Anatomy - Nervous system
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
What are the functions of the nervous system?
Sense organs receive info
Brain and spinal cord determine responses
Brain and spinal cord issue commands to glands and muscles
What are the sensory and motor divisions in the PNS?
Sensory (afferent) divisions (receptors to CNS)
Visceral sensory and somatic sensory division
Motor (efferent) division (CNS to effectors)
Visceral motor division (ANS); effectors: cardiac, smooth, glands
Sympathetic division (fight or flight)
Parasympathetic division (digestion)
Somatic motor division; effectors: skeletal
What are the 2 major anatomical and functional subdivisions?
Central nervous system (CNS)
Brain and spinal cord enclosed in bony coverings
Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
Nerve
Ganglion
What is a nerve?
Bundle of axons in connective tissue
What is a ganglion?
The swelling of cell bodies in a nerve
What are three functional properties found in all neurons?
Excitability (irritability)
Responds to changes in the body and external environment stimuli
Conductivity
Produce traveling electrical signals between cells
Secretion
When electrical signal reaches end of nerve fiber, chemical neurotransmitters cross gaps
Define the three most basic functional categories of neurons
Sensory (afferent) neurons
Detect changes in body and external environment
- Information transmitted into brain or spinal cord
Interneurons (association neurons)
Lie between sensory and motor pathways in CNS
90% of our neurons are interneurons
process, store, and retrieve information
Motor (efferent) neuron
Send signals out to muscles and gland cells
Organs that carry out responses called effectors
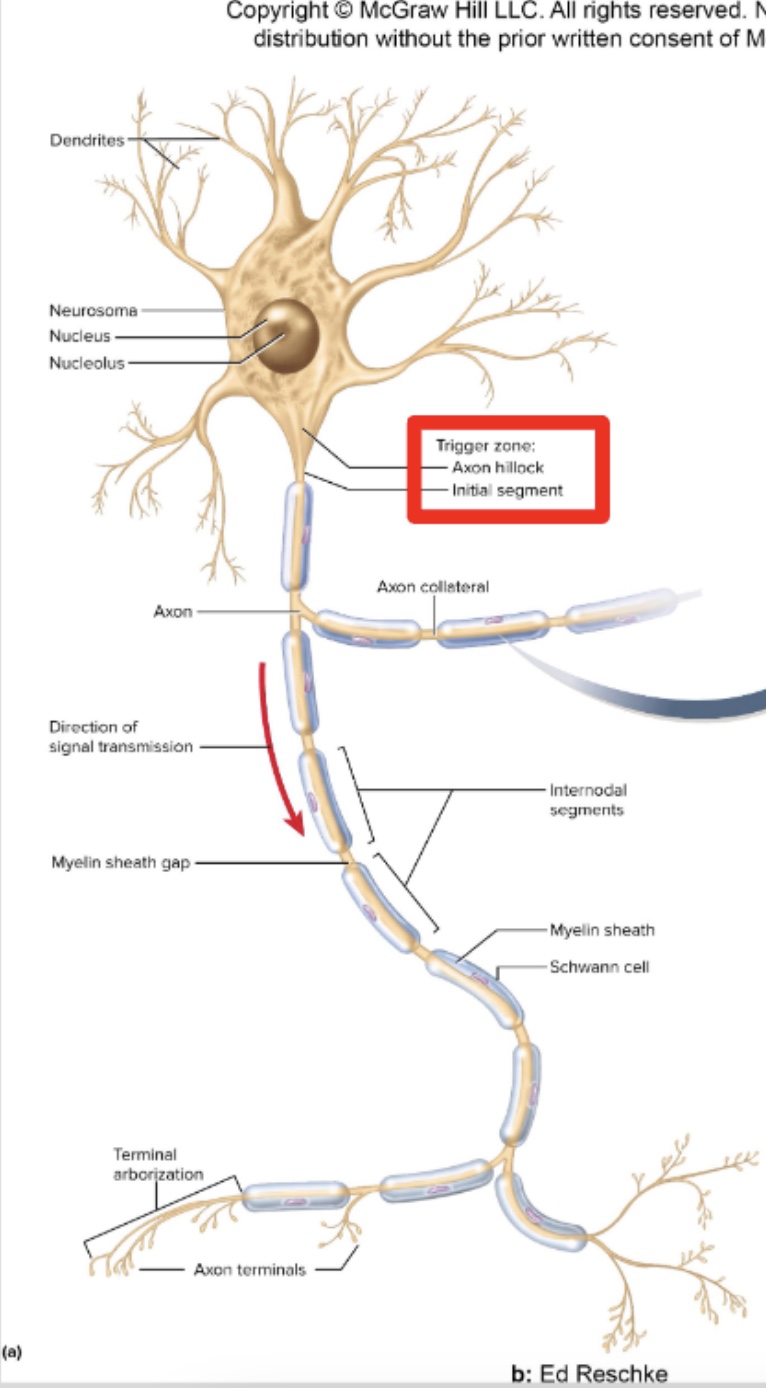
Identify the parts of a neuron
Cell body = soma
Small dendrites receive signals
Single axon = (nerve fiber) arise from axon hillock for rapid conduction
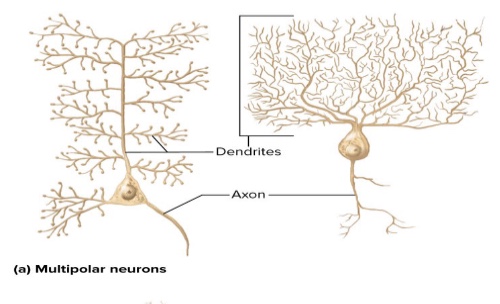
What are four structural classes of neurons? Where are they located?: Multipolar neurons
Brain
Spinal cord
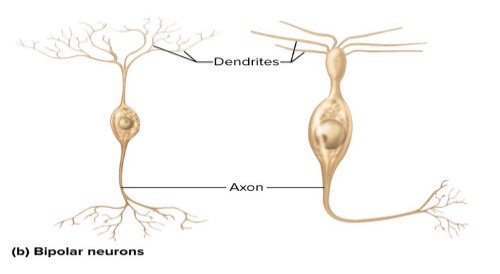
What are four structural classes of neurons? Where are they located?: Bipolar neurons
