EXAM 3 Gen Bio
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/134
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:02 PM on 12/3/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
135 Terms
1
New cards
two assumptions if early studies of inheritance
1. Each parent contributed equally to offspring in reciprocal crosses (supported)
2. hereditary determinants blend in offspring (non supportive)
2. hereditary determinants blend in offspring (non supportive)
2
New cards
Gregor Mendel
studies refuted the early assumptions
studied inheritance in pea plants (only two possibilities)
- started with true breeding plants and allowed for them to self pollinate for similar offspring
studied inheritance in pea plants (only two possibilities)
- started with true breeding plants and allowed for them to self pollinate for similar offspring
3
New cards
law of segregation
-two alleles will separate into different gametes
- egg or sperm only get one of two alleles
- egg or sperm only get one of two alleles
4
New cards
law of independent assortment
each member of a pair of homologous chromosomes separates independently of the members of other pairs so the results are random
- doesn't always apply to genes on the same chromosome; but they do segregate independently
- doesn't always apply to genes on the same chromosome; but they do segregate independently
5
New cards
Mendel's sample experiment steps
1. prevent self fertilization
2. pollinate
3. collect seeds (peas)
4. plant peas
5. examine offspring
2. pollinate
3. collect seeds (peas)
4. plant peas
5. examine offspring
6
New cards
character
observable, physical feature (flower color)
7
New cards
trait
a form of a character (purple flowers or white flowers)
8
New cards
heritable trait
passed from parent to offspring
9
New cards
hybridization
crossing 2 true breeding plants
- round seeds X wrinkled seeds
- results: F1 all round, F2: 3:1 round:wrinkled
- round seeds X wrinkled seeds
- results: F1 all round, F2: 3:1 round:wrinkled
10
New cards
recessive traits in Mendel's experiment
the traits that disappear in the F1 generation (wrinkled seeds)
11
New cards
dominant trait in Mendel's experiment
the trait that appears in the F1 generation (round seeds)
12
New cards
particulate theory
