Photosynthesis (IB Biology HL)
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
light-dependent reactions
set of reactions in photosynthesis that use energy from light to produce ATP and NADPH. This occurs on the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts.
light-independent reactions
These are chemical reactions that convert carbon-dioxide to glucose (organic molecules) (don't call these "dark" reactions). Carbon fixation occurs here. Takes place in the stroma
action spectrum
A diagram that shows the amount of photosynthesis occurring at the different visible wavelengths of the Electromagnetic spectrum
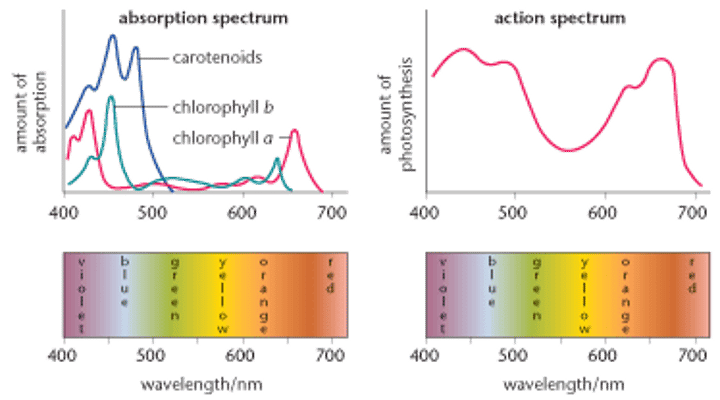
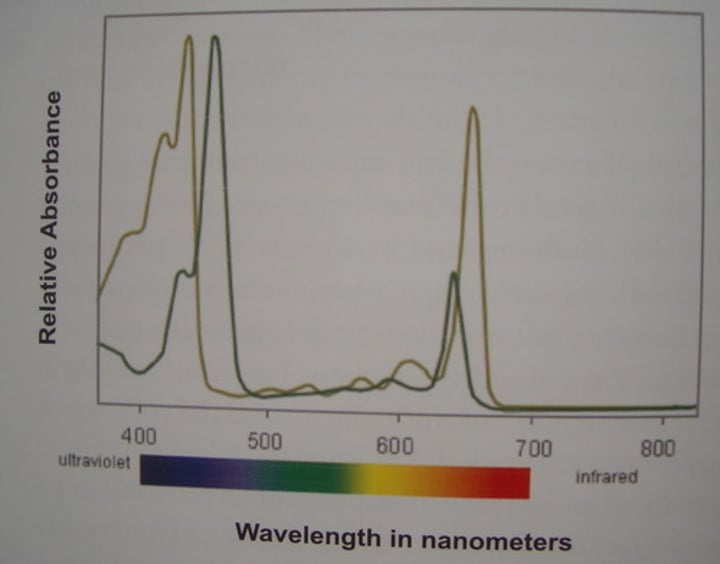
absorption spectrum
Diagram showing the amount of light absorbed by photosynthetic pigments at different wavelengths of the Electromagnetic Spectrum
wavelength
Each color is composed of a different _______ and frequency. Allows us to scientifically identify different colored lights. The unit of measure is nm.
photosynthesis
It is the process of converting water, carbon dioxide and light energy to oxygen and ATP (from light energy to chemical energy)
violet-blue
The color with wavelengths of around 200nm to 500nm. Around 70 to 90 percent of this type of light is absorbed by both chlorophyll 'a' and 'b'.
green-yellow
The photosynthesis that occurs here is due to accessory pigment (carotene/xathophll); Lowest % use of light in photosynthesis;(500nm - 600nm)
orange-red
Photosynthesis occurs here when the wavelength is around 650nm-750nm. At around 40-50%, this type of light is absorbed by chlorophyll a and b for photosynthesis
chlorophyll
The green pigment inside a thylakoid that activates from light energy, and is the main phtotsynthetic pigment.
chlorophyll a
Green pigment- does not absorb green light waves. It is the only pigment that can actually participate directly in the light reactions
xanthophyll
Pigment that causes photosynthesis when the wavelength of light 500-600nm (green/yellow)
carotene
Accessory pigment in plants that helps absorb red/orange light
photoactivation
occurs when chlorophyll molecules absorb light, the energy from the light rasies electrons to a high energy state
photosystem II
One of two light-harvesting units of a chloroplast's thylakoid membrane; it uses the P700 reaction-center chlorophyll; only used In non-cyclic photophophorylation
photosystem I
It is a back up system involved in cyclic photophosphorylation when there is not enough NADH.
