Microbial Biotechnology Midterm
1/313
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
314 Terms
Symbiosis
From Greek endo, meaning “inside,” and symbiosis, meaning “to live with”
Mutualism
Commensalilsm
Parasitism
Amensalism
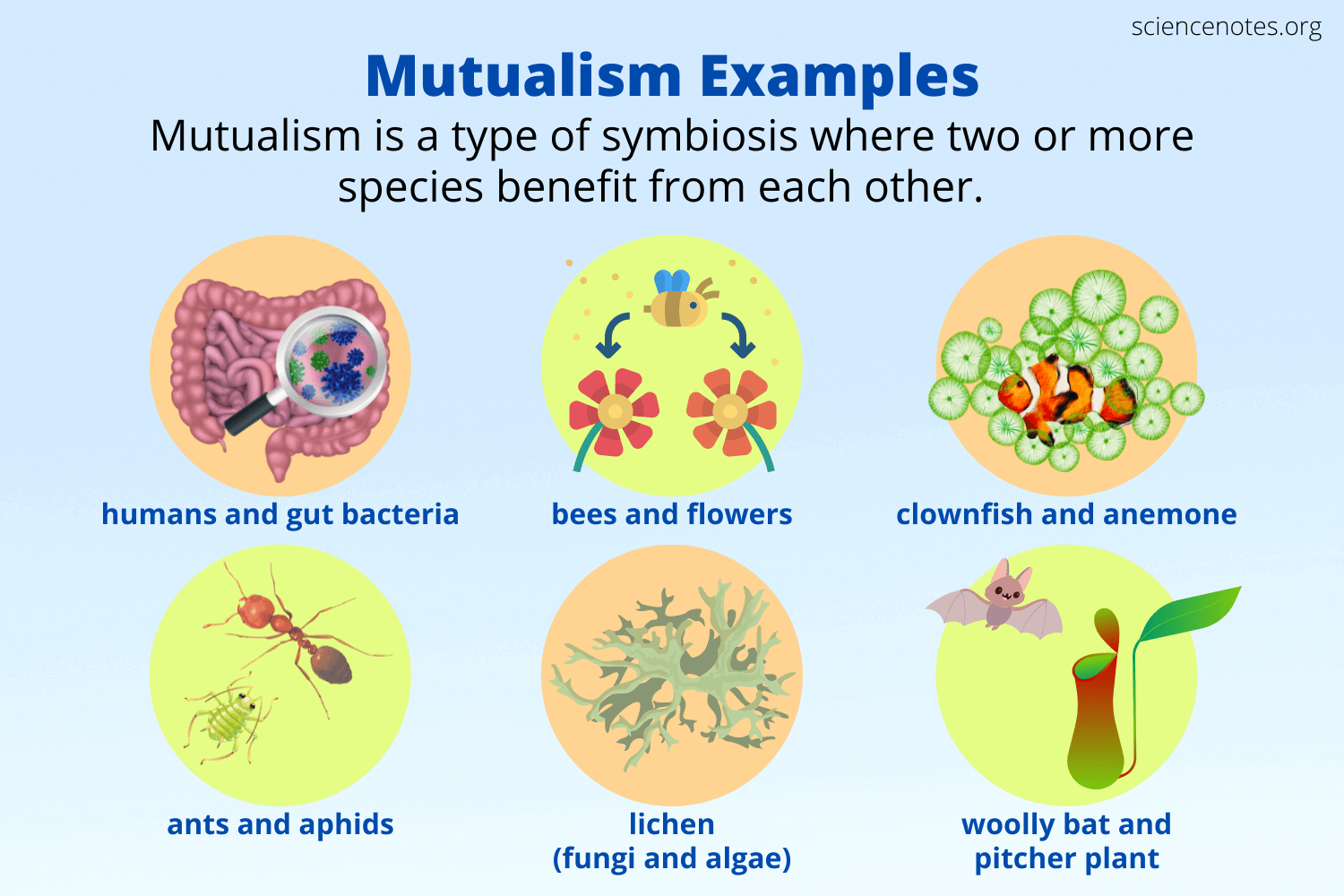
Mutualism
both symbionts and hosts benefit
Ex: Human guts provide a moist environment and nutrients for gut microbiota and microbes provide vitamin precursor
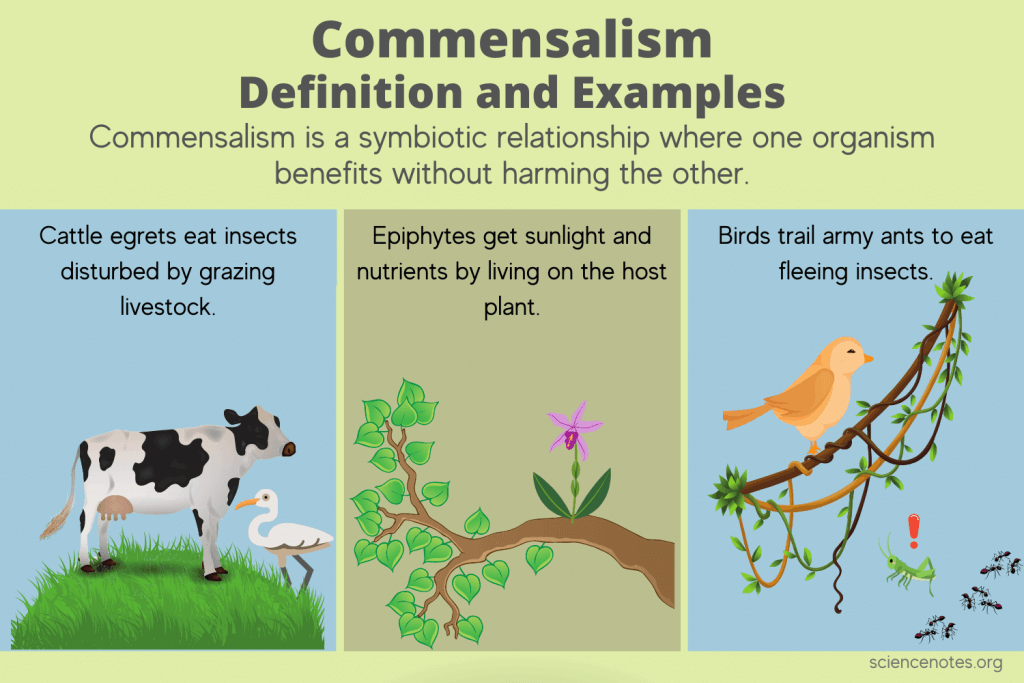