the heritable units were desecrate particles
-each parent has two particles for each character, one from each parent
-each parent has two particles for each character, one from each parent
13
New cards
Mendel's model
STUDY IN NOTES
14
New cards
alleles
different forms of a gene
15
New cards
homozygous
true breeding individuals have 2 copies of the same allele (SS or ss)
16
New cards
heterozygous
Individuals have two different alleles (Ss)
17
New cards
phenotype
physical appearance of an organism
18
New cards
genotype
the genetic makeup of an organism
19
New cards
test cross
how to determine the genotype of an organism- cross an unknown with a homozygous recessive
20
New cards
monohybrid cross
plants are heterozygous for only one trait
21
New cards
dihybrid cross
when two traits are both hybrid
22
New cards
SsYy linked or segregated?
If linked: gametes would be SY or sy; F2 would have three times more spherical yellow than wrinkled green
If independent: gametes could be SY, sy, Sy or sY; F2 would have 9 different genotypes; phenotypes would be 9:3:3:1
If independent: gametes could be SY, sy, Sy or sY; F2 would have 9 different genotypes; phenotypes would be 9:3:3:1
23
New cards
results of Mendel's 2nd experiment
recombinant phenotypes resulting in a 9:3:3:1 ration
24
New cards
probability
event certain to occur - probability = 1
event NOT to occur - probability = 0
event NOT to occur - probability = 0
25
New cards
dihybrid cross
probability that F2 seeds will be spherical is 3/4: probability of heterozygote + probability of homozygote 1/2 + 1/4= 3/4
joint probability that a seed will be spherical and yellow 3/4 x 3/4 = 9/16
joint probability that a seed will be spherical and yellow 3/4 x 3/4 = 9/16
26
New cards
mutation
rare, stable, inherited changes in the genetic material
27
New cards
wild type
allele present in most of the population other alleles are mutant
28
New cards
mutant
alternative phenotype
29
New cards
polymorphic
locus with wild-type allele present less than 99% of the time
30
New cards
mendelian rule breakers
co-dominance, blood group system, incomplete dominance
31
New cards
co-dominance
two alleles at one locus produce phenotypes that are both present in the heterozygote
EX: Roan cattle
WW- color
W'W'- white
WW'- both
EX: Roan cattle
