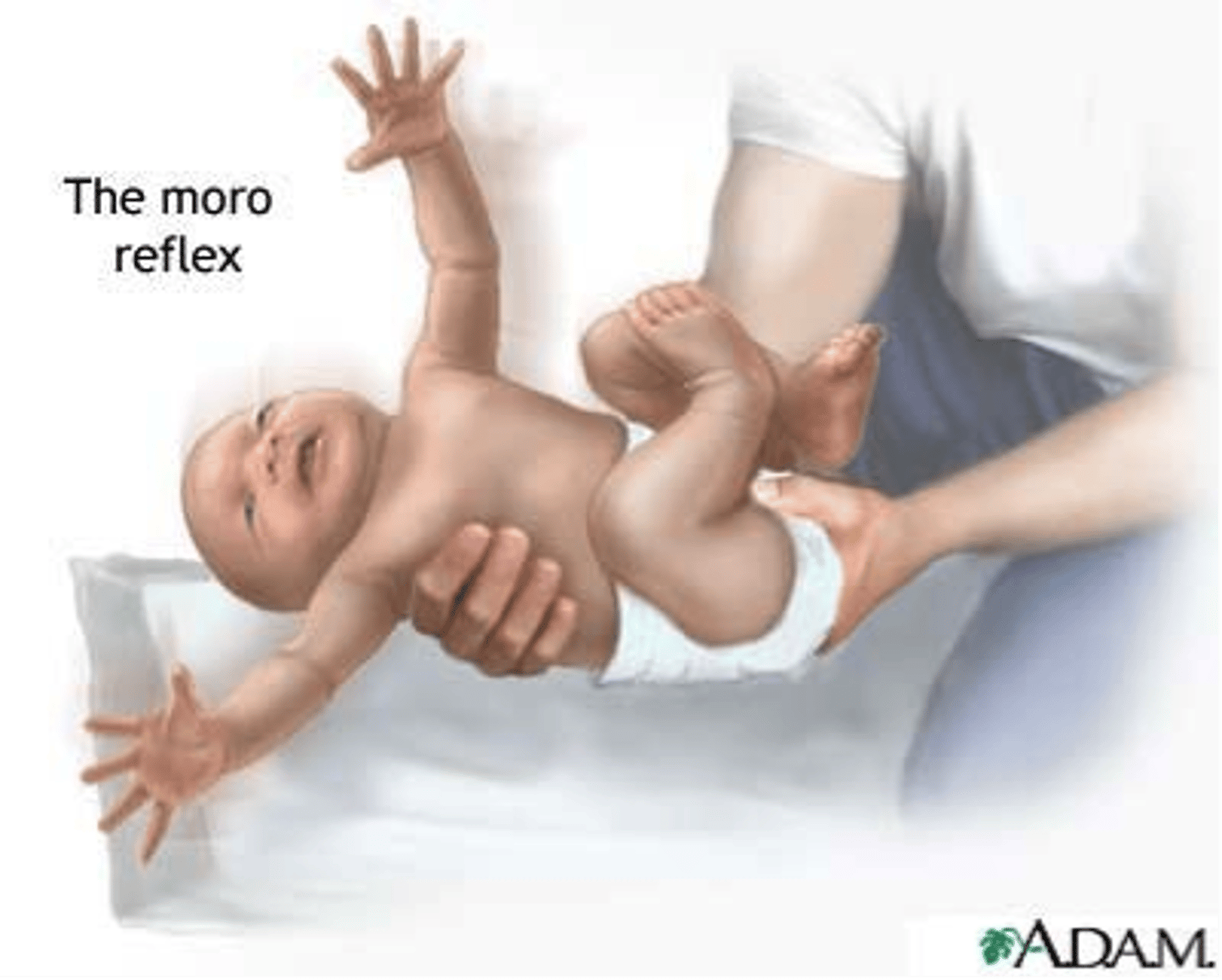

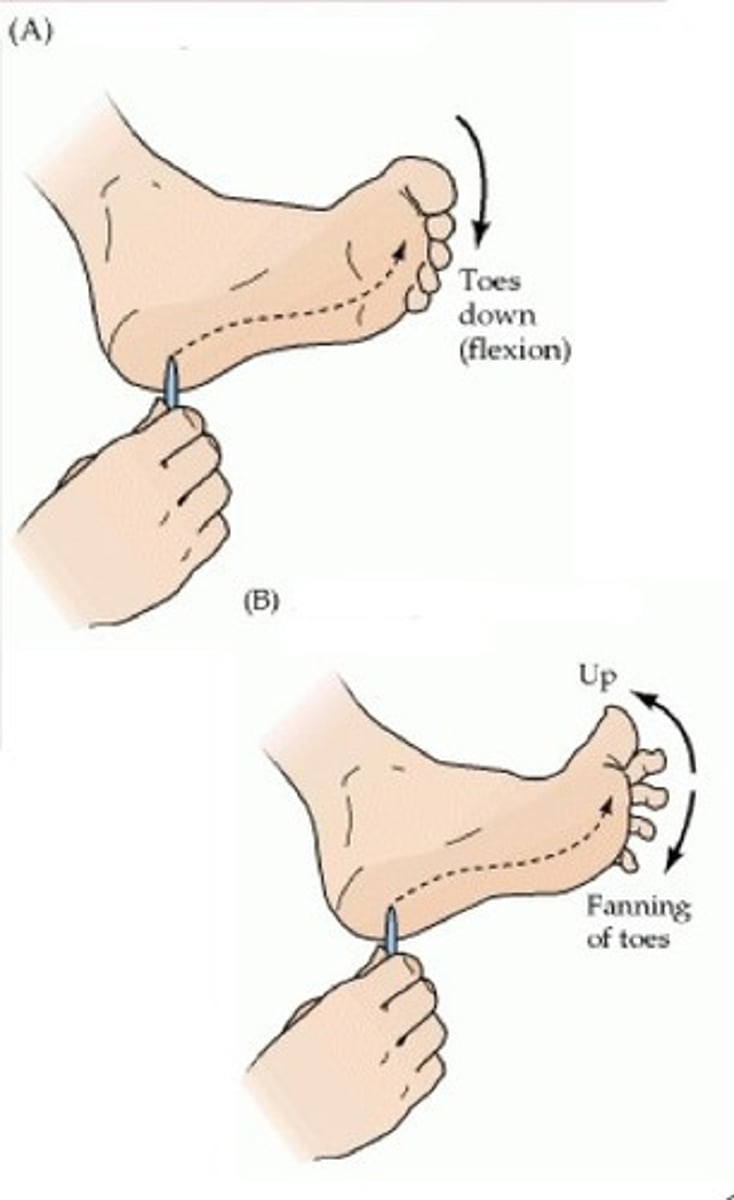
plantar reflex
(Babinski sign)
curling toes down when sole of foot is stimulated, normal in adults
Babinski ->Big toes curls
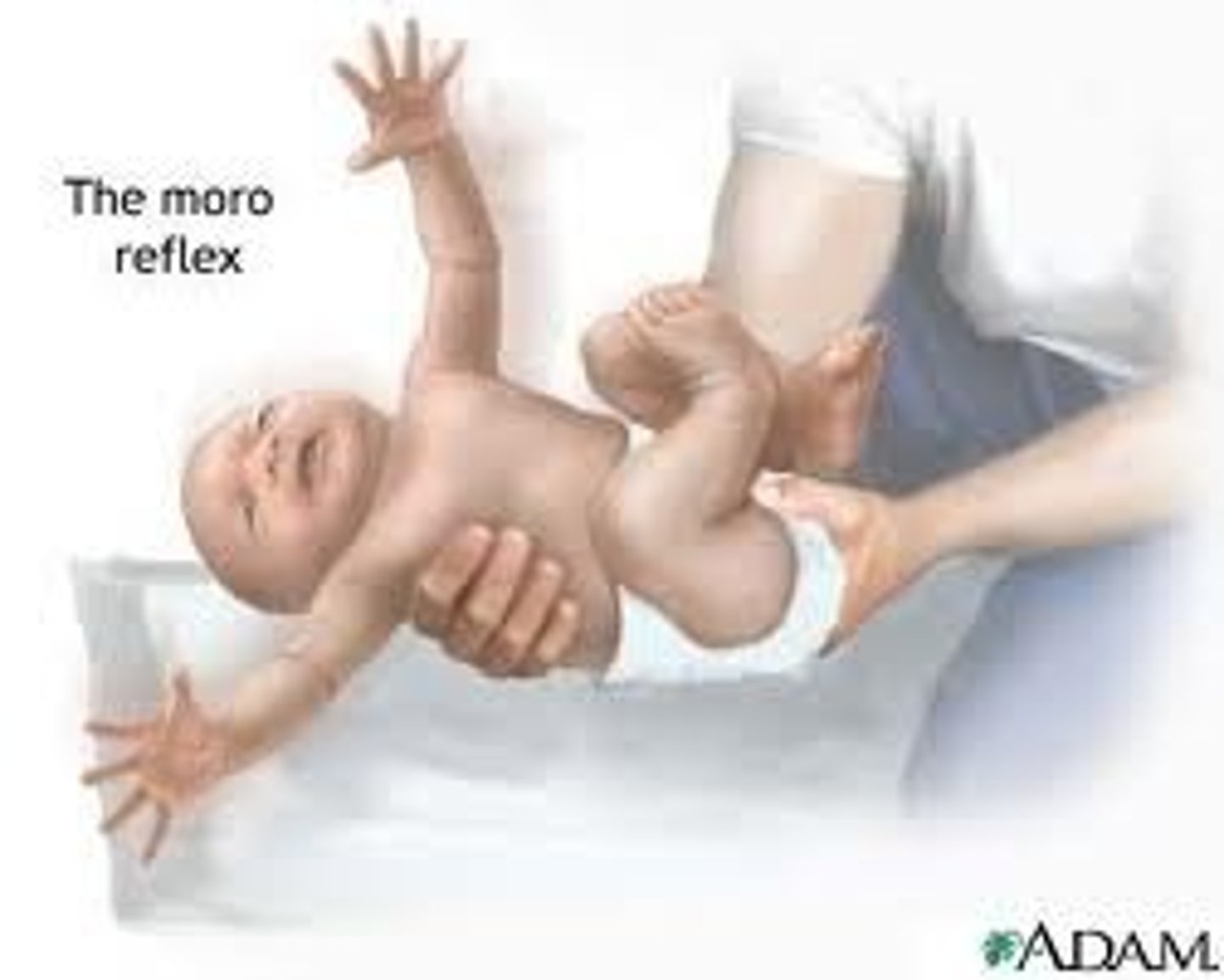
Moro reflex
Reflex in which a newborn strectches out the arms and legs and cries in response to a loud noise or an abrupt change in the environment
Moro-> Morons would do this to their baby
puberty
Sexual maturation; the end of childhood and the point when reproduction is first possible

