High-Risk Newborns: Complications and Care
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
Intrauterine Growth Restriction
Limited fetal growth during advanced gestation.
Small for Gestational Age (SGA)
Weight below 10th percentile for gestational age.
Intrauterine Growth Restriction (IUGR)
Growth restriction due to various maternal factors.
Symmetrical IUGR
Proportional growth restriction in all body parts.
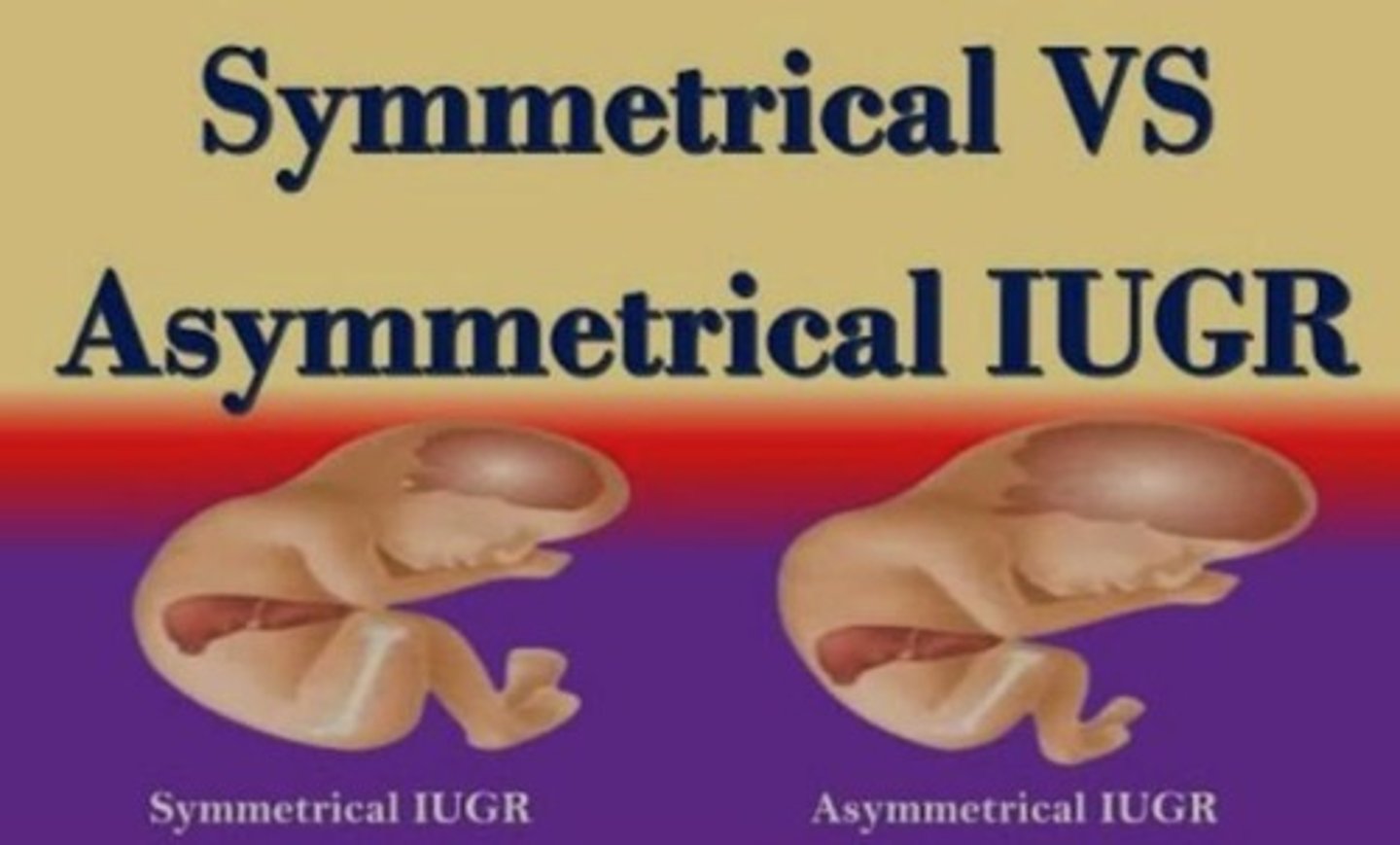
Asymmetrical IUGR
Normal head/body length, but low birth weight.
Hypoxia
Decreased oxygen supply to the fetus.
Aspiration Syndrome
Meconium aspiration before or during birth.