Commensalism
One symbiont benefit without affecting the other
Ex: Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) is a commensal bacterium that can live on human skin without causing disease
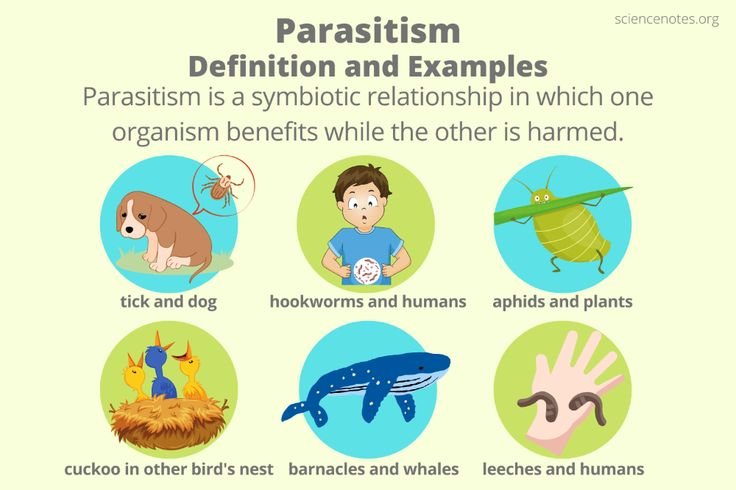
Parasitism
Host is damaged while symbionts benefits
Ex: Mycobacterium tuberculosis in human lungs
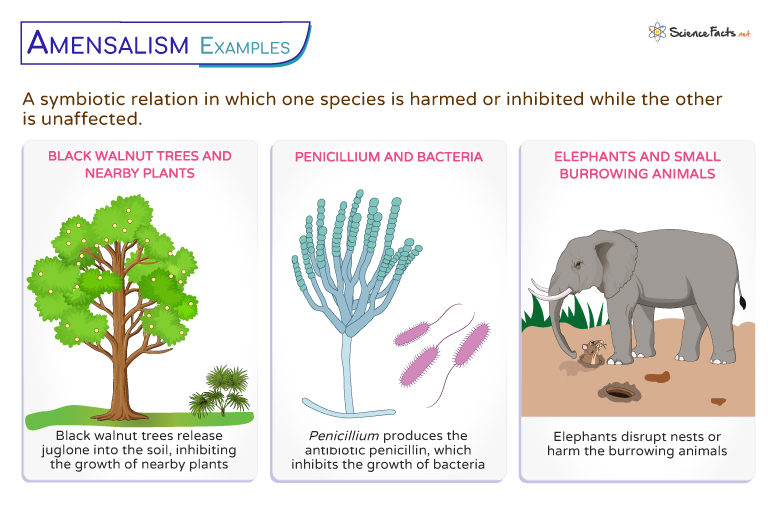
Amensalism
One symbionts is harmed while second symbiont is unharmed/benefit
Microflora (microbiota)