primary sex characteristics
the body structures (ovaries, testes, and external genitalia) that make sexual reproduction possible
secondary sex characteristics
nonreproductive sexual characteristics, such as female breasts and hips, male voice quality, and body hair
menarche
first menstrual period

menopause
Cessation of menstrual periods owing to a lack of ovarian hormones

Alzheimer's disease
an irreversible, progressive brain disorder, characterized by the deterioration of memory, language, and eventually, physical functioning
the hippocampus that creates new memories and the hypothalamus with old memories

assimilation
According to Piaget, the process by which new ideas and experiences are absorbed and incorporated into existing mental structures and behaviors
aSSimilation
Same Stuff
(ppl tried to assimilate the indians-- make the indians act and look like americans)

accommodation
Adapting our current understandings (schemas) to incorporate new information.
aCCommodation -> CHANGES YOUR SCHEMA
LEARNING NEW THINGS

egocentrism
in Piaget's theory, the preoperational child's difficulty taking another's point of view
big EGO -> only thinking about their point of view
artificialism
Form of thought where children tend
to believe that everything is the product of human
creation.
ARTIFICIAL -> fake-> man made

animism
Life to inanimate things
Animism-> "animate" and children think that inanimate objects are alive

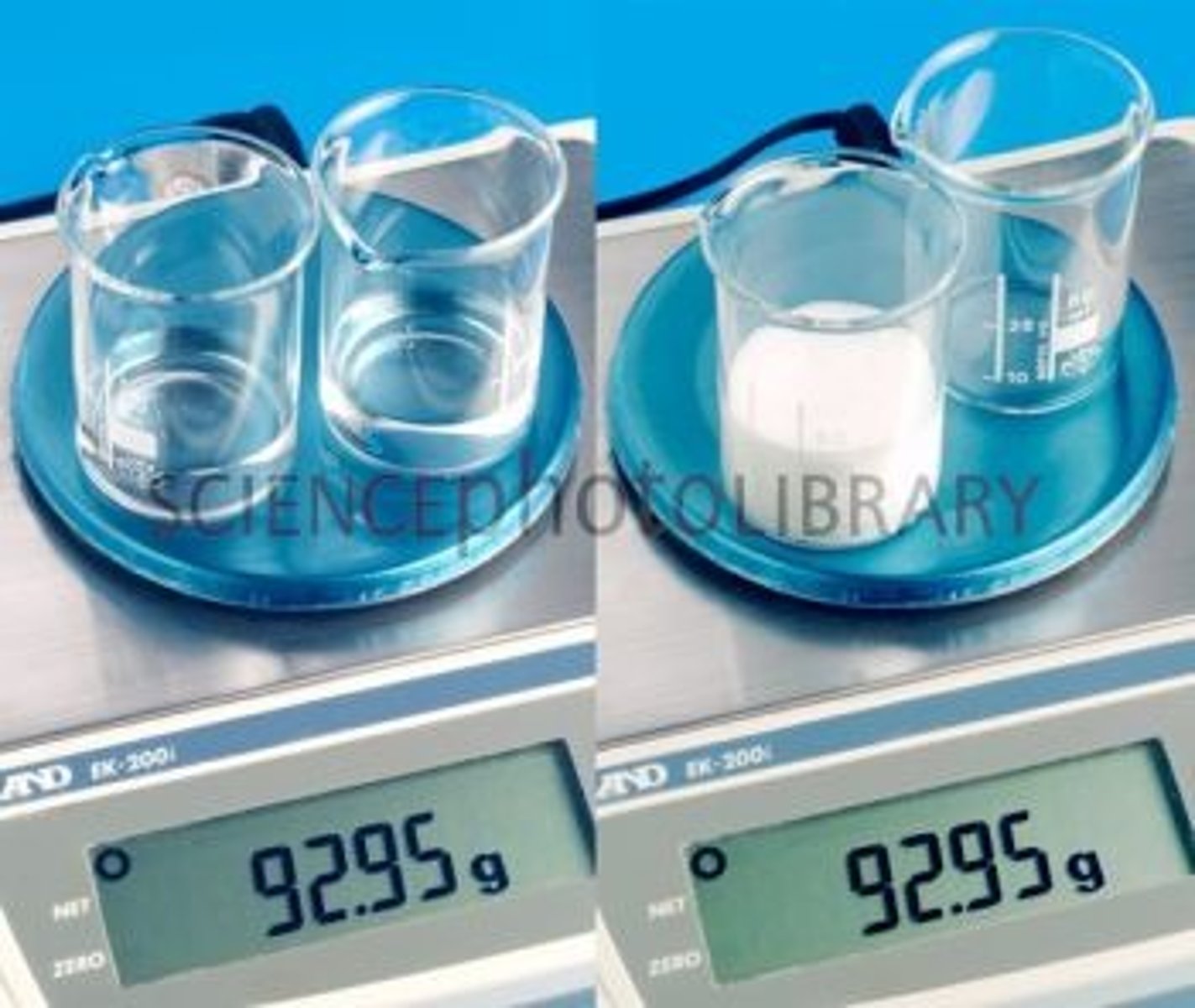
conservation
Ability to recognize that objects can be transformed in some way, visually or physically, yet still be the same in number, weight, substance, or volume
develops during the concrete operational stage

reversibility
Reversibility A mental process that allows for a reversal in chain of events of the original condition
ex: When a ball deflates the child understands air can be put back in it and the child can play with it again.
imaginary audience
A cognitive distortion experienced by adolescents, in which they see themselves as always "on stage" with an audience watching

personal fable
type of thought common to adolescents in which young people believe themselves to be unique and protected from harm

theory of mind
able to take on perspectives of others
OPPOSITE with egocentrism
concrete operational stage
ppl with austim usually struggle with this

Lev Vygotsky's theory
this theory is the difference between what a learner can do with help and what they can do without help.
autism
a disorder that appears in childhood and is marked by deficient communication, social interaction, and understanding of others' states of mind
struggle w Theory of Mind

Lawrence Kohlberg
Famous for his theory of moral development in children; made use of moral dilemmas in assessment
Preconventional
‐Avoid Punishment
‐Gain reward
Conventional
‐Gain approval
‐Obey rules
Post Conventional
‐Mutual agreement based on common good
‐Universal principle that precedes over social rules
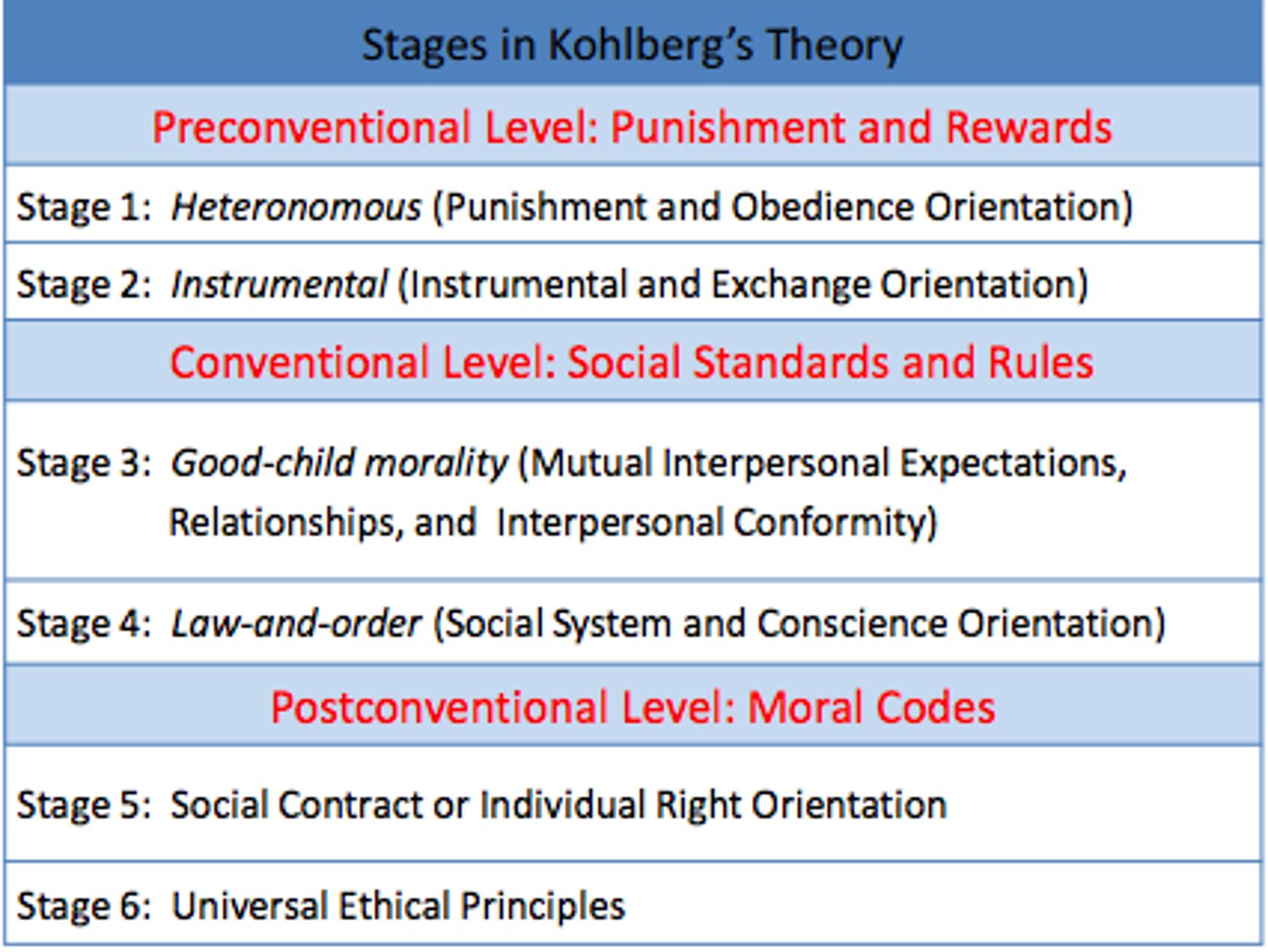
preconventional morality
first level of Kohlberg's stages (preschool and grade school) of moral development in which the child's behavior is governed by the consequences of the behavior
- automatic obedience to avoid punishment

conventional morality
second level of Kohlberg's stages of moral development in which the child's behavior is governed by conforming to the society's norms of behavior
COneventional-> Caring about COps (behavior of society)

postconventional morality
third level of Kohlberg's stages of moral development in which the person's behavior is governed by moral principles that have been decided on by the individual and which may be in disagreement with accepted social norms

