Hip + Pelvis Projections
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Merrill's Atlas - CH 8
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
For an AP Pelvis projection, what should the ASIS - to - table distance be?
equal on both sides
For an AP Pelvis projection, how much should both feet be rotated?
15 - 20 degrees
For an AP Pelvis projection, in which direction are the feet rotated?
medially
Where should the top of the IR be for an AP Pelvis projection?
1 to 1.5 in (2.5 to 3.8 cm) above the iliac crests
What is the collimation for an AP Pelvis projection?
14 × 17 in (35 × 43 cm)
What distance should the ilia and greater trochanters be for an AP Pelvis projection?
equidistant at the sides of the image
What is the AP Oblique projection for femoral necks also called?
Cleaves Method
For a bilateral AP Oblique projection of the femoral necks, where should the IR be centered?
1 in (2.5 cm) above pubic symphysis
How could the feet be positioned for a bilateral AP Oblique projection of the femoral necks?
soles of the feet are touching one another
For a unilateral AP Oblique projection of the femoral necks, where should the IR be centered?
ASIS
How could the foot on the affected side be positioned for a unilateral AP Oblique projection of the femoral necks?
foot could be moved up to the opposite knee as much as possible
How much should the thigh(s) be abducted for an AP Oblique projection of the femoral necks?
45 degrees
What can happen if the thigh is abducted too much for an AP Oblique projection of the femoral necks?
superimposition of femoral neck w/ greater trochanter
How should the femoral necks be positioned, relative to the IR, in an AP projection of the hip?
parallel to IR
What is the collimation for an AP projection of the hip?
10 × 12 in (24 × 30 cm)
What is a Lateral projection of a hip also called?
Lauenstein + Hickey Method
How much should the thigh on a Lateral projection of a hip be flexed?
to almost a right angle at the hip
Where is the CR directed for a Lateral projection of the hip?
midpoint between ASIS and pubic symphysis
What is the Axiolateral projection of the hip also called?
Danelius - Miller Method
How should the thigh be oriented in an Axiolateral projection of the hip when the knee and hip are flexed?
almost vertical
How much should the affected limb be rotated for an Axiolateral projection of the hip?
15 to 20 degrees medially
Where should the IR be placed for an Axiolateral projection of the hip?
along the curvature of the hip, touching the body right above the iliac crest
What should the lower border of the IR be parallel to in an Axiolateral projection of the hip?
femoral neck
What is the AP Oblique projection of the acetabulum also called?
Judet Method
What anatomy is displayed for an AP Internal Oblique projection of the acetabulum?
acetabulum posterior rim + iliopubic column (IPIP)
What anatomy is displayed for an AP External Oblique projection of the acetabulum?
acetabulum anterior rim + ilioischial column (EAIS)
What side touches the bed for an AP Internal Oblique projection of the acetabulum?
unaffected side
What side touches the bed for an AP Internal Oblique projection of the acetabulum?
affected side
Where is the CR directed for an AP Internal Oblique projection of the acetabulum?
2 in (5 cm) below ASIS
Where is the CR directed for an AP External Oblique projection of the acetabulum?
pubic symphysis
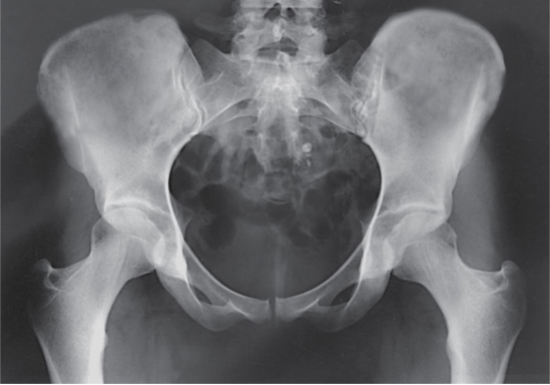
What is the projection and anatomy shown in this image?
AP Pelvis
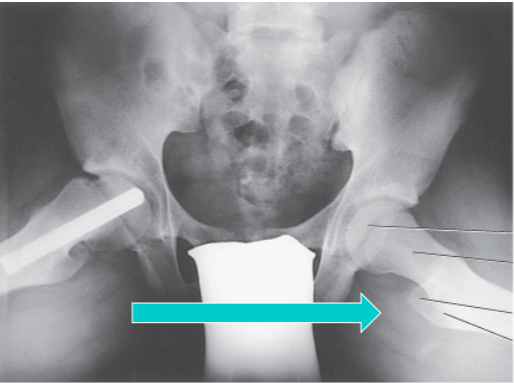
What is the projection and anatomy shown in this image?
AP Oblique Femoral Necks
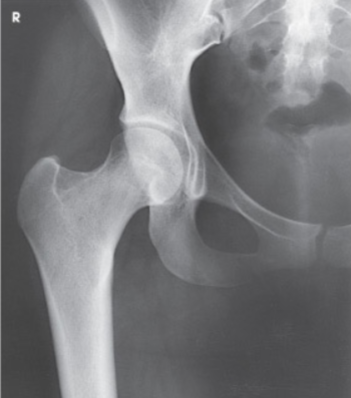
What is the projection and anatomy shown in this image?
AP Hip
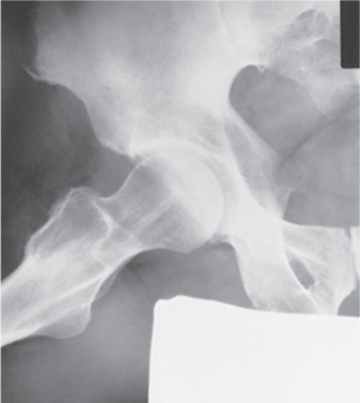
What is the projection and anatomy shown in this image?
Lateral Hip
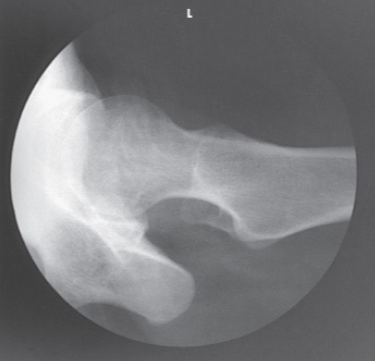
What is the projection and anatomy shown in this image?
Axiolateral Hip
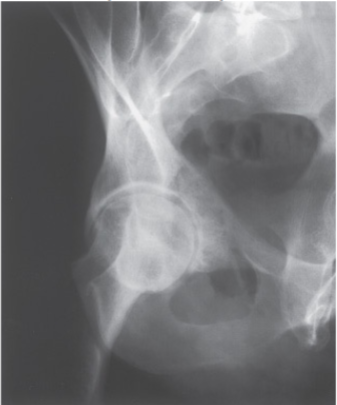
What is the projection and anatomy shown in this image?
AP Internal Oblique Acetabulum
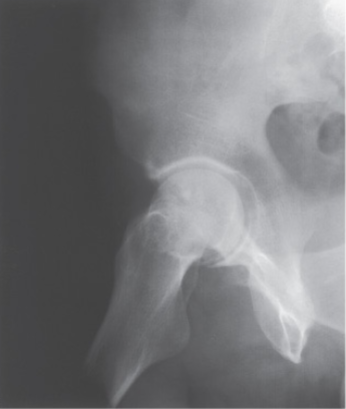
What is the projection and anatomy shown in this image?
AP External Oblique Acetabulum