Urinalysis
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
What is the normal composition of the urine?
The majority of urine composition is composed of water, but there are a variety of solids that compose it as well
1) Proteins
→ Tamm-Horsfall (uromodulin) is secreted in the thick ascending limb and helps stabilize minerals in order to prevent crystal formation
2) Waste Products
→ Urea
→ Creatinine
→ also responsible for ridding the body of endogenous and exogenous metabolites
3) Minerals
→ Citrate being the largest one, acts to help prevent salts from precipitating into crystals
What are the six major components Dipstick Urinalysis
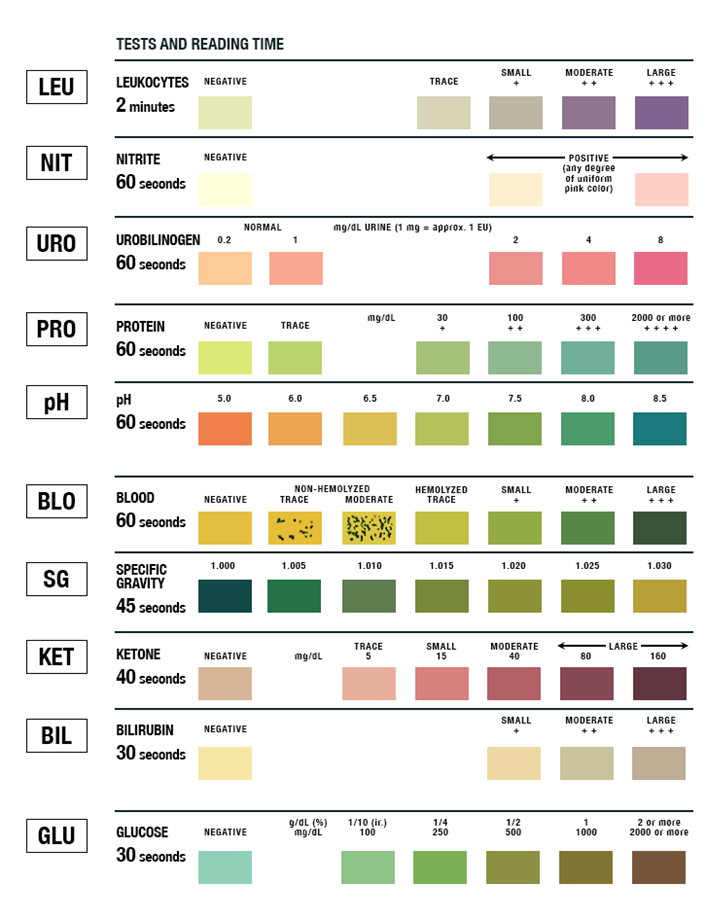
1) Leukocyte Esterase
→ enzyme produced by white blood cells, if positive indicates the presence of white blood cells in the urine
2) Nitrite
→ created in the presence of certain bacteria that can metabolize nitrate to nitrite
3) Protein
→ determined via a reaction with tetrabromophenol blue which will undergo a color change in the presence of proteins and at different pHs
→ albumin will bind at pH of 5-7
→ Bence Jones proteins do not bind at any pH
4) Blood
→ detected via peroxidase reaction catalyzed by hemoglobin and myoglobin
5) Specific Gravity
→ the weight of urine compared to distilled urine
→ a specific gravity of 1.010 is isosthenuria, meaning that the weight of the urine is equal to protein-free plasma
6) Ketones
→ detected by sodium nitroprusside interaction with acetoacetic acid
What are the identifiable cells underneath urinary sediment?