Carol Gilligan
Presented feminist critique of Kolhberg's moral development theory; believed women's moral sense guided by relationships
Carol =girl name
Gill= boy name
*the diff between the girl and boys moral sense

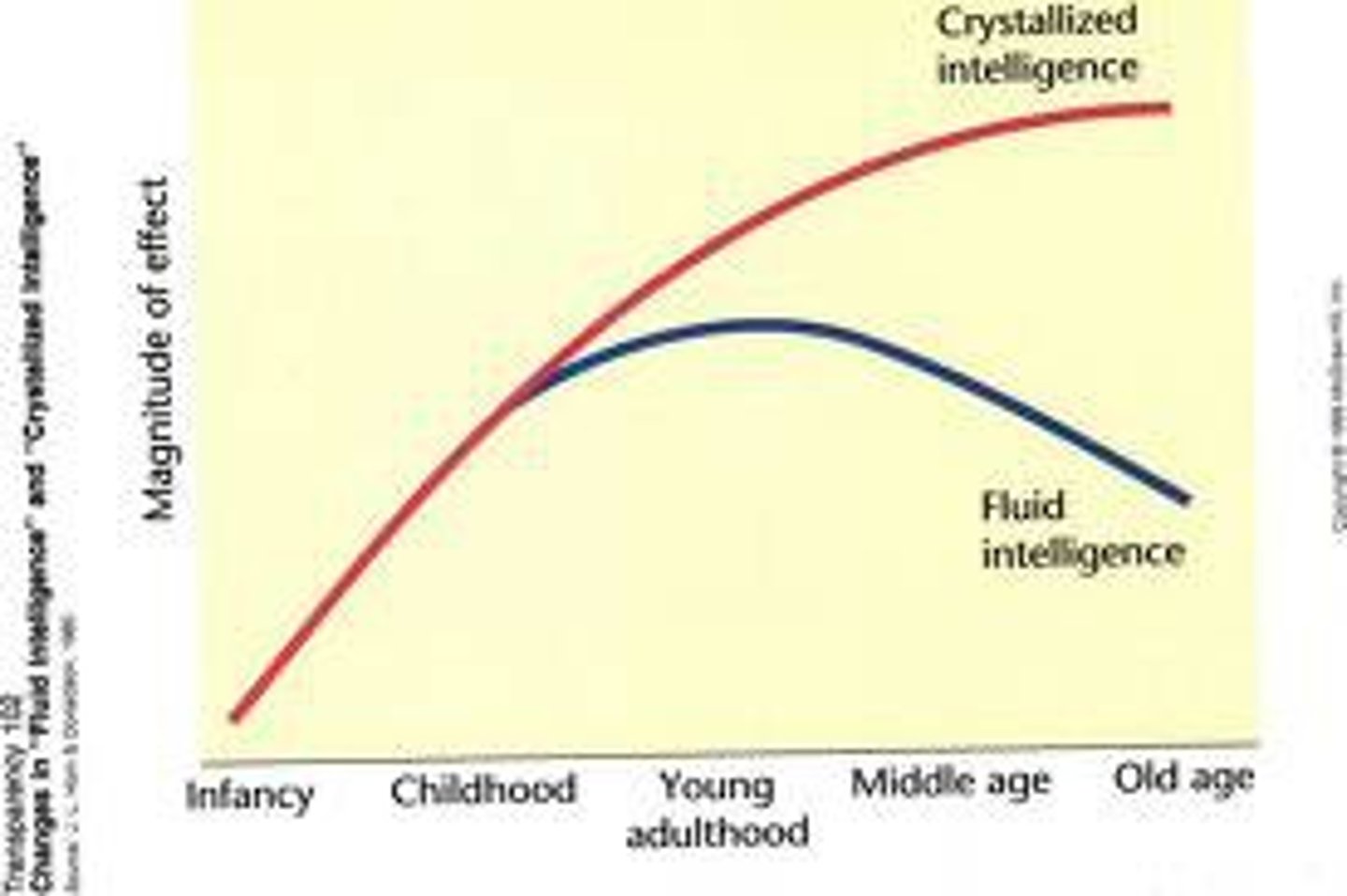
crystallized intelligence
One's accumulated knowledge and verbal skills; tends to increase with age
crystals grow over the YEARS
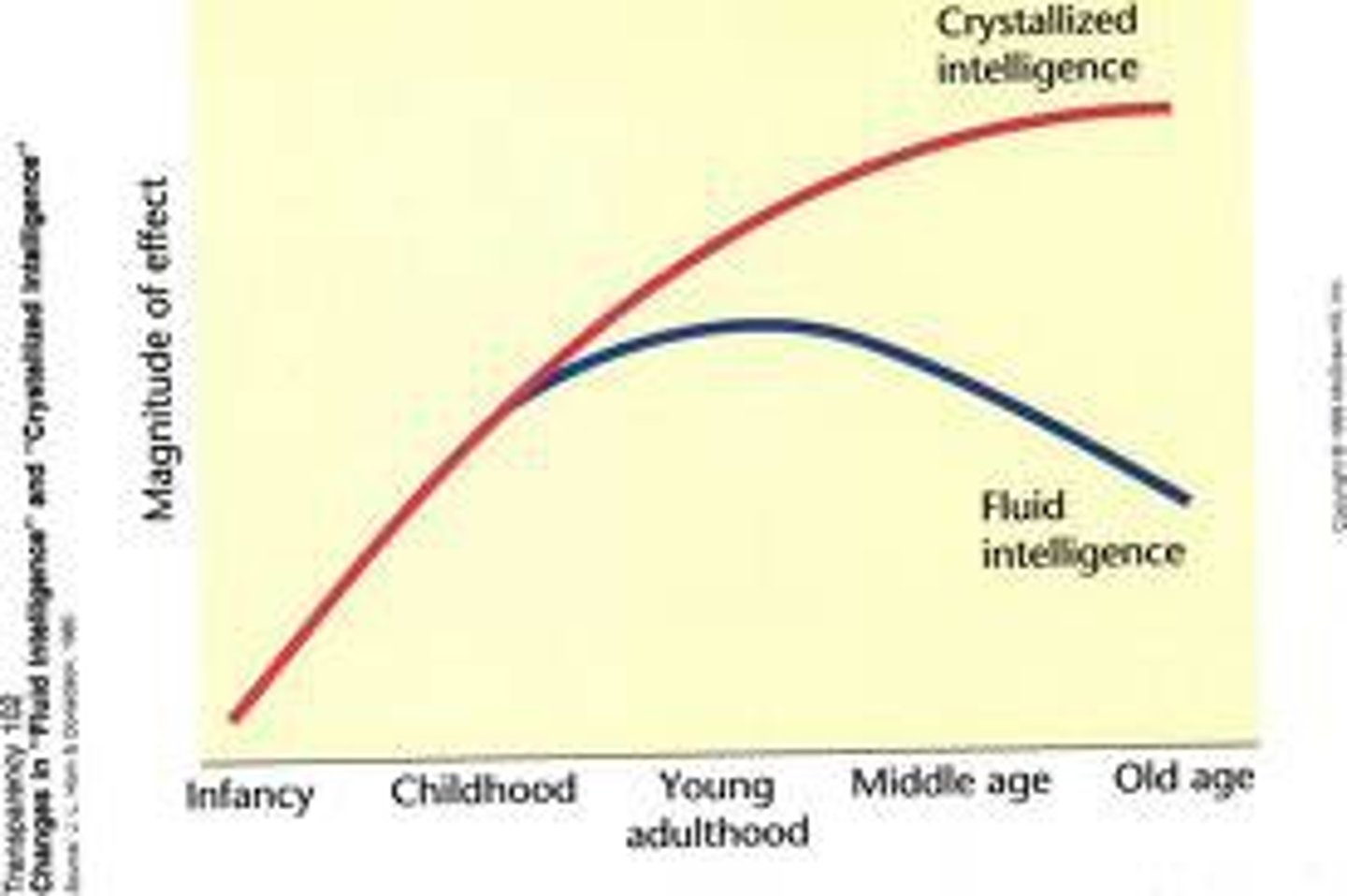
fluid intelligence
cognitive abilities requiring speed or rapid learning that tends to diminish with age ability to solve new problems, use logic in new situations, and identify patterns "street smart"
Harry Harlow
1905-1981; Field: development; Contributions: realized that touch is preferred in development; Studies: Rhesus monkeys, studied attachment of infant monkeys (wire mothers v. cloth mothers)
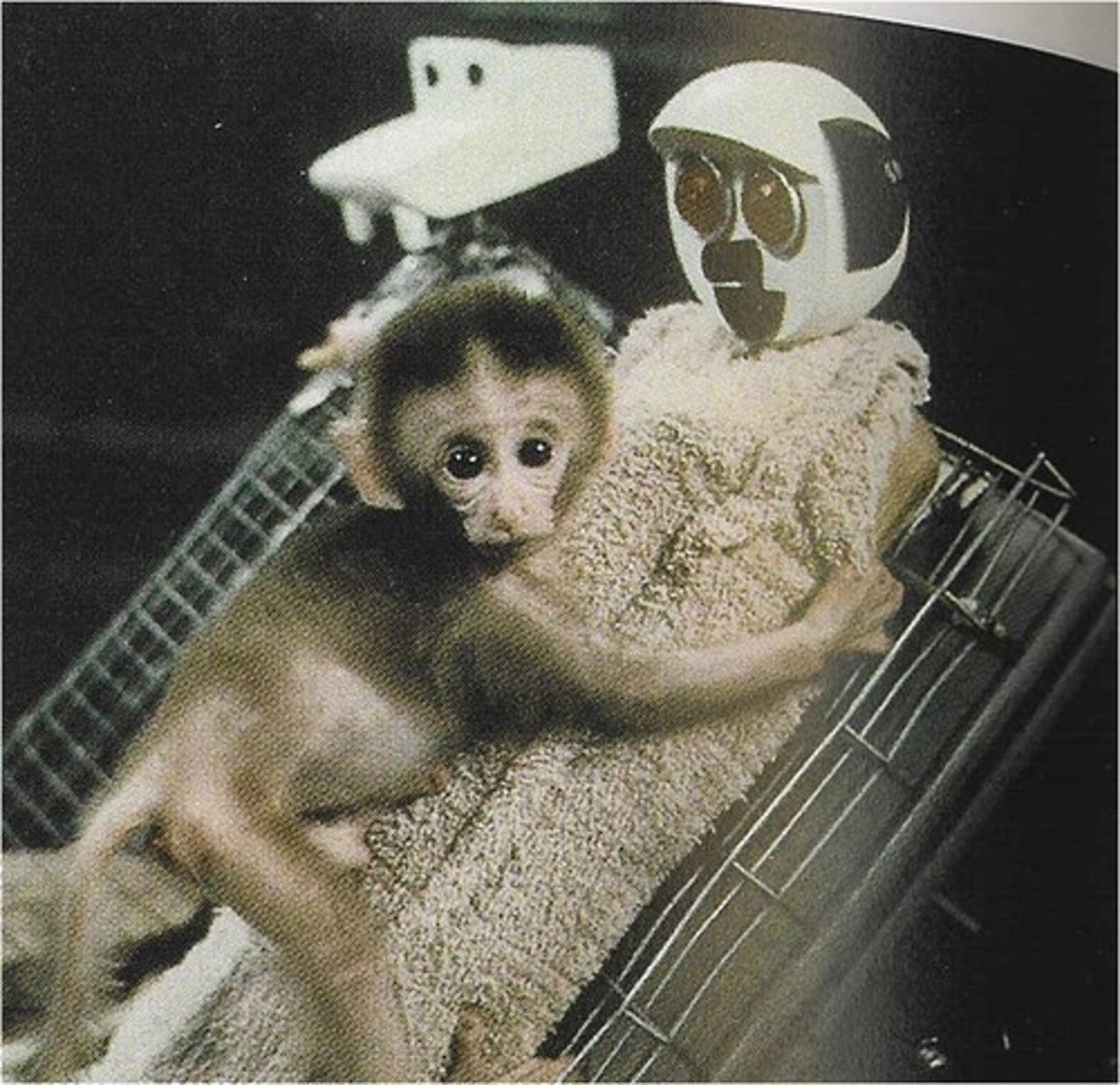

