IB Chem stuff we need to memorise AHHHHHHHH
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
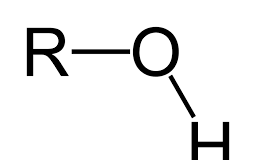
Name the class, functional group name and suffix
Alcohol, hydroxyl, -ol
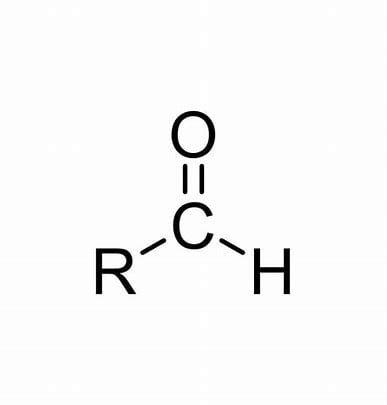
Name the class, functional group name and suffix
Aldehyde, carboxyl, -anal
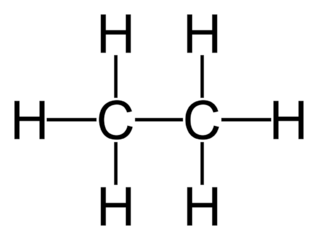
Name the class, functional group name and suffix
alkane, n/a, -ane
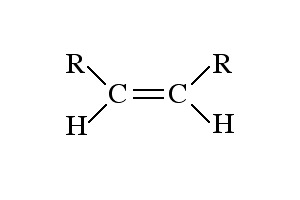
Name the class, functional group name and suffix
Alkene, alkenyl, -ene
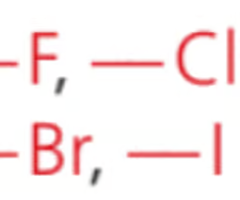
Name the class, functional group name and prefixes
halogenoalkene, halogeno, (flouro, chloro, bromo, iodo)

Name the class, functional group name and suffix
alkyne, alkynyl, -yne
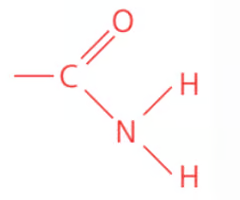
Name the class, functional group name and suffix
amide, amido, -anamide
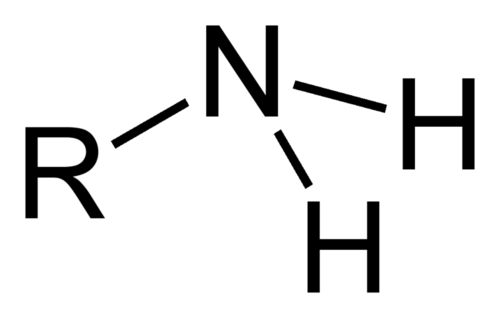
Name the class, functional group name and suffix
amine, amino, -anamine
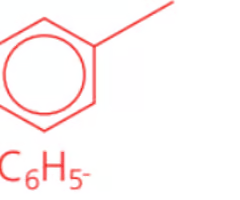
Name the class, functional group name and suffix
arene, phenyl, -benzene
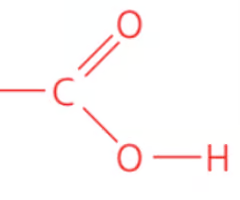
Name the class, functional group name and suffix
carboxylic acid, carboxyl (acid), -anoic acid
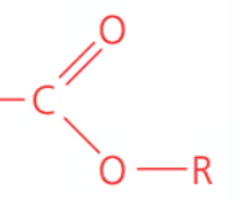
Name the class, functional group name and suffix
ester, carboxyl (ester), -anoate
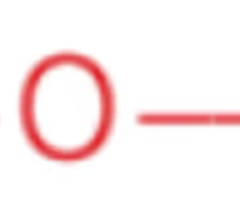
Name the class, functional group name and suffix
ether, alkoxy, -oxy[alkane]
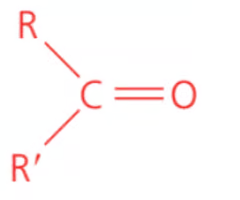
Name the class, functional group name and suffix
ketone, carbonyl, -anone
Define First Ionization Energy
Energy required to remove one mole of electrons from one mole of gaseous ions in their ground state.
