A&P - Test 3 Review
1/448
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
449 Terms
Which muscles are called muscle cells? Which are elongated
Skeletal and smooth muscle cells (not cardiac) are elongated and are called muscle fibers
What is the longest types of muscle cells?
skeletal
is skeletal muscle voluntary?
Yes - only subject to conscious control
Which type of muscle is striated and voluntary?
Skeletal
Which type of muscle is striated and involuntary?
Cardiac
Which type of muscle is visceral, nonstriated, and involuntary?
smooth
Movement, maintain posturem stabilize joints, and heat generation are all functions of what?
Muscle
Skeletal muscle cells are also referred to as?
a) Striations
b) Sarcolemmas
c) Muscle fibers
d) Involuntary muscle cells
c) Muscle fibers
Which of the following is NOT a normal function of muscle tissue?
maintaining posture
generating heat
secreting hormones
stabilizing joints
producing movement
secreting hormones
Which of the following are correctly paired?
skeletal muscle; voluntary control
cardiac muscle; voluntary control
cardiac muscle; nonstriated
smooth muscle; striated
skeletal muscle; voluntary control
The ability of muscle to shorten forcibly when adequately stimulated is known as ________, and sets muscle apart from other tissue types.
excitability
elasticity
contractility
extensibility
contractility
_________ The ability to receive and respond to stimuli (shared by neurons as well).
Excitability
______ The ability to recoil to resting length after stretching.
Elasticity
________ The ability to be stretched or extended.
Extensibility
Which of the following properties is most directly associated with changes to a muscle cell's membrane potential (the voltage across the plasma membrane)?
contractility
extensibility
elasticity
excitability
excitability
________, also termed responsiveness, is the ability of a cell to receive and respond to a stimulus by changing its membrane potential. For example, a neurotransmitter released by a nerve cell may cause the depolarization of the muscle cell's sarcolemma
Excitability
Which connective tissue surrounds the whole muscle?
1) Epimysium
2) Endomysium
3) Perimysium
1) Epimysium
the _______ is the outermost muscle sheath, which encloses the entire muscle
Epimysium
Which of the following is NOT found within a skeletal muscle?
