Egyptian art from old to new kingdom (9-16-2025 and 9-18-2025)
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Benben stone
-The primordial mound of earth that rose out of the sea of chaos uponwhich the creator god Ra first appeared
-Symbol of creation
-Associated with the sun, rebirth, and the triumph of order over chaos
-Pyramids mimicked the shape of the mythical original benben stone
-Pyramidion (the capstone placed at the apex of pyramids later in theOld Kingdom) were also a symbolic representation
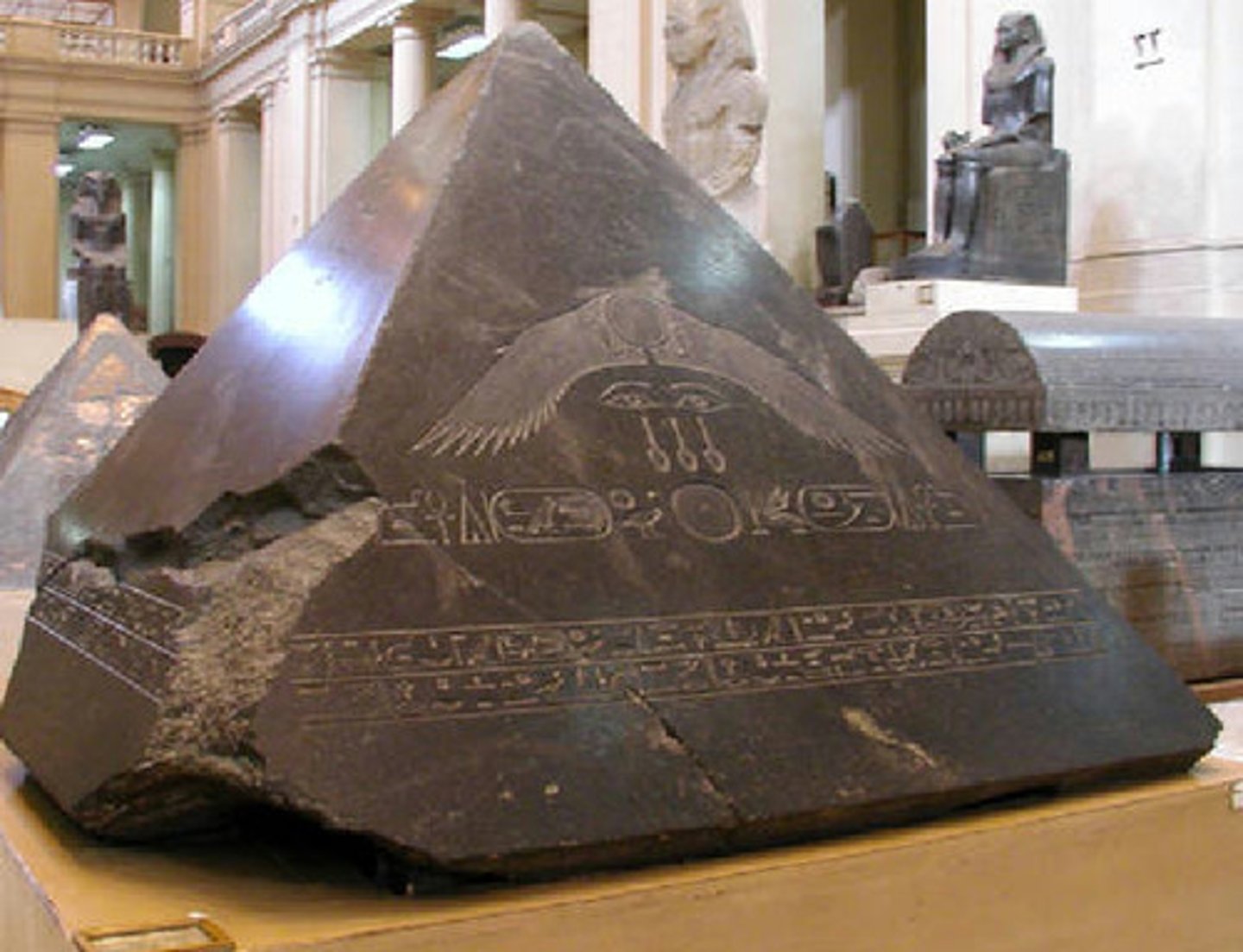

Pyramidion
Capstone that tops off pyramids in Egypt during the Old Kingdom of Egypt
Cult
Religious rituals that are meant to glorify or honor one individual (like the dead pharaoh) to recognize them as being semi-divine or divine

Nemes
a distinctive striped head cloth worn by pharaohs in ancient Egypt as a symbol of royal authority and divine status
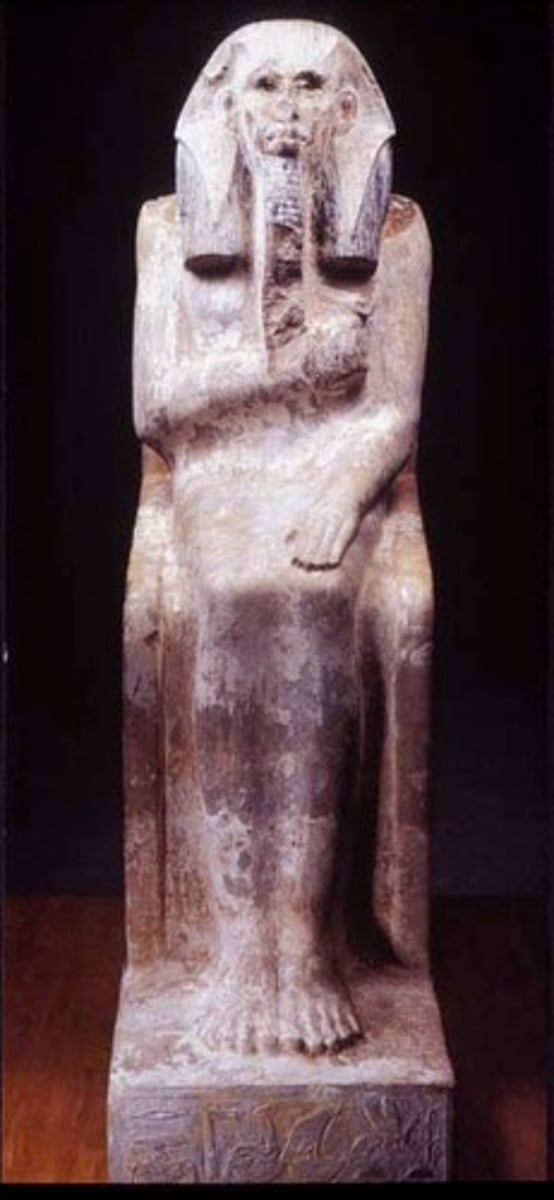

Shendject
a short, kilt-like garment that was worn in ancient Egypt, especially by pharaohs, noblemen, and military personnel

Portico
a projecting structure with a roof supported by columns. Functions as porch or roof area.
Clerestory
a raised wall with windows that brings light into a building's interior by rising above adjoining lower roofs or space