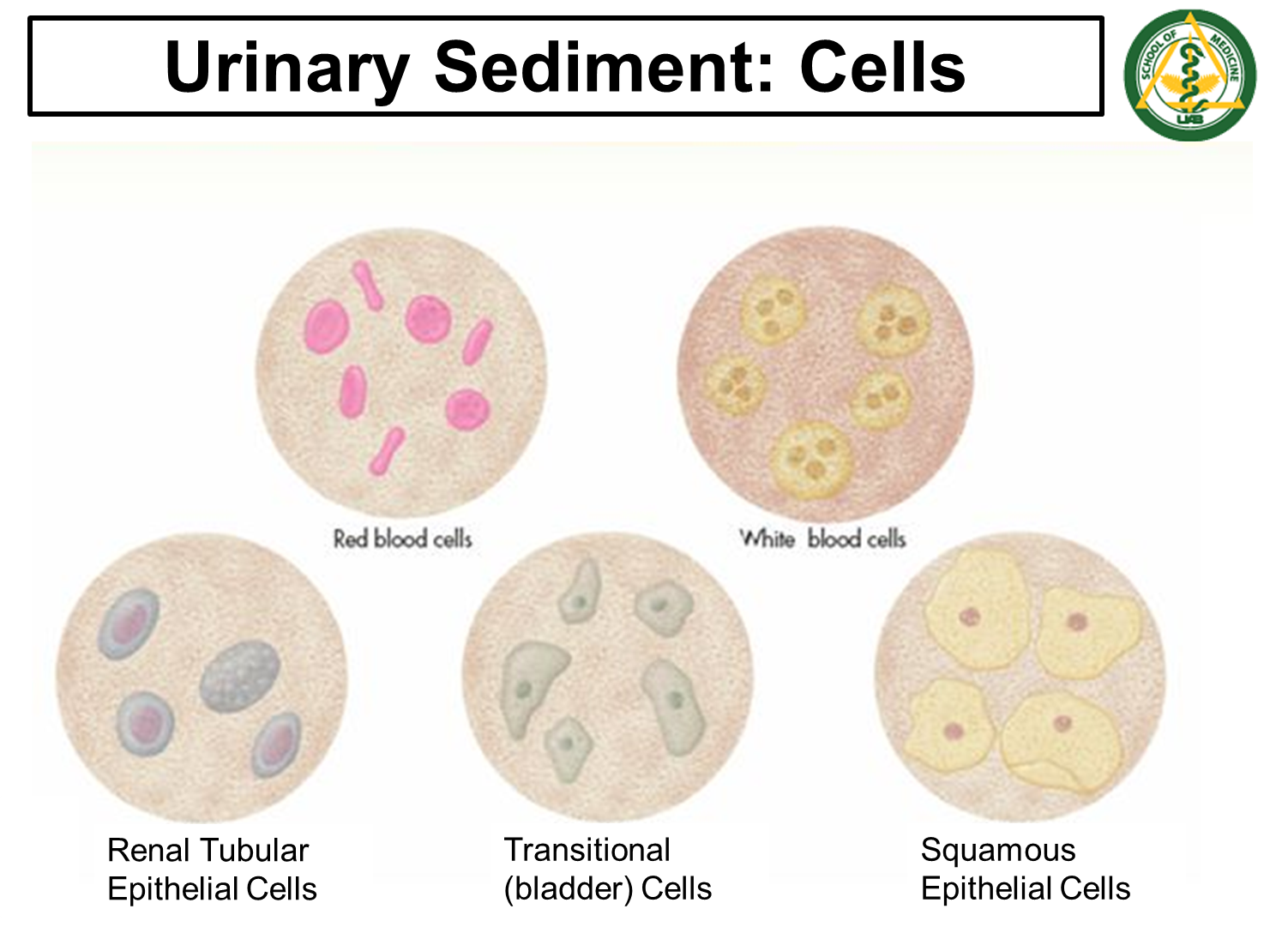
There are five urine cells that can be identifiable in the urine:
1) Red Blood Cells
2) White Blood Cells
3) Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells
4) Transitional Bladder Cells
5) Squamous Epithelial Cells
Important to know that squamous > transitional > renal in terms of size
What are Dysmorphic Red Blood Cells?