Define Electron Affinity
energy change that occurs when one mole of electrons is added to one mole of gaseous atoms
Define electronegativity
the ability of an atom to attract electrons in a covalent bond
Define Ligand
A species that uses a lone pair to form a dative/coordinate bond with a metal ion
What is the overall state of ammonium (NH4)
+1
What is the oxidation state of hydroxide ion (OH)
-1
What is the oxidation state of nitrate ion (NO3)
-1
What is the oxidation state of hydrogen carbonate (HCO3)
-1
What is the oxidation state of carbonate ion (CO3)
-2
What is the oxidation state of sulfate ion (SO4)
-2
What is the oxidation state of phosphate ion (PO4)
-3
Formal Charge General Rules?
Get formal charge for each atom
FC = V - (Sticks + Stones)
Sticks - Bond line
Stone - unbonded electron
Get total for each atom, lowest formal charge will be best.
If tie, make sure negative value of formal charge is with most electronegative element.
HNMR spectra
Shift ppm - functional group
Integrated Area - Relative Number of Protons in hydrogen environment
Splitting - n + 1 rule → (Total Neighboring H+ ions) +1 of neighboring hydrogen environments
The ratio of split peak heights in HNMR
Pascal’s Triangle
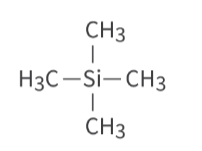
What is TMS, what is its shift and why is it used as a reference for HNMR?
tetramethyl silane, 0ppm, unreactive+non-toxic, volatile so it is easily removed and can be analysed, all protons in TMS are equivalent this produces a strong signal away from other signals
Define Hess’ Law
Enthalpy change for a reaction is independent of the pathway between initial and final states
Define Le Chatelier’s Principle
when a system at equilibrium is subject to a change, it will respond in such a way to minimise the effect of the change
Define lattice enthalpy
the enthalpy change needed to convert 1 mole of solid crystal into its scattered gaseous ions, (HL → it is positive and is proportional to the product of the ionic charges and inversely proportional to the sum of ionic radii)
Fuel Cells vs Conventional Techniques
In Fuel cells, electrical energy is derived directly from a chemical reaction without the need for multiple transformations of energy, highly energy efficient compared to their classic counterparts.
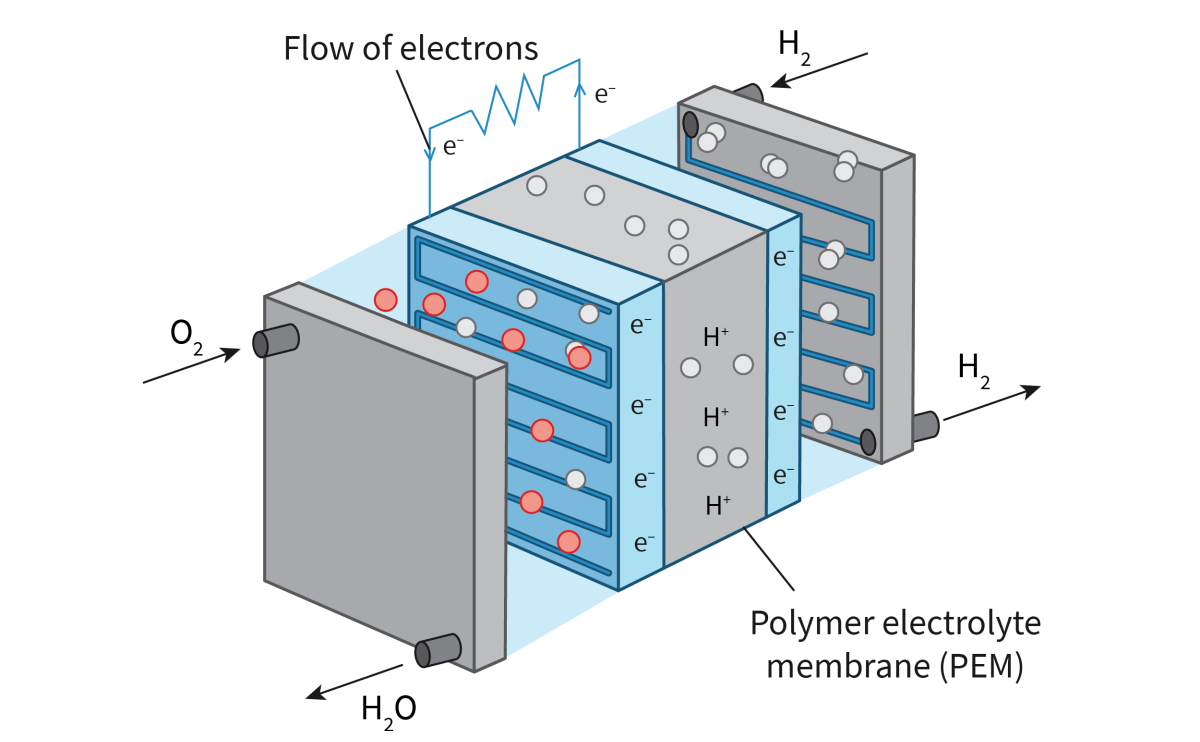
Describe a Fuel Cell
A fuel cell consists of a spontaneous exothermic chemical reaction that is divided in two regions. These two half-reactions are separated by a polymer electrolyte membrane, but connected by a wire. The wire allows for the flow of electrons from one half of the reaction to the other. These electrons released are from an oxidation reaction and are used on the other side. The flow of electrons creates a current.