Microbes that colonize the body without causing disease
______ protects fetus from microbes.
Amniotic membrane and fluid
Commensal organism
an organism that lives in close association with another organism
Microbes normally found at various nonsterile body sites
Resident microbiota
A part of normal microbiota throughout life
Mostly commensal
Found on skin and mucous membranes (of the digestive tract, respiratory tract, distal portion of urethra, and vagina)
Transient microbiota
Duration: 1 hour to months
Found in the same regions as resident microbiota
Cannot persist because:
Competition from other microorganisms
Transient outnumbered resident microbiota because of anitibiotics
Elimination by the body’s defense cells
Chemical or physical changes in the body
Upper Respiratory Tract Resident Microbiota
Microbiota of the trachea and bronchi are sparse compared to those in nose and mouth
Microbes in alveoli are axenic → no natural microbiota
Axenic microbe
a microbe that is grown in a culture free of other organisms
Upper Digestive Tract Resident Microbiota
Microbes colonize surfaces of teeth, gingiva, lining of cheeks, and pharynx
Microbes found in large number in saliva
Dozens of unidentified microbes
Lower Digestive Tract Resident Microbiota
Strictly anaerobes bacteria, while some facultative anaerobes are also resident
Stomach bacteria love acidic enviroment
Female Urinary and Reproductive Resident Microbiota
Microbiota changes based on the menstrual cycle because of acidity changes
Urine flow prevents extensive colonization in urethra & bladder
Male Urinary and Reproductive Resident Microbiota
Urine flow prevents extensive colonization in urethra & bladder
Eye & Skin Resident Microbiota
Microbiota live in dead layers of the skin and hair follicles of the epidermis
Microbiota in dermis and hypodermis are axenic
Tears washes microbiota from eyes
_______ prevents microbial contamination and newborns get established their microbiota during ___ from their ___.
Anemiotic fluid and placenta
1st month of life
Environment (breathing, breast feeding, etc.)
Microbial antagonism
The competition between normal microbes and pathogens for nutrients and space
Reinforces the body’s defense by limiting the ability of pathogens to colonize the skin and mucous membranes (synthesizing antimicrobial compound)
Commensal bacteria
Microorganisms that live on the body's surfaces without causing harm and can enhance immune system
____ can protect against colorectal cancer by activating ____
Enterotoxin
Enterotoxin acts as a superantigen that triggers massive activation of T cells →increase in intracellular calcium levels
Changes in normal microbiota are caused by:
Long-term antimicrobial therapy
Hormonal changes
Stress
Change in diet
Exposure to overwhelming number of pathogens
Immune suppression are caused by
Diseases
Malnutrition
Emotional or physical stresses
Extreme of age (very old or young)
Usage of radiation or chemotherapy
Immunosuppressive drugs in transplants
Reservoir of Infection
Sites where pathogens are maintained as a source of infection
Human carriers
Humans who harbor and transmit a pathogen—often without symptoms (asymptomatic) or after recovery (convalescent carriers).
Animal reservoir
Animals that naturally harbor a pathogen, often without showing symptoms, and serve as a long-term host.
Zoonoses
Diseases that are naturally spread from their usual animal host (either domesticated or sylvatic) to humans
True/False: Humans are usually dead-end host to zoonotic pathogens
True.
This is true because humans often do not transmit diseases to animals because human waste is clean of pathogens in the body, and not many animals feed on human carcasses.