WW- color
W'W'- white
WW'- both
32
New cards
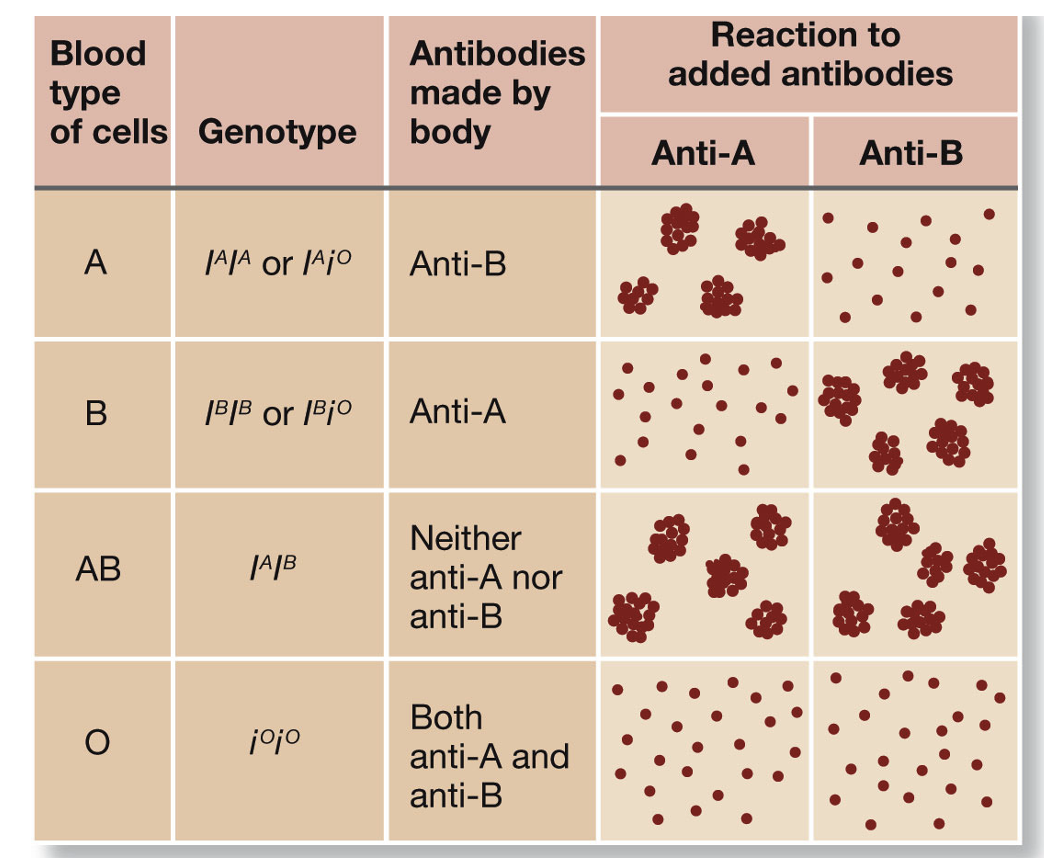
Blood (ABO) group system
3 alleles at 1 locus
33
New cards
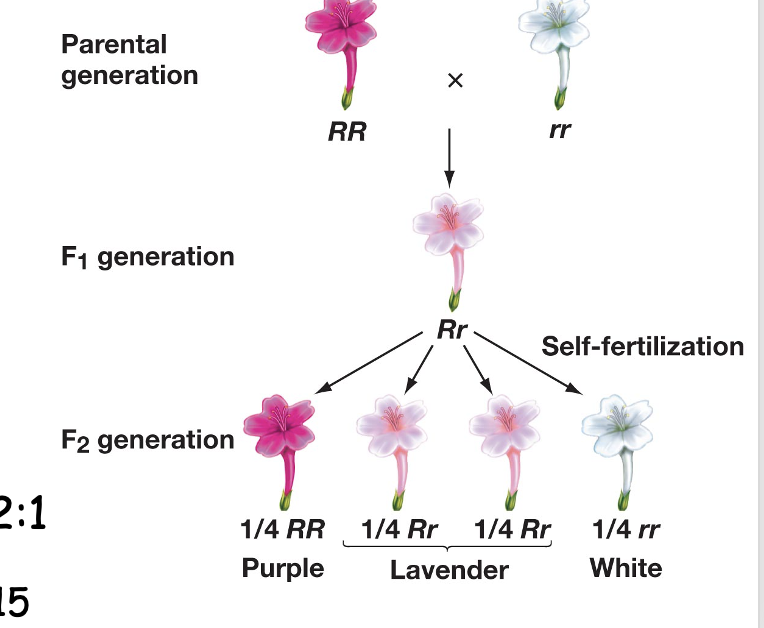
incomplete dominance
2 alleles result in a combined phenotype
Ex: crossing a dark pink and white flower resulting in offspring that is lighter pink
Ex: crossing a dark pink and white flower resulting in offspring that is lighter pink
34
New cards
polydactyly
birth defect characterized by the presence of more than the normal number of fingers or toes
DOMINANT TRAITS AREN'T ALWAYS THE MOST COMMON
DOMINANT TRAITS AREN'T ALWAYS THE MOST COMMON
35
New cards
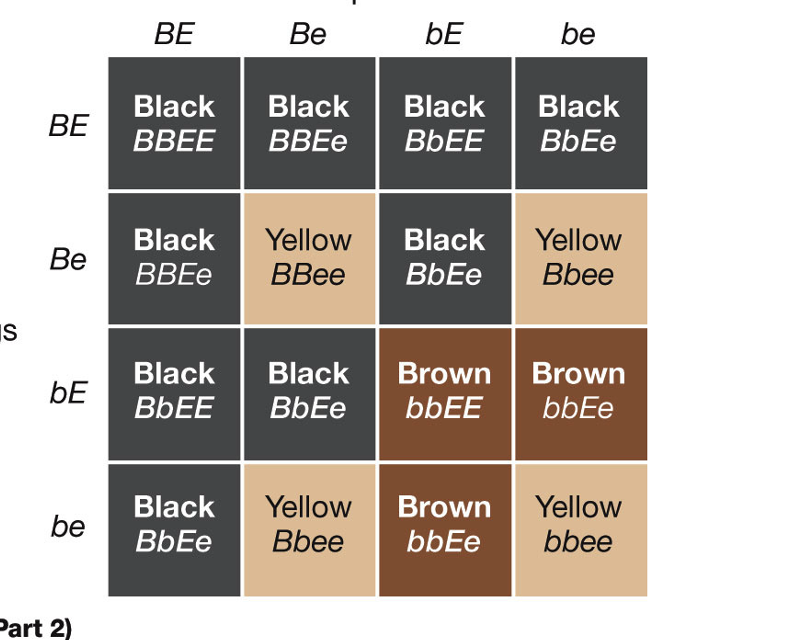
Epistasis
Greek: stopping, standing over
- one locus (gene) alters the phenotype of a second gene
Ex: color in labs
- allele B (black) dominant to b (brown)
- allele E (pigment deposition) is dominant to e (no pigment deposit, yellow)
- one locus (gene) alters the phenotype of a second gene
Ex: color in labs
- allele B (black) dominant to b (brown)
- allele E (pigment deposition) is dominant to e (no pigment deposit, yellow)
36
New cards
trihybrid cross
LOOK AT NOTES PRACTICE
37
New cards
Drosophila experiment
didn't yield expected ratios according to law of independent assortment
- genes inherited were said to be linked
- all of the loci on a chromosomes form a linkage group
found: genes are linked for eye color with genes that determine sex
- genes inherited were said to be linked
- all of the loci on a chromosomes form a linkage group
found: genes are linked for eye color with genes that determine sex
38
New cards
sex is determined by...
a single sex chromosome or by a pair
also which chromosome fertilizes the egg
also which chromosome fertilizes the egg
39
New cards
autosomes
both sexes have two copies of all other chromosomes
40
New cards
XX
female
41
New cards
XY
male
produce two kinds of gametes- half carry a Y and half carry a X
produce two kinds of gametes- half carry a Y and half carry a X
42
New cards
SRY gene
on the Y chromosome
-encodes a protein involved in primary sex determination
-encodes a protein involved in primary sex determination
43
New cards
DAX 1 gene
on the x chromosome which produces a anti-testis factor
44
New cards
if SRY gene is present...