Hypothermia
Inability to maintain normal body temperature.
Hypoglycemia
Low blood sugar levels in newborns.
Polycythemia
Increased number of immature red blood cells.
Large for Gestational Age (LGA)
Weight above the 90th percentile for gestational age.
Complications of LGA
Includes birth trauma and hypoglycemia risks.
Diabetic Mother Newborn
May be SGA or LGA due to maternal diabetes.
Hypocalcemia
Low calcium levels in newborns.
Hyperbilirubinemia
Elevated bilirubin levels causing jaundice.
Birth Trauma
Injuries during delivery, such as shoulder dystocia.
Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS)
Breathing difficulties due to surfactant issues.
Congenital Malformations
Structural defects present at birth.
Cold Stress
Excessive heat loss leading to hypothermia.
Jaundice
Yellowing of skin due to bilirubin buildup.
Risk Factors for Neonatal Morbidity
Includes low socioeconomic status and no prenatal care.
Hypoglycemia
Blood sugar less than 40-45 mg/dl.
Signs of Hypoglycemia
Tremors, seizures, apnea, cyanosis, lethargy.
Apnea
Condition of forgetting to breathe.
Cyanosis
Skin turning blue due to oxygen deficiency.
Temperature Instability
Inability to maintain normal body temperature.
Nursing Considerations hypoglycemia
Check blood sugar at 1 hour of life.
Feeding Protocol
Feed baby or use IV dextrose if low.
Prematurity Definition
Newborn delivered before 38 weeks gestation.
Incidence of Prematurity
Occurs in 12% of live births.
Complications of Prematurity
Affects cardiovascular, respiratory, GI, GU systems.
Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS)
Insufficient surfactant causing breathing difficulties.
Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)
Abnormal blood flow in the heart.
Thermoregulation Issues
High surface area to mass ratio causes heat loss.
Poor Feeding Reflexes
Includes poor sucking, swallowing, and gag reflex.
Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NEC)
Severe intestinal condition in premature infants.
Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)
Decreased in premature infants affecting fluid processing.
Hepatic Complications
Immature liver leads to low iron stores.
Hyperbilirubinemia
Excess bilirubin due to immature liver function.
Immunologic Risks
Higher infection risk necessitating maternal breastmilk.
Neurodevelopment Risks
Brain development interruption leads to IVH, ICH.
Apnea
Cessation of breathing for at least 20 seconds.
Prematurity
Birth before 37 weeks gestation.
Sudden Infant Death Syndrome
Unexpected death of an infant during sleep.
Retinopathy of Prematurity