What reaction takes place on the cathode of a methanol fuel cell? REDCAT (remember state symbols!)
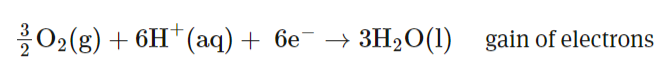
What reaction takes place on the anode of a methanol fuel cell? ANOX (remember state symbols!)
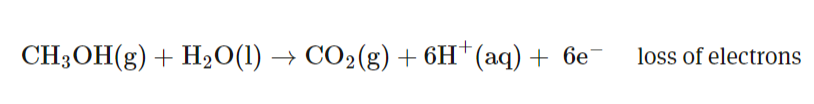
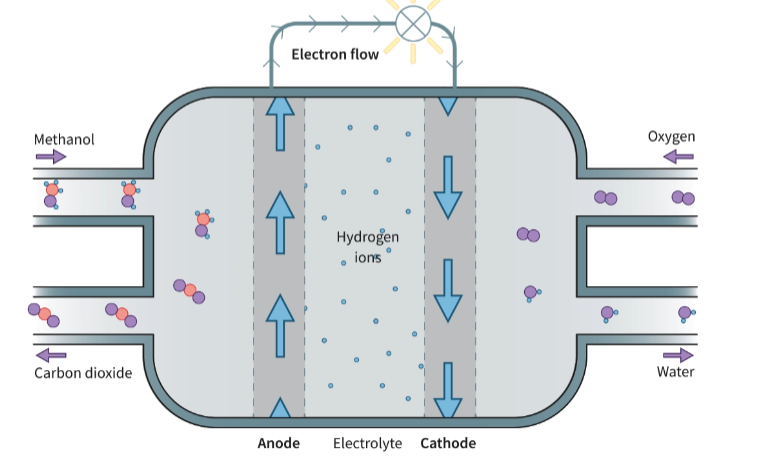
What is the overall reaction of a methanol fuel cell? (remember state symbols!)
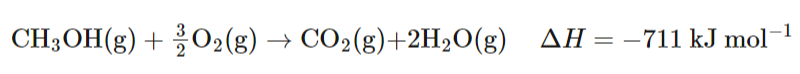
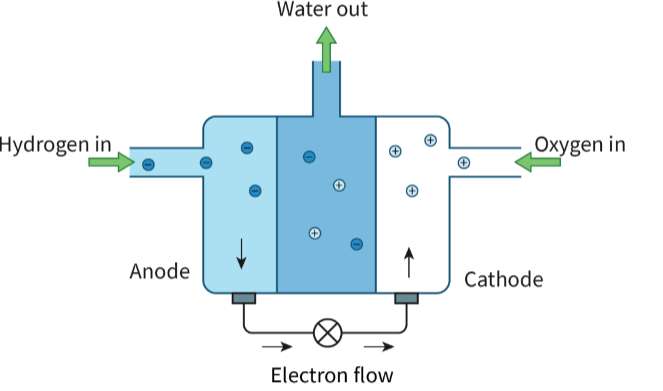
Describe the net reaction in a Hydrogen Fuel Cell (remember state symbols!)