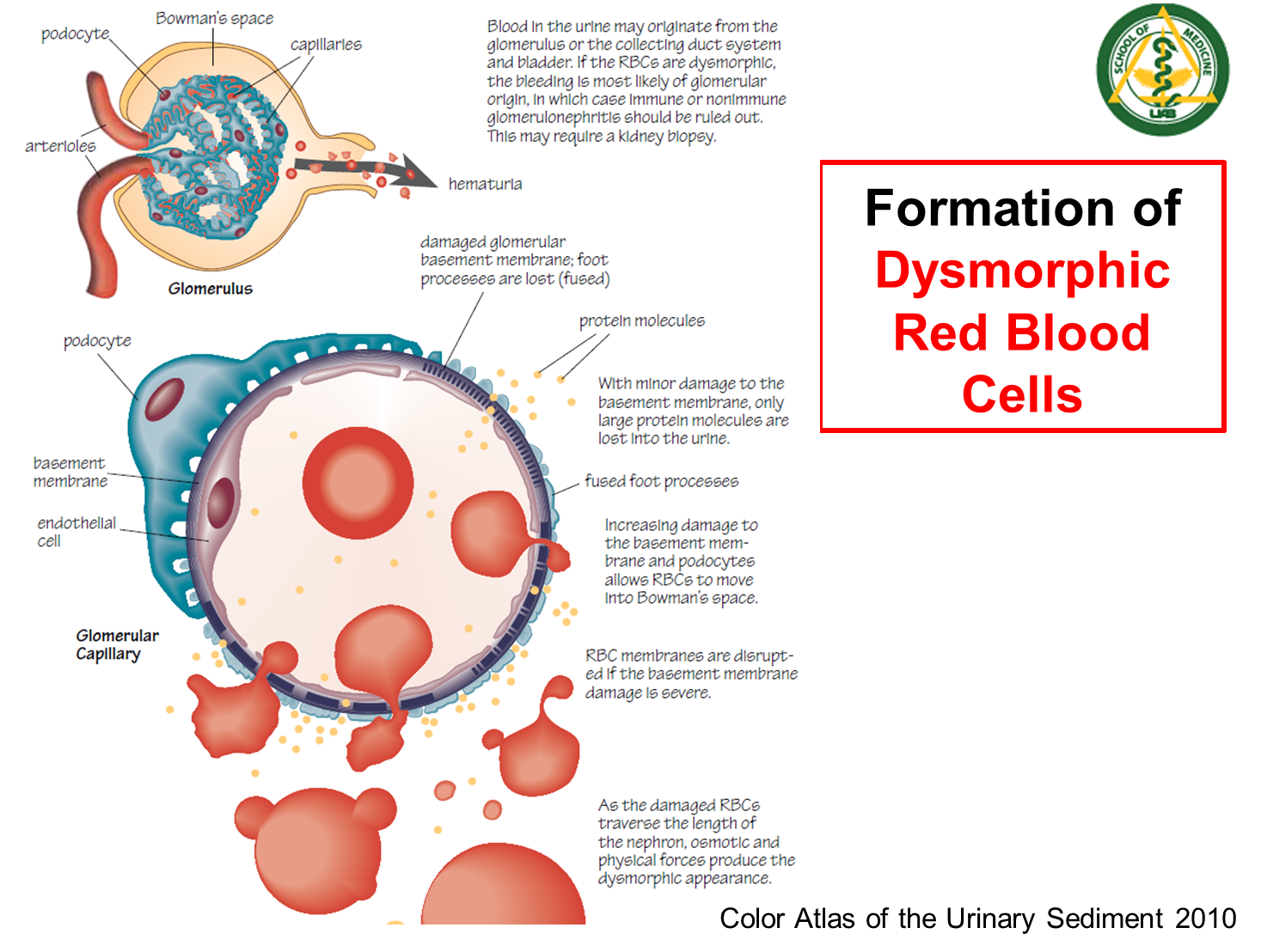
Dysmorphic Red Blood Cells are RBCs that have squeezed through the glomerular filtration barrier
→ as the red blood cell squeezes through the filtration barrier, they become oddly shaped “mickey mouse” or blebbed shaped
What are Casts?