Why are zoonoses hard to eridicate?
Zoonoses are difficult to eradicate because of the extensive amount of hosts that are involved in the progressed. This is even more costly if there is a large human-to-reservoir contact and a mass amount of reservoir.
Another factor that should be noted is that if the animal has a similar physiology to humans, then the zoonoses would have a greater impact on the human body.
Nonliving Reservoirs
Inanimate objects or environments (abiotic factor) where pathogens can survive and potentially infect humans or animals
Contamination
The mere presence of the microbes in or on the body and these microbes can either be resident or transient microbiota
Infection
The invasion and growth of germs once they have been established in the body. It should be noted that most infection goes unnoticed so an infection does equal disease.
Infection cycle
Steps that note the infection process from when the pathogen/parasite enters or begins to grow to when it spreads to another host.
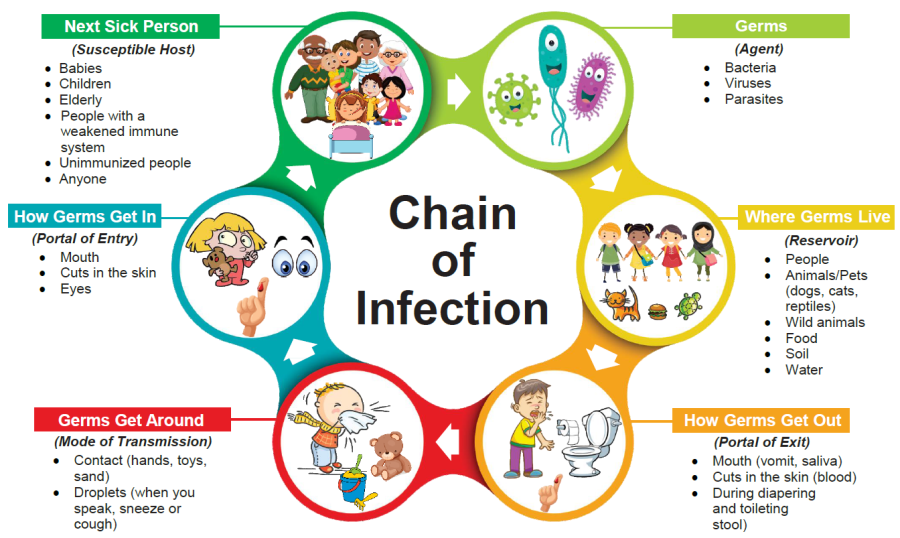
Fomites (= fomes)
Inanimate objects through which pathogens can be relayed to host
Vectors
Animate objects, such as insects, serve to carry infectious agents from one animal to another
Reservoir
An animal, bird, or insect that normally harbors the pathogens. Reservoirs are critically important for the survival of a pathogen and as a source of infection
What are examples of contact transmission? What are some disease that are spread by the transmission?
Direct contact: Hand shaking, kissing, sex, biles
Cutaneous anthrax
Genital warts
Herpes
Indirect contact: Shared items such as glass, toothbrushes, toys, etc
Common cold
Enterovirus infections
Influenza
Droplet transmission: Droplets from sneezing from within 1 meter
Whooping cough
Streptococcal pharyngitis
What are examples of vehicle transmission? What are some disease that are spread by the transmission?
Airborne: dust particles or droplets carried within 1 meter
Chickenpox
Pulmonary anthrax
Tuberculosis
Waterborne: streams, swimming pools
Campylobacter infections
Cholera
Giardia diarrhea
Foodborne: Poultry, seafood, meat
Botulism
Typhoid fever
Tapeworms
What are examples of vector ransmission? What are some disease that are spread by the transmission?
Mechanical: on bodies of flies, roaches
E. coli
Trachoma
Biological: lice, mites, mosquitoes, ticks
Chagas’ disease
Malaria
Plague
Biological vectors
Transmit pathogens
Hosts for the multiplication of a pathogen during some stage of pathogen’s life cycle
Typically biting arthropods (mosquitoes, ticks, fleas, bloodsucking flies and bugs, mites, etc.)
Mechanical vectors
Just transmit pathogens
Not hosts for the pathogens: passively carrying pathogens to new hosts on their feet or other body parts
What are the four major pathways of Portals of Entry?