Focus question: The pharaoh in the Old Kingdom had been viewed as a mortal embodiment of the god Horus, but not himself a god. How did the perception of the king change during the Middle and New Kingdoms and how did this change show up in art and architecture?
Old kingdom: Funerary architecture emphasizes the ritual separation between cultic activities for the deceased pharaoh and those for the gods• Focus on solar symbolism related to the concept of the king as the "son of Ra"and his status as solar celestial being after death.
Middle Kingdom: Pharaoh relationed with Osiris and cycle of dealth/rebirth. Mortuary complexes become part of the landscape, strengthening the connection betweent he king and the sacred landscape• Imagery and symbolism relate to death/rebirth and cosmic integration.
New Kingdom: The king is presented as a divine intermediary and co-ruler with the gods• Imagery of the ruler is now incorporated into the fabric of the god's temple precincts and the pharaoh publicly appears in festivals and ceremonies that demonstrated his divinity
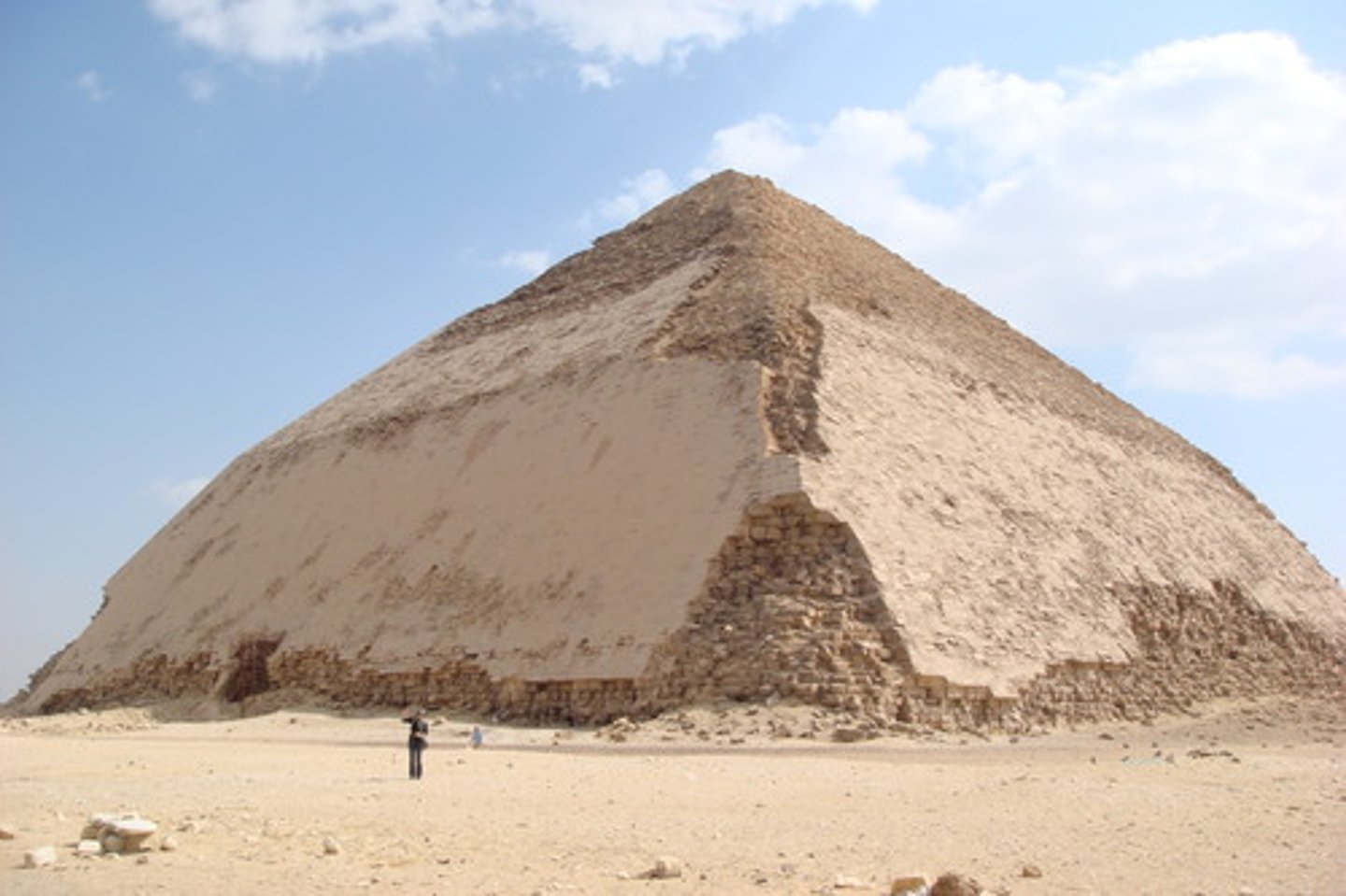
Bent Pyramid of Sneferu at Dashur
-Part of Old Kingdom
-The bent pyramid is shaped this way due to structural instability issues when building the monument

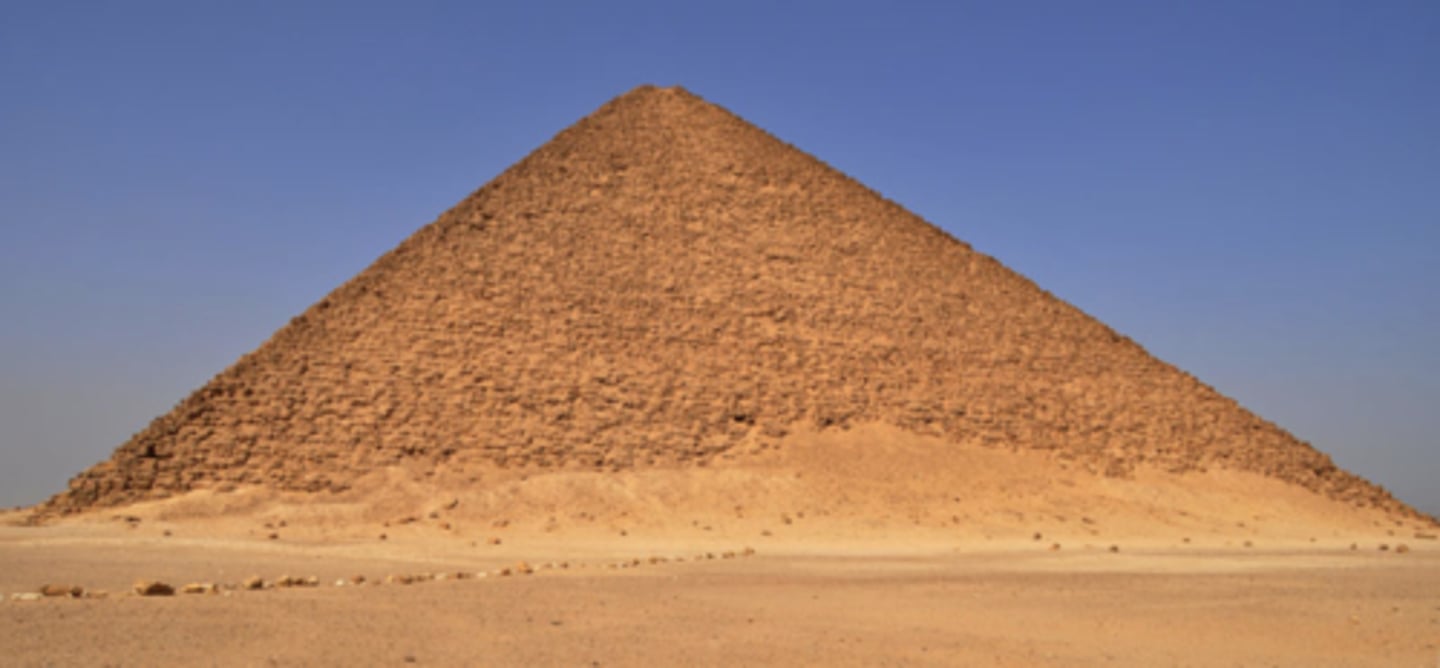
Red Pyramid of Sneferu at Dashur
-First true pyramid
-pinkish hue of the limestone used to build it
-Major change from funerary complex from Djoser. Change is with religious beliefs and ruling techniques. The new pyramid is less focused on spaces needed by the ruler to maintain ruling but now prioritizes monuments and being a place of worship for the people to come to. Pharoah is not a god when he dies, he is with the gods.