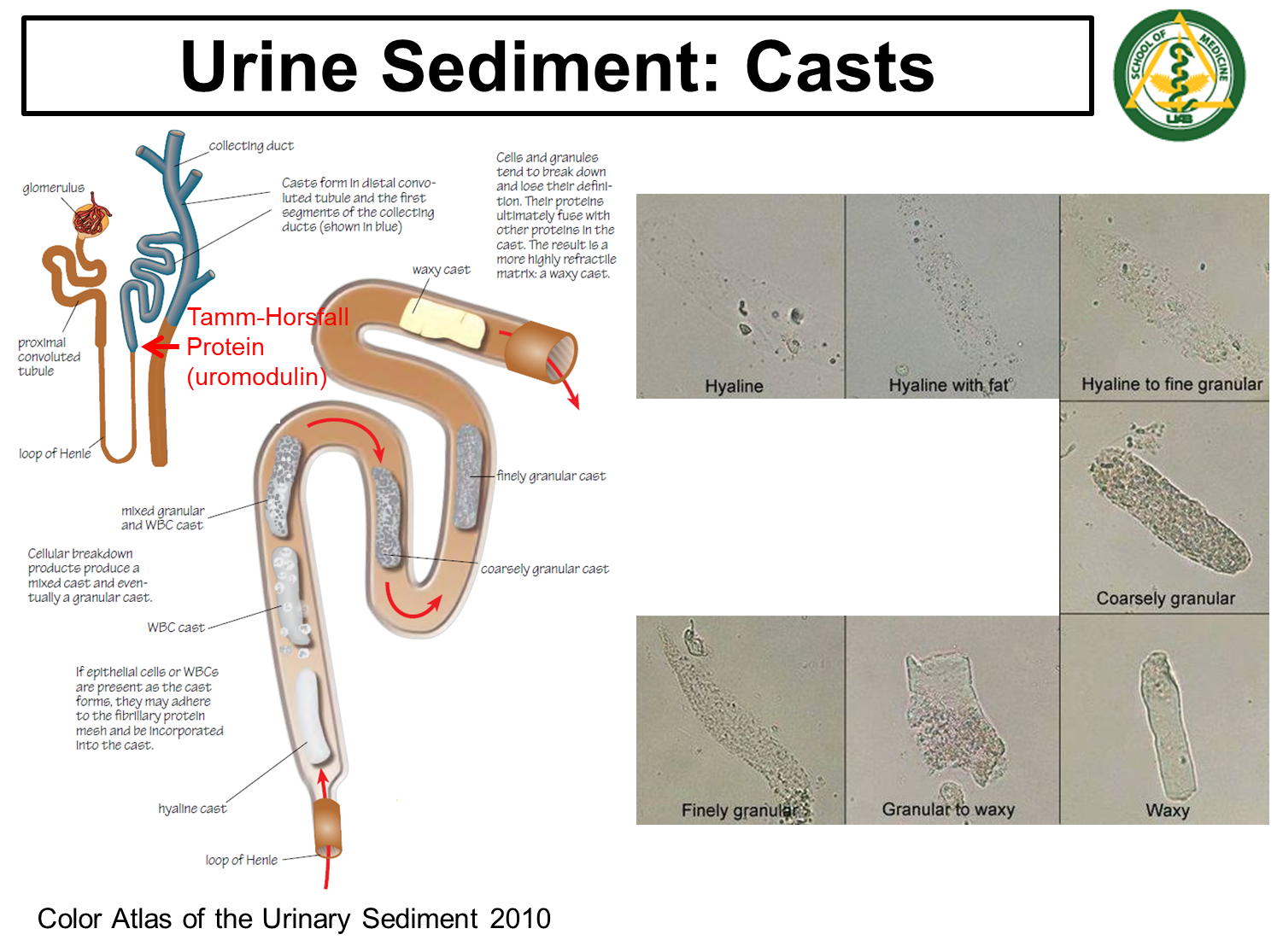
Casts are cylindrical structures formed at the distal convoluted tubule and collecting ducts
→ these structures are composed of Tamm-Horsfall protein which are secreted from the ascending limb and will adhere to different items located within the distal tubules
→ these casts help us to know that the items in the urine originate from the kidney and not from the bladder or the urinary tract
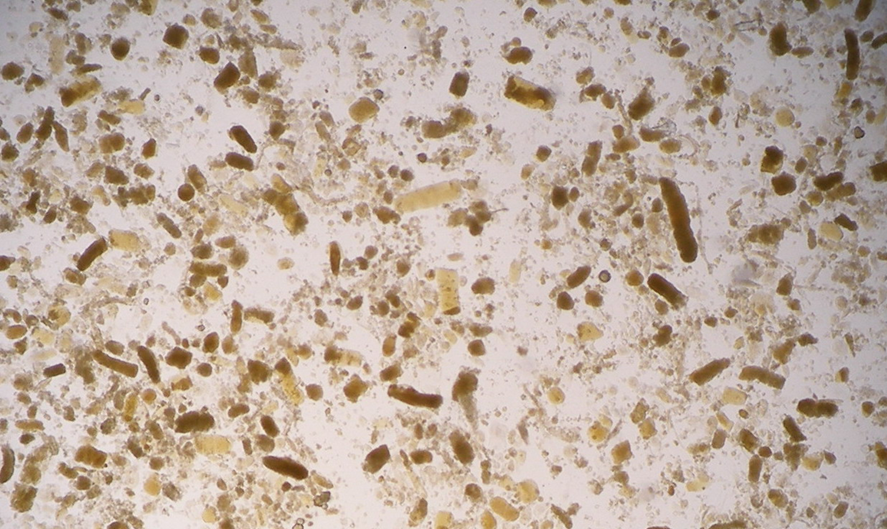
What Cast is identifiable on this image?