Skin
Mucous membrane
Placenta
Parental routes
Portal of entry: Skin
Outer layer of packed, dead, skin cells usually acts as a barrier to pathogens because they provide no nutrition
Some pathogens can enter through openings or cuts
Others enter by burrowing into or digesting the outer layers of skin
Portal of entry: Mucous membranes
Line the body cavities that are open to the environment
Respiratory, gastrointestinal, urinary, and reproductive tracts, and conjunctiva
Provide a moist, warm environment that is hospitable to pathogens
Respiratory tract is the most common site of entry - entry is through nose, mouth, and eyes
Pathogens able to survive the acidic pH of the stomach may use the gastrointestinal tract as a route of entry
Portal of Entry: Placenta
Typically are effective barrier to most pathogens (<2% of pregnancy, pathogens can cross the placenta and infect embryo or fetus)
Some pathogens that can cross the placenta are:
Toxoplasma gondii
Treponema pallidum
Rubivirus
Parovirus B19
Portal of Entry: Parenteral route
Not a true portal of entry but a means by which the portal of entry can be circumvented
Pathogens deposited into tissues beneath the skin or mucous membranes
True/False: Many portals of exits are the same as portals of entry
True. Pathogens often leave hosts in materials in the body that secrete or excrete
Disease
Invading pathogen that alters the normal functions of the body
Referred to as morbidity
____ are subjective characteristics of disease gelt only by the patient and ___ are objective manifestations of diseases that can be observed or measured by others
Symptoms; Sign

Syndrome
A group of symptoms and signs that are characterize a disease or abnormal conditions
Asymptomatic/ sub-clinical
Infections that lack symptoms but may still have signs of infection
carcino-
cancer
carcinogenic: giving rise to cancer
col-, colo-
colon
colitis: inflammation of the colon
dermato-
skin
dermatitis: inflammation of the skin
-emia
pertaining to the blood
viremia: viruses in the blood
endo-
inside
endocarditis: inflammation of the lining of the heart
-gen, gen-
give rise to
pathogen: giving rise to disease
hepta-
liver
hepatitis: inflammation of liver
idio-
unknown
idiopathic: pertaining to a disease of unknown cause