Sensory (ear and nose)
Retina

What are four structural classes of neurons? Where are they located?: Unipolar neurons
Single process leaving soma
Carries single to spinal cord (touch or pain)
Skin
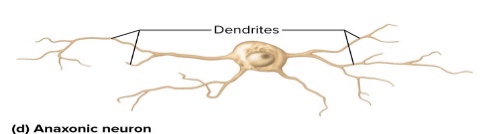
What are four structural classes of neurons? Where are they located?: Anaxonic neurons
No axons: multiple dendrites
Do not produce action potential
Communicate to local cells through dendrites
How do neurons transport materials (proteins, organelles, etc.) between the cell body and tips of the axon?
Anterograde - away from soma and down the axon
Retrograde - up the axon and toward the soma
What are the 6 types of cells that aid neurons and their functions?: Oligodendrocytes
Form myelin sheath in brain and spinal cord, insulates
What are the 6 types of cells that aid neurons and their functions?: Ependymal cells
Line cavities of brain and spinal cord; secrete and circulate cerebrospinal fluid
What are the 6 types of cells that aid neurons and their functions?: Microglia
Phagocytize and destroy microorganisms, foreign matter, and dead nervous tissue
What are the 6 types of cells that aid neurons and their functions?: Astrocytes
Cover brain surface and nonsynaptic regions of neurons; form supportive framework in CNS; induce formation of blood-brain barrier
What are the 6 types of cells that aid neurons and their functions?: Schwann cells
Form neurilemma around all PNS nerve fibers and myelin around most of them; aid in regeneration of damaged nerve fibers
What are the 6 types of cells that aid neurons and their functions?: Satellite cells
Surround somas of neurons in the ganglia; provide electrical insulation and regulate chemical environment of neurons
What is myelin?
Insulating layer around a nerve fiber
What is the role of myelin in the PNS?
Hundred of layers wrap the axon
Outermost coil → schwann cell (neurilemma)
What is the role of myelin in the CNS?
No neurilemma or endoneurium
Oligodendrocytes myelinate several fibers
Insulation speeds up conduction
What is a myelin sheath?
Node of Ranvier - between Schwann cells
What is the relationship of unmyelinated axons to their supportive cells?
