ap bio unit 5 review
Meiosis and Genetic Diversity
Meiosis Process
- meiosis: allows parents to pass genetic information onto offspring by maintaining a consistent number of chromosomes being passes along while allowing for genetic diversity between parent and offspring; used in gamete formation
- forms haploid (n) gametes from diploid (2n) parent cells
- when a haploid (n) egg cell is fertilized by a haploid (n) sperm, the resulting zygote has the correct diploid (2n) number of chromosomes
- meiosis and fertilization ensure that each subsequent generation has the same number of chromosomes
- different from mitosis:
- mitosis: results in two genetically identical diploid (2n) daughter cells after 1 round of division
- meiosis: results in four genetically different haploid (n) daughter cells after 2 rounds of division
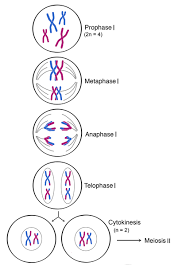
Meiosis 1
first stage of meiosis; aka the reduction division phase; occurs after DNA replication
consists of four parts: prophase 1, metaphase 1, anaphase 1, and telophase 1
prophase 1: nuclear membrane breaks down and chromosomes condense/become visible (same as mitosis); homologous chromosomes pair up and genetic recombination occurs (different from mitosis)
- genetic recombination: aka crossing over; causes genetic diversity in resulting cells
metaphase 1: chromosomes line up in homologous pairs along center of cells (different from mitosis (chromosomes line up in single column, not pairs))
anaphase 1: pairs of homologous chromosomes separate (different from mitosis (sister chromatids separate and move to opposite ends of cell)); there are the same number of chromosomes at the end of anaphase 1 as there are at the beginning of the phase (different from mitosis)
telophase 1: two nuclei are formed, followed by cytokinesis, resulting in two haploid (n) cells (different from mitosis (two nuclei are formed and after cytokinesis, two diploid (2n) cells are formed))
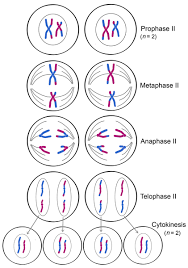
Meiosis 2
second round of division; consists of the same four stages but without DNA replication like in meiosis 1
prophase 2: chromosomes condense again and become visible