Pyramids of Giza
All built by 4th dynasty pharaohs (Khufu, Khafre, and Menkaure)
Khufu:
first to be build, largest.
Would've been built with white limestone on the outside. Sun would've been shining off of it
Passage ways inside. Burial chambers throughout.
-Unfinished chamber built into bedrock of the pyramid
Spirits of king are worshiped as a deified ancestor
-Architecture still shows how a king is respected as a celestial king even after life. Don't turn king into god, but make him the eternal sovereign of egypt. Separation in cultic duties to the gods and as the pharaoh.
Khafre:
The only pyramid with the sphinx out of the three. Protective feature and likely built to guard pathway from the funerary complex
-Sphinx gate at Hattusha (from the Hittites) can be compared to this. Shows how the societies have been in contact with each other even if this consisted with battle
Menkaure:
last pyramid
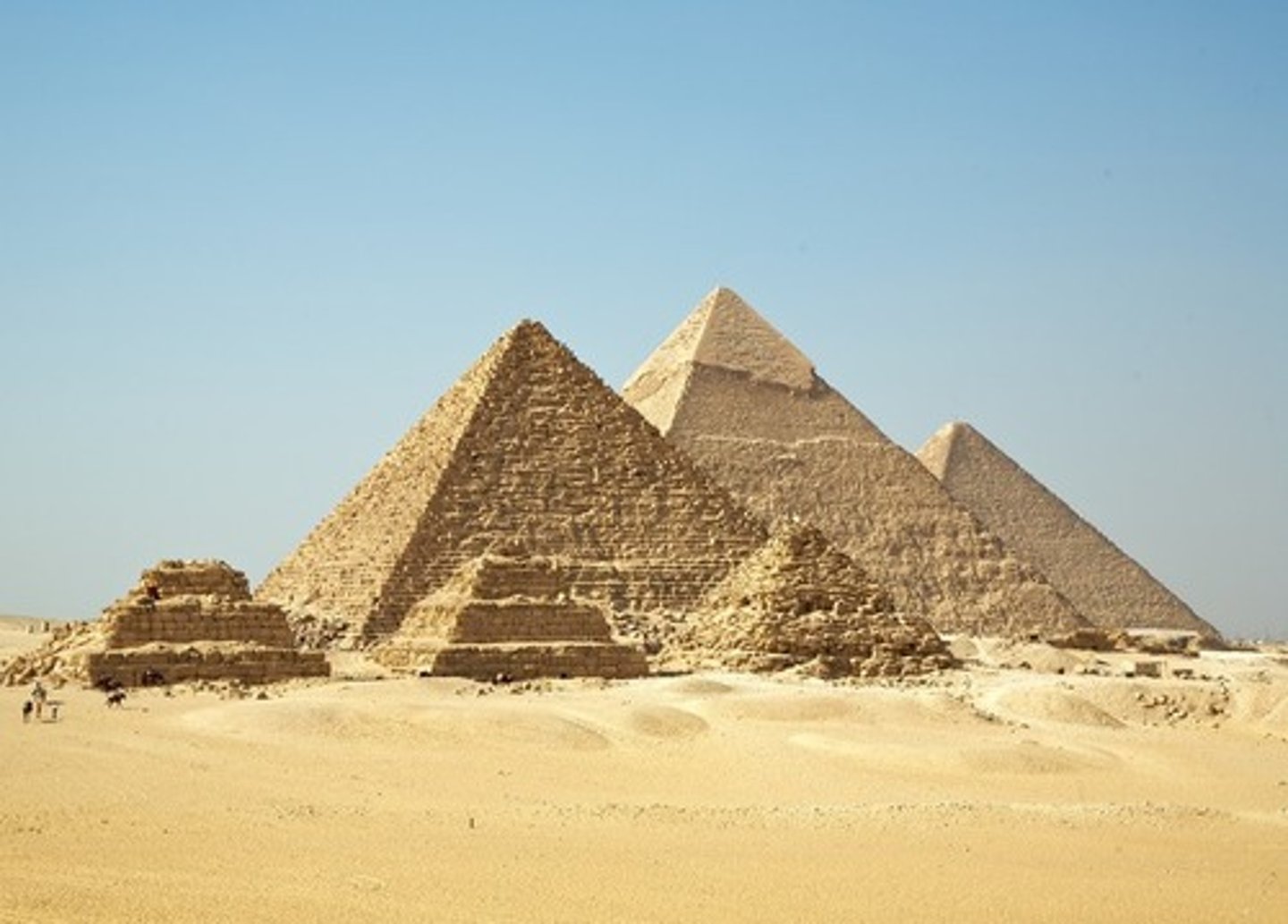

Great sphinx of Giza
Krafre is the only pyramid with the sphinx out of the three. Protective feature and likely built to guard pathway from the funerary complex
⭐ Compared toSphinx gate at Hattusha (from the Hittites). Shows how the societies have been in contact with each other even if this consisted with battle.
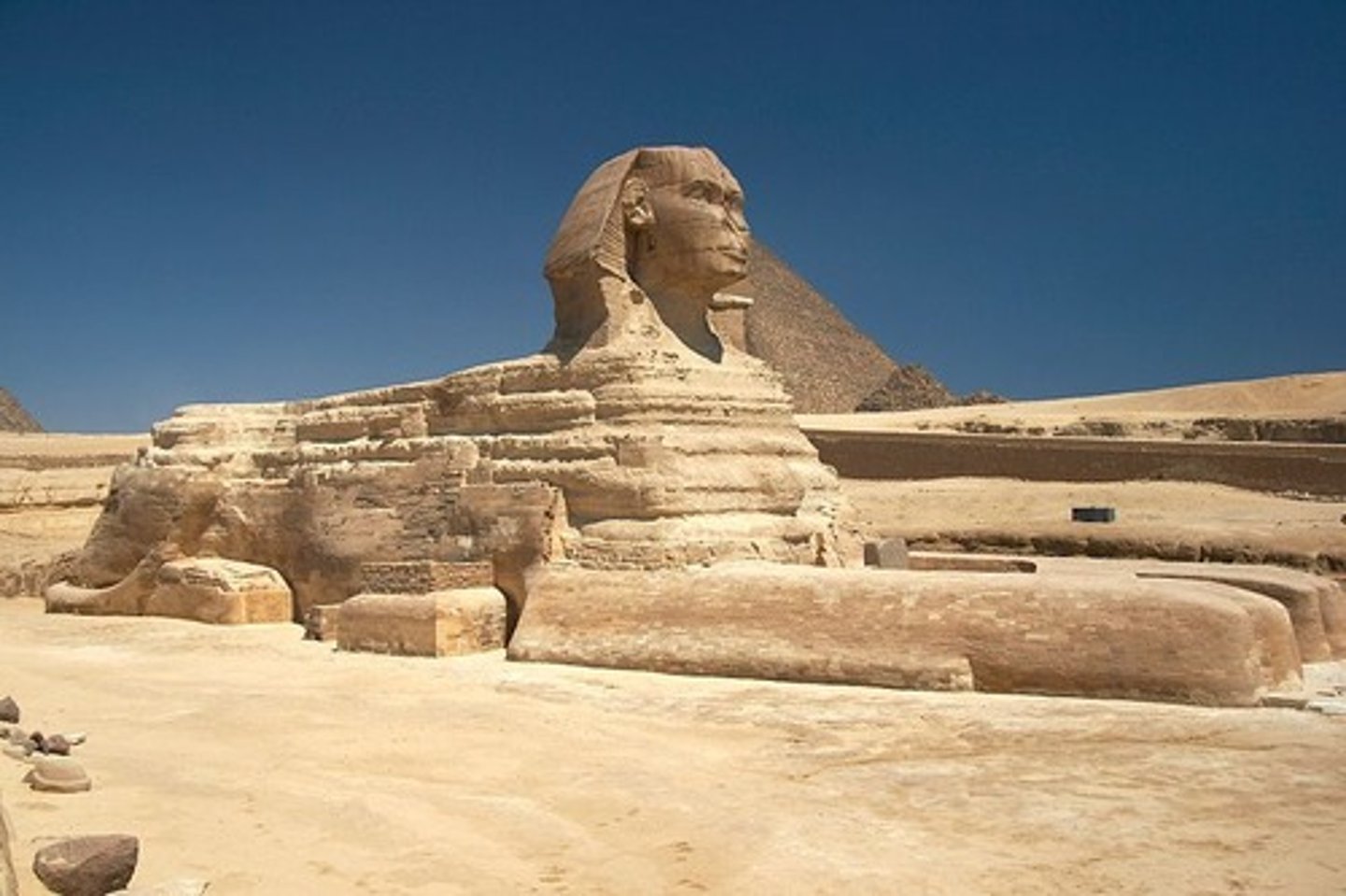