PNS → “unmyelinated” cells have one Schwann cell wrapped around
Nerve fibers go through Schwann cells
Small fibers bundle and go through single channel
What are the steps to nerve regeneration in the PNS?
Observe normal nerve fiber (at NMJ)
Cut nerve fiber → stops protein synthesis
Degeneration: distal fibers begin and local Schwann cells follow (soma swell, some neurons die
Early regeneration: regeneration tube (Schwann cells produce molecute for growth (cell-adhesion))
Late regeneration: guides growing tube to original damaged cells
Regenerated fiber: regrowth and connection with original fibers (ex. muscle)
Explain why a cell has an electrical charge difference (potential) across its membrane: Electrical potentials
Concentration difference in charged particles
Living cells are polarized
Currents are created by NA+ and K+ pumps
Explain why a cell has an electrical charge difference (potential) across its membrane: Resting Membrane Potential
RMP ~-90 mV
More negative inside than outside cell
K+ ions are more influential
Permeable plasma membrane
ICF is negative (pulls Na+ inside cell)
Reaches equilibrium
Na+ ions trickle in
Reduces voltage to ~-70 mv
Na+-K+ pump is ~70% of ATP in nervous system
Signals disrupt it and must work to stabilize RMP
How does stimulation of a neuron cause a local electrical response in its
membrane?
Depolarization
Neuron stimulation by chemical (pain, smell, etc.)
Opens Na+ channel
Combats negativity inside cell
Plasma membrane changes toward zero
What are the 4 types of local potentials?
Graded - Depends on stimulus
Decremental - Weaken leaving point of origin
Reversible - Stop in stimulation, returns to RMP
Excitatory or Inhibitory - Important for information processing
Explain how local responses generate a nerve signal.
The response begins at a dendrite, spreads through the soma, travels down the axon, and ends at the synaptic knobs.
What are the 5 types of neurotransmitters and their functions?
Acetylcholine - regulates cardiac contractions, BP, peristalsis, and glandular secretions
GABA - reduces excitability by inhibiting nerve transmission
Glycine - antioxidant, anti-inflammatory
Aspartic acid - hormone production, release; normal nervous system function
Glutamic acid - protein formation
What are the 2 types of neuromodulators?
Monoamines
Catecholamines (epi, NE, and dopamine)
- Motor control, cognition, memory, endocrine system modulation
Indolamines
- Regulates serotonin and histamine
Neuropeptides
Analgesia; reward; food intake; metabolism, reproduction; social behaviors; learning; and memory
What are 4 ways the stimulation of a postsynaptic cell is stopped?
Excitatory or inhibitory
Depends on receptor of receiving cell (post synaptic neuron)
Cholinergic Synapse (Diffusion of Ach)
Acetylcholine (Ach) - excites muscle
Inhibits cardiac
Inhibitory GABA-ergic Synapse
CI- channel targeted
Andrenergic Synapse (G protein m
What are the characteristics of neural integration?
Summation
Adding up postsynaptic potentials and responding in the “trigger zone”
Facilitation
One neuron enhancing the next
Inhibition
One neuron (presynaptic) suppresses the next
Explain how the nervous system translates complex information into a simple code
Neural coding - All information that is sent to the CNS and everything within the CNS is sent as action potentials
How does the CNS know what is what?
Qualitative information (eg taste or hearing) depends upon which neurons fire.
Quantitative information depend on:
Different neurons have different thresholds
Stronger stimuli causes a more rapid firing rate (6 action potentials per second vs. 600)
Explain how neurons work together in groups to process information and produce effective output
Neural pools consists of interneurons
How does memory work?
Pathway through the brain
Synapses are permanently fixed for life
Respond and modify due to experience
Created or deleted in 1-2 hours
Synaptic plasticity: ability to change
Trained “muscle memory”
What are the three types of memory?
Immediate (Sensory)
Short-Term
Long-Term (emotional vs procedural)
Immediate (sensory) memory
Able to retain for a few seconds
Important for reading
Short-term memory
Few seconds to hours
Working memory
Long-term (emotional vs procedural)
Can last up to a lifetime
Limited amount
What causes us to forget things?
When neural circuits cease to fire
Necessary when retaining tons of information
What are the 4 functions of the spinal cord?