metaphase 2: chromosomes line up in a single line along the center of each cell (like in metaphase of mitosis)
anaphase 2: sister chromatids separate and move to opposite ends of cell; each sister chromatid will have its own centromere; at then end of anaphase 2, the separated sister chromatids are now considered separate chromosomes
telophase 2: each of the cells split in half, resulting in 4 haploid (n) gametic cells
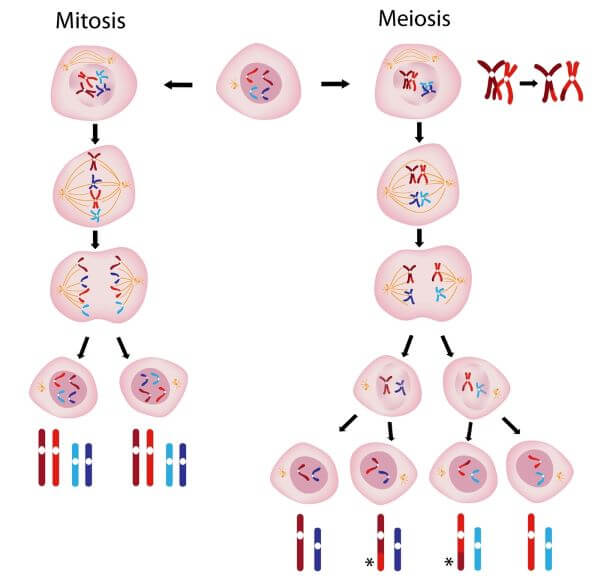
Meiosis vs. Mitosis
| mitosis | meiosis | |
|---|---|---|
| purpose | asexual reproduction, growth, and repair | sexual reproduction |
| DNA replication | occurs once (before start of mitosis) | occurs once (before start of meiosis 1) |
| cell division | one round | two rounds |
| result | two genetically identical diploid (2n) cells | four genetically diverse haploid (n) gametes |
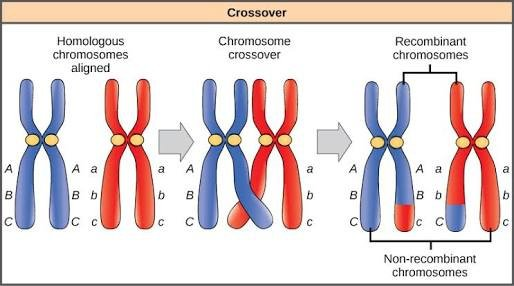
How Meiosis Causes Genetic Diversity
synapsis during prophase 1: homologous chromosomes pair up during synapsis to form tetrads; homologous chromosomes within tetrads can exchange genetic information through genetic recombination
- genetic recombination: generates new combinations of genetic material on each chromatid that may be passed onto offspring; increases genetic diversity of the species
- linked genes: genes that are close together and often inherited on the same chromosome
- frequency of genetic recombination between genes on the same chromosome can be used to generate genetic maps that show the relative positions of genes on chromosomes
- genes that are farther apart will have higher recombination frequency; genes that are closer will have a lower recombination frequency
- translocations: mutations between non-homologous chromosomes; can generate new combinations of genetic material, but if they occur in the middle of the gene, they may inactivate the gene resulting in an unfavorable phenotype
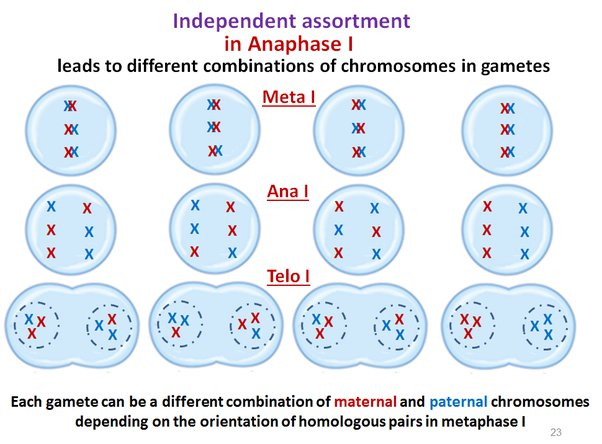
random assortment during metaphase 1: homologous chromosome pairs line up randomly at the center of the cell, resulting in different pairs of the paternal and maternal chromosome on either side