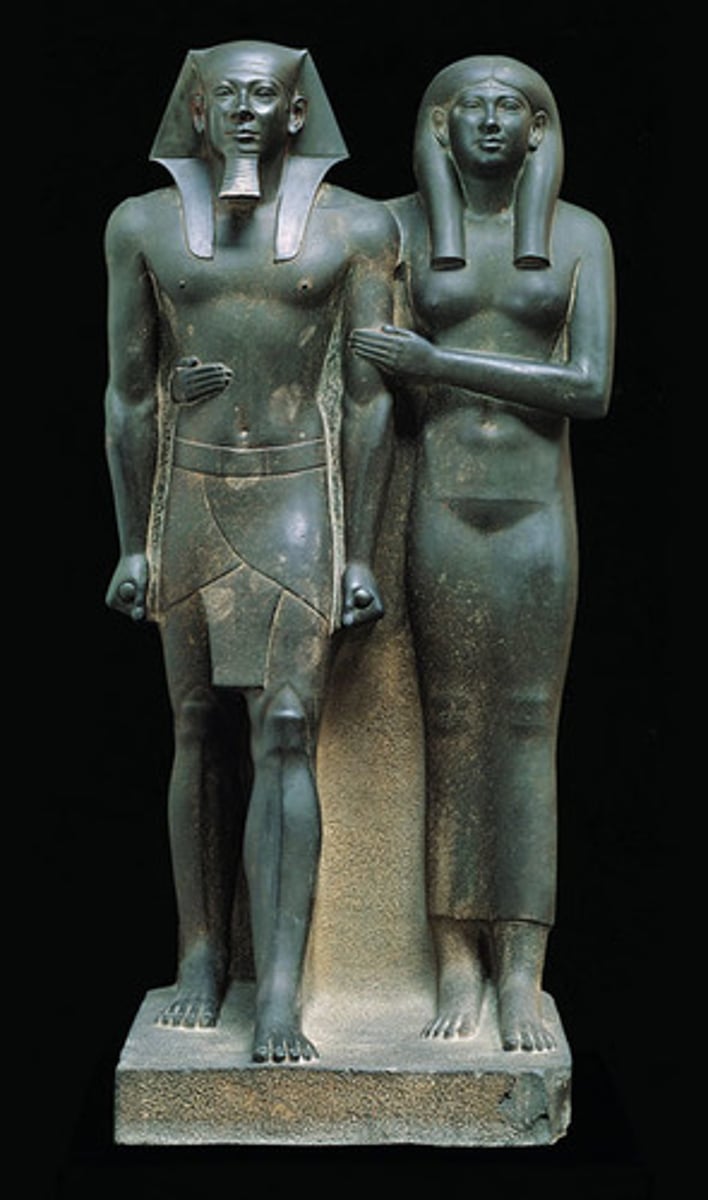
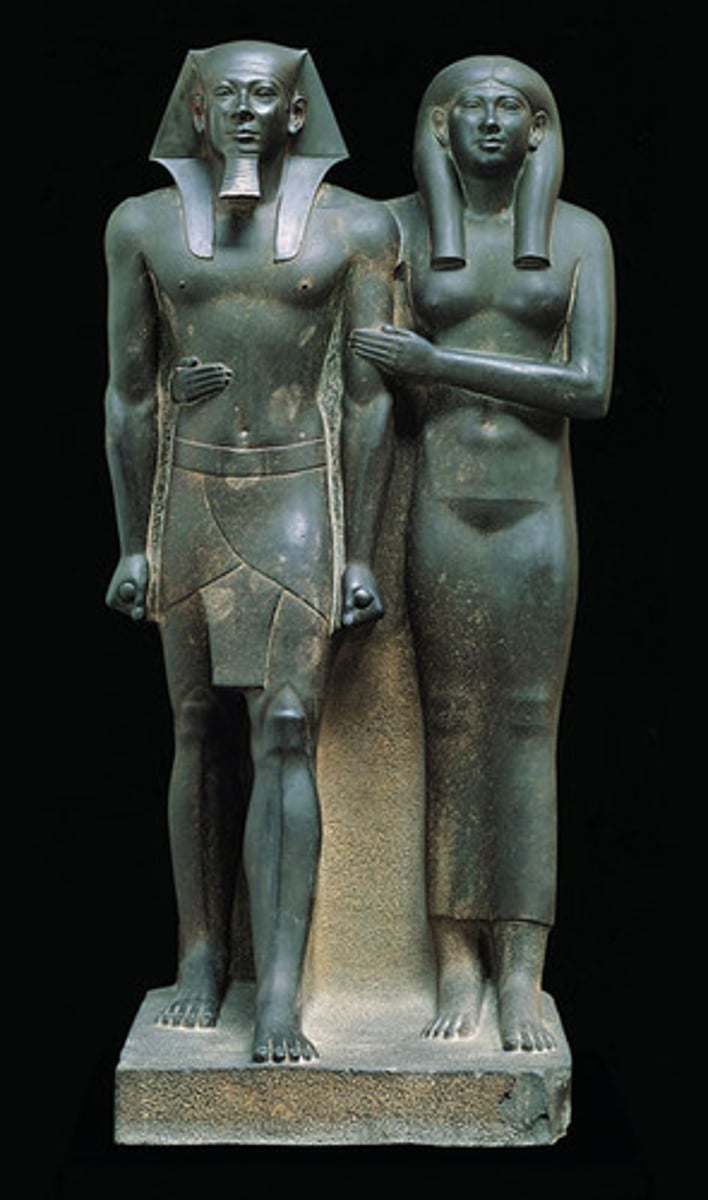
Statue of Menkaure and Queen
-Cultic form.
-For worship and to maintain the spirit of the king. People pray to this statue as the pharaoh who is a celestial king because he has direct contact with God.
-Nemes: distinctive headcloth worn by pharaohs in egypt
-Shendjet: a short, kilt like garment that was worn in ancient Egypt, especially by pharaohs, noblemen, and military personnel
Style:
-Naturalism with facial features despite being 'ideal/perfect' being. Somewhat individualized
Generic statue
-Shows some form of protectiveness as queen has arm around pharaoh
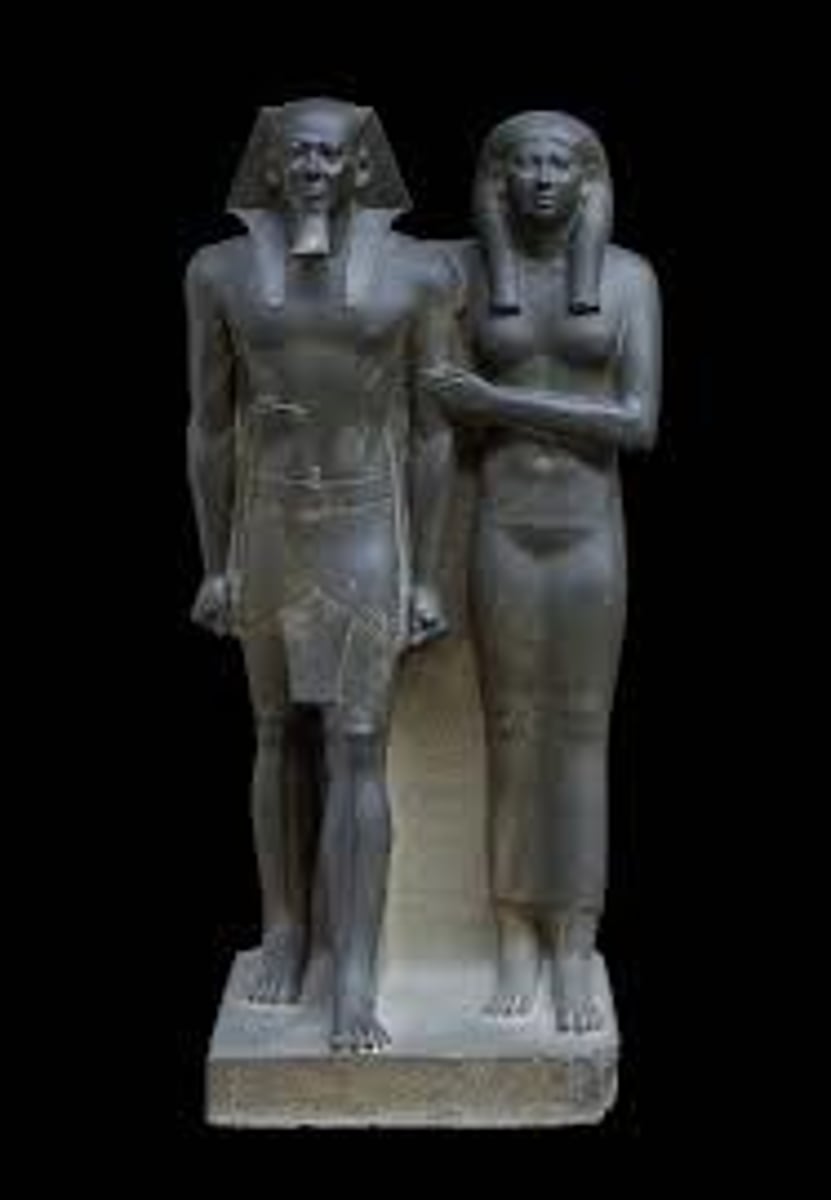