a) Blood vessels
b) Connective tissue proper
c) nervous tissue
d) Osseous tissue
Osseous tissue
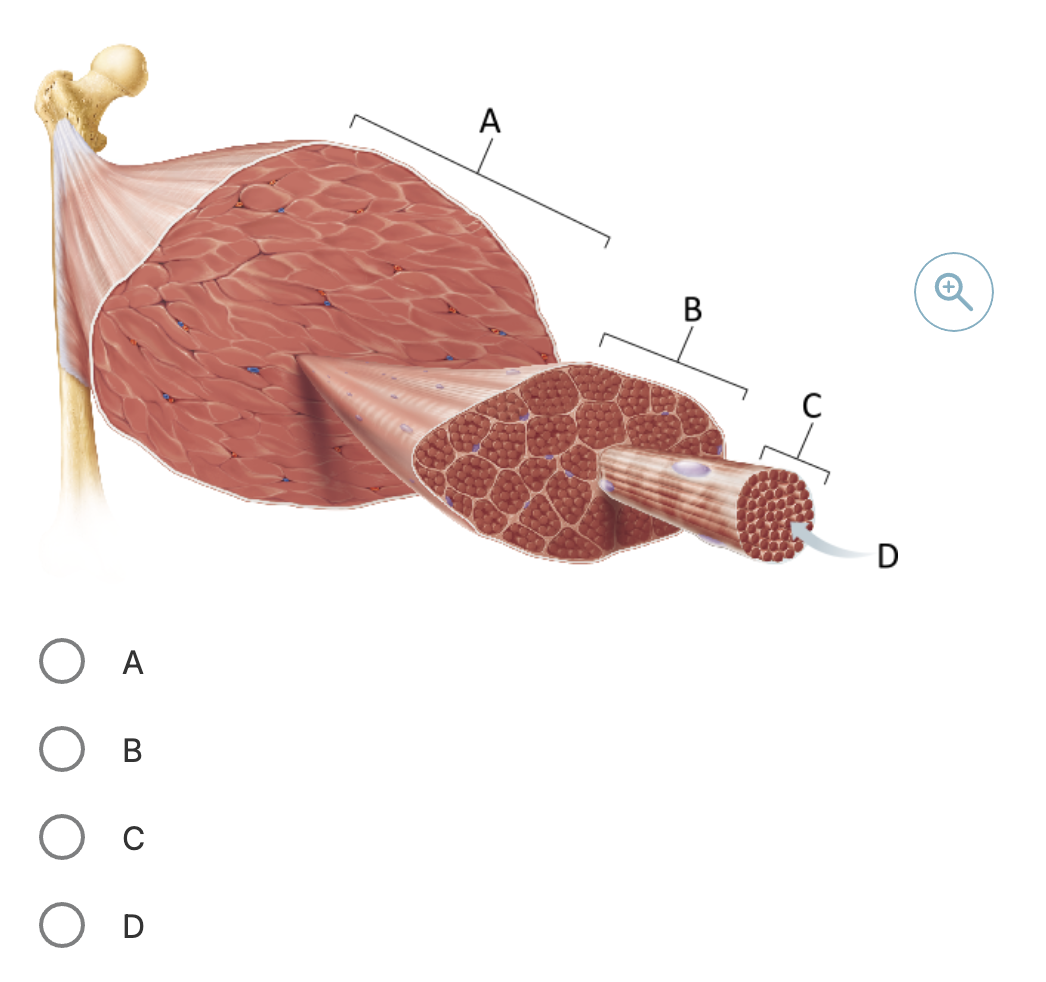
Which structure in the figure corresponds to a single skeletal muscle cell?
C
a skeletal muscle cell is commonly termed a ?
muscle fiber
Which of the following corresponds to a single fascicle?
B
A _______ is an organized group of muscle fibers (cells).
fascicle
Which term best identifies a skeletal muscle cell?
muscle fiber
myofibril
sarcomere
muscle fascicle
muscle fiber
_____ muscle cells fuse during development to form the mature, multinucleated muscle fibers.
Skeletal
Which of the following surrounds an individual muscle cell?
fascicle
perimysium
endomysium
epimysium
endomysium
Which of the following is the smallest structual unit?
a) Myofilament
b) Fascicle
c) Myofibril
d) Muscle fiber
e) Sarcomere
a) Myofilament
Which one of the following structures is incorrectly paired?
a) Sarcoplasmic reticulum - membranous organelle that stores and releases calcium ions
b) Sarcomere - bordered at the end of by a Z disc
c) T-tubule - extension of the sarcolemma
d) A band - composed mostly of protein actin
d) A band - composed mostly of protein actin
Which of the following does NOT change length during shortening results from muscle contraction?
a) The H zone
b) The distance between Z discs
c) Thin myofilaments
d) The I band
c) Thin myofilaments
Which muscle cell structure stores calcium ions that are used to trigger the contraction?
the sarcoplasmic reticulum
the myofibril
the sarcolemma
glycosome
the sarcoplasmic reticulum
The ____________ is an intracellular organelle that stores and releases calcium ions into the sarcoplasm (cytoplasm of a muscle cell).
sarcoplasmic reticulum
___________: Contains the contractile proteins (actin and myosin), but does not store calcium.
Myofibril
___________: The plasma membrane of a muscle cell — it conducts action potentials but doesn't store calcium.
Sarcolemma
_______: Organelles that store glycogen, not calcium.
Glycosome
The contractile, or functional, unit of a muscle fiber is __________.
troponin
the myofilament
the elastic filament
the sarcomere
the sarcomere
The sarcomere is the contractile unit of a muscle fiber and the _____ functional unit of muscle.
smallest
A sarcomere is the region of a myofibril between two successive ?