contact comfort
(Harlow) Research with Rhesus monkeys indicated that an infant's attachment is due to pleasant tactile sensations provided by a soft cuddly parent
(caregiver) = safety

critical period
an optimal period shortly after birth when an organism's exposure to certain stimuli or experience produces proper development

imprinting
The process by which certain animals form attachments during a critical period very early in life.

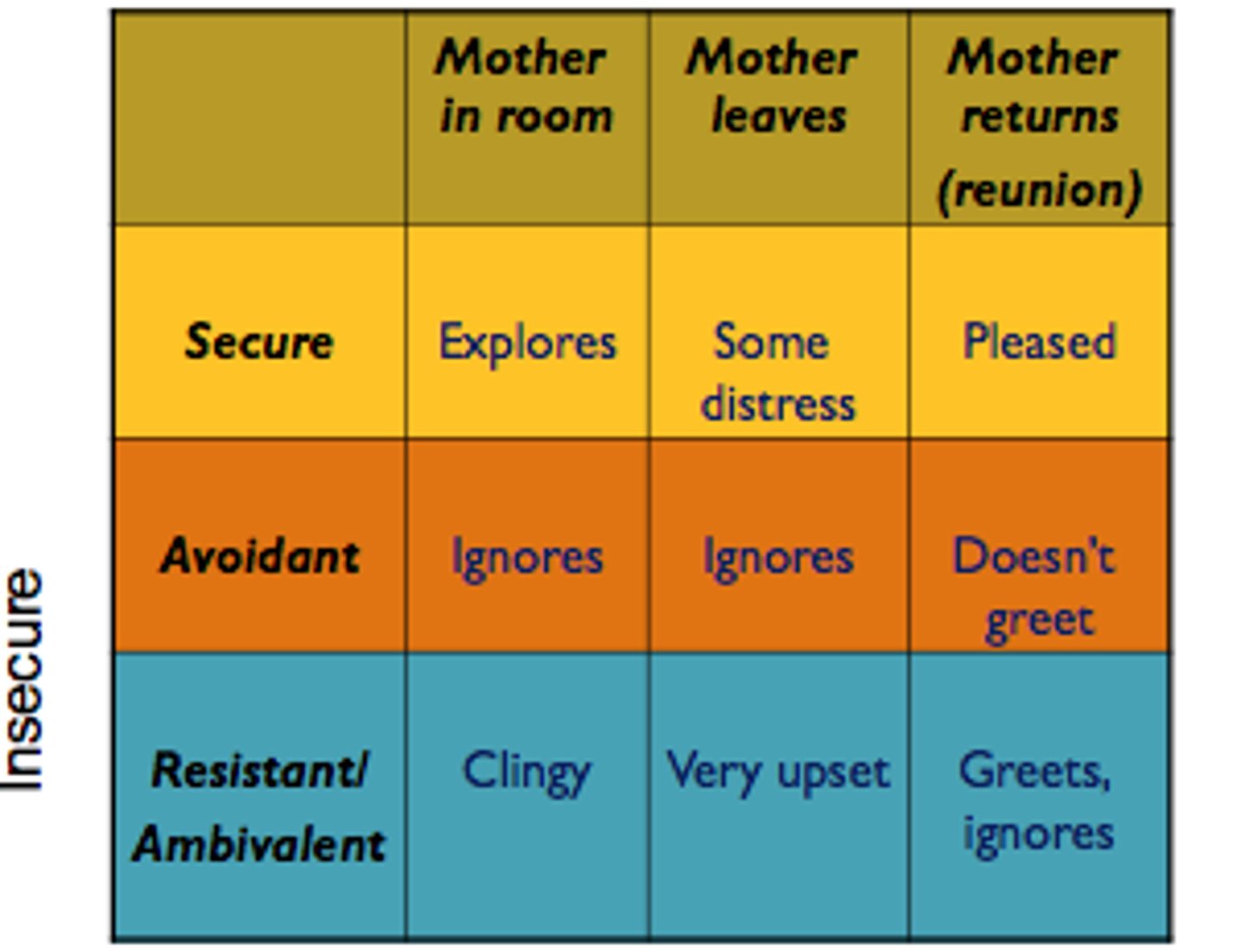
Mary Ainsworth
developmental psychology; compared effects of maternal separation, devised patterns of attachment; "The Strange Situation": observation of parent/child attachment

