Section 2 8 Periodicity
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
5 Terms
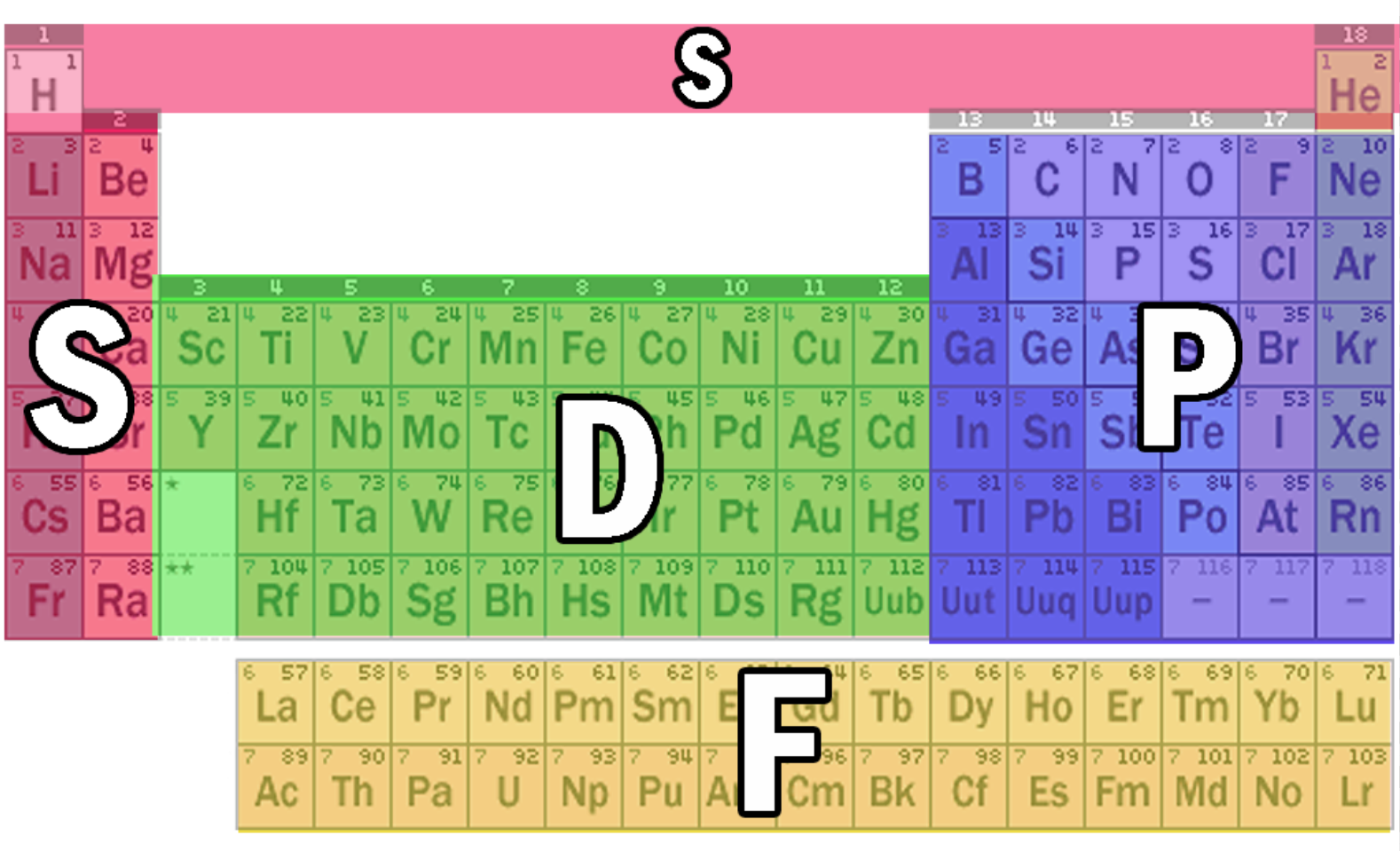
Where the S, P, D, F block is on periodic table?