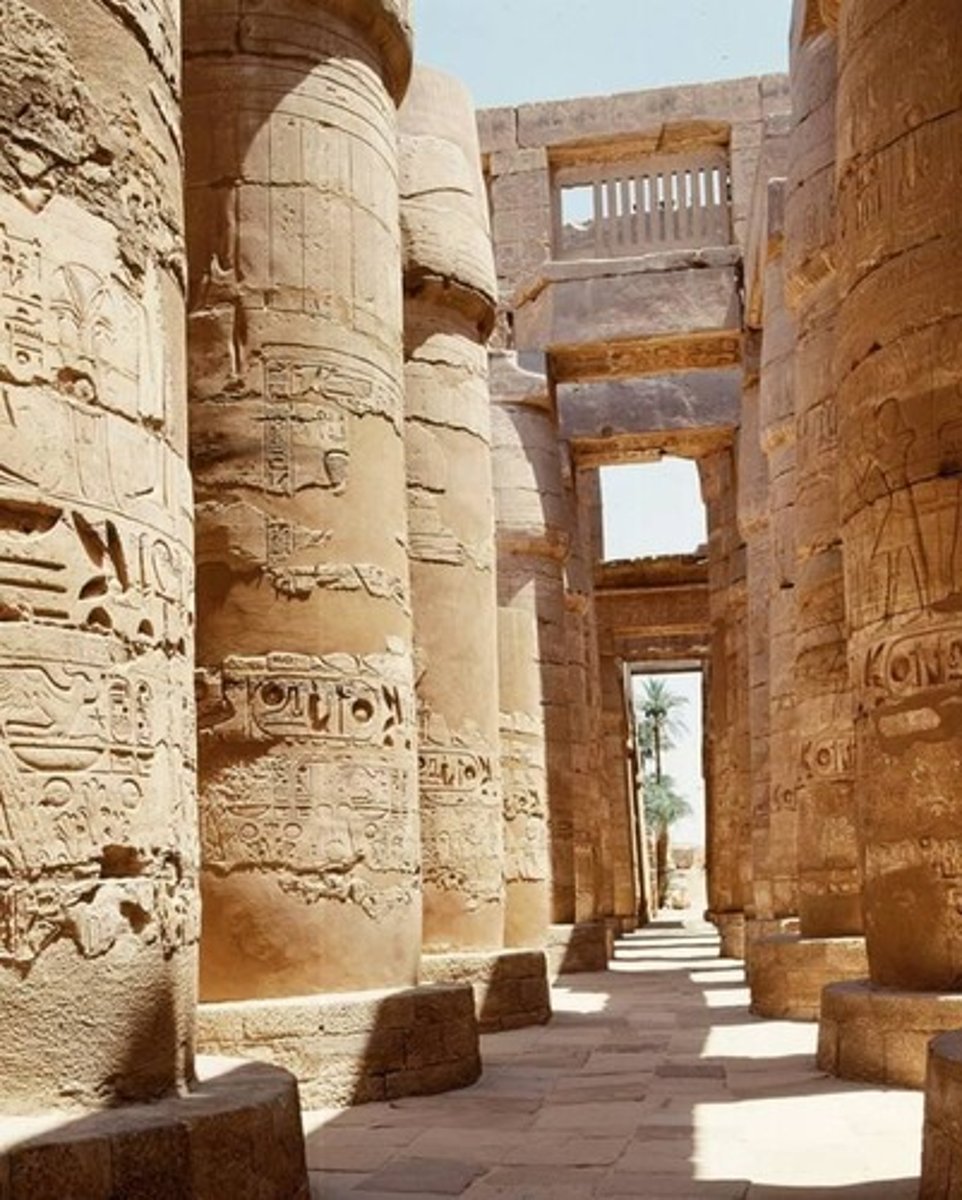
Temple precient of Amun Ra at Karnak
-Arranged between two axis
Precinct is where the Opet festival occurred when the Nile flooded. The purpose of the festival is to transfer divine powers of Amun-ra to the pharaoh. Very similar to the ritual that occurred at the pyramid of Djoser
Hypostyle hall within.
Clerestory: raised wall with windows that bring light into a buildings interior by rising above the adjoining lower roofs or spaces
The columns holding up the roof have capitals with papyrus flowers painted on them. Smaller columns have closed papyrus painted on. Flowers represent crossway to afterlife. ⭐hyroglyphs also marked on columns.
Visual motif for the people that show that they are 'allowed' to be in temple.
Bird perched in basket, praising tablets with name of Ramses. Literate scribes that all 'adore' the king.

Kemet
-Means "black land"
- symbolizes the fertile soil that Egypt had along the Nile
Ma'at
-A fundamental principle of cosmic order, truth, and justice
-The goddess of truth, justice, balance, and order

Necropolis
a large, organized burial ground containing the tombs and monuments of the elite, often built on the desert's edge, and was deeply connected to beliefs about the afterlife.
Mastaba
-form of underground burial place with slanted walls
-found within Djosers funerary complex

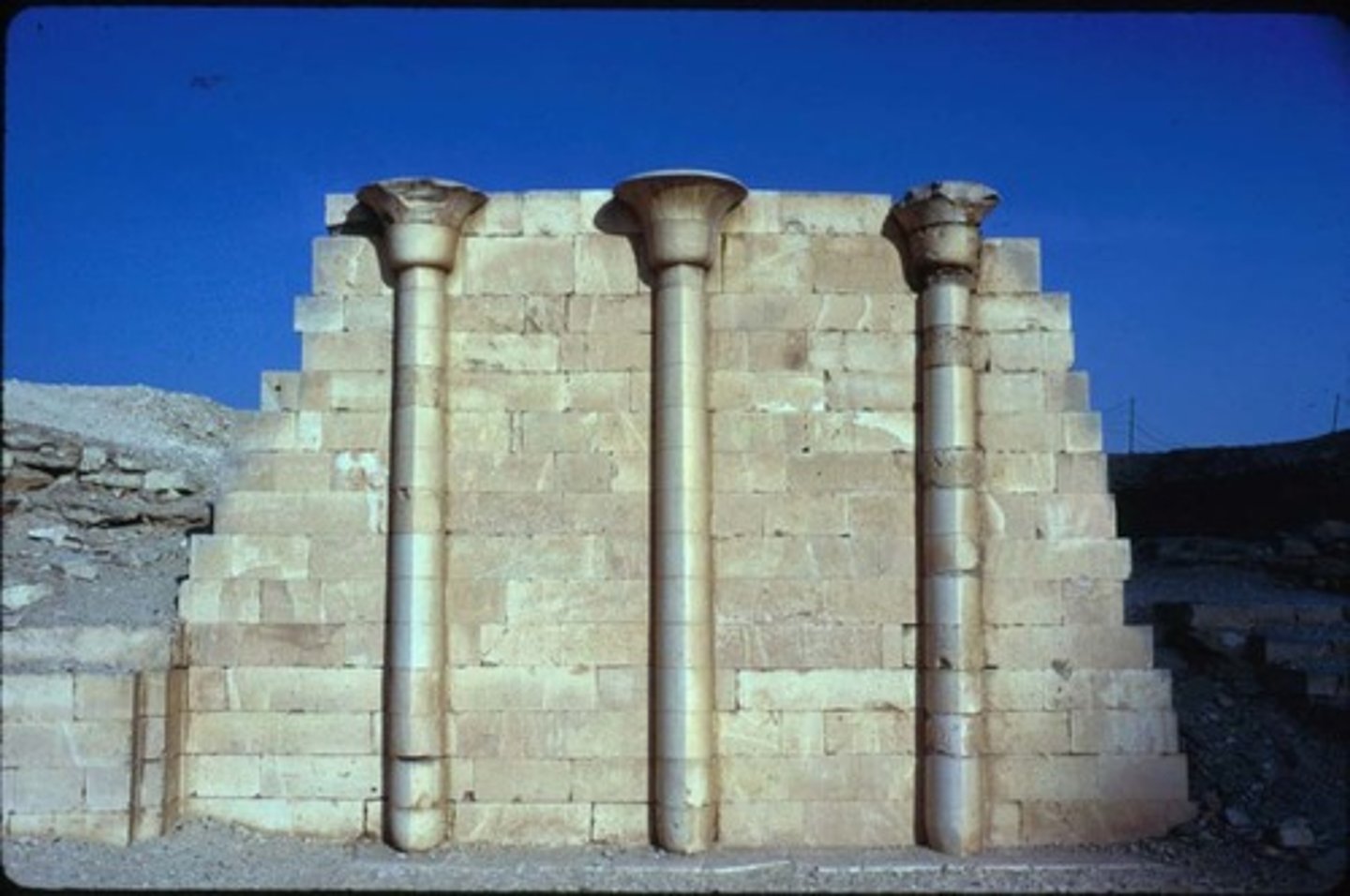
colunnade
-rows of columns to support the roof
-found at entrance of Djoser's funerary complex in Saqqara Egypt
Engaged Column
-column that is partially or almost fully integrated into the wall
-findings of papyrus columns in House of North of Djoser's funerary complex