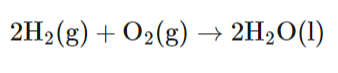
What half reaction occurs in the cathode for a hydrogen fuel cell? REDCAT
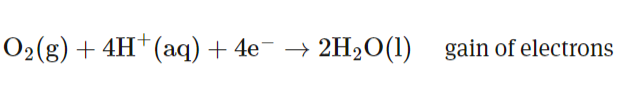
What half reaction occurs in the anode for a hydrogen fuel cell? ANOX
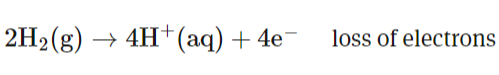
State the difference between atom economy and % yield
yield: amount of product formed as a % of the maximum mass that could be produced theoretically. This measures more of the practical success
atom economy: % of the mass (Mr) of the reactants that becomes the desired product. This measures more of efficiency in a reaction and how much product is made per mole of reactant
Define Dynamic Equilibrium (2)
When the macroscopic properties in a system remain constant (concentrations of P and R no change) and the rate of forwards and backward reactions are the same
Transition Metal Properties
variable oxidation states, forms complex ions/compounds, forms coloured compounds/ions, «para»magnetic compounds/ions
why is zinc not a transition metal?
completely filled d-orbital
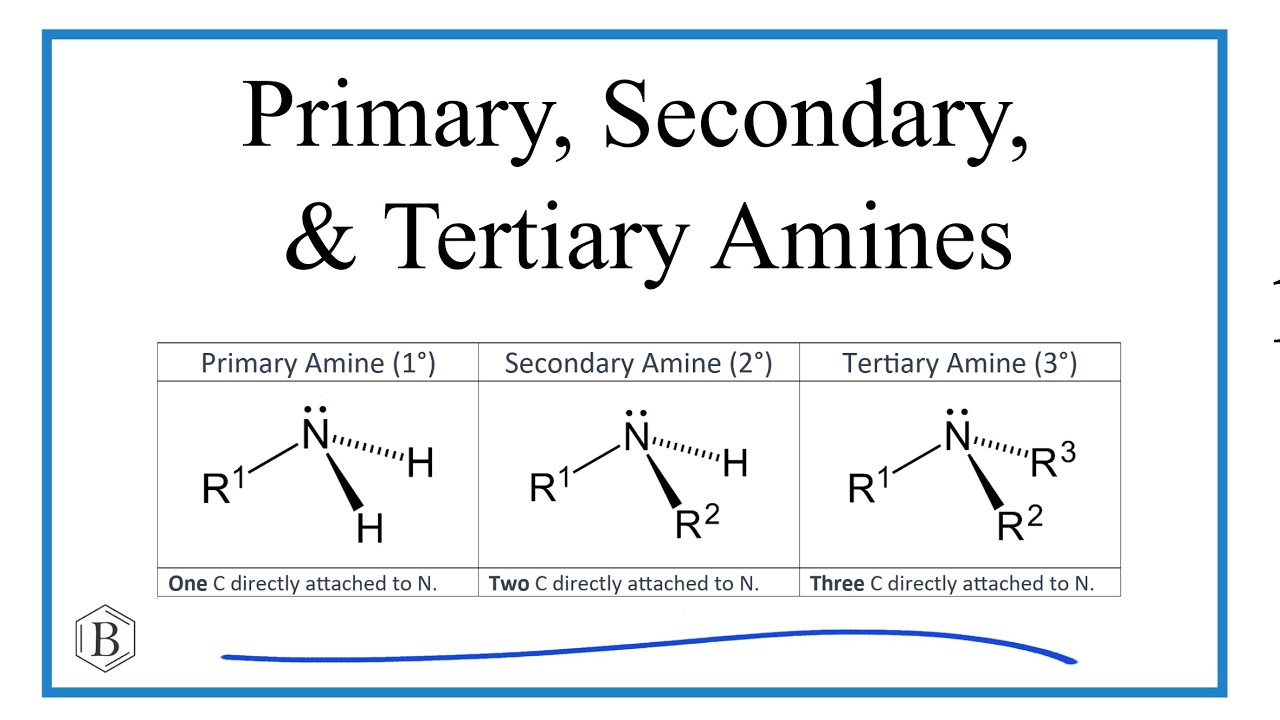
Classification of Amines (Primary, Secondary vs Tertiary)
Number of Carbons connected to it.