Z discs
The _____ primarily consists of thin and thick myofilaments.
sarcomere
The sliding filament model of contraction states that __________.
during contraction, the thin myofilaments slide past the thick myofilaments so that the actin and myosin myofilaments no longer overlap
during contraction, the thin myofilaments slide past T tubules so that the Z discs are overlapping
during contraction, the thin myofilaments slide past the thick myofilaments so that calcium ions can be released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum
during contraction, the thin myofilaments slide past the thick myofilaments so that the actin and myosin myofilaments overlap to a greater degree
during contraction, the thin myofilaments slide past the thick myofilaments so that the actin and myosin myofilaments overlap to a greater degree
In a relaxed muscle fiber, the thick and thin myofilaments overlap only at the ends of the?
A band.
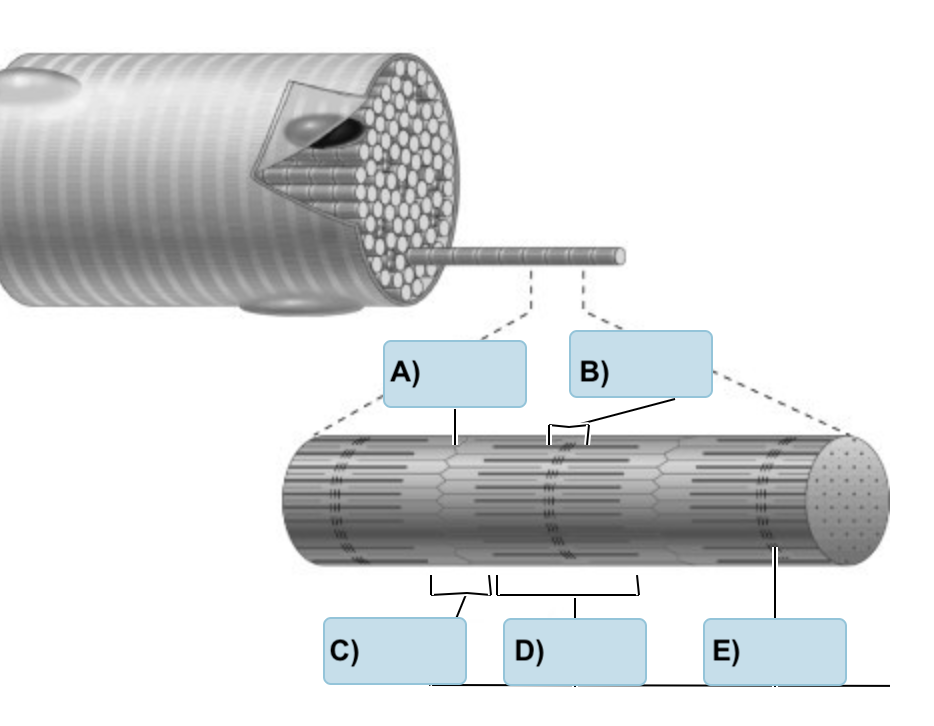
Label the following
(Z Disc, M Line, A Band, H Zone, I Band
A) Z disc
B) H zone
C) I Band
D) A BAnd
E) M Line
What is the role of tropomyosin in skeletal muscles?
Tropomyosin serves as a contraction inhibitor by blocking the myosin binding sites on the actin molecules.
Tropomyosin is the receptor for the motor neuron neurotransmitter.
Tropomyosin is the chemical that activates the myosin heads.
Tropomyosin serves as a contraction inhibitor by blocking the actin binding sites on the myosin molecules.
Tropomyosin serves as a contraction inhibitor by blocking the myosin binding sites on the actin molecules.