Ka
Force/life of a person after death. Their 'double'
Ba
spiritual essence of a person after death and represented in hieroglyphs with a bird head.
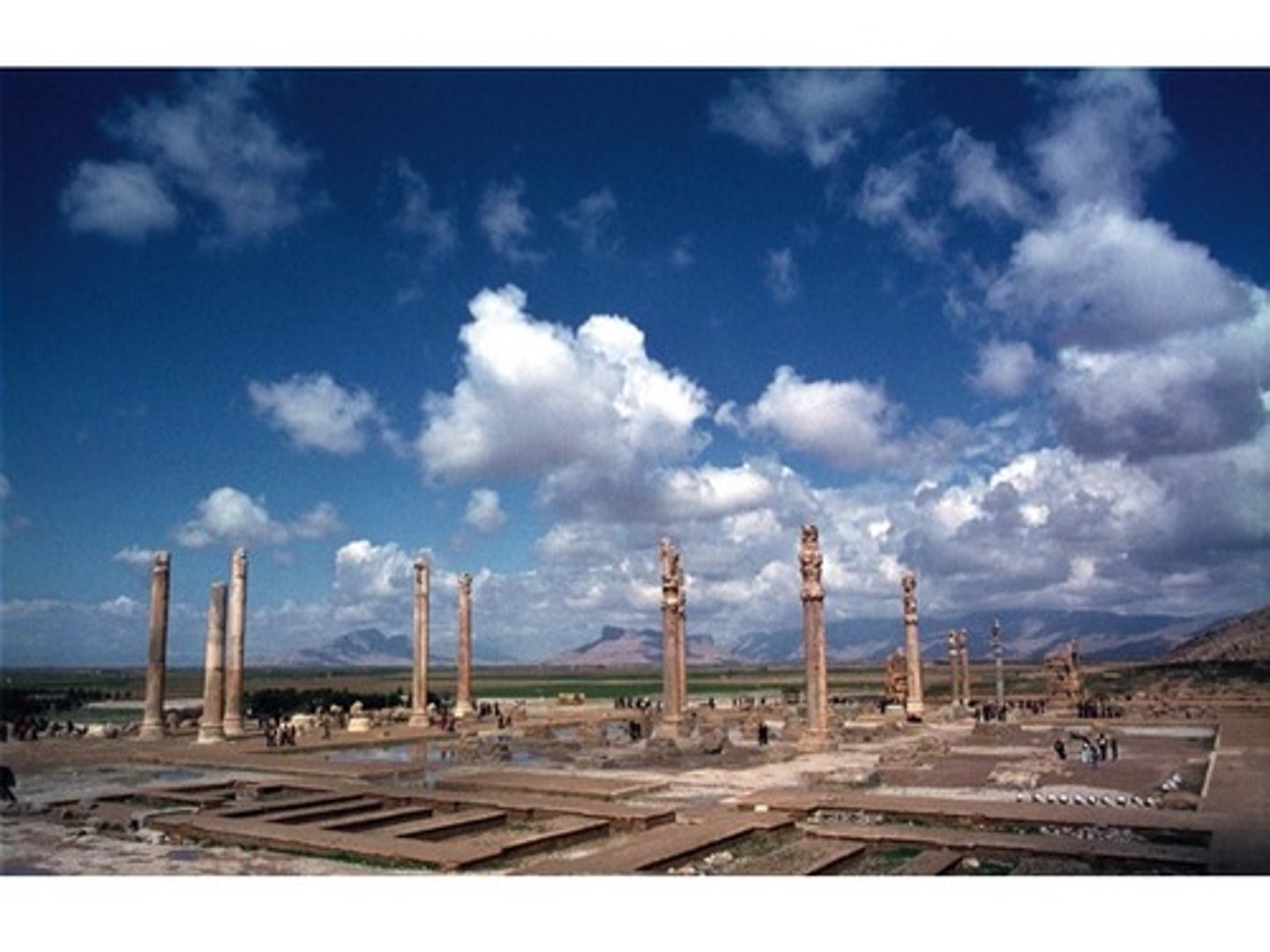
The Apadana in Persepolis (*in Achaemenid empire)
-Distinctive capitals (top section at the tip of the column with decorative features). Capitals have horses and other animals on the top. Persian style
Assyrian palace styles shown in capitals.
-Hypostyle hall where ceremonies are held.
-Gate of Almations: main entrance to the city that incorporated wall similarities with other empires
-Processional relief carvings with satrapy and hellenization

