Human Body Systems Independent Study Guide
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
How is the human body organized?
The human body is organized into cells, tissues, organs, and systems.
What are the four types of tissues and their functions?
1. Epithelial: covers body surfaces and lines cavities; 2. Connective: supports and binds other tissues; 3. Muscle: facilitates movement; 4. Nervous: transmits impulses for communication.
What is homeostasis and why is it important?
Homeostasis is the maintenance of a stable internal environment, crucial for the proper functioning of cells and overall health.
What are feedback systems? Describe positive and negative feedback.
Feedback systems are mechanisms that regulate body functions. Positive feedback amplifies a response (e.g., childbirth), while negative feedback reduces a response to maintain balance (e.g., temperature regulation).
What are the four phases of digestion?
1. Ingestion: taking in food; 2. Digestion: breaking down food; 3. Absorption: nutrients entering the bloodstream; 4. Elimination: expelling waste.
What are the four types of teeth and their functions?
1. Incisors: cutting food; 2. Canines: tearing food; 3. Premolars: crushing food; 4. Molars: grinding food.
What stops swallowed food/water from entering the lungs?
The epiglottis stops food/water from entering the lungs by covering the trachea during swallowing.
Describe the path food travels from mouth to anus.
Mouth → Esophagus → Stomach → Small intestine → Large intestine → Anus.
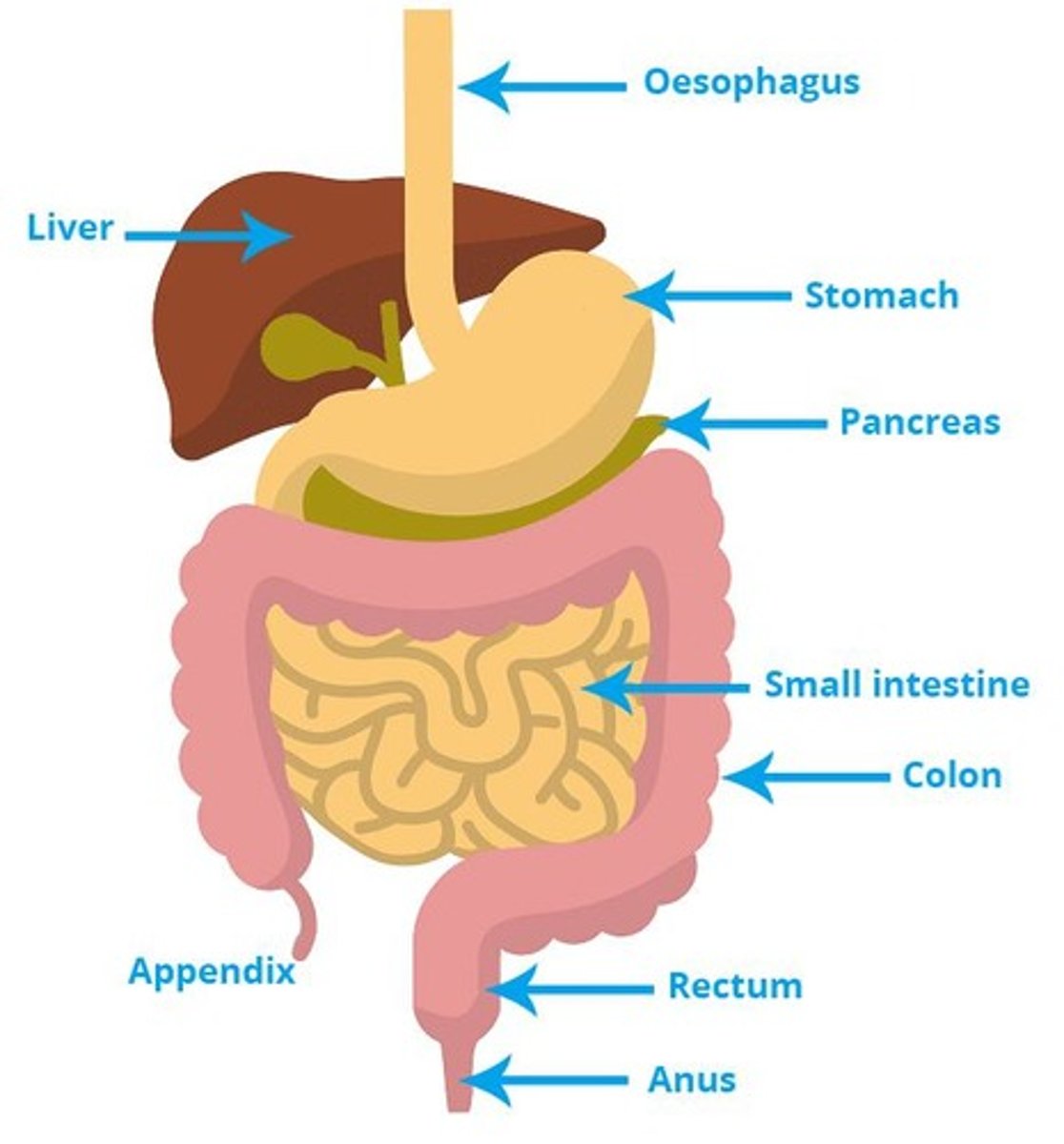
What are the functions of the pancreas, liver, and gallbladder?