-itis
inflammation of a structure
meningitis: inflammation of the meninges ( a thin layer that surrounds the brain
endocarditis: inflammation of the endocardium
-oma
tumor or swelling
papilloma: wart
-osis
condition of
toxoplasmosis: being infected with Toxoplasma
-patho, patho-
abnormal
pathology: study of disease
septi-
literally rotting; refers to presence of pathogens
septicemia: pathogens in the blood
terato-
defects
teratogenic: causing birth defects
tox-
poison
toxin: harmful compund
Etiology
the study of cause, set of causes, or manner of causation of a disease or condition
What are the categories of diseases?
Hereditary
Congenital
Degenerative nutrional
Endocrine (hormonal)
Mental
Immunological
Neoplastic (humor)
Infectious
Idiopathic
Nocosomial
Hereditary disease
Disease caused by errors in the genetic codes received from parents
Ex: Sickle-cell anemia
Congenital disease
Anatomical and physiological (structural and functional) defects present at birth; caused by drugs (legal and illegal), X-ray exposure, and infections
Ex: Fetal alcohol syndrome
Degenerative disease
Result from aging
Ex: Renal failure
Nutritional disease
Result from a lack of some essential nutrients in diet
Ex: Kwashiorkor
Endocrine (hormonal) disease
Due to excesses or deficiencies of hormones
Ex: Dwarfism
Mental disease
Emotional or psychosomatic
Ex: Skin rash
Immunological disease
Hyperactive or hypoactive immunity
Ex: Allergies
Neoplastic (tumor) disease
Abnormal cell growth
Ex: Benign tumors
Infectious disease
Caused by an infectious agent
Ex: Colds
Iatrogenic disease
Caused by medical treatment or procedures; are a subgroup of hospital-acquired diseases
Ex: Surgical error
Idiopathic disease
Unknown cause
Ex: Alzheimer’s disease
Nosocomial disease
Disease acquired in health care setting
Ex: Pseudomonas infection
Germ theory of disease
Disease caused by infection of pathogenic microorganisms
Proposed in the 19th century by Louis Pasteur
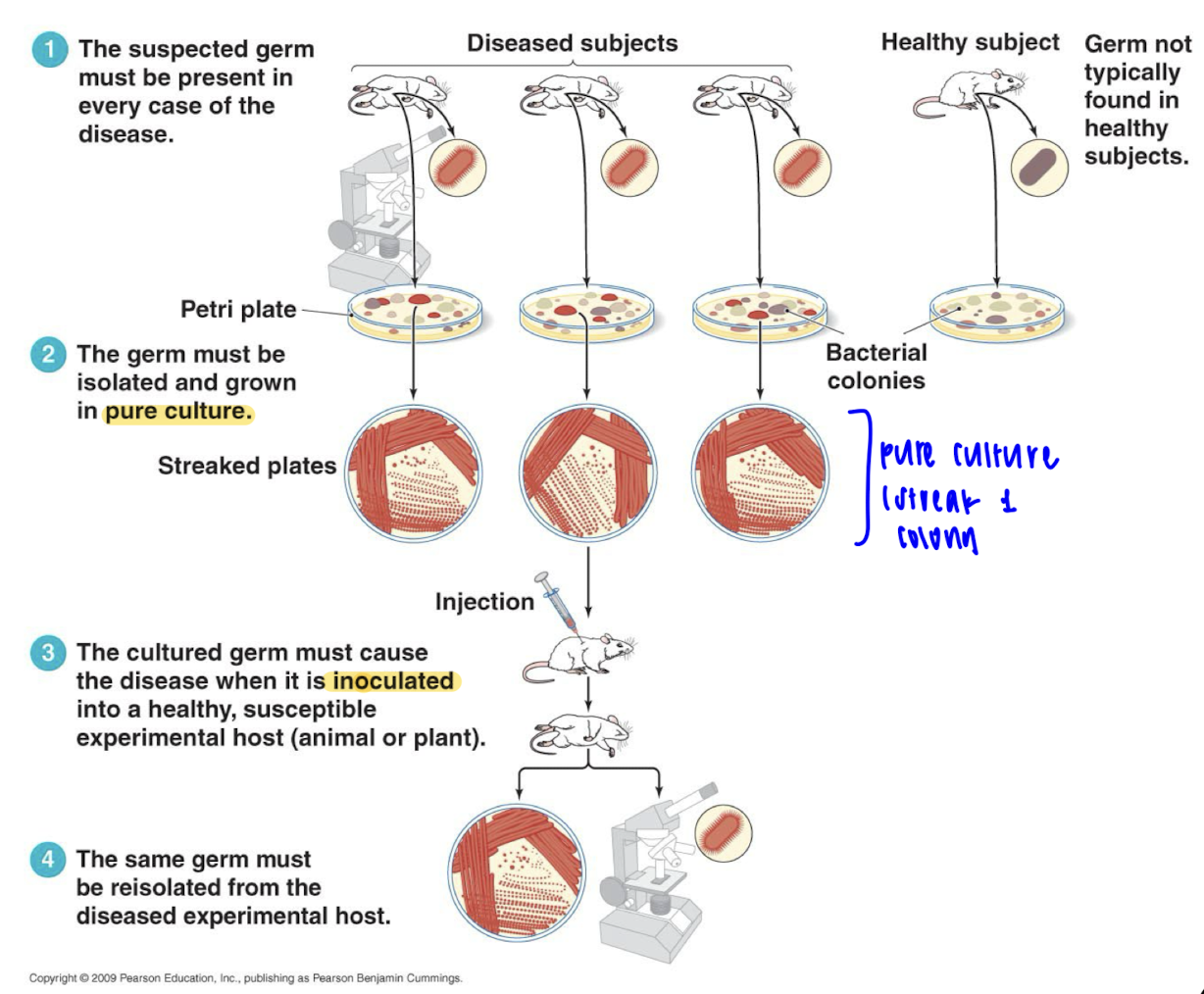
Koch’s Postulate
1) be present in all cases of the disease
2) be isolated from diseased patients
3) cause disease when reintroduced to a healthy susceptible animal model
4) then be isolated again from the new host.
When are the Koch’s postulates exception?