strange situation test
Ainsworth tested for her research studies of attachment.
A parent-infant "separation and reunion" procedure that is staged in a laboratory to test the security of a child's attachment
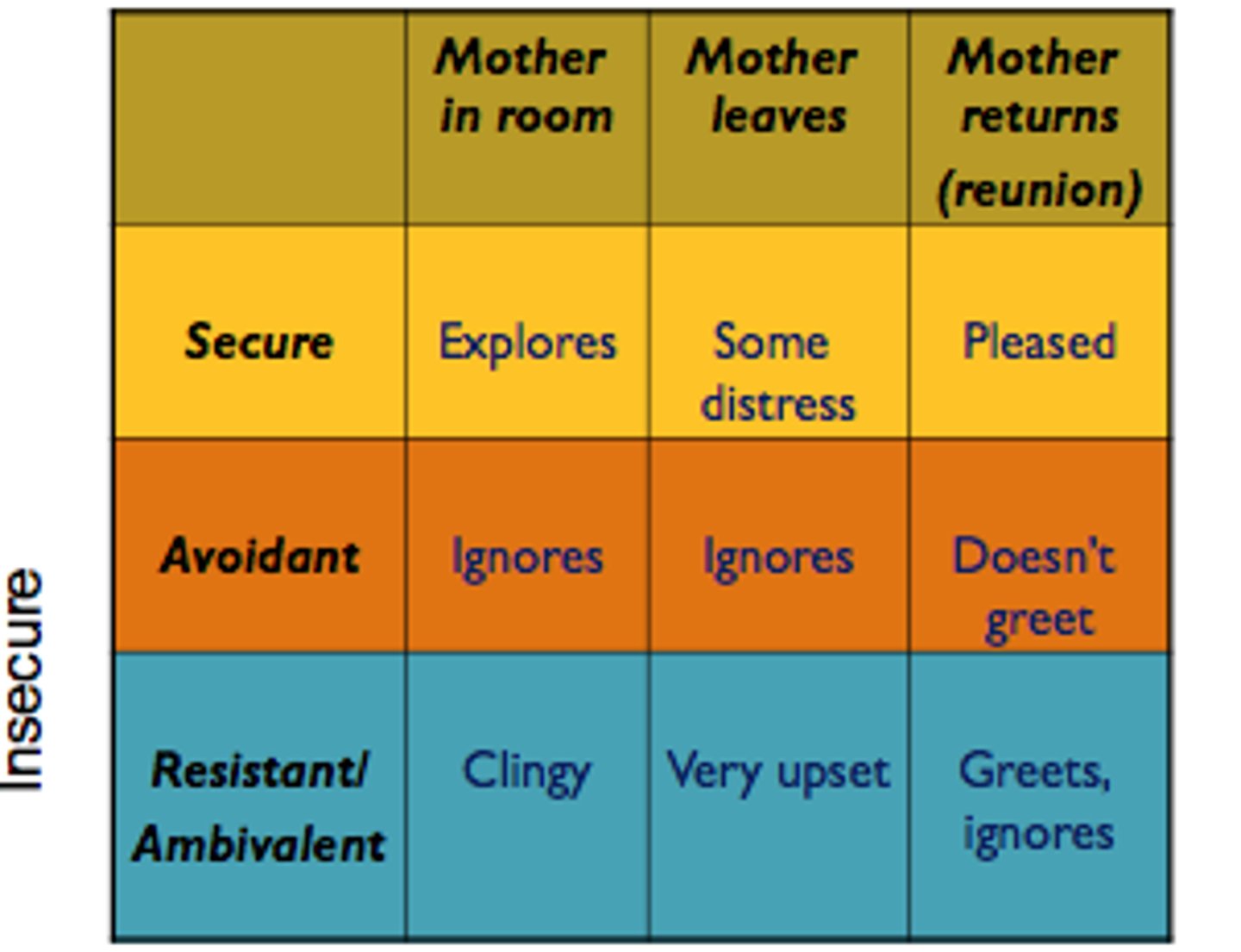
secure attachment style
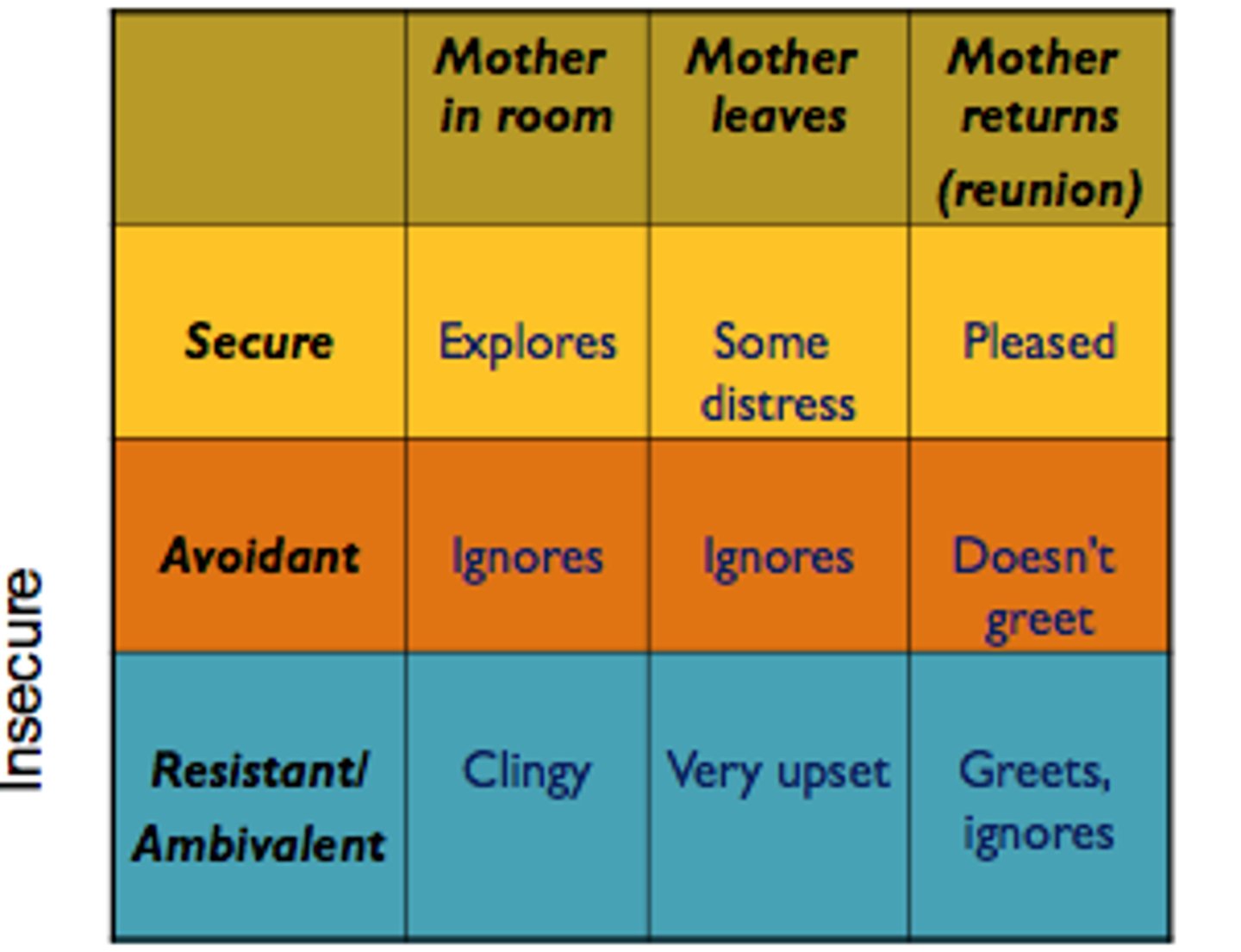
insecure anxious att. style
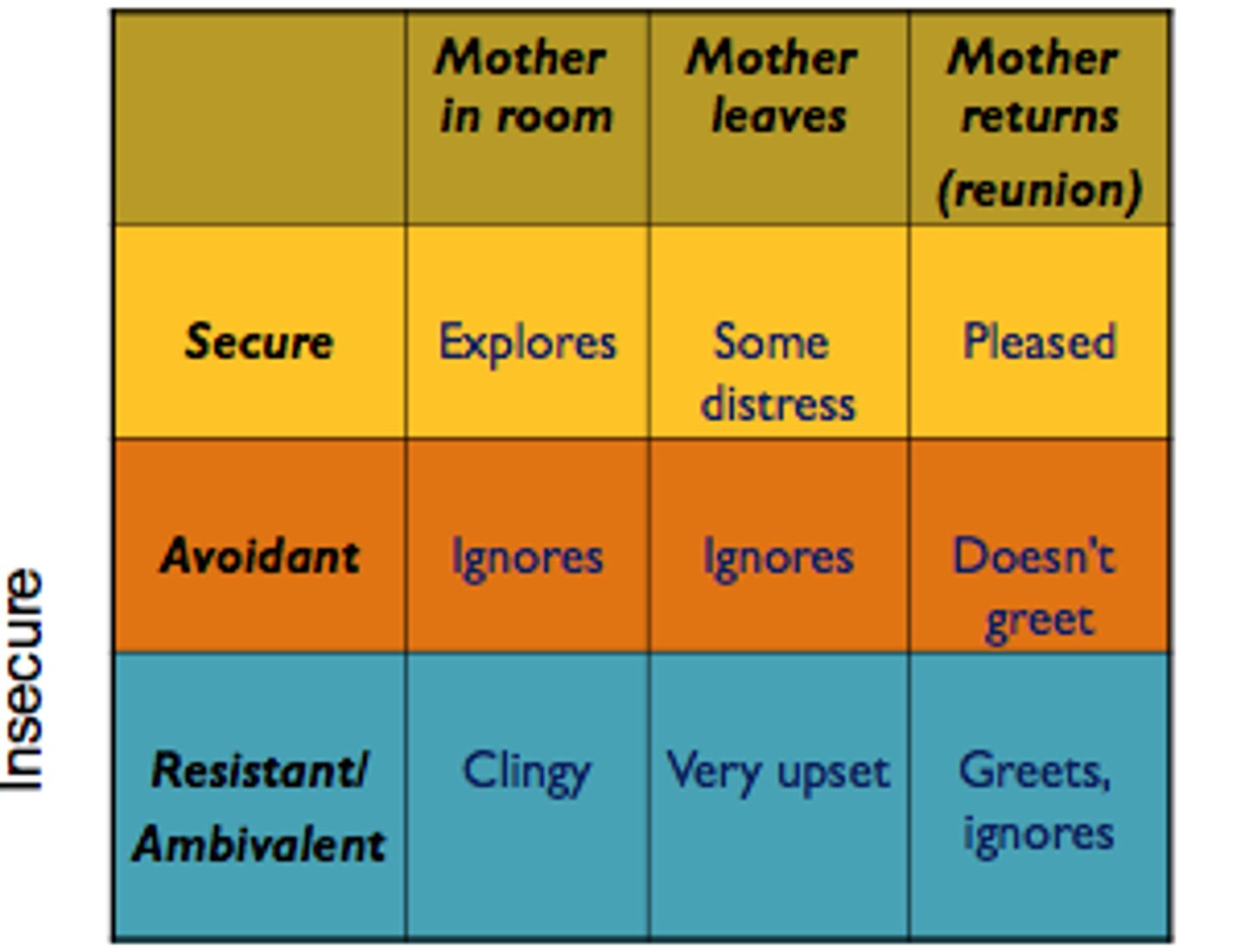
insecure avoidant att. style
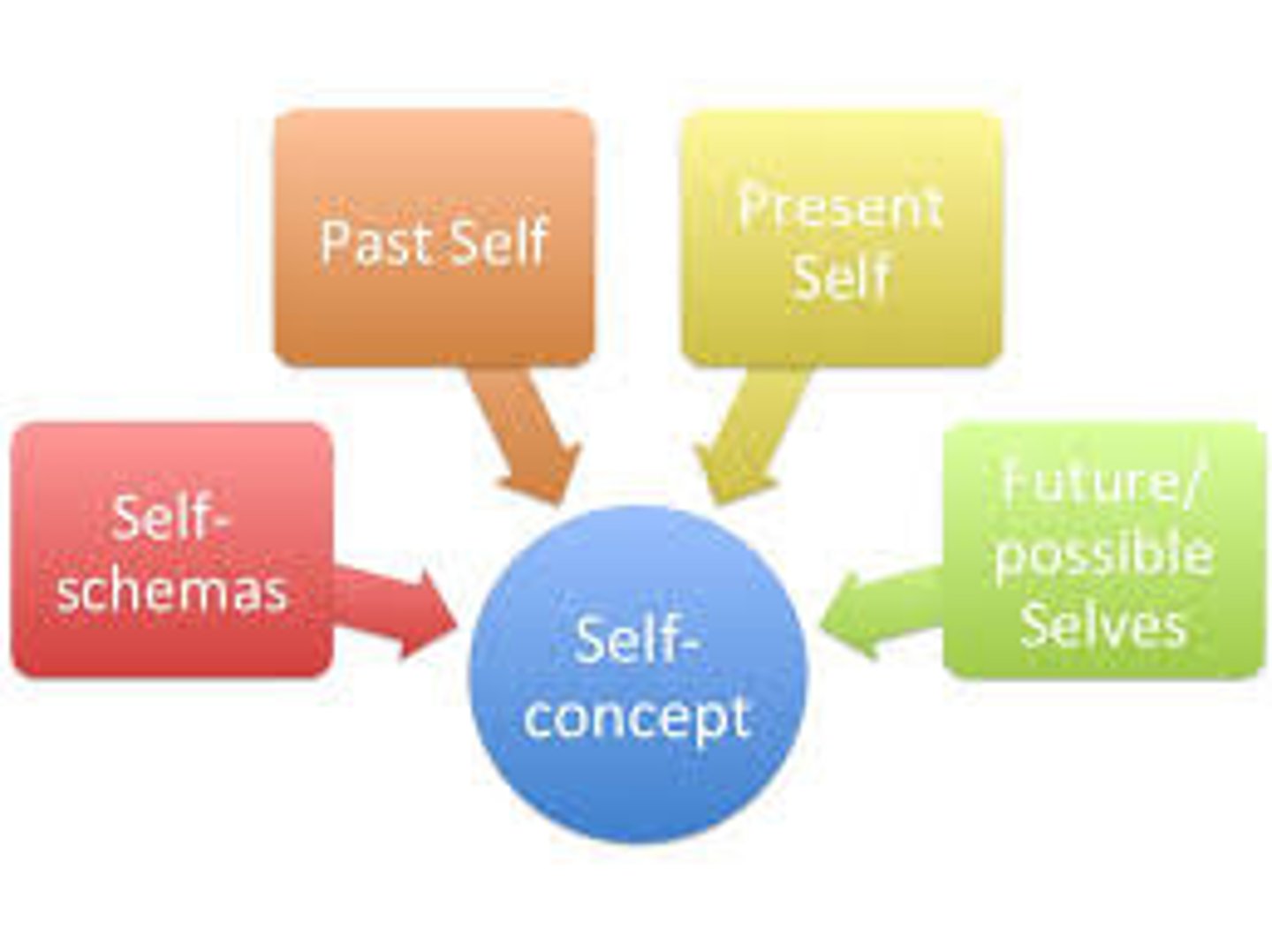
self-concept
a sense of one's identity and personal worth
operational stage
authoritative
authority= someone who enforces with meaning/purpose