non-cyclic photophosphorylation
producing ATP using energy from an excited electron from photosystem II (straight line), this is in the presence of light which is used for photolysis and the building up af a H+ concentration in order to combine phosphate to ADP to make ATP, while also producing NADPH for the Calvin Cycle
-The light-independent reactions usually proceed by the pathway learned earlier (light dependent reactions). the electrons proceed in a linear fashion through photosystems, being used to make ATP and ultimately to reduce NADP+ to NADPH
cyclic photophosphorylation
Electrons traveling through the e- transport chain are not transferred to NADPH. These e- are recycled to the H+ pump protein from photosystem 1.
ATP
Produced as a result of the high concentrations of the protons in the thylakoid space during the Light Dependent reactions. Used during the Light Independent reaction.
ADP + P
Converted to ATP with the help of ATP synthase
NADPH
Reduces glycerate 3 phophate during the Calvin cycle. Carries H+ and e- from Light dependent to Light Independent reactions.
NADP+
Accepts e- from the end of the ETC and excess H+ in order to make NADPH for the light independent reactions
H+
H+ ions are pumped across thylakoid membrane into stroma to provide ATP for photosynthesis.
thylakoid
Area where light-dependent reaction occurs, and is arranged in stacks in the chloroplast.
thylakoid membrane
Area between the stroma and lumen where the Hydrogen (proton) passes through and helps the ADP+P convert to ATP
stroma
The thick fluid between the granum which supports the cell - location of Calvin Cycle enzymes
thylakoid space
space bound by the membrane of the thylakoid organelle where H+ concentration is built for ATP production
e-
Comes from photolysis of water; used to pump H+ into thylakoid space
water
the source of oxygen and e- in the light-dependent reactions
photolysis
The splitting of water molcules
oxygen
produced during the light dependent reaction as a bi-product of photolysis
Calvin cycle
Light independent reaction that occurs in three steps: carbon fixation, reduction, and regeneration of RuBP
carbon fixation
the combining of ribulose biphosphate and carbon dioxide to form a temporary 6 carbon molecule. Also known as carboxylation reaction. (conversion of inorganic carbon dioxide to organic molecule)
rubisco
The enxyme that catalyzes the reaction of carbon fixation of carbon dioxide and ribulose bisphosphate. This enxyme is also known as ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase.
ribulose bisphosphate
Organic substance that is part of calvin cycle. Catalyzed by rubisco with CO2. Molecule that is carboxylized during the calvin cycle.
carbon dioxide
One of the limiting factors; without this the amount of glycerate 3-phosphate produced is limited.
triose phosphate
A molecule that is generated through the Calvin Cycle. Ribulose Biphosphate goes through the the carboxylation reaction, producing glycerate-3-phosphate as a result. Through the reduction reaction of glycerate-3-phosphate, this molecule is made. For every 6 of these molecules, 5 will be used to regenerae RuBP and 1 will be used to produce glucose phosphate.
reduction
Gain of electrons and H+
granum
Stacks of thylakoids in a chloroplast
limiting factor
Factor that is responsible for decreasing the maximum rate of photosynthesis
rate-limiting step
The slowest step of the photosynthesis reaction; decreases the rate of photosynthesis as a whole; determined by external environmental factors (limiting factors) such as temperature, CO2 concentration and light intensity
temperature
One of the limiting factors that slows down the process of the Calvin Cycle by slowing down the function of enzymes. The rate limiting step affected by this limiting factor is the point where carbon dioxide is fixed.
light intensity
One of the limiting factors; when this is poor, there is a shortage of ATP and NADPH. Without these products, the light independent reactions can't occur as glycerate 3-phosphate cannot be reduced. Therefore a shortage of these products will limit the rate of photosynthesis.
C4 plant
A plant that changes Co2 into a four carbon compound before entering the Calvin cycle for photosynthesis. Allows plants to be more adapted for hot and dry environments.
CAM plant
Crassulacean acid metabolism. This plant stores carbon dioxide at night, and releases it during the day increasing the efficiency of photosynthesis. (stomata only open during night)
Carbon fixation
The incorporation of a gaseous carbon molecule into an organic compound by an autotroph
autotroph
organism that has the ability to make its own organic compounds for energy use
chloroplast envelope
outer membrane of chloroplast
Melvin Calvin
scientist that used Chlorella in order to determine the steps of the light independent reactions and carbon fixation