- nondisjunction: when homologous pairs fail to separate (during anaphase 1) and end up in the same gamete
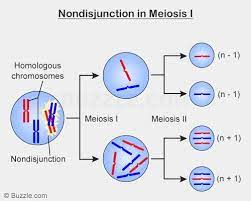
- aneuploidy: occurs when nondisjunction gamete is fertilized; atypical number of chromosomes
- down syndrome: common form of aneuploidy where an individual has 3 copies on chromosome 21 instead of 2 copies
Mendelian Genetics and Probability
Mendelian Genetics
- mendel’s law of segregation: states that an organism carries 2 variations of every trait (alleles), one from each parent, and the alleles segregate independently into gametes
- the segregation occurs during anaphase 1 of meiosis; one allele ends up in each gamete
- when two gametes join during fertilization, the offspring has 2 alleles for each trait
- mendel’s law of independent assortment: states that genes for different traits segregate independently of one another (occurs during metaphase 1 of meiosis)
Pedigrees and Punnet Squares
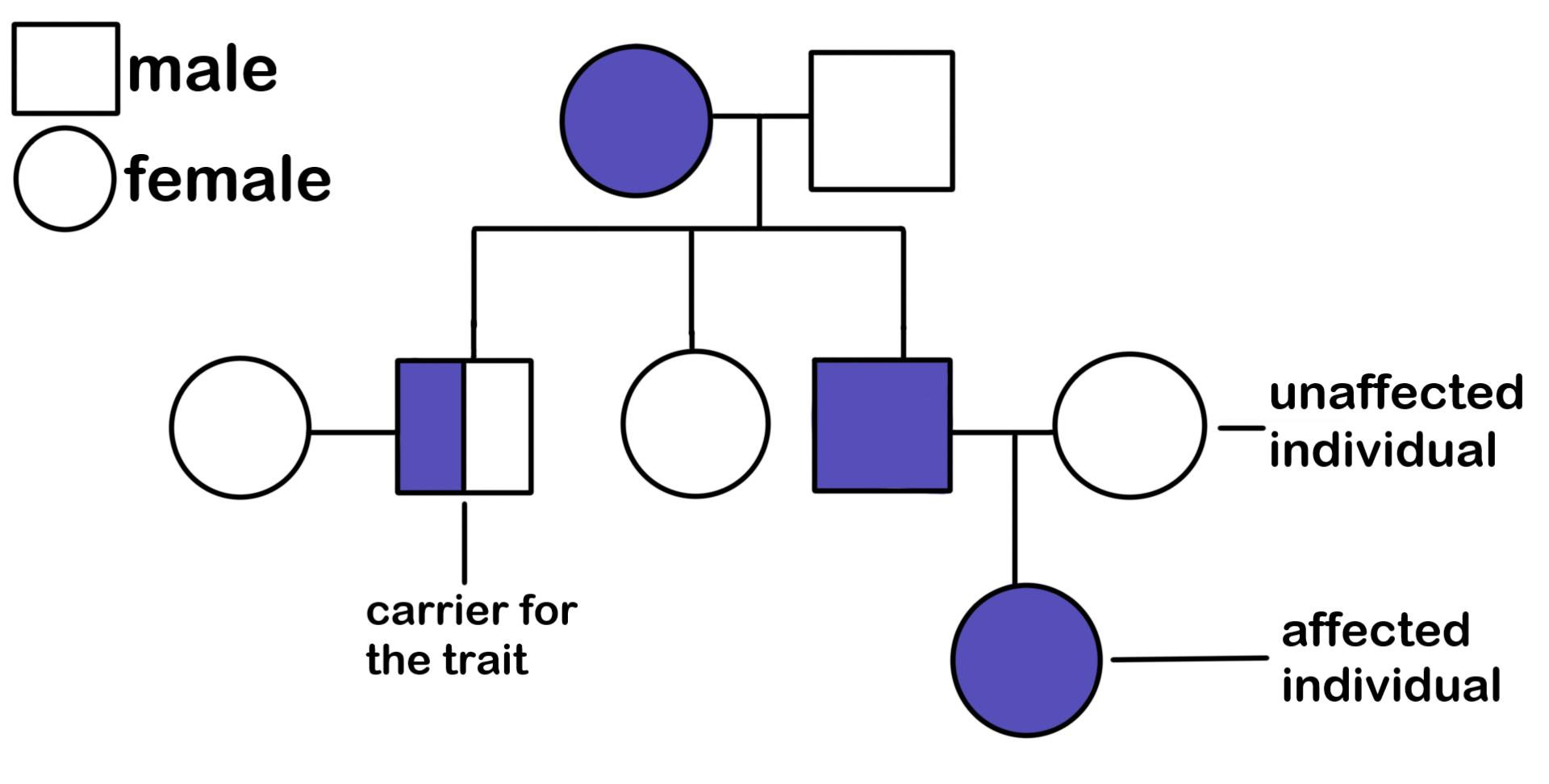
pedigree: chart that illustrates the inheritance of a trait through several generations
- horizontal lines: between individuals to show offspring produced together
- vertical lines: coming from horizontal line to represent the produced offspring and a new generation forming
- circles: typically represent females
- squares: typically represent males
- shaded: shows individuals that carry the displayed trait
need-to-know terms:
- dominant trait: tends to be expressed in at least one parent to show up in offspring; only one allele is required for the trait to be expressed
- recessive trait: often expressed in offspring, but not either parent (parents are heterozygous for trait); both alleles are required for expression of trait
- sex-linked: appear more often in males than females due to lack of 2nd x chromosome to mask expression of trait
- genotype: genetic makeup of alleles for the trait
- phenotype: physical expression of genotype
- homozygous: having two copies of the same allele for a trait
- heterozygous: having different copies of alleles for the trait
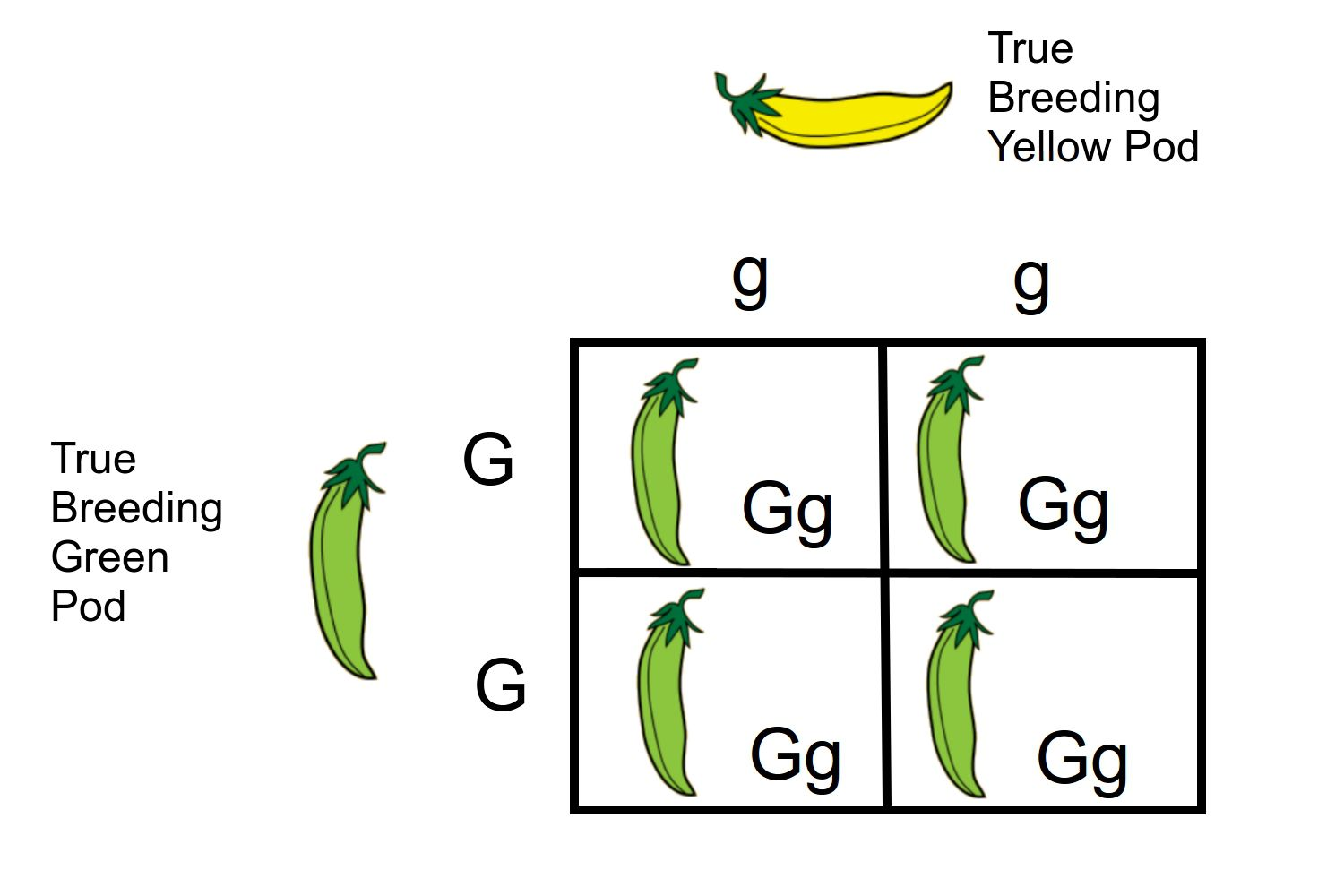