authoritarian
very strict
Like a dictator

permissive
describes a parenting style that is characterized by the parent making few demands on the child

neglecting
to pay no attention or too little attention to; disregard
basic trust
ERIK ERIKSON
period of infancy in the first years of life where children who are loved and cared for develop trust and security.

ERIk ERIKSON theory
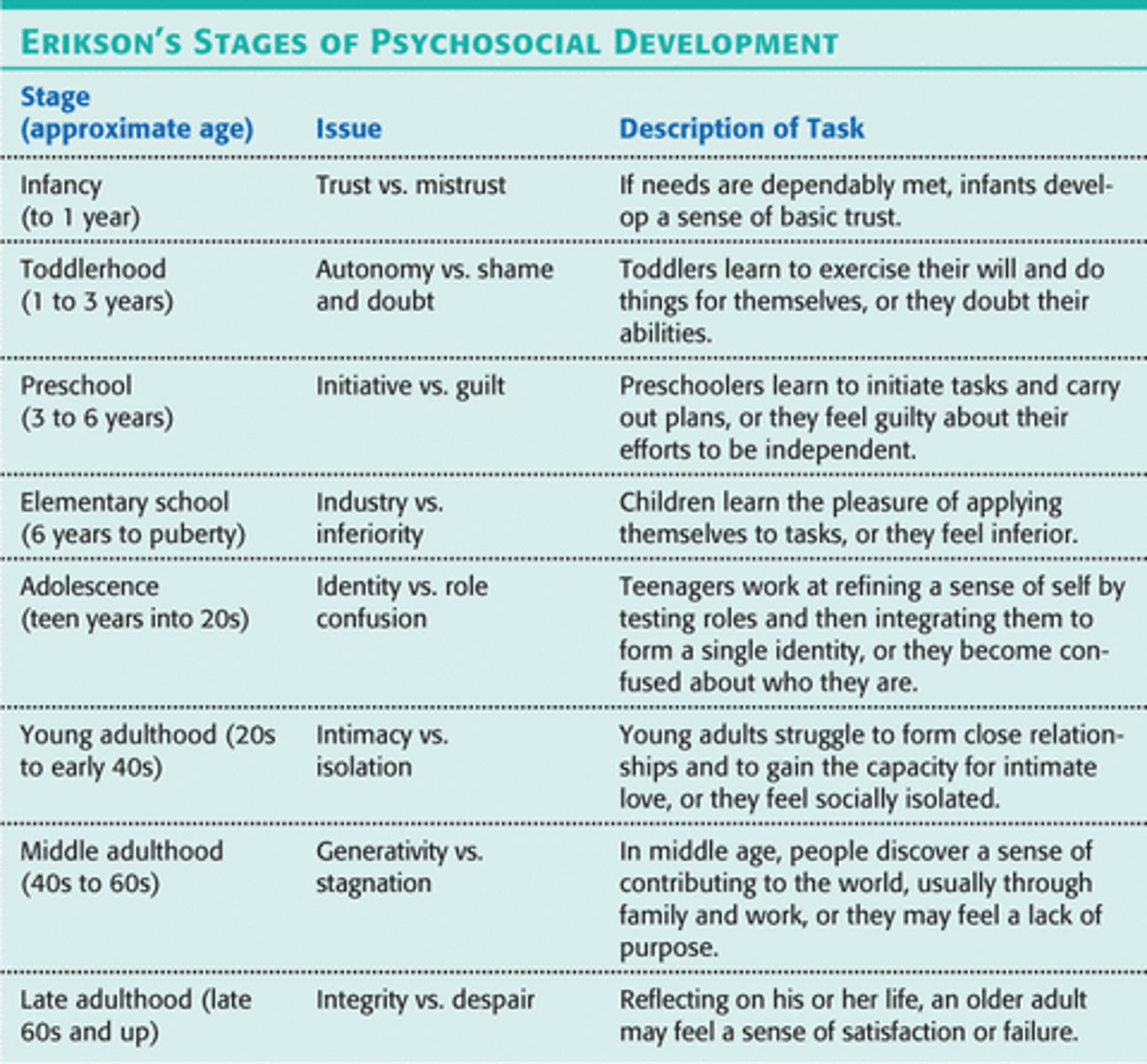
trust vs. mistrust
infant- 1yr
A conflict infants have during their first stage of social development during which they have trouble trusting the world around them as a predictable place.

autonomy vs. shame & doubt
1-3 yrs.
independence
success=autonomy
Failure=doubt and shame
exert control, exercise choice and self restraint

initiative vs. guilt
3-6yrs.
Sense of purpose,power, environment.
Erikson's third stage in which the child finds independence in planning, playing and other activities

industry vs. inferiority
6-12 yrs, good: competence, exercise his/her abilities and intelligence in the world, be able to affect world in the way that the child desires self-confidence

identity vs. role confusion
adolescence - 12 to 19yrs - adolescents try to figure out "who am I?" They establish sexual, ethnic, and career identities or are confused about what future roles to play
intimacy vs. isolation
19- 25 yrs. Erikson's stage in which individuals form deeply personal relationships, marry, begin families and work on career goals.