Correlations of Apadana to other socieities (*in Achaemenid empire)
-columns from egypt
-capitals from Mesopotamian iconography blended with Persian forms
-releif carvings from Mesopotamian architecture
-layout from Assyrian empire
-lamassu from Mesopotamian empires
-floral motifs from Greece, Mesopotamia and Egypt
Question to know for test:
Which statement about the Temple of Amun at Jebel Barkal below is FALSE.
a) The Temple of Amun at Jebel Barkal was originally constructed by the Egyptian pharaohs soon after they conquered the Kerma Kingdom of Kush around 1550 BCE.
b) As the birthplace of Amun, the Temple at Jebel Barkal was also the origin of "royal ka," the force or spirit that the god Amun passed on to each pharaoh, giving him the right to rule.
c) The Temple of Amun at Jebel Barkal was expanded and refurbished by Piye, the first king of the Napatan Dynasty of Kush and also the first pharaoh 25th Dynasty of Egypt.
d) The Temple of Amun at Jebel Barkal was of very little importance, both religiously and symbolically, to the peoples of Egypt and Nubia.
d) The Temple of Amun at Jebel Barkal was of very little importance, both religiously and symbolically, to the peoples of Egypt and Nubia.
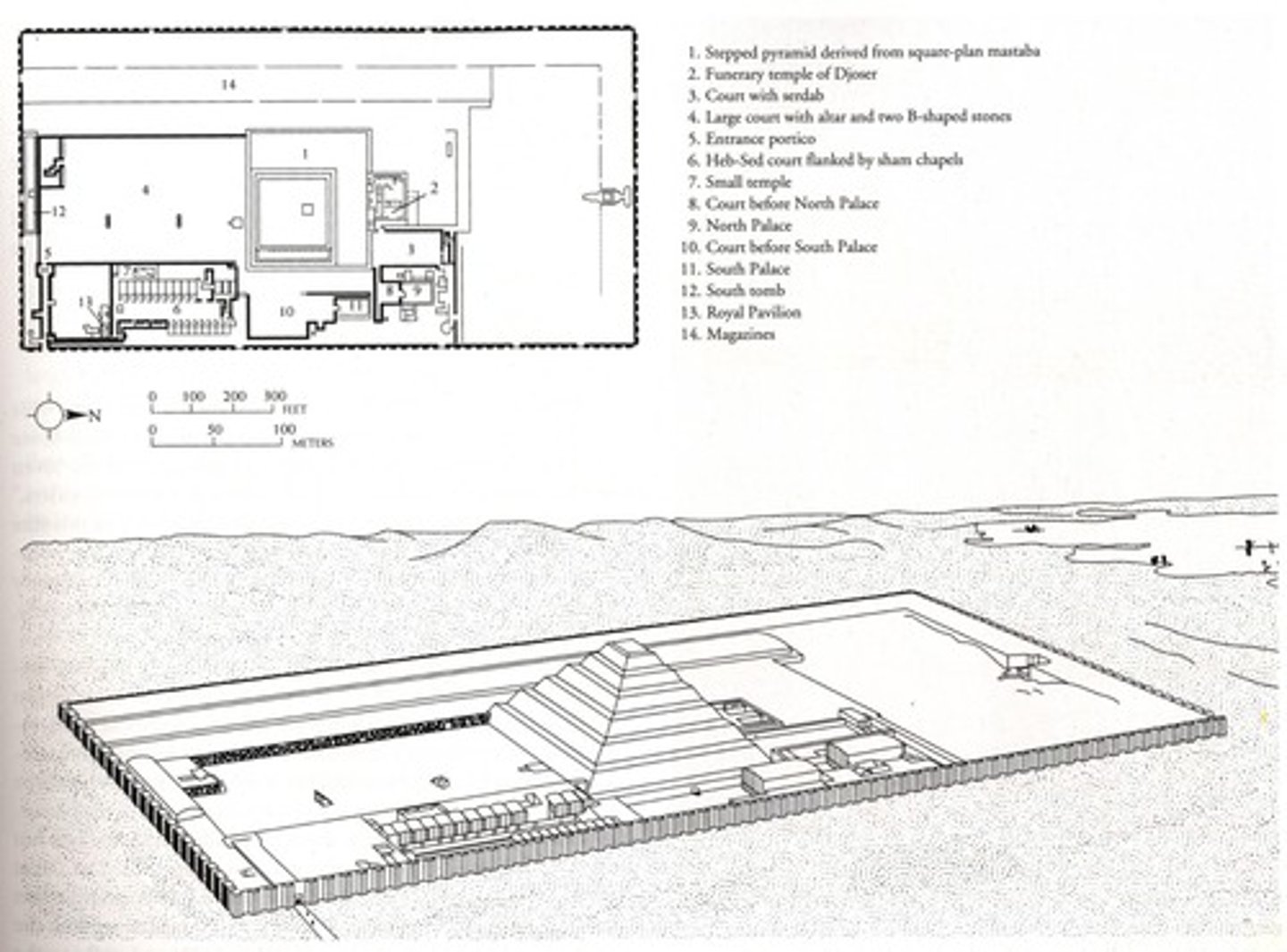
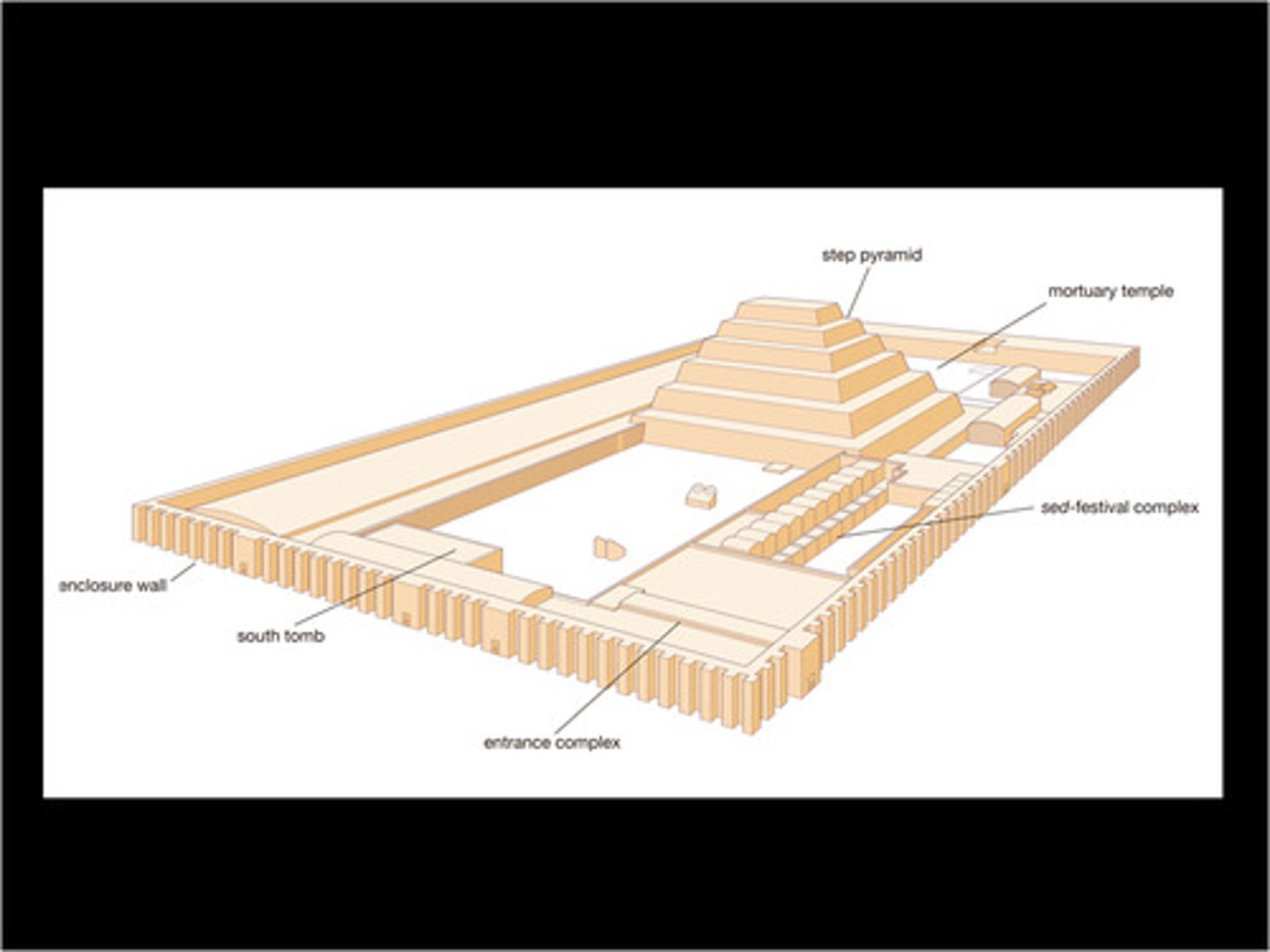
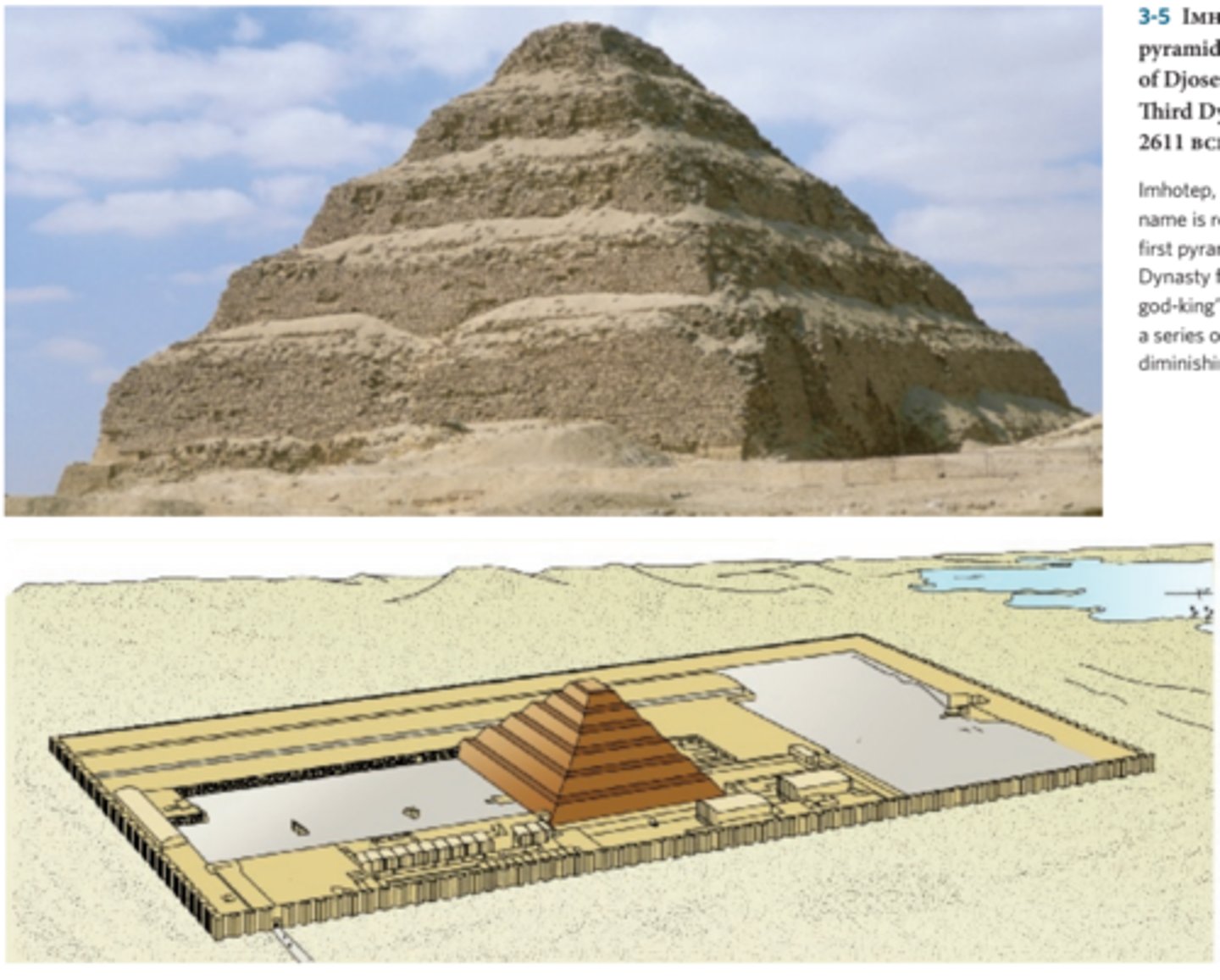
Funerary complex and step pyramid of Djoser
Complex:
-engaged column
-papyrus column
-Shares basic shape with mastaba tombs
-Oriented on the north-south axis
-Ka statues
Step pyramid:
-first monument made of entirely stone. Marks transition from mudbrick to stone for important buildings.
-Djoser was buried here
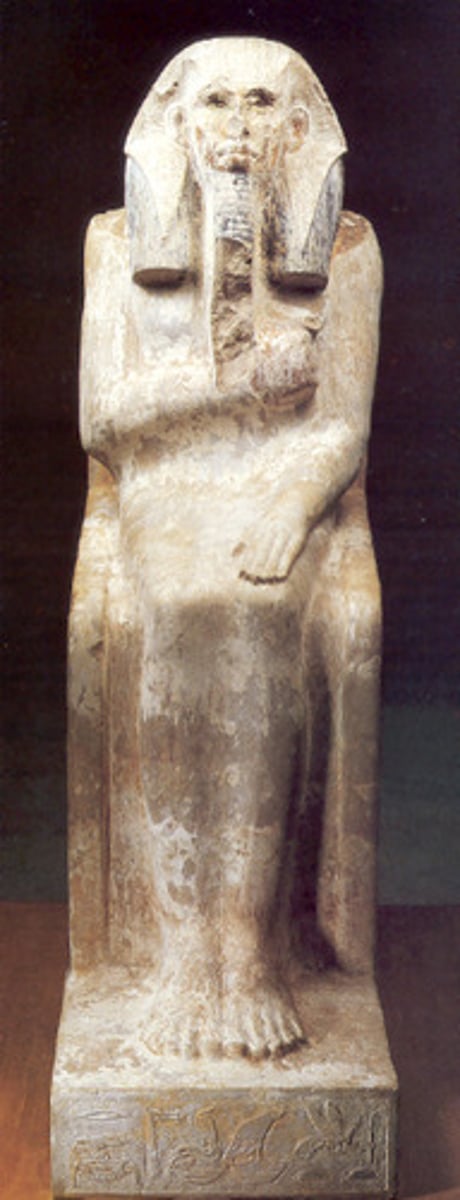
Ka statue of Djoser
-statue of pharaoh so the Ka of Djoser can return. Believed that Ka could overlook processions within the pyramid.