mono-hybrid cross: simple cross between two alleles from each parent to show 4 possible combinations of the alleles in the offspring
dihybrid cross: more complex cross between two alleles for two traits from each parent to show 16 possible allele combinations in the offspring
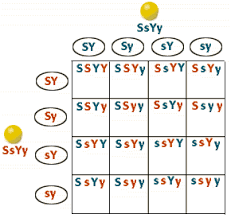
test cross: a cross between an organism with a dominant phenotype (whose genotype is unknown) and an organism with a recessive phenotype
- organism with dominant phenotype is homozygous: all offspring of test cross will show dominant phenotype
- organism with dominant phenotype is heterozygous: only 1/2 of offspring will show dominant phenotype and other 1/2 will show recessive phenotype
Non-Mendelian Genetics
- most traits do not follow mendelian genetic laws
- ratios of phenotypes often are not accurately predicted with punnet squares
- non-mendelian genetics may be the result of:
- linked genes
- multiple genes coding for the same phenotype
- non-nuclear inheritance
- environmental effects
Linked Genes
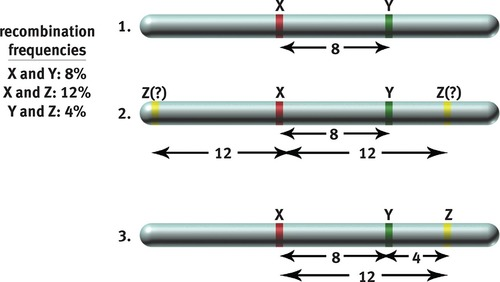
linked genes: genes that are close together on the same chromosome and often are inherited together because of their low recombination frequency
- unlinked genes: on separate chromosomes, so they are less likely to be inherited together
genetic recombination may occur between linked genes during prophase 1 of meiosis
- the farther apart the genes are, the more likely it is that recombination will occur between them
- recombination frequencies an be used to map distances between genes on a chromosome
- map units: measurement for distance between genes
- ex. recombination frequency of 10% would mean there are 10 map units between the 2 genes
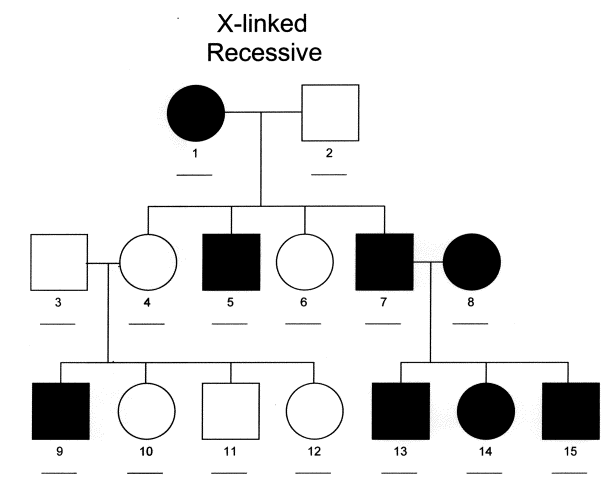
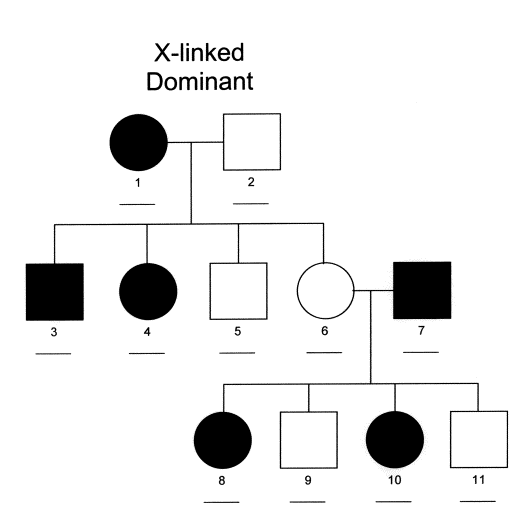
Sex-Linked Genes
autosomes: chromosomes that aren’t directly involved in sex determination; most genes are located on autosomes
- males and females are equally as likely to inherit genes on autosomes
sex chromosomes: are directly involved in sex determination; there are 23 pairs in humans (number of chromosomes vary between species)
- males and females are not equally as likely to inherit genes on certain sex chromosomes because males are XY and females are XX