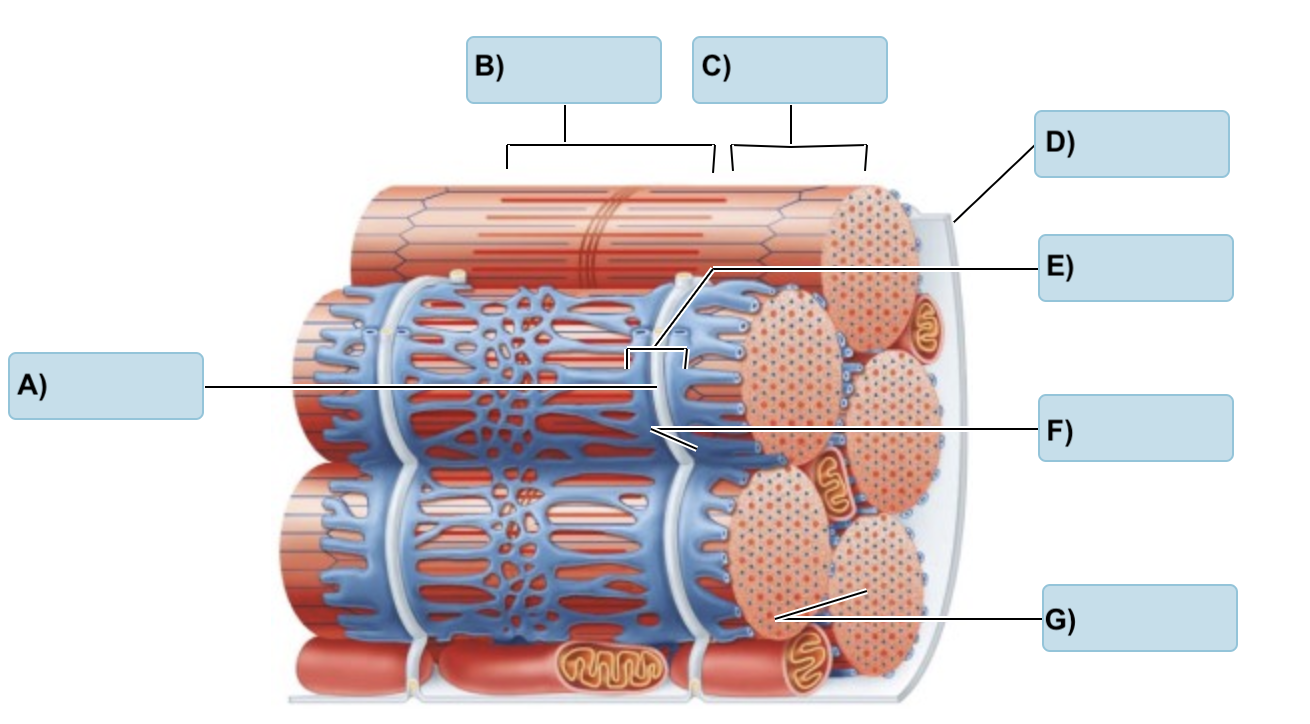
Label the following:
(T Tubule, Myofibrils, I Band, Triad, Sarcolemma, A band, terminal cisterns)
A) T tubule
B) A Band
C) I Band
D) Sarcolemma
E) Triad
F) Terminal cisterns
G) Myofibrils
Voltage gated Na+ and K+ channels are associated directly with which of the following events during stimulation of a muscle fiber?
a) Release of ACh into the synaptic cleft
b) Propagating the AP along the sarcolemma
c) End plate potential at the junctional folds
d) Release of Ca2+ from the SR
b) Propagating the AP along the sarcolemma
Which of the following occurs last among the events that trigger cross bridge formation?
a) Arrival of an AP at the axon terminal of a motor neuron
b) binding of ACh to receptors
c) Depolarization of the sarcolemma
d) Binding of Ca2+ to troponin
d) Binding of Ca2+ to troponin

place in the correct order of occurrence from left to right the events that occur at the neuromuscular junction after the action potential reaches the axon terminal

Which of the following is/are mechanism(s) to end neural transmission at the neuromuscular junction?
ACh is taken up by the axon terminal via endocytosis.
ACh is broken down into acetic acid and choline by the enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE).
ACh diffuses away from the synaptic cleft.
ACh binds to ACh receptors.
ACh is broken down into acetic acid and choline by the enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE).
ACh diffuses away from the synaptic cleft.