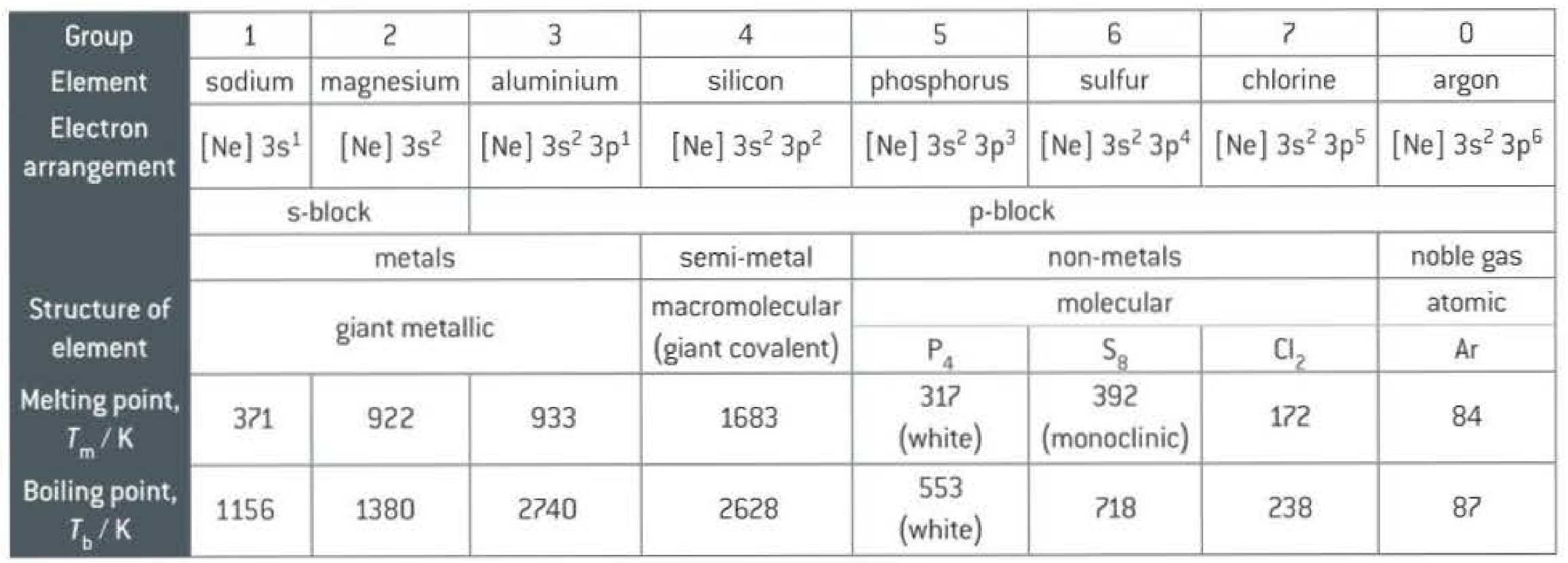
Some trends across period 3: (BP, structure, electronic configuration)
Key point: S8 > P4 > Cl2 Important due to van der waals forces sulfur has higher BP than phosphorus
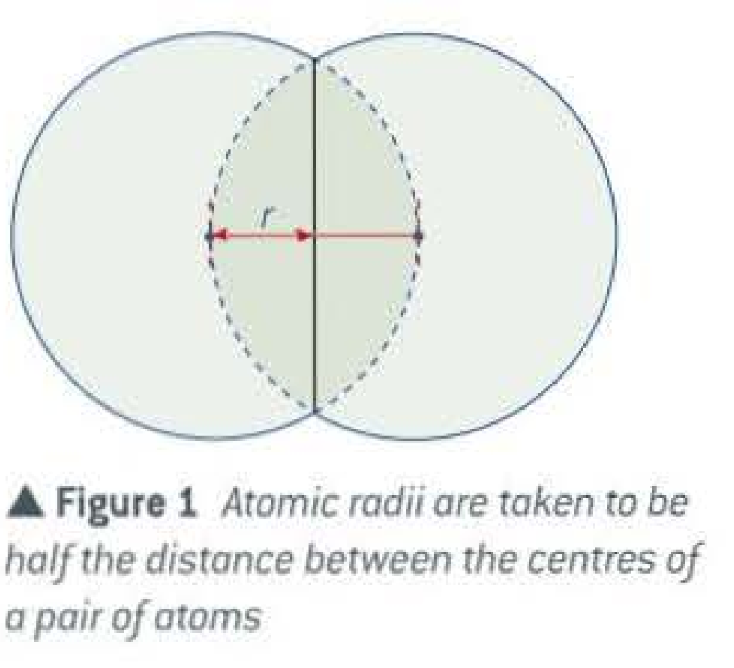
Define atomic radius:
Half the distance between the centers of a pairs of atoms
As you go across period 3, what happens to atomic radius?