Conduction - bundles of fibers pass info up and down spinal cord
Neural Integration - neurons receive, process, and send out info
Locomotion - repetitive, coordinated actions of several muscle groups
Reflexes - involuntary responses to stimuli; involves brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves
What are the four regions of the spinal cord and the basis for their names?
Cervical
Thoracic
Lumbar
Sacral
What are the 2 enlargements of the cord and why the cord is wider at these points?
Cervical - rise to nerves of the upper limbs
Lumbar - issues nerves to the pelvic region and lower limbs
What is the Medullary Cone and the Cauda Equinae?
Medullary Cone - tapered tip of cord
Cauda Equinae - nerve roots resemble horse’s tail
Name the 3 spinal meninges, in order from superficial to deep.
Dura mater - collagenous membrane surrounded by epidural space filled with fat and blood vessels
Arachnoid mater - layers of simple squamous epithelium lining dura mater and loose mesh fibers filled with CSF (subarachnoid space)
Pia mater - delicate membrane adherent to spinal cord
What is gray matter? What are the horns and process associated with it?
Gray matter - butterfly shaped; neuron cell bodies with little myelin (info processing)
2 posterior (dorsal) horns - sensory
Interneuron process - in cervical and lumbosacral enlargements
Motor control/sensation in limbs
2 anterior (ventral) horns - motor
Lateral Horn - T2 → L1 of spinal cord
What is white matter?
White matter - Myelinated axons (info pathways)
Surrounds gray matter
Axons bundles ‘funiculus’
Divided into smaller fiber compartments
Spinal tracts
What the 5 types of spinal tracts?
Ascending - carries info up spinal cord
Descending - conducts motor impulses down
Decussation - cross over from left to right, up or down
Contralateral - origin and destination on opposite sides
Ipsilateral - origin and destination on same side
What are the meanings of the first through third order neurons in ascending tract?
1st - detects stimulus; transmits to brain/spinal cord
2nd - continues to thalamus
3rd - carries to cerebral cortex
What is the difference between upper and lower motor neurons in the descending tracts?
Upper - neurosoma in cerebral cortex
Lower - axon in brain/spinal cord
What is a nerve and the structure?
A nerve is a bundle of nerve fibers (axons)
Epineurium - covers nerves
Perineurium - surrounds fascicle
Endoneurium - separates individual nerve fibers
What is the structure of a ganglion?
Dorsal root ganglion - cluster of neuron cell bodies in nerves in the PNS; sensory cell bodies
How many spinal nerves are there? What is their relationship to the spinal cord?
31 pairs of spinal nerves (1st cervical above C1)
Nerves exit at intervertebral foramen
What are the names and locations of the five nerve plexuses?
Cervical (neck), C1 to C5
Brachial (armpit), C5 to T1
Lumbar (lower back), L1 to L4
Sacral (pelvis), L4, L5, and S1 to S4
Coccygeal, S4, S5, and C0
What are dermatones?
How spinal nerves receive sensory input from a specific area of skin
What makes up the brachial plexus?
Musculocutaneous - mixed-skin of forearm/elbow joint
Axillary - mixed-skin of lateral shoulder and arm; shoulder joint
Radial - mixed-skin of posterior arm; forearm and wrist
Median - mixed-skin of lateral 2/3 of hand; tips of digits
Ulnar - mixed-skin of palmar and digits III-IV
What is the sciatic nerve?
Major nerve extending from the lower end of the sc down the back of the thigh
What are reflexes?
Quick, involuntary stereotyped reactions of glands or muscle to sensory stim; automatic
Rostral v Caudal
Rostral - toward forehead
Caudal - toward cord
What are the three principal divisions of the brain?
Cerebrum
Cerebellum
Brainstem
Gyri v Sulci
Gyri - folds
Sulci - grooves
Where is gray matter located?
Neuron cell bodies, cell bodies, dendrites, and synapses
Forms cortex over cerebrum and cerebellum
Forms nuclei deep within brain
Where is white matter located?
Bundles of axons
Forms tracts that connect parts of brain
What are the germ layers of development?
Endoderm (innermost)
Gut lining
Mesoderm (middle)
Mesenchyme
Intramembranous Ossification
Ectoderm (outermost)
Development of nervous system
What happens at the 4th week of development (embryonic)?
Development of forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain
What happens at 5th week of development (fully developed)?