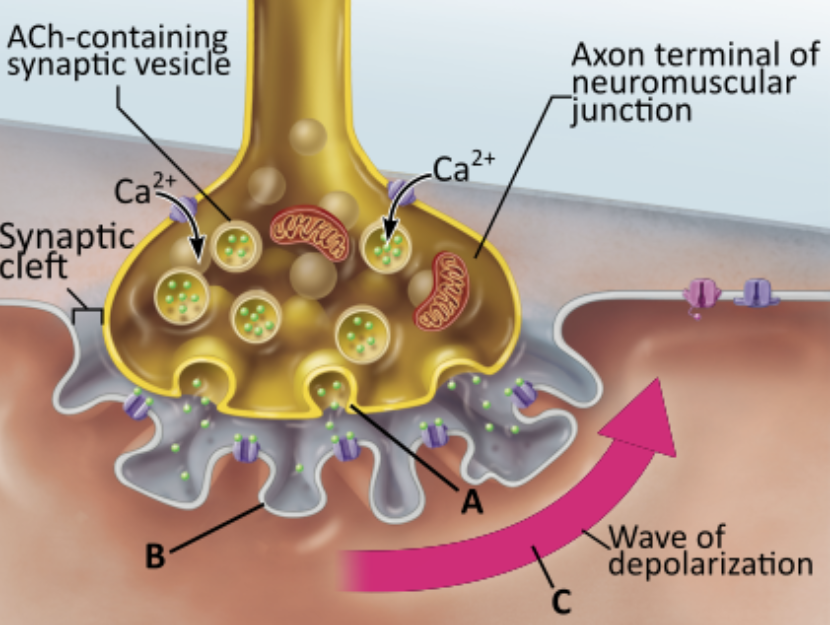
What event directly triggers the release of neurotransmitter shown in A?
diffusion of Ca2+ into the axon terminal
diffusion of Na+ out of the axon terminal
diffusion of K+ into the axon terminal
diffusion of Na+ into the axon terminal
diffusion of Ca2+ into the axon terminal
A nerve impulse arrives at the axon terminal triggering the opening of Ca2+ channels, which allows for the diffusion of Ca2+ into the terminal. This in turn leads directly to the release of neurotransmitters by _______.
exocytosis
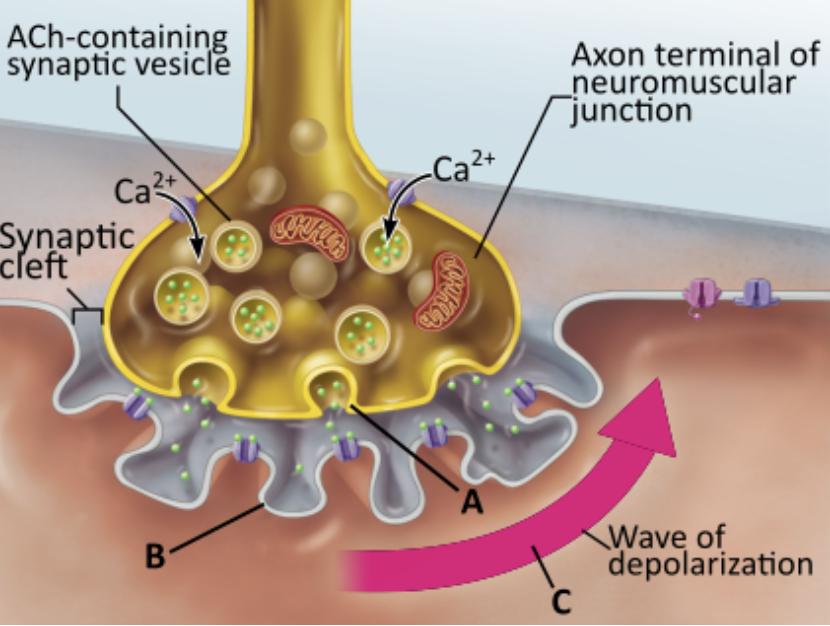
Which statement accurately describes the event indicated by B?
Diffusion of acetylcholine into the muscle fiber triggers the opening of an ion channel.
Binding of acetylcholine to a receptor triggers the opening of an ion channel.
The binding of acetylcholine directly causes the formation of a wave of depolarization.
Diffusion of Ca2+ into the muscle fiber triggers the diffusion of acetylcholine out of the muscle fiber.