As you go across the group, the proton number increases, while no additional electron shells to provide more shielding. So, stronger electrostatic forces of attraction between the positive protons and negraive electrons so the radius of atom decreases.
(note: radius increases going down the group)
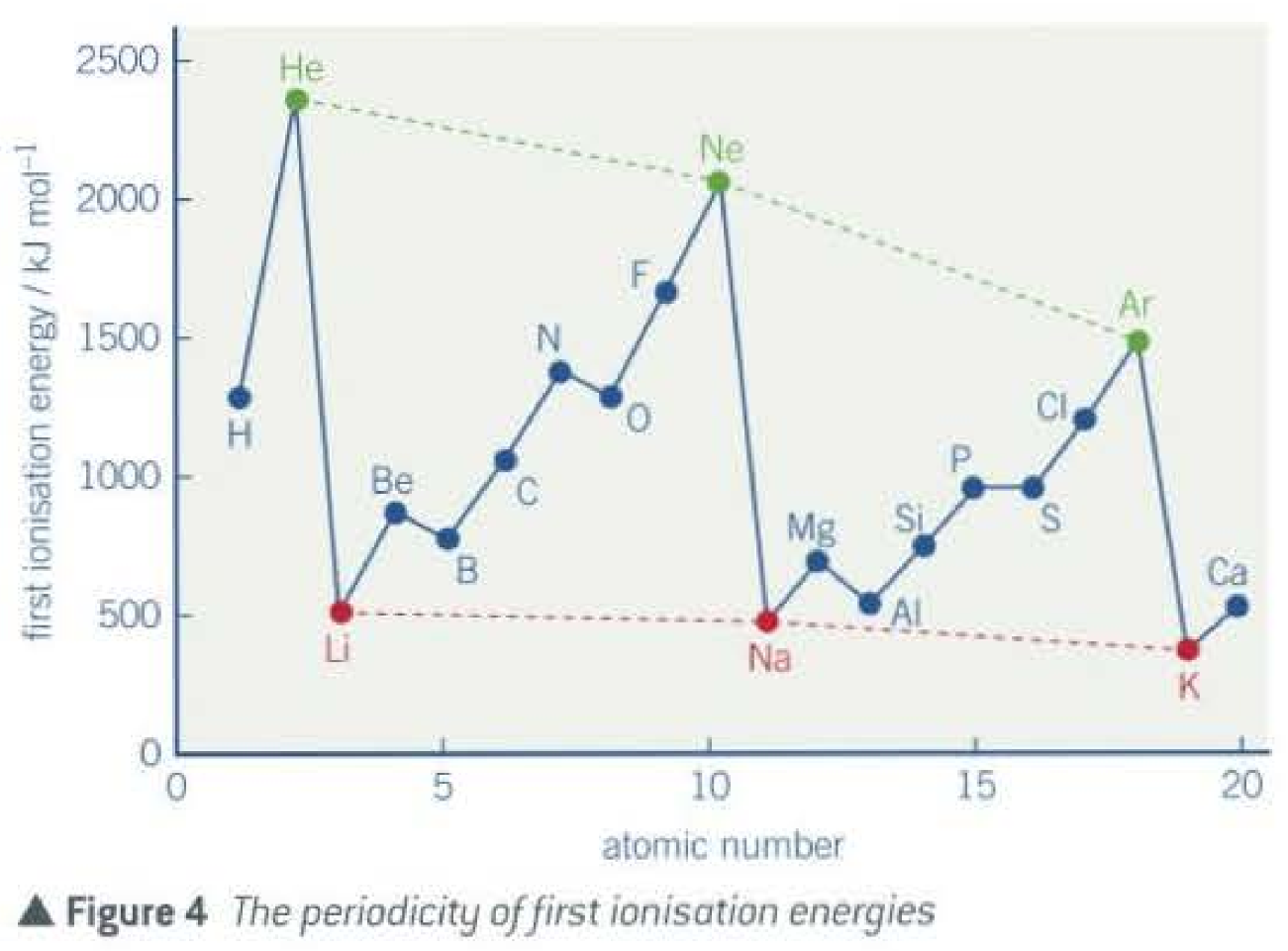
The trends in first ionisation energy across period 3
Since the radius of atom decreases across the period, more energy required to remove one electron from outermost shell.
Key: remember the pattern to the graph