Forebrain divides
Telencephalon
Cerebral hemisphere develops
Diencephalon
Thalamus and hypothalamus
Hindbrain divides
Metencephalon
Pons and cerebellum development
Myelencephalon
Medulla oblongata
What are the 3 meninges of the brain?
Dura mater - outermost, tough membrane
Forms dural venous sinuses draining blood from brain
Forms supportive structures
Arachnoid - in spinal cord
Subarachnoid and subdural spaces
Pia mater - in spinal cord
Subarachnoid and subdural spaces
What are the 3 ventricles of the brain, locations and the passages that connect them?
Lateral ventricles
Location: cerebral hemispheres
Interventricular foramen
Connects lateral and 3rd ventricles
Third ventricle
Location: single vertical space
Cerebral aqueduct
Allows flow of CSF from 3rd to 4th ventricle
Fourth ventricle
Protects from trauma
Central canal connects down and through spinal cord
What are ventricles lined with?
Ependymal cells that produce CSF
What is the choroid plexus? How is it connected to ependyma?
Spongy mass of blood vessels on the floor of each ventricle
Connected to ependyma:
Ependyma - neuroglia (looks like cuboidal epithelial)
Lines ventricles and canals; covers choroid plexus
Produces CSF
What are the methods of flow, reabsorption, and the functions of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)?
Flow:
Fills ventricles and subarachnoid space
Constantly reabsorbed
Functions:
Buoyant - floats brain so it neutral
Protection - cushions from hitting skull
Chemical stability - rinses wastes
Absorption:
Absorbed into venous sinus through arachnoid villi
What are the steps of flow of CSF?
CSF is secreted by choroid plexus in each lateral ventricle
CSF flows through interventricular foramina into 3rd ventricle
Choroid plexus in 3rd ventricle adds more CSF
CSF flows down cerebral aqueduct to 4th ventricle
Choroid plexus in 4th ventricle adds more CSF
CSF flows out two lateral apertures and one median aperture
CSF fills subarachnoid space and bathes external surfaces of brain and spinal cord
At arachnoid villi, CSF is reabsorbed into venous blood of dural venous sinuses
What is the significance of the brain barrier system?
Receives 15% of blood supply
Utilizes 20% of oxygen and glucose
Function of Medulla Oblongata
All nerves that connect the brain to the spinal cord pass through
Function of Cerebellar peduncles
Connects cerebellum to the pons and midbrain
Function and structures of the midbrain
Connects the hindbrain and forebrain
Superior colliculi
Controls extrinsic eye muscles
Respond to visual stimulus
Inferior colliculi
Receives signals from inner ear to relay to the thalamus and other parts of the brain
Describe what the reticular formation is, the location and functions
Loose web of gray matter
Runs vertically through the brain stem and upper spinal cord
Functions:
Somatic motor control
Cardiovascular control
Pain modulation
Sleep and consciousness
Habituation
What are the functions of the cerebellum?
Evaluation of sensory input
Coordination and locomotor ability
Spatial perception
Timekeeping center
Predicting movement
Distinguish pitch and similar sounding words
Planning and scheduling
What are the 2 major components of the diencephalon and their functions?
Thalamus
Receives all sensory information going to the cerebral cortex
Relays signals from cerebellum to motor cortex
Emotional and memory
Hypothalamus
Hormone secretion
Autonomic NS control
Thermoregulation
Food and water intake
Sleep and circadian rhyths
Memory
Emotional behavior
Identify the five lobes of the cerebrum and their functions
Frontal
Thought
Memory
Mood
Motivation
Parietal
Taste
Somatic sensation
Sensory integration
Visual processing
Occipital
Visual awareness and processing
Temporal
Hearing
Smell
Emotion
Learning
Insula
Taste
Pain
Visceral sensation
Consciousness
What are the three types of tracts in cerebral white matter?
Projection tracts - extend vertically between higher and lower brain and sc
Commissural tracts - cross from one cerebral hem to another
Association tracts - connect different regions with the same hem
What are the 3 locations of cerebral gray matter?
Cerebral cortex
Stellate cells
Pyramidal cells
Pyramidal cells
Limbic system
What is the limbic system?
Important system of emotions and control
Directly connects higher and lower brain functions
What are the 3 main parts of basal nuclei?