Muddy-Brown Granular Casts
→ formed from acute tubular necrosis to the proximal tubules
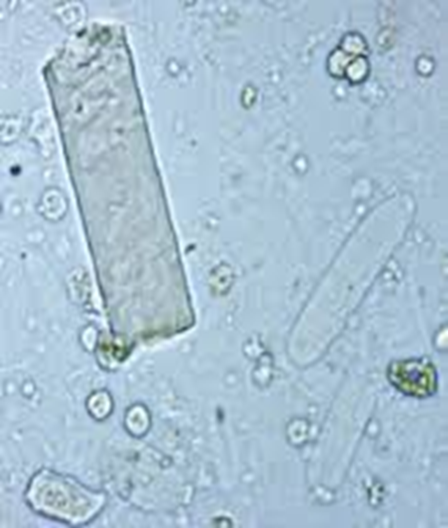

What Cast is identifiable on this image?
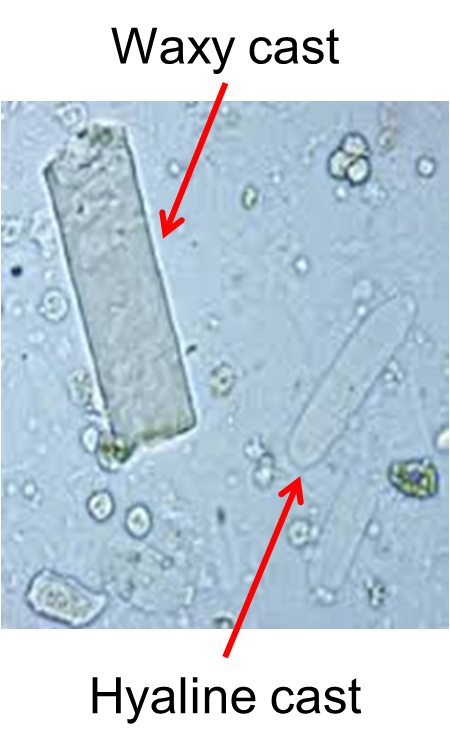
Waxy Cast
→ formed from the degeneration of granular casts, containing Tamm-Horsfall protein that has undergone prolonged stasis
→ always abnormal and is indicative of chronic kidney disease and advanced renal failure
Hyaline Cast
→ comprised of mostly Tamm-Horsfall protein and is colorless and transparent
→ normal or may be caused by low blood flow to the kidney or dehydration
What are the Cellular Casts?