Oxidation state for carbon ions
For each bond,
C-H -1 (Carbon more e.neg than H so it pulls electrons towards)
C-X (where X is more electronegative) +1 (X pulls towards leaving C more +ve)
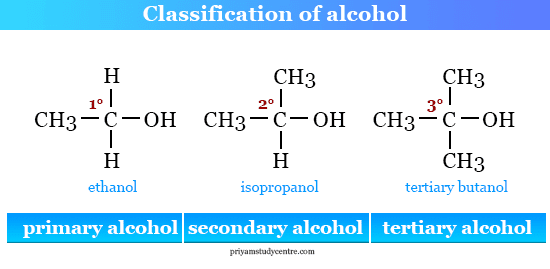
Classifications of alchohols
how many carbons are 2 away? (1 - primary, 2- secondary, 3- tertiary)
Aldehydes can be synthesised how?
Oxidation of Primary Alchohols
Reagents: Primary Alchohol (E.g. Ethanol), Acidified Potassium Di Cromate K2Cr2O7 (Dilute with H2SO4)
Conditions: Distillation
Specific temperature (any more would result in further oxidation to carboxylic acids being formed)
Carboxylic Acids can be synthesised how?
Oxidation of Primary Alcohols
Reagents: Primary Alchohol, Acidifed Potassium Di Cromate
Conditions: Reflux, we want product to come back done and be oxidised again.
Ketones can be synthesised how?
Oxidation of Secondary Alcohols
Reagents: Secondary Alcohol, Acidifed Potassium Di Cromate
(Heat, 1 product only)
Why can't tertiary alcohols be oxidised?
No H atoms bonded to carbon that hydroxyl is bonded to, cannot oxidise without breaking the carbon C-C chain
Quantitative color change for when aldehyde becomes carboxylic acid while being synthesised
Orange → Green
Color change observed when ketones are being synthesised
Orange → Green
delta H using average bond enthalpies
Bonds Broken - Bonds formed (Reactants - Products)
Define electrolyte
A solution (or liquid) that is capable of conducting an electrical charge. The solution in an electrochemical cell.
Define electrode
Conductors of electricity used to make contact with a non-metallic part of a circuit, such as a solution in a cell (the electrolyte).
Electron flow in Voltaic Cell and Electrolytic Cell follow what rule?
A to C, Anode to Cathode
This does not determine charge of each (Anode or Cathode)
Explain polarities of electrodes in voltaic vs electrolytic cells
voltaic - anode negative, cathode positive
electrolytic - anode positive, cathode negative
voltaic - redox reaction causes electron flow, so by ANOX, electrons released from anode so negative sign.
electrolytic - driven by external source, electrons first deposited in cathode so it is negative.
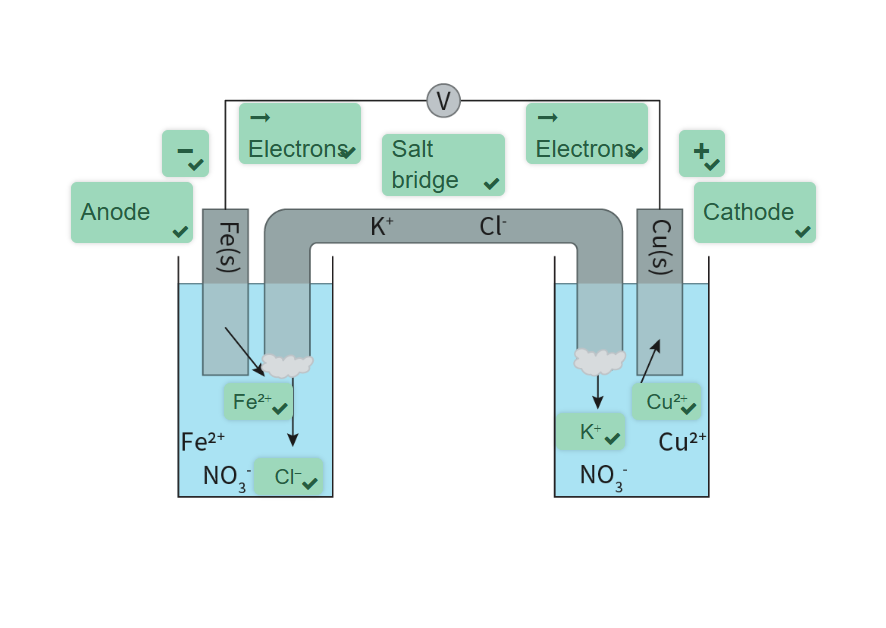
What is the purpose of a salt bridge? How do ions flow? (Voltaic Cells)
Purpose
physically separates the cathode and anode as there is no mixing of the two solutions. (Contact causes liquid junction potential ions from electrolyte may not be same charge, influencing the overall potential difference in the cell if allowed to move between solutions)
provides an electrical path for the movement of the cations and anions in the cell
Ion flow
cation and anions flow to prevent a buildup of charge and allow for continuous electron flow. Cations (+ve) flow to side that loses positive ions in the solution this happens in the cathode as a positive ion is reduced to a neutral ion. Anions flow to solution where positive ions are being released. This happens in anode where oxidation occurs.