Some pathogens are unculturable in the laboratory
Some diseases are caused by a combination of pathogens and some other cofactors
Ethical considerations prevent applying Koch’s postulates to pathogens that require a human host
Some diseases that can be cause by more than one pathogen
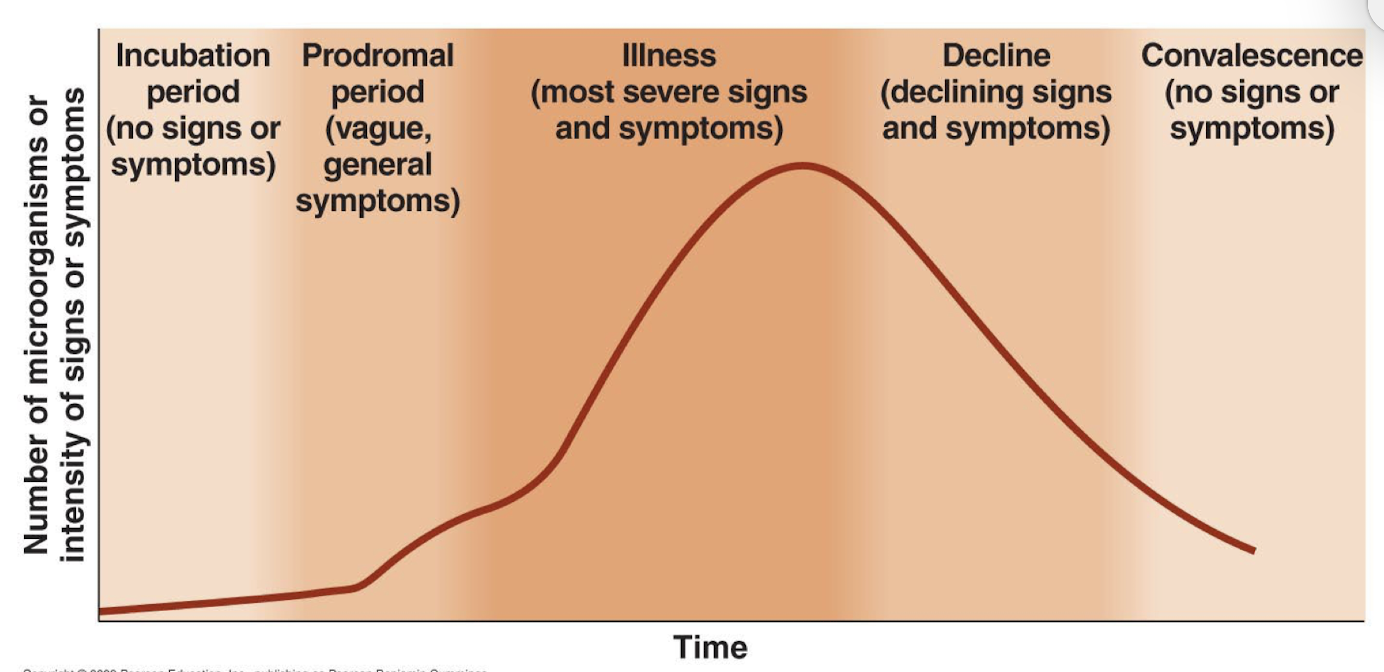
What are the stages of infectious disease?
Incubation period
Time between infections and first symptoms
Determined by virulence, infectious dose, health of host, nature of pathogen, its generation, and site of infection
Prodromal period
A short time of generalized, mild symptoms (optional)
Illness
The most severe stage (highest peak) of an infectious disease
Signs and symptoms are most evident
Typically host immune system has not yet fully responded
Decline
Body gradually returns to normal with highest immune response
Convalescence
The patient recovers from illness
How can diseases can be classified?