generativity vs. stagnation
20-40yrs
According to Erikson, the stage during middle adulthood in which people consider their contributions to family and society.
**may feel a lack of purpose-- try and bring positive changes to their life
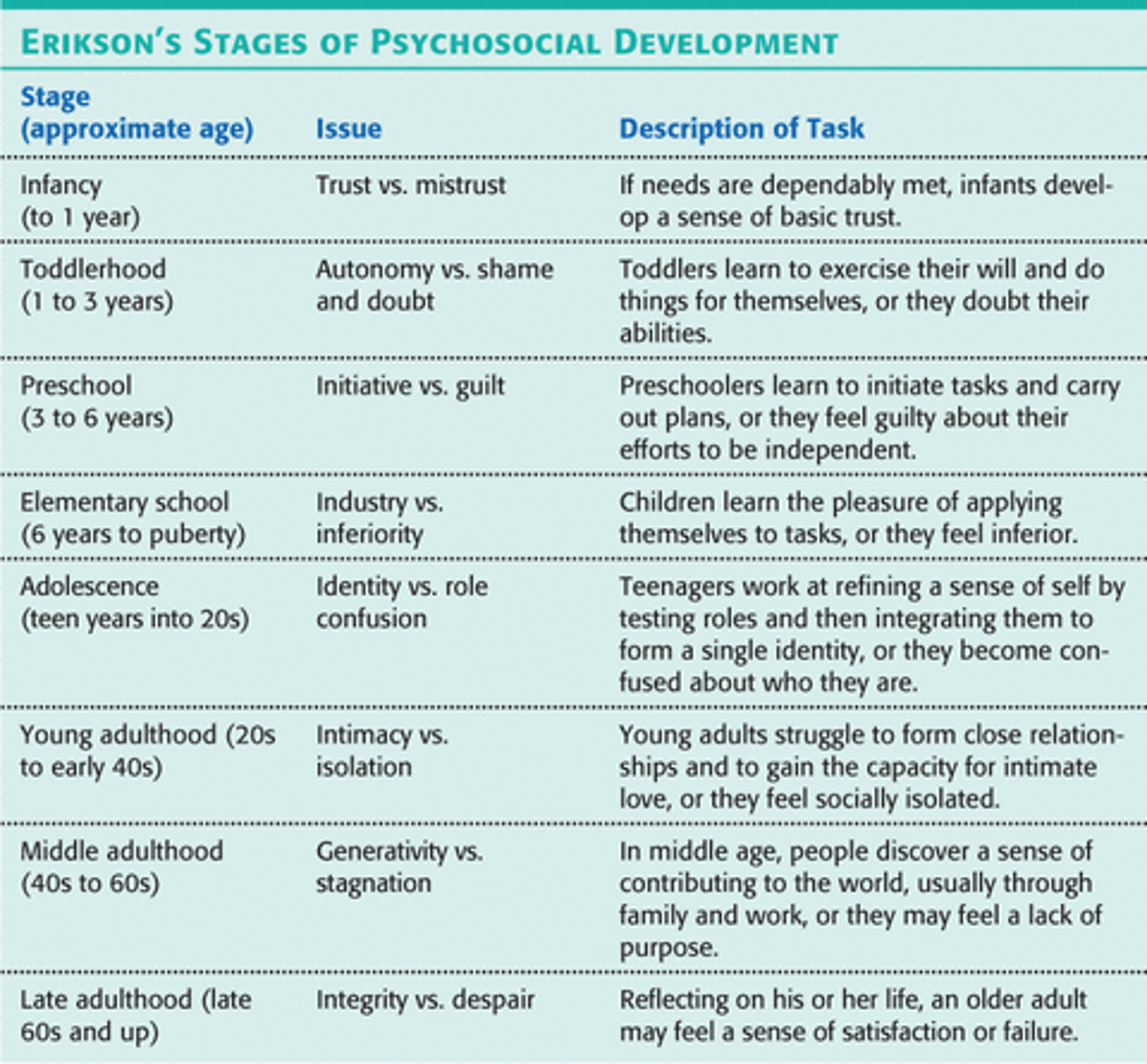
integrity vs. despair
Did I live a meaningful life?
Reflecting back on life
Wisdom
Imminent Death ‐> last stage

identity achievement
Erikson's term for the attainment of identity, or the point at which a person understands who he or she is as an individual, in accord with past experiences and future plans
who am i?
in identity vs. role confusion stage

moratorium
identity crisis
Mortstorium-> MIDDLE of crisis

foreclosure
Erikson's term for premature identity formation, which occurs when an adolescent adopts parent's or society's roles and values wholesale, without questioning and analysis
not personal identity--> based on others
Foreclosure--> Forgetting about your own beliefs/ideas

identify diffusion
An identity status characterizing individuals who are not questioning who they are and have not yet committed themselves to an identity

midlife crisis
A supposed period of unusual anxiety, radical self-reexamination, and sudden transformation that was once widely associated with middle age but that actually had more to do with developmental history than with chronological age

social clock
the culturally preferred timing of social events such as marriage, parenthood, and retirement
SOCIETY timing of SOCIAL EVENTS

stages of grief
The 5 stages are denial, anger, bargaining, depression, acceptance
DABDA

denial
Refusing to believe or even perceive painful realities

anger

bargaining
What stage of grieving occurs when the potential loss has been accepted, but the person makes deals to get more time?

depression
A prolonged feeling of helplessness, hopelessness, and sadness

acceptance
5th Stage of Grief

gender vs. sex
Gender role identity is a state of mind as well as body; biological gender does not totally determine whether he or she will exhibit sex-typed traits
gender roles
attitudes and activities that a society links to each sex

gender identity
one's sense of being male or female

social learning theory
The theory that we learn social behavior by observing and imitating and by being rewarded and punished

gender schema theory
the theory that children learn from their cultures a concept of what it means to be male and female and that they adjust their behavior accordingly

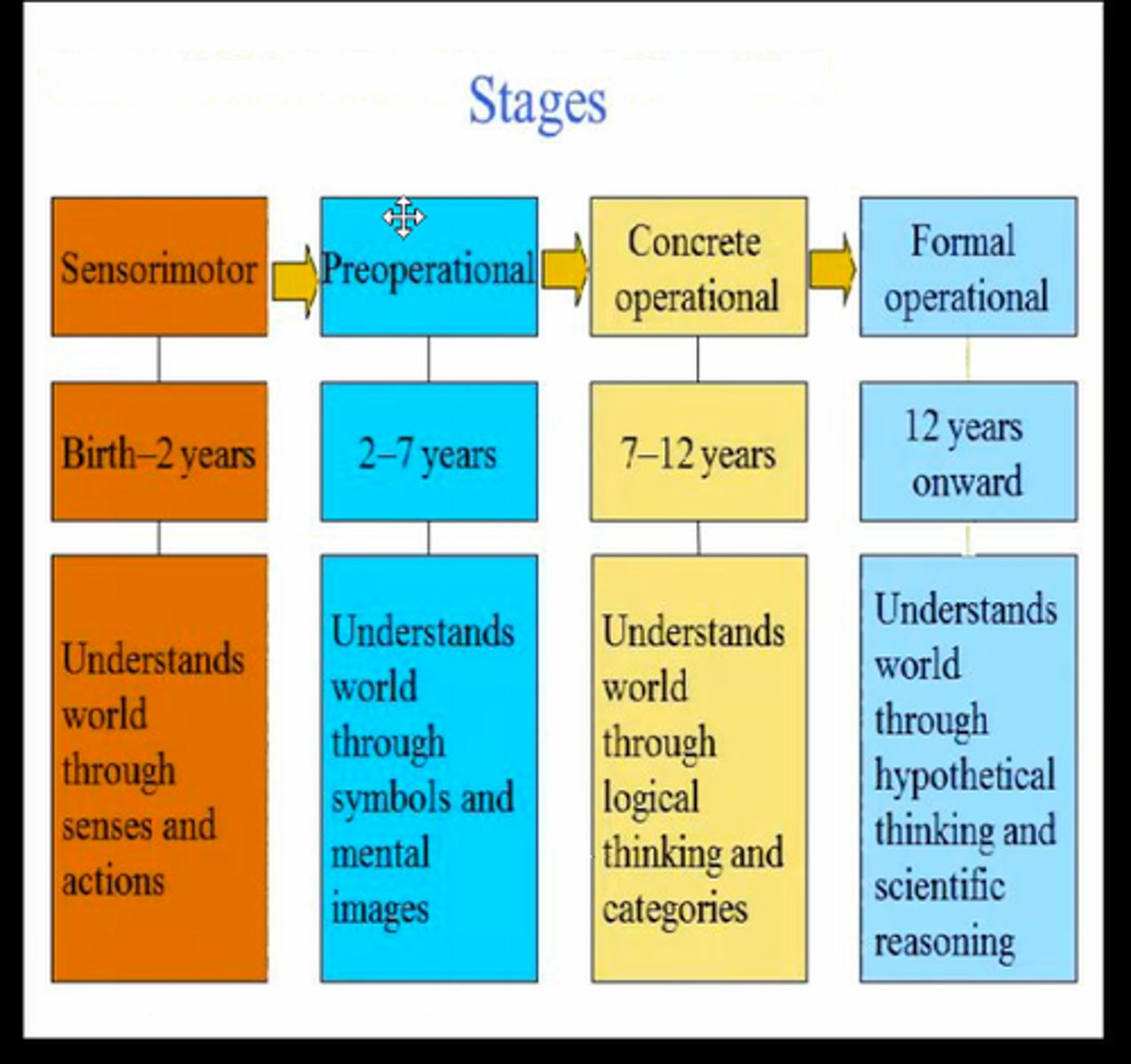
Cognitive Development stages
piaget
Some Pigs Can Fly Others Eat Canned Ham
Sensorimotor stage----- Object Permanence
Preoperational stage--- Egocentrism
Concrete operational -- Conservation
formal operational------ Hypothetial Reasoning