inhibits DAX 1 maleness inhibitor and the embryo develops testes
45
New cards
If SRY gene is NOT present
DAX 1 functions to inhibit maleness and the embryo develops ovaries
46
New cards
sex linked genes
many genes unrelated to sex are on the X chromosome
For recessive genes
---- Females: inherit recessive from both parents
------Males: inherit recessive from mother (hemizygous), inherit Y from father
For recessive genes
---- Females: inherit recessive from both parents
------Males: inherit recessive from mother (hemizygous), inherit Y from father
47
New cards
linkage
genes connected based on physical location
48
New cards
parental types
when linked, the phenotypes we expect
49
New cards
recombinants
the products of crossing over between the genes
50
New cards
absolute linkage
rare genes at different loci on the same chromosomes do sometime separate
- genes may recombine during prophase I of meiosis by crossing over
- chromosomes exchange corresponding segments, The exchange involves two chromatids in the tetrad both chromatids become recombinant
- genes may recombine during prophase I of meiosis by crossing over
- chromosomes exchange corresponding segments, The exchange involves two chromatids in the tetrad both chromatids become recombinant
51
New cards
crossing over
recombination of linked genes during meiosis
- average 1-3 cross over per pair
- average 1-3 cross over per pair
52
New cards
frequencies are greater...
for loci that are farther apart
53
New cards
recombinant frequency
how often we see recombinants
# of recombinants/ total offspring
- can be used to make genetic maps
# of recombinants/ total offspring
- can be used to make genetic maps
54
New cards
genetic map
shows arrangement of genes along a chromosome
- can be applies to find relative distance on chromosomes
- higher chance of recombination between distant genes than nearby genes
- can be applies to find relative distance on chromosomes
- higher chance of recombination between distant genes than nearby genes
55
New cards
map unit (centimorgan)
distance between genes, recombinant frequency of 0.01= CM
56
New cards
x inactivation
females= 2 X chromosomes
male= 1 X chromosomes
- one female X chromosome is randomly is inactivated at early embryogenesis
male= 1 X chromosomes
- one female X chromosome is randomly is inactivated at early embryogenesis
57
New cards
nondisjunction
failure of chromosome or chromatids to separate, extra copy in one cell and loss in another
58
New cards
nondisjunction during meiosis
sex chromosomes
kleinfelter syndrom- XXY sterile male
Turner syndrome- XO sterile female
XYY- normal male
XXX- normal female
kleinfelter syndrom- XXY sterile male
Turner syndrome- XO sterile female
XYY- normal male
XXX- normal female
59
New cards
deletion
loss of DNA
60
New cards
duplication
repeat of DNA
61
New cards
inversion
reversal of segment
62
New cards
translocation
exchange between 2 chromosomes
63
New cards
bacteria exchanges genes by...