Taxonomic groups of causative agent
Body system they affect
Longevity and severity
How they are spread to their host
Effect on population
Acute disease
Disease in which symptoms develop rapidly and that runs its course quickly
Chronic disease
Disease with usually mild symptoms that develop slowly and last a long time
Subacute disease
Disease with time course and symptoms between acute and chronic
Asymptomatic disease
Disease without symptoms
Latent disease
Disease that appears a long time after infection
Communicable disease
Disease transmitted from one host to another
Ex: Leprosy
Contagious disease
Communicable diseases that are easily spread are typically spread via droplets or airborne
Ex: COVID
Noncommunicable diseases
Disease arising from outside of host or from opportunistic pathogen
Local infection
Infection confined to a small region of the body
Systemic infection
Widespread infection in many systems of the body; often travels in the blood or lymph
Focal infection
A form of localized infection that serves as source of pathogens for infections at other sites in the body
Primary infection
Initial infection within a given patient
Secondary infection
Infections that follow a primary infections; often by opportunistic pathogens
Epidemiology
The study of where and when diseases occur and how they are transmitted within a population
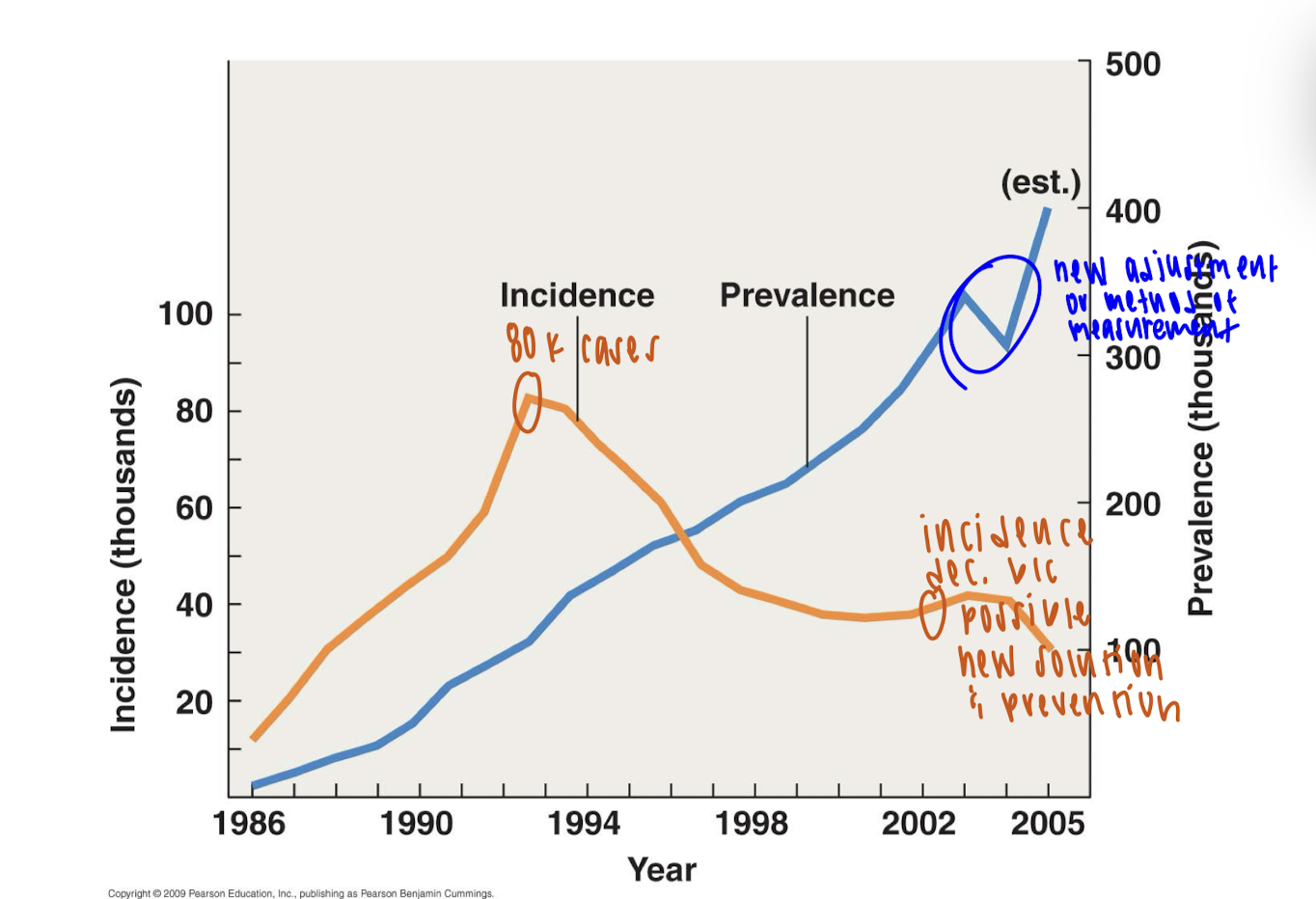
How are disease track?
Incidence - number of new cases of a disease in a given area during a given period of time
Prevalence - number of total cases of a disease in a given area during a given period of time