Nuclear Physics
1/157
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
158 Terms
What are the approximate values of radius of atom and nucleus?
Nucleus: 1fm
Atom = 0.05nm
What is the equation to work out the radius of a nucleus, given it uses electron difffraction?
sin theta = 1.22(deBroglie wavelength) / 2R (R is radius of nucleus) BOTH wavelength and R should be on order of 10^-15
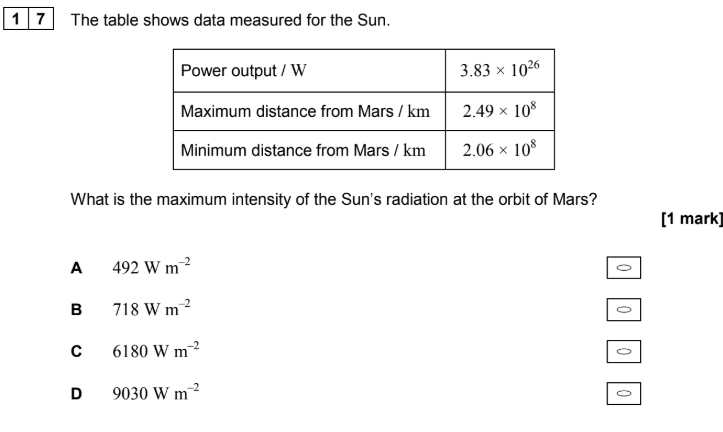
ITS IN KM!!!! Convert first, then use I = P/A

NOT
B
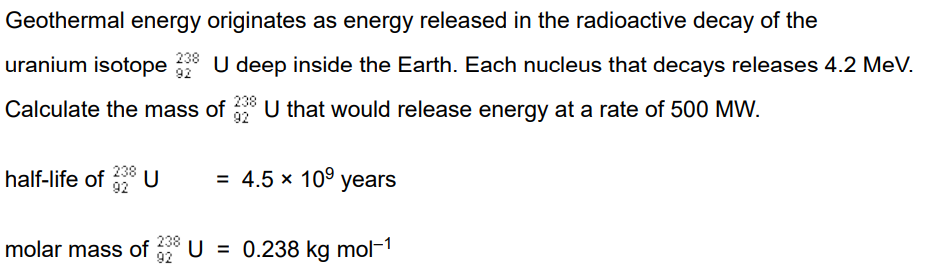
5 marks
Find number of nuclei in 1 kg
Find activity (since the definition is the number of decaying nuclei per second)
Then you have the number of decaying nuclei in 1kg, you are given how much energy 1 nucleus (atom) gives out so multiply to find out how much energy the 1kg gives out.
Then take the total energy required, divide by this number and that is total kg required.


7 marks
A slow-moving neutron is in collision with a nucleus of an atom of the fuel which causes fission. Describe what happens in the process. (3 marks)
Say absolutely everything!!!:
Neutron is absorbed by U-235 to form U-236
Nucleus splits into 2 smaller daughter nuclei (NOT PRODUCTS!)
Also releases 2-3 neutrons (in order to further induce fission reactions)


What does an activity of 1 Bq mean?
1 decay per unit time (The amount of nuclei that decay per unit time is 1)
What is molar mass of 24Na11? (24 is nucleon number)
24 (since molar mass is nucleon number!!!)
In a nuclear reactor, neutrons are released with high energies. The first few collisions of a neutron with the moderator transfer sufficient energy to excite nuclei of the moderator. Describe and explain the nature of the radiation that may be emitted from an excited nucleus of the moderator. (2 marks)
Gamma radiation
as the energy gaps are large (in a nucleus) as the nucleus de-excites down discrete energy levels to allow the nucleus to get to the ground level / state mark for reason
What is the distance of closest approach an estimate for?
Radius of the nucleus
What are Nucleon and Proton number values on axis for graph?
Proton = 90
Nucleon = 120
What is gamma? (2 marks)
Short wavelength, High frequency EM radiation.
How do smoke detectors work?
Utilize alpha particles.
They travel few cm’s in air, allowing current to flow.
When smoke present, blocks them completing the circuit, which sets the alarm off.
How are beta minus radiation used in controlling thickness of material sheets?
Source of beta radiation one side of sheet, detector on the other.
For constant reading, the material must be same thickness, so if detector too high, roller compress more, if too low, compress less.\
2 qualities of radioactive decay?
Random and spontaneous
What decay can produce gamma?
Annihilation & Electron capture
What is half life of technetium 99?
6 hours
How can you ensure you measure an accurate count rate?
Take multiple readings (of count) and take AVERAGE
Who proposed the idea that atoms were spheres that couldn’t be broken down?
John Dalton (in 1804)
Who proposed the idea of the plum pudding model?