Pancreas: produces digestive enzymes and insulin; Liver: detoxifies blood and produces bile; Gallbladder: stores bile.
Where are Salivary Amylase, Pepsin, and Bile produced and what are their functions?
Salivary Amylase: produced in salivary glands, breaks down carbohydrates; Pepsin: produced in the stomach, digests proteins; Bile: produced in the liver, emulsifies fats.
How does the skin contribute to the excretory system?
The skin excretes waste through sweat, regulating temperature and removing toxins.
How do the kidneys maintain homeostasis?
The kidneys regulate fluid balance, electrolytes, and blood pressure, filtering waste from the blood.
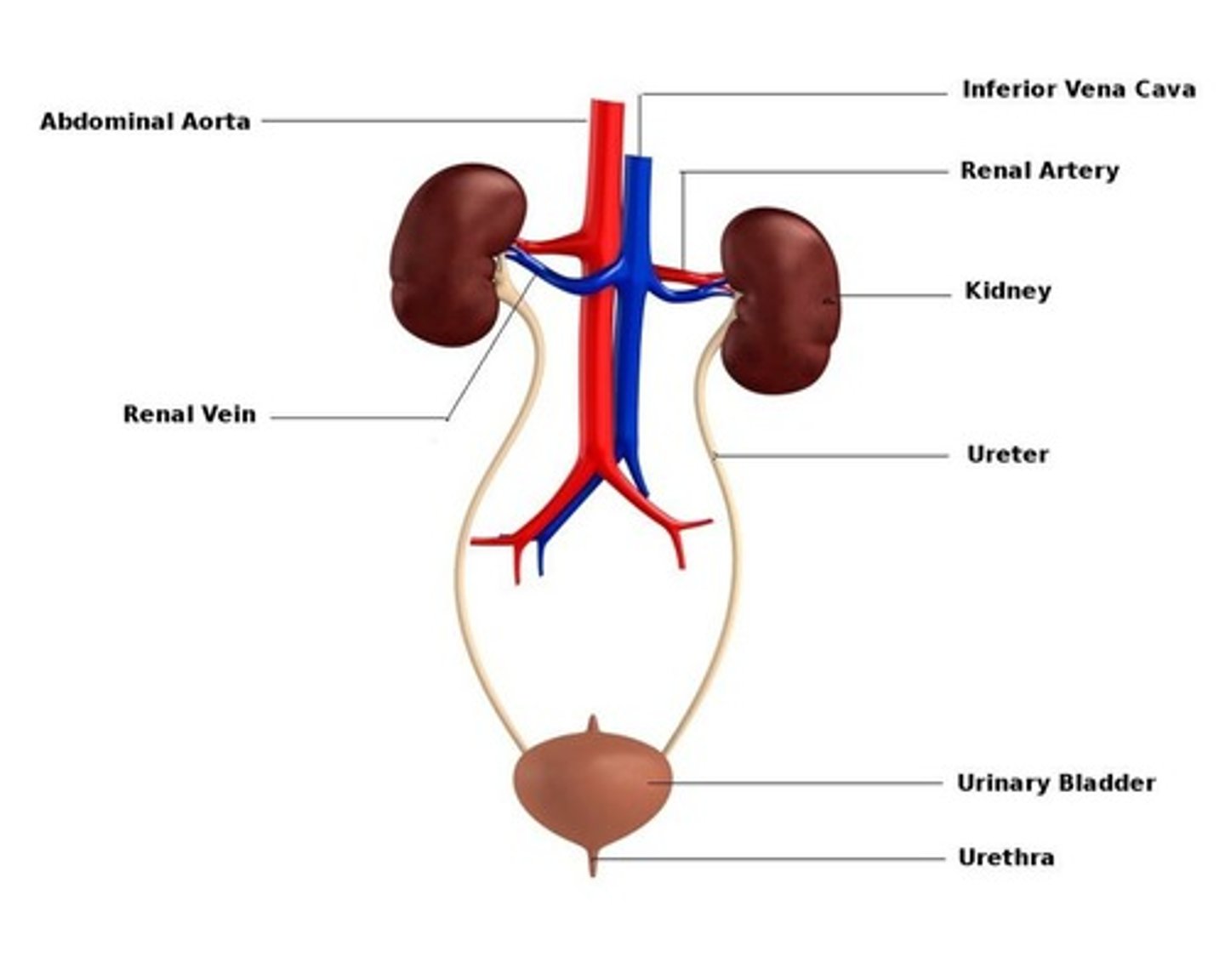
What materials are filtered from the blood in the kidneys?
Waste products, excess salts, and water are filtered from the blood.
What materials do not leave the bloodstream during filtration?
Red blood cells, white blood cells, and large proteins do not leave the bloodstream.
What is dialysis?
Dialysis is a medical procedure that removes waste and excess fluid from the blood when kidneys fail.
What are the parts and functions of the Central Nervous System?