Binding of acetylcholine to a receptor triggers the opening of an ion channel.
Binding of acetylcholine to its receptor opens chemically (ligand) gated ion channels that allow Na+ and K+ to diffuse across the ?
sarcolemma
Which step precedes all of the other listed steps?
The sarcoplasmic reticulum is activated.
Na+ rushes into the cell.
An action potential starts on the sarcolemma.
ACh is released by the motor neuron.
ACh is released by the motor neuron.
The first step toward generating a skeletal muscle contraction is nervous stimulation of the muscle fiber in order to ?
generate an action potential.
The site of muscle stimulation, where the nerve ending communicates with the muscle fiber, is called the ?
neuromuscular junction.

Place the events that occur during excitation-contraction coupling in the correct order from left to right.

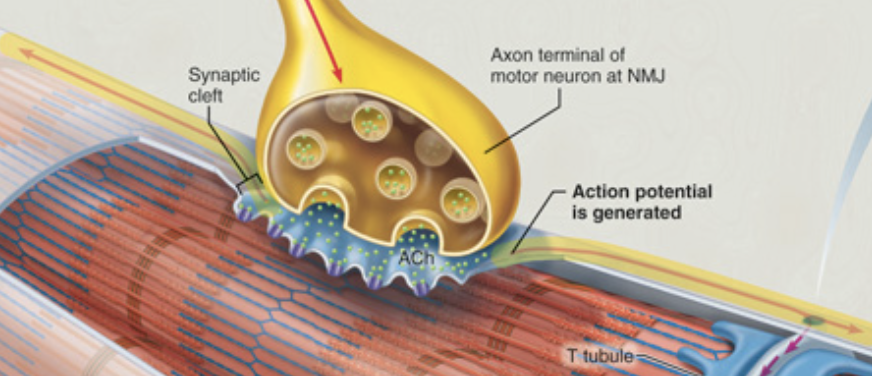
Consider how the action potential that initiates contraction is delivered to the muscle cell.
Which of the choices below correctly describes how an action potential generated at the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) is converted to excitation in the muscle fiber?
An action potential in the motor neuron directly triggers an action potential at the sarcolemma.
An action potential in the motor neuron causes ACh to be released into the synaptic cleft. Binding of ACh to sarcolemma receptors initiates graded potentials.
ACh binds at a receptor in the motor neuron, which initiates graded potentials.
An action potential in the motor neuron causes ACh to be released into the synaptic cleft. Binding of ACh at the membrane receptor initiates a direct action potential.
An action potential in the motor neuron causes ACh to be released into the synaptic cleft. Binding of ACh to sarcolemma receptors initiates graded potentials.
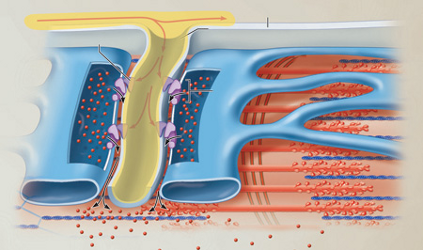
The action potential propagates along the sarcolemma. As the action potential spreads down the T tubules of the triads, voltage-sensitive tubule proteins change shape.
How does the shape change of these proteins lead to contraction?
It allows calcium to exit the cytoplasm and enter the cisterns.
It facilitates ACh's binding to the sarcolemma.
It permits calcium to exit the cistern and enter the T tubule.
It allows calcium to exit the sarcoplasmic reticulum and enter the cytosol
It allows calcium to exit the sarcoplasmic reticulum and enter the cytosol.
As the action potential propagates, it changes the shape of _______ proteins.
These proteins are linked to calcium channels in the terminal cisterns of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. When these proteins' calcium channels open, a massive amount of _____ flows into the cytosol.