- traits that are coded for by sex-linked recessive alleles are more likely to be expressed in males because they only have one X chromosome
- females may also express a sex-linked trait, but they would need to inherit the trait from both parents to express it
examples:
- if male has sex-linked dominant trait: all his daughters would get it
- if female has sex-linked dominant trait: sons and daughters would have 1/2 chance of getting it
Multiple Gene Inheritance
- some traits are produced by multiple genes acting on the phenotype
- example: height in plants is determined by 3 genes (A, B, and C), and each dominant allele present makes the plant taller
- AABBCC plant: very tall
- aabbcc plant: very short
- AaBbCc plant: middle height
- many other genotypes (ex. aaBbCc, AaBBcc, etc. would still result in a height in the middle of the range)
Non-Nuclear Inheritance
- mitochondria and chloroplasts have DNA separate from nuclear DNA
- genes on mitochondrial or chloroplast DNA do not follow the inheritance patterns of genes on nuclear DNA
- during gamete formation: eggs produced in animals and ovules produced in plants are much larger than sperm (in animals) and pollen (in plants), so they contribute much more mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) than sperm or pollen do
- non-nuclear genes demonstrate maternal inheritance
- non-nuclear maternal vs. sex-linked:
- in sex-linked: sex-linked genes are located on a sex chromosome (usually the X) in the nucleus; it can be inherited from the father or mother
- in non-nuclear: genes are located on the mitochondria or chloroplast; can only be inherited from mother
Environmental Factors Affecting Phenotype
- phenotype = genotype + environment
- phenotypic plasticity: the ability of the same genotype to produce different phenotypes in response to different environmental factors
- examples:
- when flowers of hydrangea plant grow in basic pH soil, the flowers are pink; when the flowers grow in acidic pH soil, the flowers are blue
- humans being exposed to UV light can stimulate the expression of genes involved in melanin production