Eye issues from hyperoxygenation in premature infants.
Cardio/Respiratory Monitoring
Continuous tracking of heart and breathing functions.
Nutrition for Premature Infants
Feeding every 3 hours as tolerated.
Thermoregulation
Maintaining body temperature in newborns.
Infection Prevention
Hand washing is crucial for newborn safety.
Postmaturity
Birth after 42 weeks gestation, rare occurrence.
Hypoglycemia
Low blood sugar due to depleted stores.
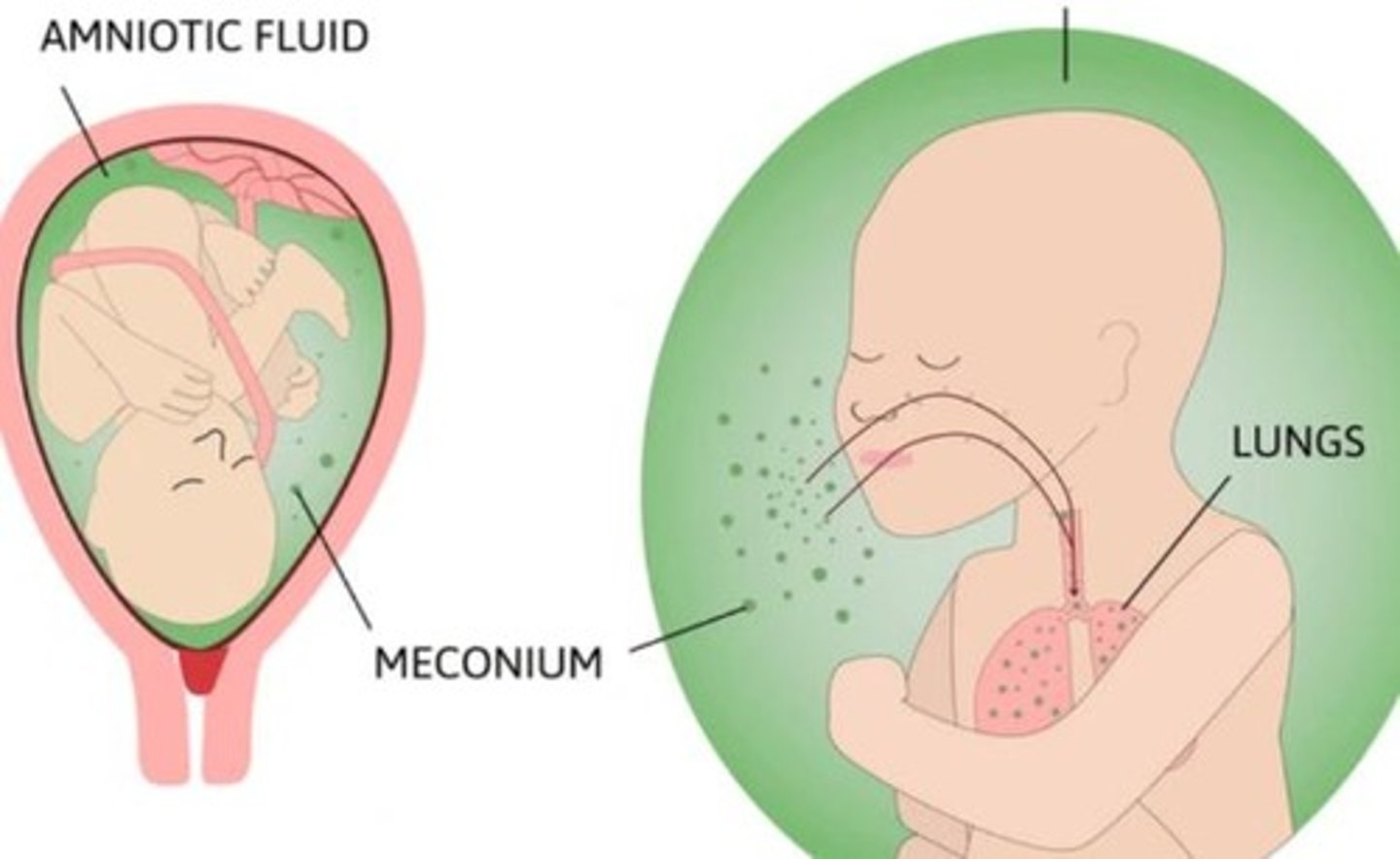
Meconium Aspiration
Inhalation of meconium causing respiratory distress.
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
Disorder from maternal alcohol exposure during pregnancy.
Physical Features of FAS
Short stature, microcephaly, thin appearance.
Long-term Complications of FAS
Impulsive behavior, learning disabilities, cognitive issues.
Substance Abuse Risks
Includes asphyxia, infection, and low APGAR scores.
Withdrawal Symptoms
Occur around 24 hours post-delivery in infants.
Newborn Drug Screen
Urine test for drugs collected immediately after birth.
Social Service Consultation
Involvement for assessing maternal care capabilities.
Behavioral Problems
Emotional and social issues in substance-exposed infants.
Congenital Anomalies
Physical defects present at birth due to substance exposure.
Developmental Problems
Delayed physical, cognitive, or social growth in infants.
Skin-to-Skin Contact
Promotes bonding if infant is stable enough.
Withdrawal Symptoms
Signs like vomiting, diarrhea, and irritability.
Abstinence Scoring
Total score of withdrawal symptoms severity.
Small Frequent Feedings
Helps alleviate withdrawal symptoms in infants.
GI Status Monitoring
Observe for vomiting or diarrhea in infants.
Comfort Techniques
Swaddle, pacifier, and calm infant to soothe.
Skin Protection
Use desitin to prevent skin excoriation.
Decrease Stimulation
Quiet nursery to prevent infant agitation.
Metabolic Screening
Screening done after 24 hours of age.
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
Amino acid disorder causing cognitive disabilities.
Galactosemia
Carbohydrate metabolism disorder affecting newborns.
Homocystinuria
Cystathionine beta synthase deficiency disorder.
Congenital Hypothyroidism
Thyroid hormone deficiency present at birth.
Sickle Cell Anemia
Genetic disorder affecting red blood cells.
Cystic Fibrosis
Genetic disorder affecting respiratory and digestive systems.
Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS)
Common infant condition due to low surfactant.
Tachypnea
Rapid breathing rate over 60 breaths per minute.