conjunction
64
New cards
sex pilus
a projection that initiates contact between bacterial cells
65
New cards
conjunction tubes
cytoplasmic bridge that forms between cells
66
New cards
plasmids
small circular chromosomes besides the main one, can move between the cells during conjunction
67
New cards
Frederick Griffith
studied strep phenomena
68
New cards
2 strains
1. S (smooth)- causes you to get sick (virulent)
2. R (rough)- non virulent (doesn't cause you to get sick)
2. R (rough)- non virulent (doesn't cause you to get sick)
69
New cards
heated S strain
not virulent
70
New cards
heat killed s strain + R strain
virulent
- bacteria that grew was smooth
R strain was transformed
- bacteria that grew was smooth
R strain was transformed
71
New cards
DNA
genetic material that has the ability to perform transformation
72
New cards
4 nitrogenous bases
1. adenine
2. guanine
3. cytosine
4. thymine
2. guanine
3. cytosine
4. thymine
73
New cards
purines
adenine and guanine
74
New cards
pyrimidines
cytosine and thymine
75
New cards
DNA structure (Watson and crick, pauling, Franklin)
bases are on the interior
2 strands run antiparallel
helix and uniform diameter
2 strands run antiparallel
helix and uniform diameter
76
New cards
A-T
two hydrogen bonds
77
New cards
C-G
3 hydrogen bonds
78
New cards
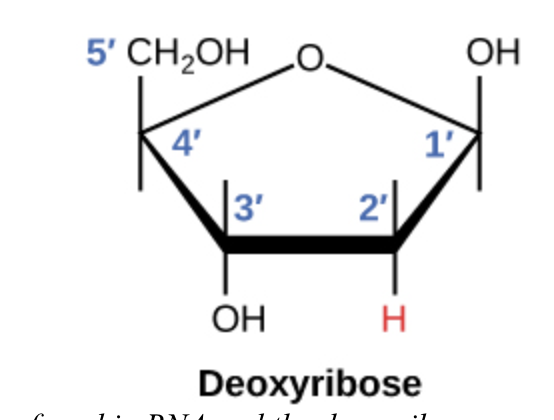
deoxyribose structure
sugar of DNA
- 5- carbon
- 1st carbon nitrogenous base attaches
- 3, 4, 5 DNA backbone
- 5- carbon
- 1st carbon nitrogenous base attaches
- 3, 4, 5 DNA backbone
79
New cards
essential characteristics of DNA
1) stores genetic information
2) genetic material is subject to mutations
3) genetic material is precisely replicated in cell division
4) genetic material is expressed as a phenotype
2) genetic material is subject to mutations
3) genetic material is precisely replicated in cell division
4) genetic material is expressed as a phenotype
80
New cards
conservative method
- takes old stand and copy it exactly the same
- old strands would go to one cell and new copy went to the other
- old strands would go to one cell and new copy went to the other
81
New cards
semi- conservative method
each cell got an old copy and new copy THIS IS TRUE
82
New cards
dispersive
DNA chopped into pieces and mismatched into each cell
83
New cards
gel electrophoresis
Gel electrophoresis is a technique used to separate DNA fragments according to their size. DNA samples are loaded into wells (indentations) at one end of a gel, and an electric current is applied to pull them through the gel. DNA fragments are negatively charged, so they move towards the positive electrode.
84
New cards
semiconservative DNA replication steps
1) unwind parental DNA
- separate two strands
2) add new nucleotides by complimentary base pairing
- linked by phosphodiester bond
- separate two strands
2) add new nucleotides by complimentary base pairing
- linked by phosphodiester bond
85
New cards
helicase
unwinds/ separates 2 strands of DNA
86
New cards
dna polymerase
synthesizes DNA in 5'-3' direction (specifically III)
87
New cards
Primer
RNA sequence to start replication
-cant add DNA from nothing - needs a 3' hydroxl group
-cant add DNA from nothing - needs a 3' hydroxl group
88
New cards
leading strand
synthesized DNA that is continuous
89
New cards
lagging strand
strand is made backwards, starting from primer and is in fragments
90
New cards
Okazaki fragments
fragments on the lagging strand
91
New cards
single stranded binding protein
hold strand apart
92
New cards
topoisomerase
relieves supercoiling tension
93
New cards
DNA polymerase I
removes primer, writes DNA on lagging strand, can't make phosphodiester bond between 3 OH group and phosphate
94
New cards
DNA ligase
seals nick left by Pol I (makes phosphodiester bond)
95
New cards
overhang
every time we synthesize DNA the extreme end gets an overhang because primer is removed in turn getting shorter
96
New cards
telomeres
repeated the same sequence (TTAGGG) cap the end of the chromosome to protect it
97
New cards
telomerase
extends the ends of chromosomes, reverse transcriptase- works backwards
98
New cards
DNA-----> RNA ------> protein
-----------> transcription --------------> translation
99
New cards
errors in replication
- DNA polymerase error rate 1/10 s bases
- 60,000 mutations/ replication
- 60,000 mutations/ replication
100
New cards
proofreading activity
can reread what is added and if wrong it can fix it (3'-5' exonucleotylic activity) , error rate decrease