J.J. Thompson
What was the idea of the plum pudding model?
Sphere of positive charge, with negatively charged electrons stick in it.
What was the expected outcome of the Rutherford scattering experiment?
Alpha particles would be seen at a small angle either side of the centre they were fired at, since not much repulsion would occur since the atom was thought to be overall neutral.
State the main interaction when an alpha particle is scattered by a gold nucleus.
Electromagnetic
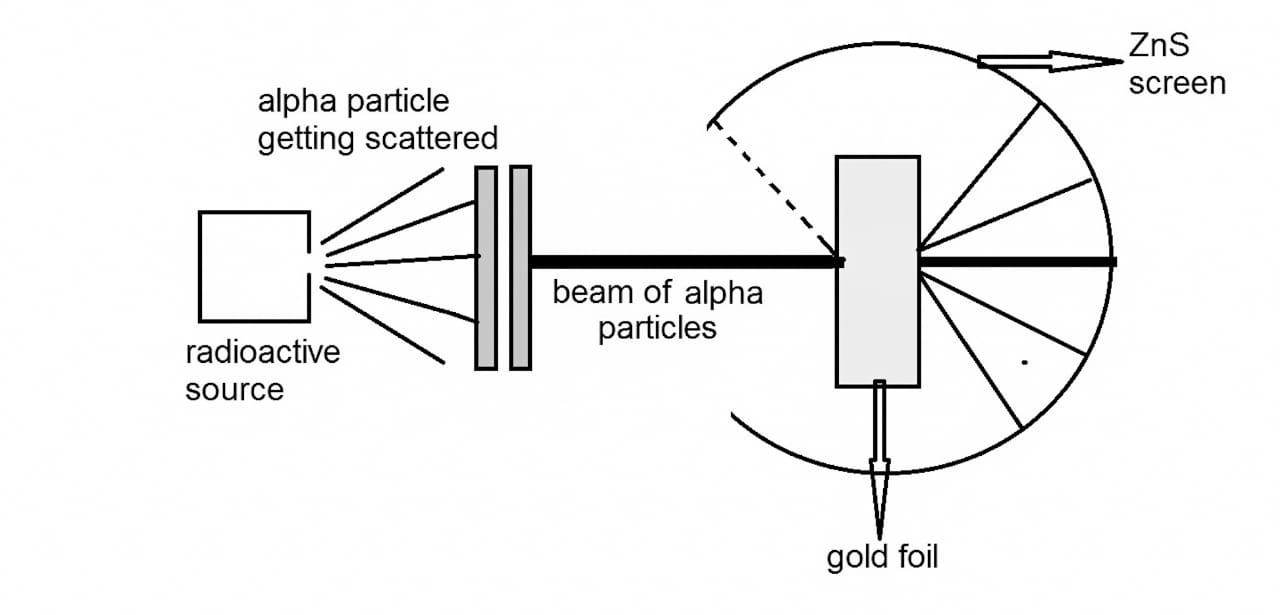
How was the Rutherford scattering experiment conducted?
Stream of alpha particles from a radioactive source fired towards a thin gold foil. Entire experiment was encased around a fluorescent screen so that any alpha particles that struck it would produce a flash of light. This was then counted at different angles.
What are the ionization rate of Alpha and Beta?
Alpha particles: ~10,000 ionizations per mm in air.
Beta particles: ~100 ionizations per mm in air.
Why must a vaccum chamber be used in Rutherford’s scattering experiment?
Prevention of α particle interaction with air: If the chamber were not a vacuum and contained air or other gases, the α particles would collide with air molecules before reaching the gold foil. This would scatter or absorb the α particles, preventing them from interacting with the gold atoms as intended. A vacuum ensures the α particles travel directly to the foil without interference.
What were the observed results?
Most alpha particles went straight through, however some deflected at an angle greater than 90 degrees.
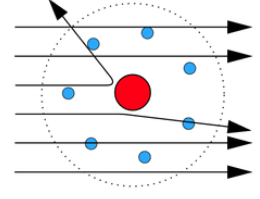
What is the Kinetic energy at the start of the alpha scattering experiment (largest distance from the nucleus) equal to?
The electrical potential energy at the SHORTEST distance from the nucleus, due to conservation of energy.
What were the 4 conclusion that could be made from the Rutherford scattering experiment?
1) The atom was mostly empty space, since most alpha particles travelled straight through
2) The nucleus must be a concentrated, dense positive charge since the positively charged alpha particles were repelled and deflected by a large angle.
3) The nucleus must have a large mass, since the fast travelling alpha particles (with high momentum) are deflected by the nucleus.
4) The nucleus must be tiny since very few alpha particles are deflected by an angle greater than 90 degrees.