How to determine reactivity using standard reduction potentials
Lower, More negative, is more unfavorable to reduce so it is more likely to oxidise
Name suitable reducing agents to reduce ketones, carboxylic acids, aldehydes back to alcohols
Sodium BoroHydride (NaBH4)
Lithium Aluminum Hydride (LiAlH4)
Hydride ions H- (H+ and a pair of electrons), are responsible for attacking the carbon ions and initiating reduction
Physical vs Chemical Equillibrium
Physical Equilibrium:
A closed system that exists during a physical change where the rate of the forward process is equal to the rate of the reverse process. (E.g. evaporation rate = condensation rate) So, there is no change in macroscopic / observable properties.
Chemical Equilibrium:
Chemical equilibrium involves reversible chemical reactions where reactants convert to products and products revert to reactants at equal rates. Rate of Forward equal Rate of Backward reaction.
Give 2 reactions that show the amphoteric nature of aluminum oxide
Al2O3 (s) + 6HCl (aq) → 2AlCl3 (aq) + 3H2O (l)
Al2O3 (s) + 2NaOH (aq) + 3H2O (l) → 2Na[Al(OH)4]
Strong Acids
HCl, H-(Halogen EXCEPT FLOURINE), HNO3, H2SO4, HClO4
Weak Acids
CH3COOH,H2CO3,HF, H3PO4
Strong Base
(Group1/2 metal)-OH
Weak Base
NH3, Organic + Amines (NH2)
State Physical and Chemical evidence on the resonant structure of benzene.
Physical Evidence
All C–C bond lengths are identical
All bond angles are identical
Electron density map shows equal distribution across all bonds
X-ray crystallography shows delocalized electrons and equal bond lengths
Chemical Evidence
Higher bond enthalpy than a single bond but lower than a double bond
Does not undergo addition reactions like alkenes; can undergo substitution reactions → stable ring
Ideal Gas assumptions
Gas particles move in constant, random, straight-line motion.
Intermolecular forces between particles are negligible.
Collisions between particles and container walls are perfectly elastic—no energy is lost.
The volume of individual gas particles is negligible compared to the space between them.
The average kinetic energy of gas particles is directly proportional to the absolute temperature (in kelvin)
A Gas is most ideal when…
There is low pressure => gasses are farther apart so more negligible IMF, high temperature => increased Ek, less likely to be influenced by IMF
A Gas is most real/ least ideal when…
High Pressures => Closer together, more significant IMF, at low temp => less Ek, so more likely for effects of IMF to be felt by gas molecules
Markovnikov’s rule for electrophilic addition
The electrophile will go to the carbon with the most hydrogens attached creating the most stable carbon cation intermediate
Ecell equals
E Cathode - E Anode (flip sign for oxidation from standard reduction potential)
Determine whether SN1 or SN2 will happen for a secondary alcohol given a solvent
SN1 will occur when there is polar protic solvents e.g. water or alcohol because they can stabilize the carbon cation intermeidate
SN2 Will occur when there is polar aprotic solvents e.g. acetone because they don’t stabilize carbo cation leaving it vulnerable to nucleophilic attack