The Central Nervous System consists of the brain and spinal cord, responsible for processing information and coordinating responses.
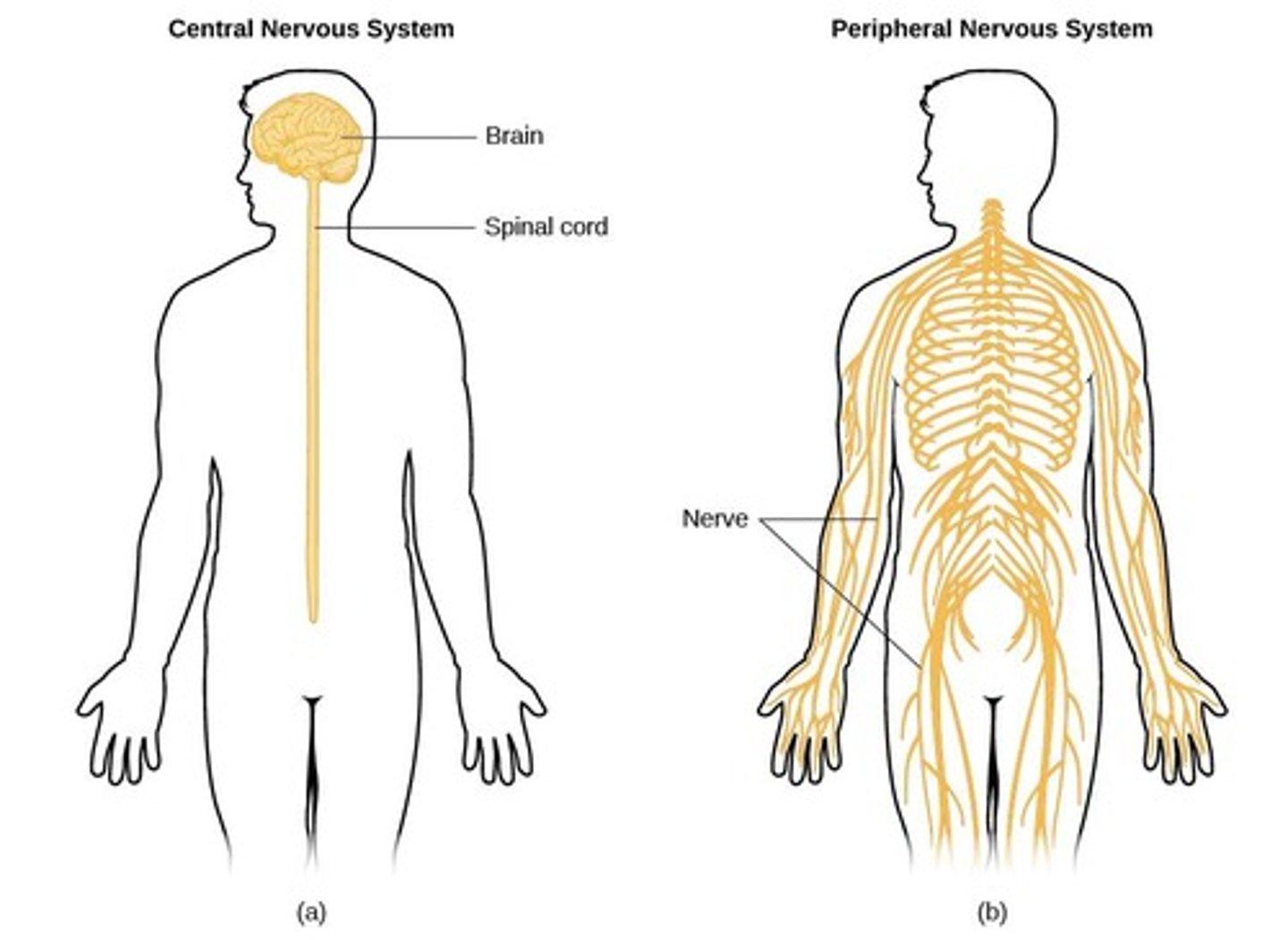
What are the parts and functions of the Peripheral Nervous System?
The Peripheral Nervous System includes all nerves outside the CNS, connecting the CNS to limbs and organs.
What are the three types of neurons?
1. Sensory neurons: transmit sensory information; 2. Motor neurons: send signals to muscles; 3. Interneurons: connect neurons within the CNS.
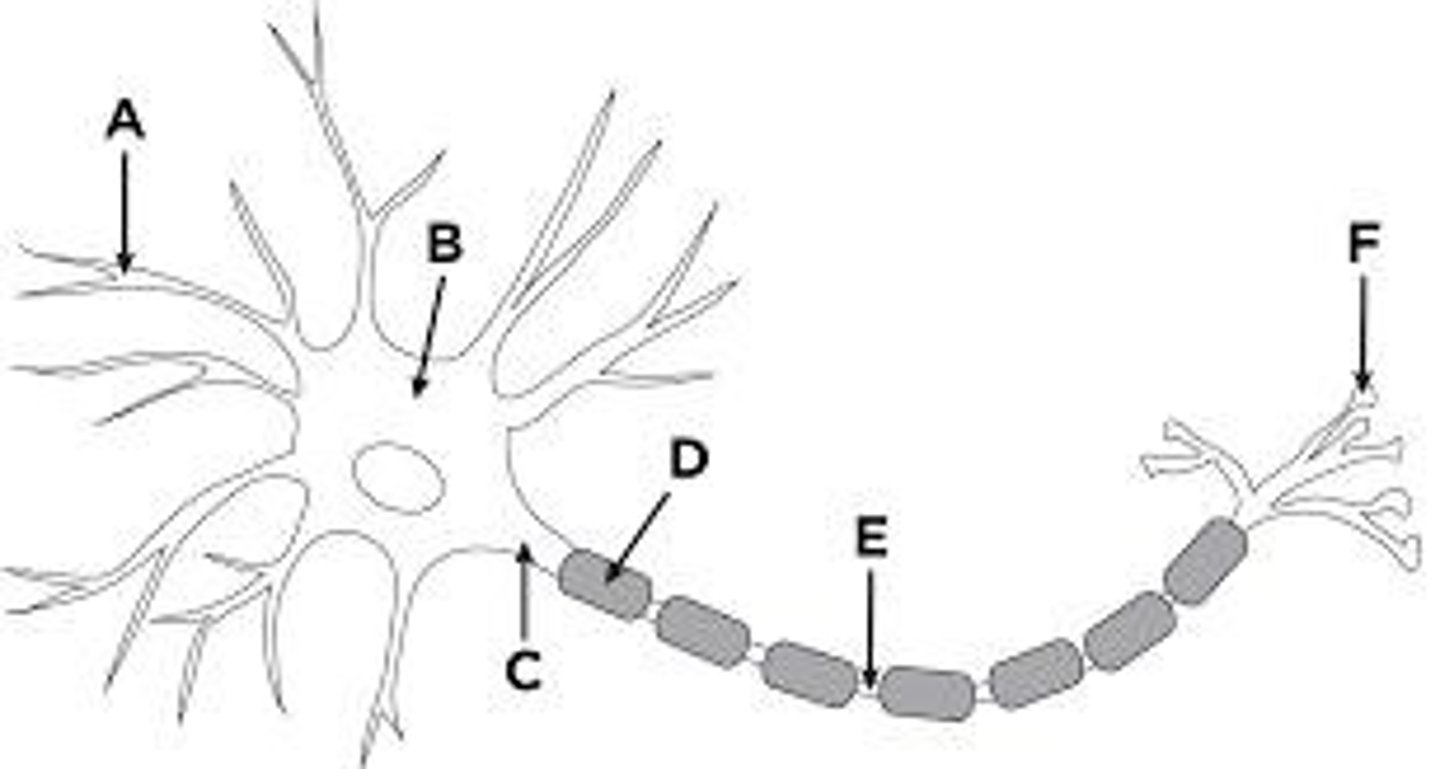
How does a nerve impulse begin and transmit?
A nerve impulse begins when a neuron is stimulated, causing a change in electrical charge that travels along the axon.
What are the functions of the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem?
Cerebrum: responsible for higher brain functions; Cerebellum: coordinates movement and balance; Brainstem: controls basic life functions.
What are the functions of the thalamus and hypothalamus?
Thalamus: relays sensory information; Hypothalamus: regulates body temperature, hunger, and thirst.
How are chemicals sensed through the nose and mouth?