Why was the nucleus hypothesised?
Since if the nucleus was only made up of protons, you would expect the charge on a massive nuclei to be much larger than that on a smaller, lower mass nuclei - which is not the case
Who discovered the neutron?
James Chadwick
Nuclear Radius & Density:
What is Coulomb’s law equation?
Qq/4piE0r
Q being charge on nucleus
q being charge on alpha particle
E0 being Permittivity of free space (8.85 × 10^-12 Fm^-1)
r = distance of closest approach.
What is Coulombs law equal to?
Initial kinetic energy = Electrical potential.
What is the difference between the force between 2 point charges law and Coulombs law to work out distance of closest approach?
Electric one = r²
Coulombs = r
What is the isotope used in medical tracers?
Technetium 99
Are both the deBroglie equation and first minimum equation both approximations?
Yes!
What does the relative intensity - angle of diffraction graph look like?
Like the single-slit diffraction graph!
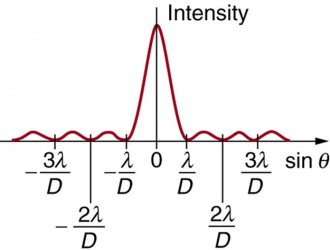
What must you make sure you multiply each whole number of charge (proton number) in Coulombs law?
x1.6×10^-19 (since asking for charge)
What is 1MeV in KeV?
1MeV = 1000KeV
What is the classification of electrons?
Leptons
What do electrons not interact with?
Strong Nuclear Force
What is the equation to work out deBoglie wavelength, in order to find out the energy of the electron?
λ = hc/E
E- energy of electron (J)
What does the A represent in the nucleus radius equation?
NUCLEON number, not PROTON number!
What is the unit for density?
Kgm^-3
What is the equation to work out the radius of the nucleus, given the scattering angle?
sin(theta) = 1.22λ/2R
How are electrons diffracted?
1 electron is diffracted by 1 nucleus.
What happens to the intensity of the maxima as the angle of diffraction increases?
Decreases
What does the diffraction pattern look like for electron diffraction?
Single-slit diffraction pattern (where the gap is a single nucleus)
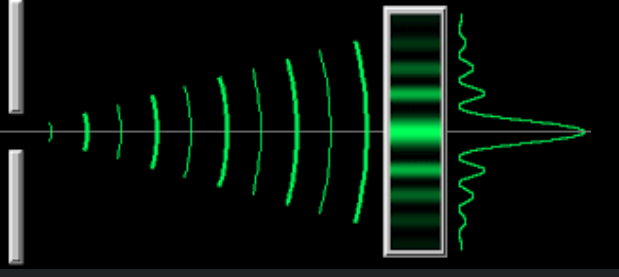
Does the intensity ever reach 0?
No
What are the axis labelled for a diffraction pattern graph of electron diffraction?
X = angle of diffraction
Y = Relative intensity
What is the size of the radius of an atom?
0.05nm (5 × 10^-11 m)
What is the size of the radius of the smallest nucleus?
1fm (1×10^-15 m)
What are molecules?
A number of atoms joined together
What does the graph of number of nuclei - radius of nucleus look like?
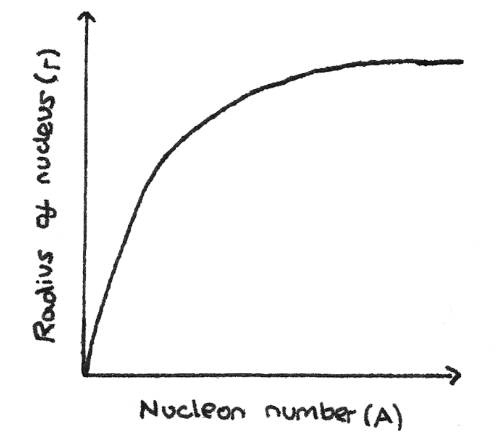
What does the graph of number of nuclei - (radius of nucleus)^1/3 look like?
Straight line through origin.
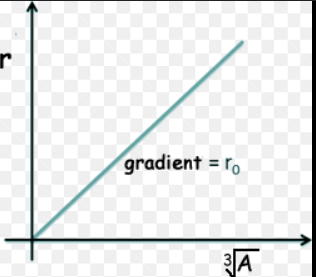
What is the equation for calculating the radius of the nucleus?
R = R0 x A^1/3
R = radius of nucleus
R0 = constant (1.4 × 10^-15m)
A = Nucleon number
What are 2 other names for nucleon number?
Mass number and Atomic number.
What is equation for volume of sphere?
4/3 x pi x r³
What are the 2 equations for calculating nuclear density?