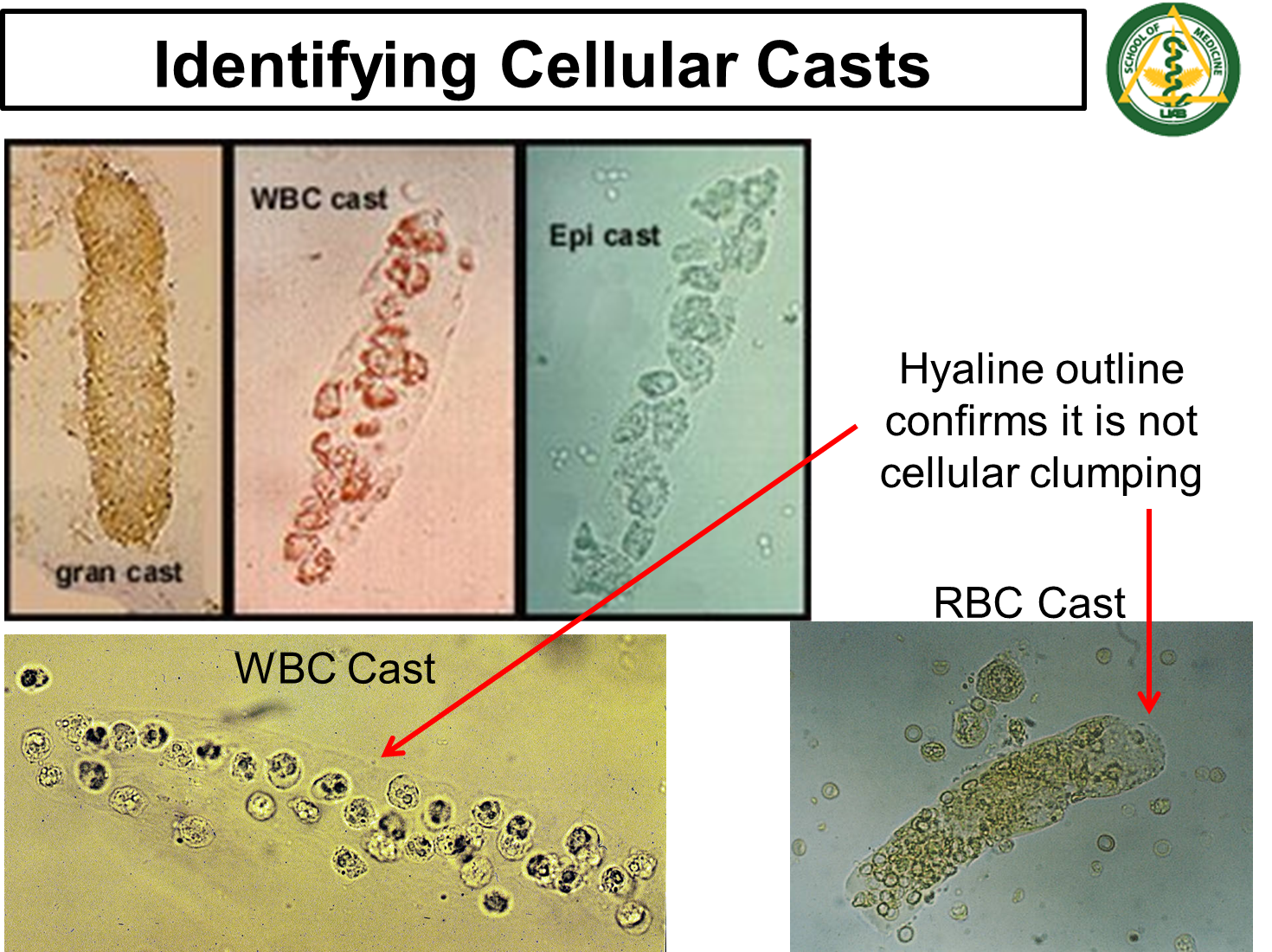
Cellular Casts are casts that are formed from the Tamm Horsfall protein (uromodulin) creating a hyaline outline which traps cells
→ can be indicative of certain pathologies depending what kind of cells are found inside the cast
What are the five pathologies associated with specific casts?

1) Pre-Renal
→ states of dehydration or low blood flow to the kidney can result in increased numbers of hyaline casts
Acute Tubular Necrosis
→ muddy-brown granular casts
→ renal tubular epithelial cell casts
Acute Interstitial Nephritis
→ white blood cells casts
Glomerulonephritis
→ Nephritic - red blood cell casts
→ Nephrotic - fatty casts
Chronic Kidney Disease
→ Waxy Casts
What Six Crystals are identifiable in urine?