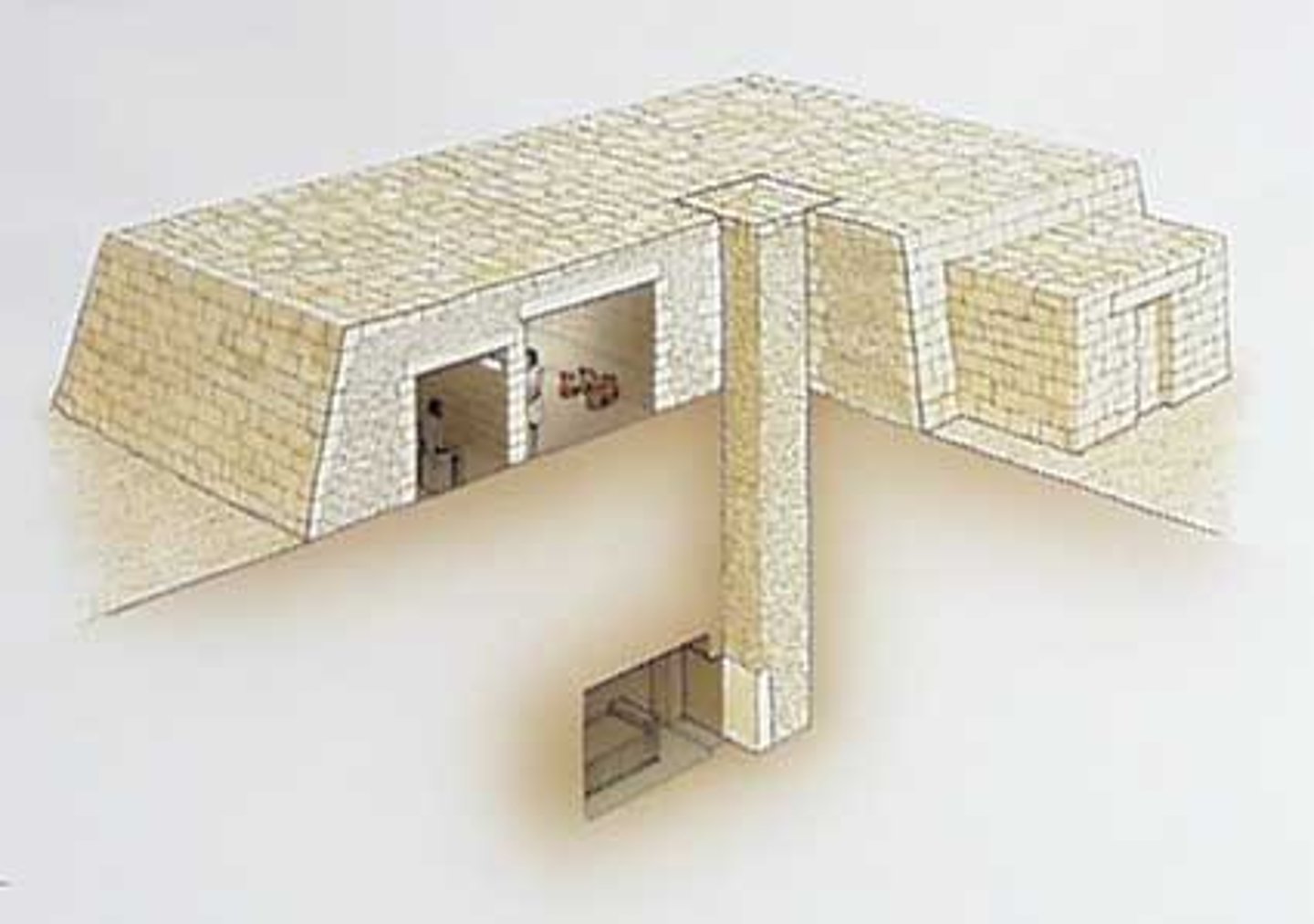
Serdab in funerary complex
-located on the north side of the step pyramid in the Serdab Court. Holes cut into wall so views can look at Ka statue
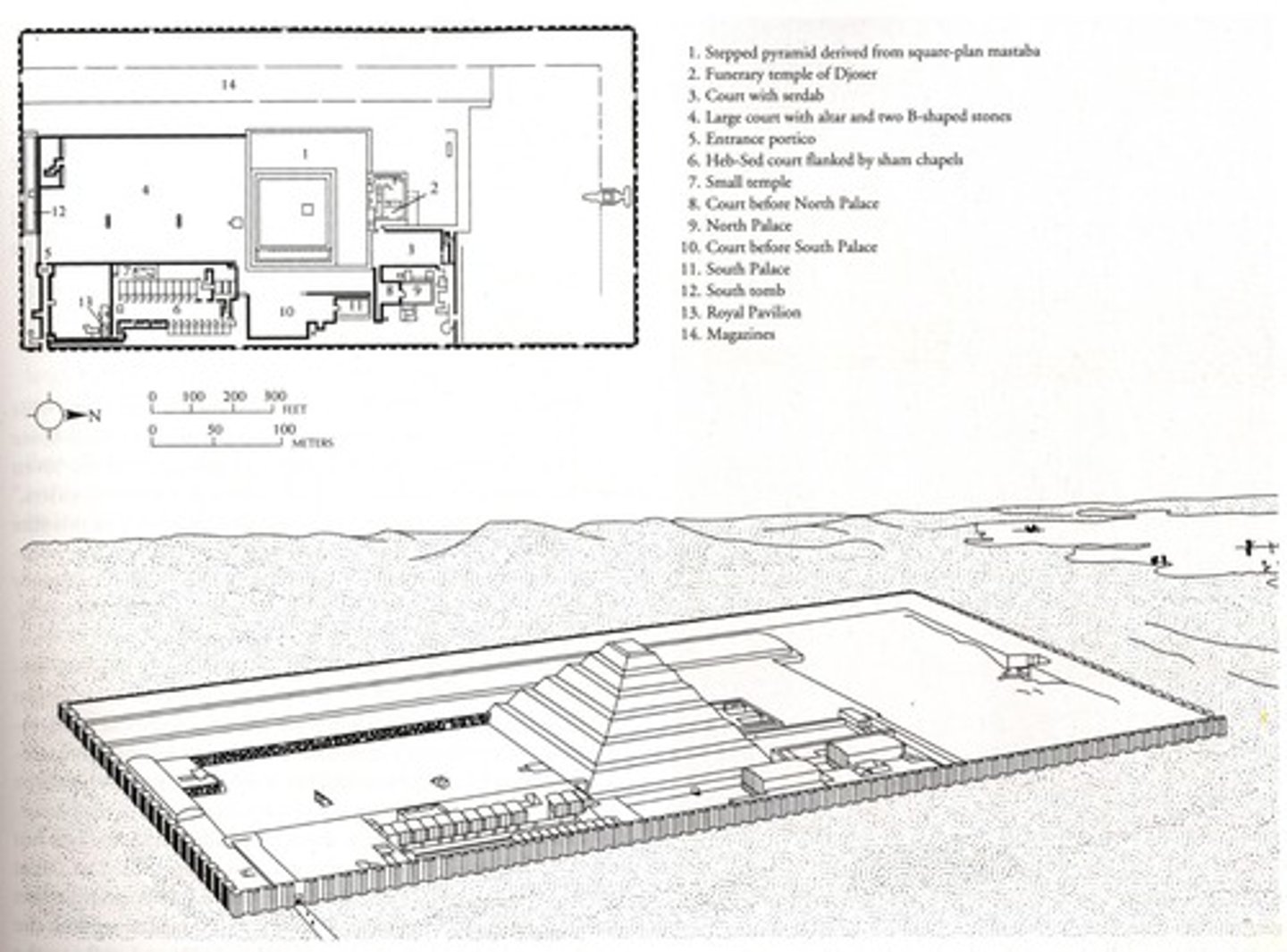
Outer wall of funerary complex
-Niched outer wall similar to the walls niched walls of Early Dynastic funerary enclosures at Abydos