Chemicals bind to receptors in the nasal cavity and taste buds, sending signals to the brain.
What are the two functions of the ear?
Hearing and balance.
Trace the path of sound through the ear.
Sound waves → Outer ear → Ear canal → Eardrum → Ossicles → Cochlea → Auditory nerve.
Trace the path of light through the eye.
Light → Cornea → Pupil → Lens → Retina → Optic nerve.
What are the functions of rods and cones in the eyes?
Rods detect light and dark; cones detect color.
How many bones are in the adult human skeleton?
There are 206 bones in the adult human skeleton.
What are the three types of joints?
1. Fibrous: immovable (e.g., skull); 2. Cartilaginous: slightly movable (e.g., spine); 3. Synovial: freely movable (e.g., knee).
What are the five freely movable joints in the body?
1. Hinge (e.g., elbow); 2. Ball-and-socket (e.g., shoulder); 3. Pivot (e.g., neck); 4. Saddle (e.g., thumb); 5. Gliding (e.g., wrist).
What is osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by weakened bones, increasing the risk of fractures.
What is the function of red and white bone marrow?
Red bone marrow produces blood cells; white bone marrow stores fat.
What are the major functions of the Lymphatic System?
The Lymphatic System helps maintain fluid balance, absorbs fats from the digestive system, and supports immune function.
What are the primary functions of the circulatory system?
Transporting oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and waste products throughout the body.
What is the connection between cholesterol and heart disease?
High levels of cholesterol can lead to plaque buildup in arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease.
What are the three types of skin carcinoma?
1. Basal cell carcinoma; 2. Squamous cell carcinoma; 3. Melanoma. Prevention includes sun protection and regular skin checks.
What is the role of the red blood cell in respiration?
Red blood cells transport oxygen from the lungs to body tissues and carry carbon dioxide back to the lungs.
What are the two major contributing factors to emerging diseases?
1. Increased human-animal interactions; 2. Global travel and trade.
What is the difference between active and passive immunity?
Active immunity develops after exposure to an antigen; passive immunity is acquired through antibodies from another source.