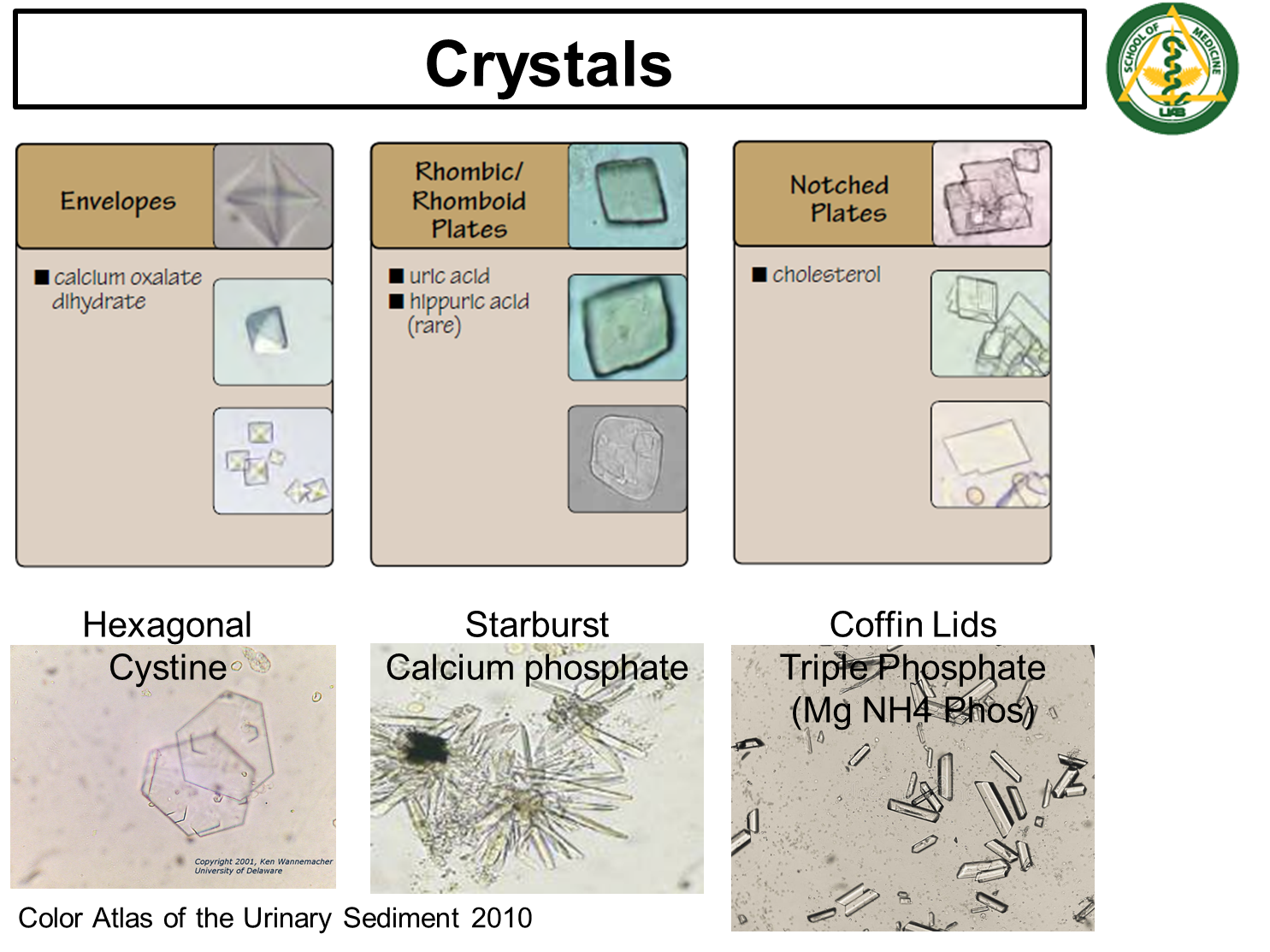
Crystals are formed from minerals in the urine
1) Envelope Shaped
→ Calcium Oxalate Dihydrate
2) Rhomboid Shaped
→ Uric or Hippuric Acid
3) Notched Plates
→ Cholesterol
4) Hexagonal
→ Cystine
5) Starburst
→ Calcium Phosphate
6) Coffin Lid Crystals
→ Triple Phosphate (Magnesium, Ammonium, and Phosphorus) - associated with urinary tract infections