Sensorimotor stage
Piaget's theory
birth- 2 years
object permanence, stranger anxiety
develop sensory impressions and motor skills
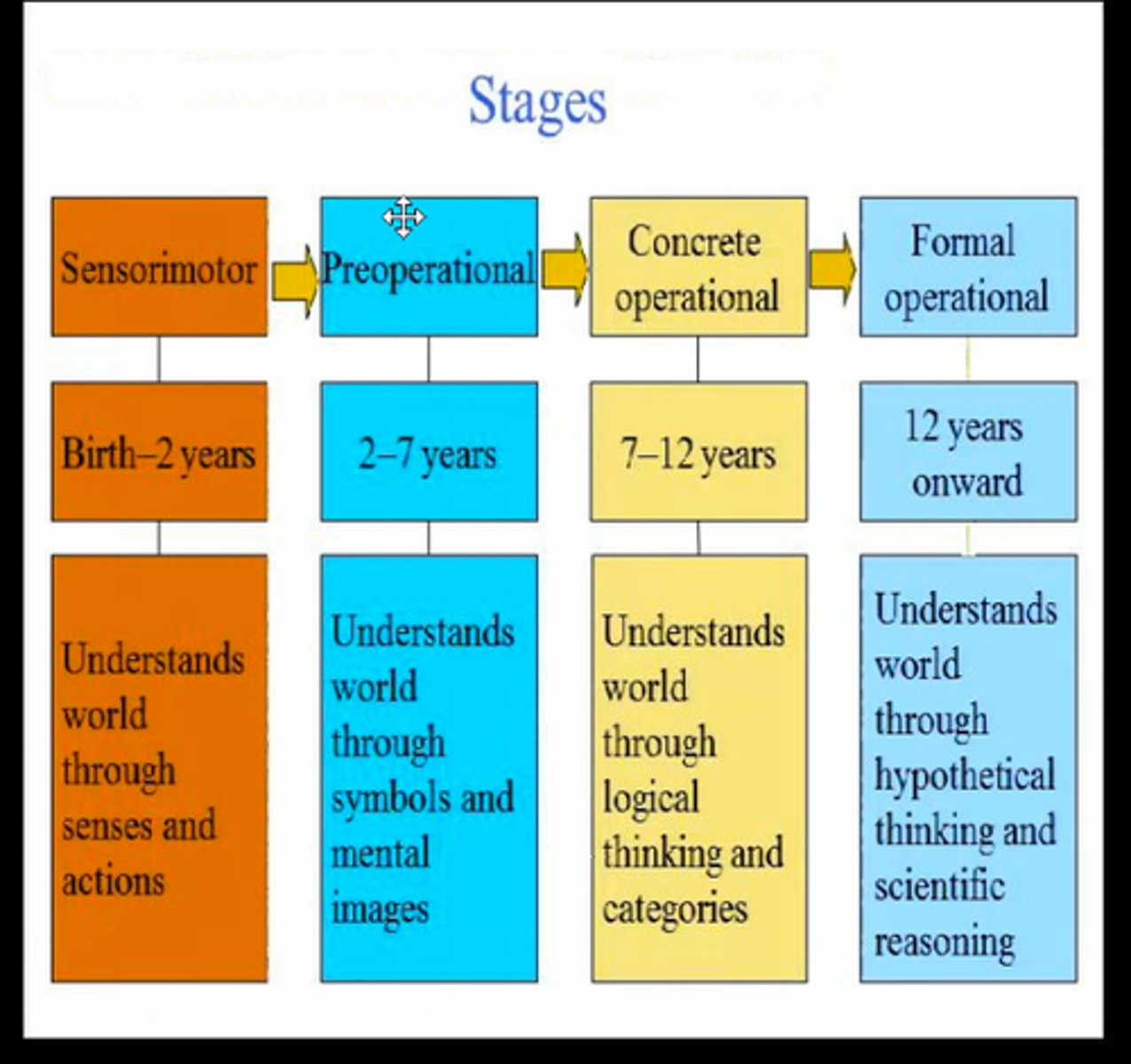
Preoperational stage
Piaget's theory
2-7 years
Egocentrism, animistic thought, centration
a child learns to use language but does not yet comprehend the mental operations of concrete logic
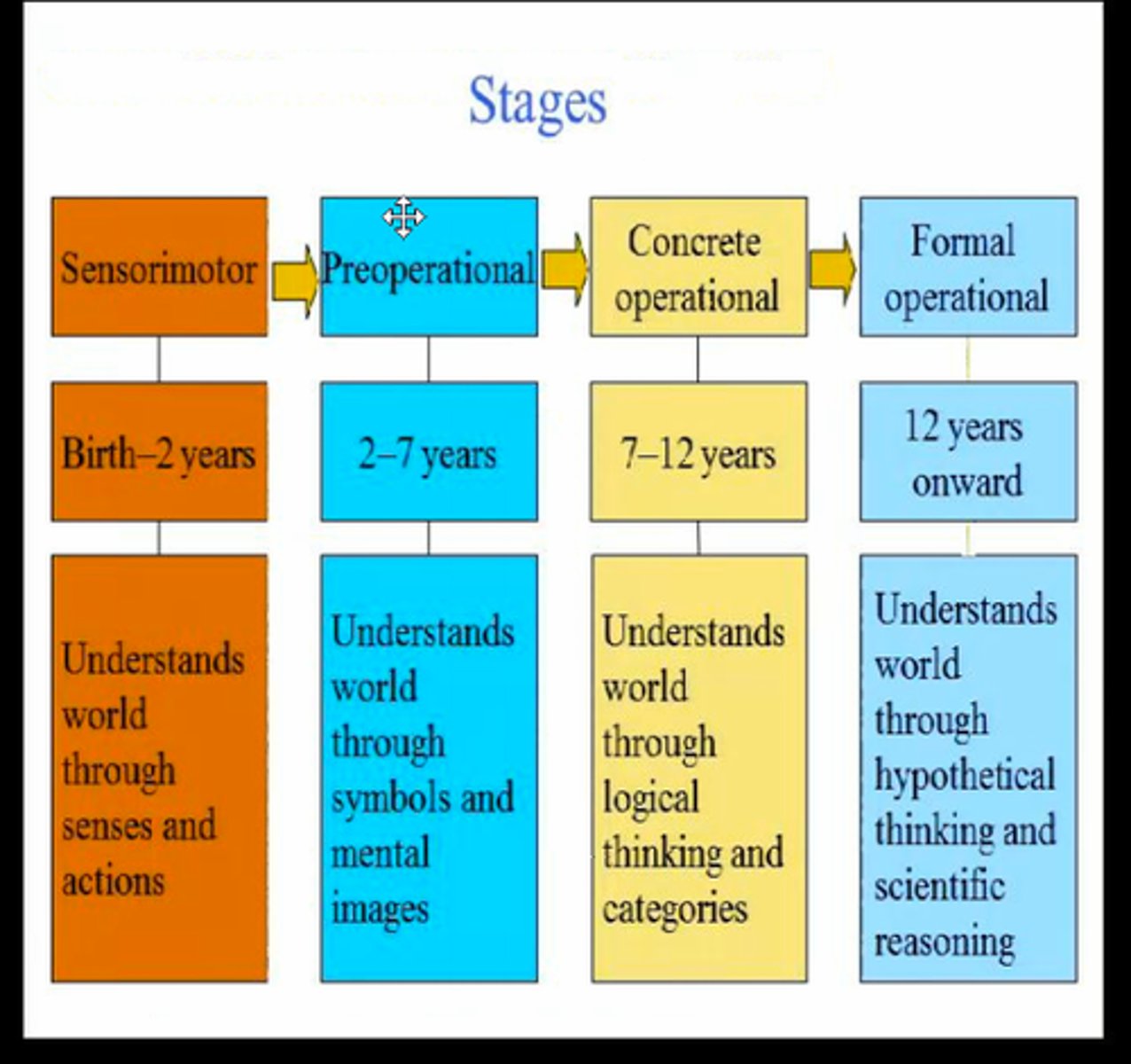
Concrete operational
Piaget's theory
7-12 years
children gain the mental operations that enable them to think logically about concrete events
CONCRETE-- hard to change mental operations
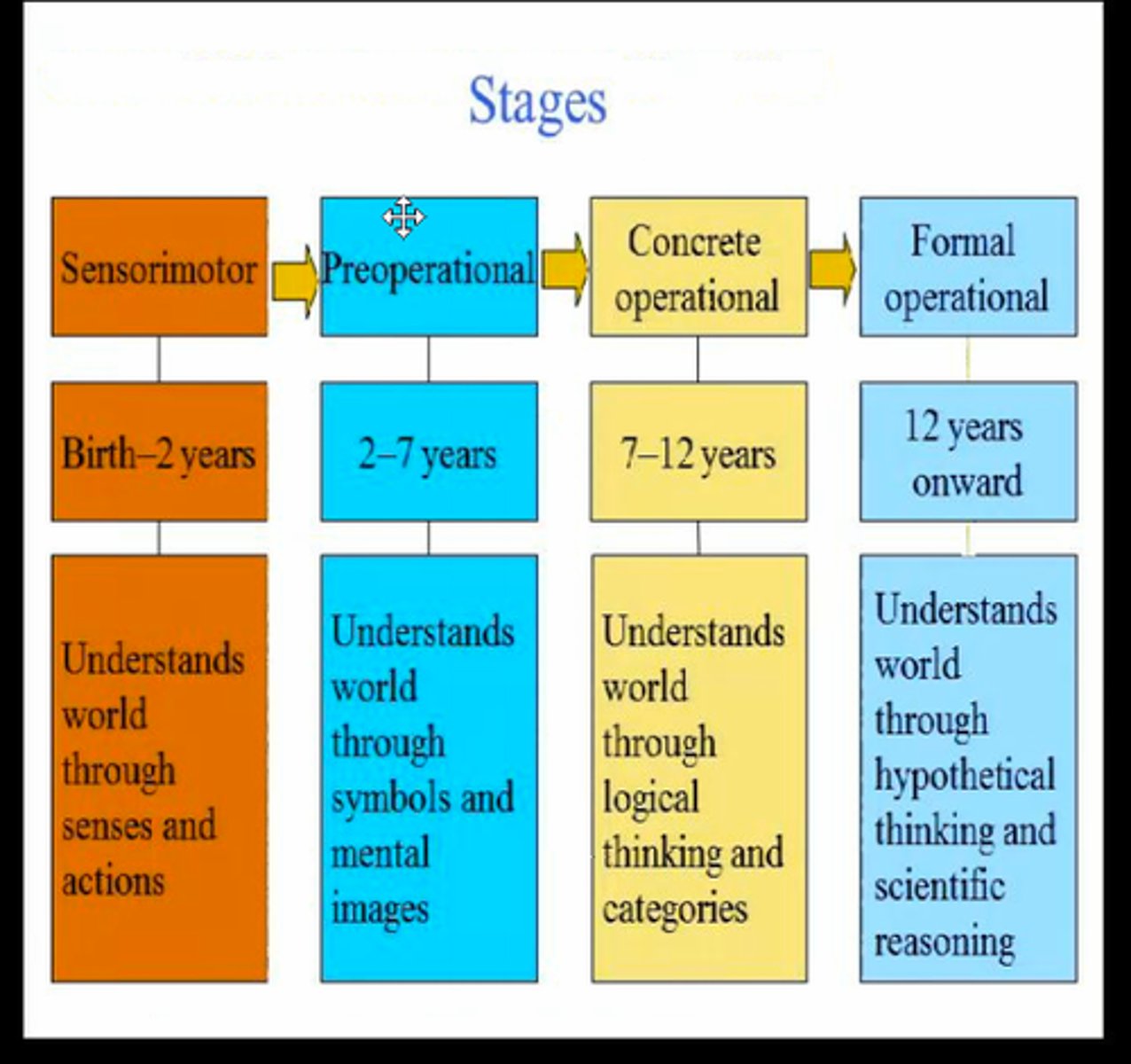
Formal operational
Piaget's theory
14- adult
hypothetical reasoning
cognitive development during which people begin to think logically about abstract concepts
object permanence
the awareness that things continue to exist even when not perceived
stranger anxiety
the fear of strangers that infants commonly display, beginning by about 8 months of age