Caudate nucleus
Putamen
Globus pallidus
What are the four types of brain waves in a EEG?
Alpha - awake bust resting, eyes closed, not concentrating
Beta - receiving sensory stim
Theta - drowsy or sleepy state
Delta — Deep state
What are the 4 stages of sleep?
1-7 minutes
Drowsy, relaxed
10-25 minutes
Light sleep, sleep spindles (neurons of thalamus and cerebral cortex interact)
20 minutes after stage 1 (theta and delta waves)
Muscles are relaxed and vital signs are low
What brain region is involved with memory?
Hippocampus of limbic system
What brain regions are involved with emotion?
Prefrontal cortex
Diencephalon
Discuss the functional differences between the right and left cerebral hemispheres
Right hemisphere - language comprehension and visuospatial tasks (artistic tasks) and control the left side of the body
Left hemisphere - control the right side of the body, educational and rational side of the brain.
language, logic, science, written, communications, numbers. skills, and reasoning.
List the 12 cranial nerves by name and their function
I - Olfactory nerve; sense of smell
II - Optic nerve; vision
III - Oculomotor nerve ; eye movement, opening of eyelid, constriction of pupil
IV - Trochlear nerve; eye movement
V - Trigeminal nerve; sensory to face and muscles of mastication
VI - Abducens nerve; provides eye movement
VII - Facial nerve;
Motor - facial expressions; salivary glands and tear, nasal and palatine glands
Sensory - taste on anterior 2/3’s of tongues
VIII - Vestibulocochlear nerve; provides hearing and sense of balance
IX - Glossopharyngeal nerve; swallowing, salivation, gagging, control of BP and respiration
X - Vagus nerve; swallowing, speech, regulation of viscera
XI - Accessory nerve; swallowing, head, neck and shoulder movement
XII - Hypoglossal nerve; tongue movements for speech, food manipulation, and swallowing
What are the functions of cranial nerves?
Send electrical signals between your brain, face, neck, torso
How does the autonomic and somatic nervous systems differ in form and function?
Somatic:
Effectors: Skeletal muscle
Cell body in CNS, thick, myelinated muscle extends in spinal nerve to skeletal muscle
Autonomic:
Effectors
Uses two-neuron chain of pre and post ganglionic neurons
How does the two divisions of the autonomic nervous system differ in general
function?
Sympathetic
Prepares body for physical activity: exercise, trauma, arousal, competition, anger, or fear
Increases heart rate, BP, air flow, blood glucose levels, etc.
Fight-orFlight
Parasympathetic
Calms body functions reducing energy expenditure and assists in bodily maintenance
Digestion and waste elimination
What is autonomic tone?
Balance between the two systems (sympathetic and parasympathetic) depending on needs
Identify the anatomical components and nerve pathways of the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions.
Sympathetic
Thoracolumbar division
Short preganglionic fibers
Preganglionic neurosomas in gray matter
Sympathetic chain of ganglia
Abdominal aortic plexus
Celiac
Superior mesenteric
Inferior mesenteric
Sympathetic Chain Ganglia
Spinal nerve route - Some postganglionic fibers exit a ganglion by way of the gray ramus to target organ (sweat glands, arrector muscles, and blood vessels of the skin).
Sympathetic nerve route - Other nerves leave by way of sympathetic nerves that extend to the heart, lungs, esophagus, and thoracic blood vessels
Splanchnic nerve route - Some fibers that arise from spinal nerves T5 to T12 pass through the sympathetic ganglia without synapsing
Parasympathetic
Craniosacral division
Arises from the brain and sacral regions of the spinal cord
Fibers travel in certain cranial and sacral nerves
Origin of long preganglionic neurons
Midbrain, pons, and medulla
Sacral spinal cord segments S2 to S4
Discuss the relationship of the adrenal glands to the sympathetic nervous system.
Adrenal cortex (outer layer)
Secretes steroid hormones
Adrenal medulla (inner core)
Sympathetic ganglion
Consists of modified postganglionic neurons without dendrites or axons
Describe the enteric plexus of the digestive tract and explain its significance
Regulates esophagus, stomach, and intestinal motility and enzyme secretion.
Name the neurotransmitters employed at different synapses of the ANS
Acetylecholine released by parasympathetics
Norepinephrine released by sympathetics