Respiratory Effort Signs
Includes grunting, flaring, and retraction.
Management of RDS
Includes steroids, surfactant, and respiratory support.
Transient Tachypnea of the Newborn (TTN)
Breathing difficulty in term and late preterm infants.
Meconium Aspiration Syndrome
Aspiration of meconium during first breaths.
Cold Stress
Excessive heat loss affecting newborn temperature regulation.
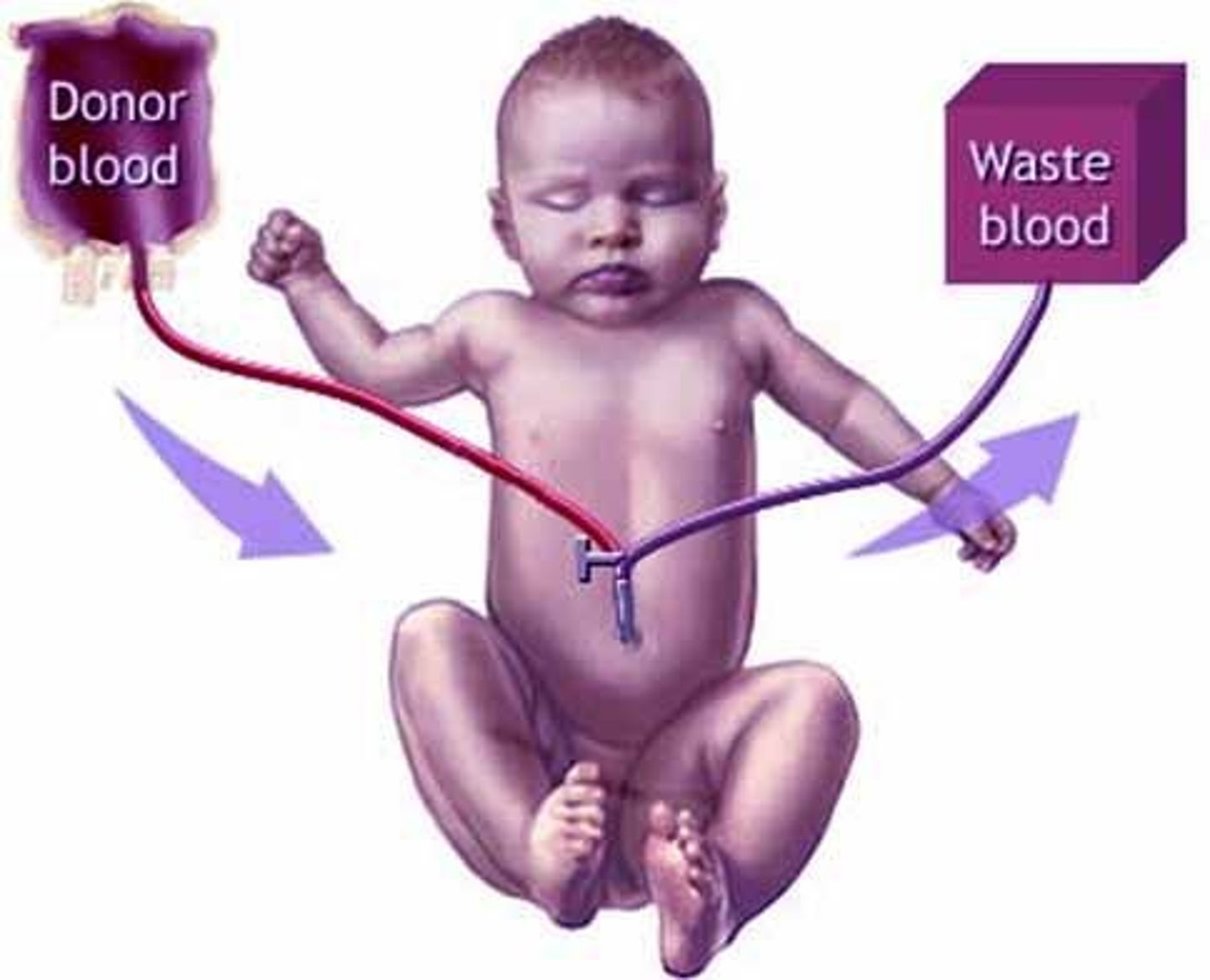
Jaundice Management
Includes phototherapy and exchange transfusion.
Kernicterus
Brain damage from unconjugated bilirubin deposition.
Hydrops Fetalis
Severe anemia and edema due to maternal antibodies.