A x m(nucleons) / 4/3 x pi x R³ (R being nucleus radius)
3 x m(nucleons) / 4 x pi x R0³ (R0 being 1.4 × 10^-15)
What is the nuclear density?
1.45 × 10^17 kg m^-3
What are the 3 conclusions that can be made about the value of nuclear densities?
Most of atoms mass is in its nucleus
The nucleus is small compared to atom
Mostly empty space inside atom

can be done without calculator!
B (remember A^1/3)
What stops alpha, beta and gamma respectively?
Skin/Paper
3mm of aluminium
Many cm of lead/ meters of concrete.
What are practical uses of Alpha, Beta and Gamma respectively?
Alpha = Smoke Detectors
Beta = Manufacturing sheets of metal
Gamma = Medicine (Radioactive tracers) or treat cancer by destroying cancerous cells
What is radioactive decay?
When an unstable nuclei breaks down to become more stable by releasing energy and/or particles.
What are 2 methods of identifying types of nuclear radiation?
Geiger Muller Tube - place paper, aluminium, lead in front
Magnetic Fields - Charged particles moving perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field are deflected in a circular path.
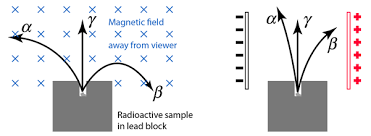
What is observed if you fire a positive and negative particle into a magnetic field?
Positive - curves one way (left for example)
Negative - curves opposite way to positive.
INTENSITY:
What are the 2 equations for Intensity?
I = k/x² (k being constant of proportionality) and (x being distance from source)
I1r1 = I2r2 (r being distance)
What is the definition of Intensity?
Amount of radiation per unit area.
Why can you use I = k/r² and sub the count rate into I?
Since the count rate varies with inverse square law. (I = 1/r²)
What are 6 sources of background radiation?
Igneous rocks
Air
Buildings and the ground
Living things
Man made medical or industrial sources
Cosmic Rays
The sun.
What is an equation linking Intensity, Power and Area?
I = P/A (Si nce units of intensity is Wm^-2)
Area being a sphere if talking about a source.
What is an equation that links intensity to activity and the area the photons cover?
I = A/4pi r² (A being activity)
Is it correct to make I1x1² = I2×2²?
Yes, since I = K/x², and the K is a constant.
Meaning, rearrange for:
I1/I2 = (R2/R1)² (DONT FORGET SQUARED!)

What is the equation to use to work out count rate at a point on a detector?
count rate = Activity x Percentage of entire sphere in comparison to detector surface area (Area of detector/4pir²)
Activity is the total number of photons that are emitted from the source into the entire sphere surrounding it.
Think of it as the percentage of the total surface area of the sphere that the detector occupies.

What happens if a detector only detects 1/400 photons, having used the equation c = A Adetector/4 pi r² and want to find out how many photons are released?
Must multiply the count rate you get by 400 since the equation calculates ALL of the photons that would hit the detector.
What is another equation for count rate involving intensity and area of detector?
count rate = Intensity x Area of detector
(Due to the definition of Intensity which is the power per unit area received at a specific distance from the source)
Difference between intensity and activity?
Intensity is the power per unit area received at a specific distance from the source.
Activity refers to the number of radioactive decays or emissions from a radioactive source per unit of time
How to convert cm² to m²?
cm² = 100×100 = 10,000 = m²
So, 1m² = cm²/10,000
What are the units of intensity?
Wm^-2
Law OF DECAY:
What is the definition of the activity of a sample (A)?
The number of nuclei that decay each second.
What is the decay constant definition?
The probability of a specific nucleus decaying per unit time. (A measure of how quickly an isotope will decay)
What is activity measured in?
Bq (1Bq = 1 decay per second)
What is the decay constant units?
S^-1
What does N represent?
Number of unstable nuclei in the sample.
How can A also be expressed?
A = - change in N/change in time
What is the decay equation, given the number of original number of unstable nuclei?
N = N0E^-lambda x t
Does the number of unstable nuclei decrease exponentially with time?
Yes (1/x)
What happens if you plot a log graph of the number of unstable nuclei remaining against time?
Linear negative graph with ln N0 (number of beginning unstable nuclei being y-intercept and gradient being - decay constant.
What is molar mass?
The mass that 1 mole of a substance would have to eb equal to its relative atomic or molecular mass. (U-233 = 238 gmol^-1)
What is the unit for molar mass?
gmol^-1
What is the equation for calculating the number of atoms in a sample?
N = n x Na
N = number of atoms in sample
n = number of moles in sample
Na = Avogrado constant (6.02×10²3)
What is the equation to work out number of moles, given the mass and molar mass?
Moles = Mass of sample/Molar mass
What can N0 and N represent?
Number of unstable atoms/nuclei in the sample.