T tubule
calcium
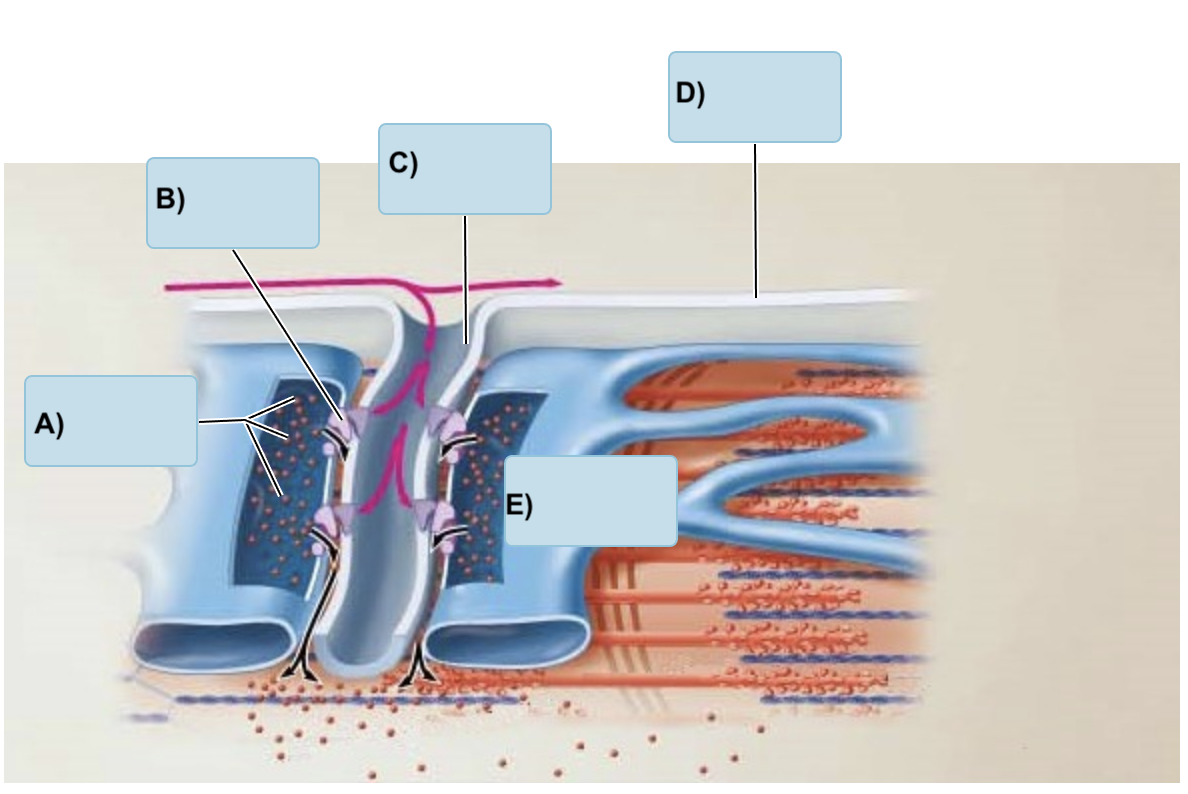
Match the following of the muscle cell
(Sarcolemma, T-tubule, terminal cistern, Ca ions, Voltage sensitive tubule protein)
A) Ca ions
B) Voltage-sensitive tube protein
C) T tubule
D) Sarcolemma
E) Terminal cistern
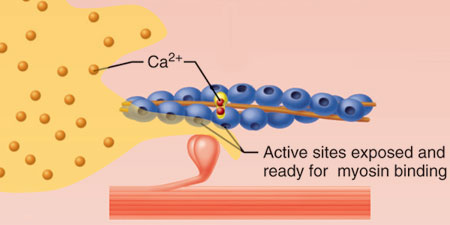
Which selection correctly describes the role of calcium in coupling?
Calcium binds to troponin, which moves tropomyosin and exposes the myosin-binding sites on actin.
Calcium binds to actin, which triggers it to bind to myosin.
Calcium binds to actin, which triggers troponin to fall off and expose myosin-binding sites.
Calcium binds to tropomyosin, which moves tropomyosin and exposes the myosin-binding sites on actin.
Calcium binds to troponin, which moves tropomyosin and exposes the myosin-binding sites on actin.
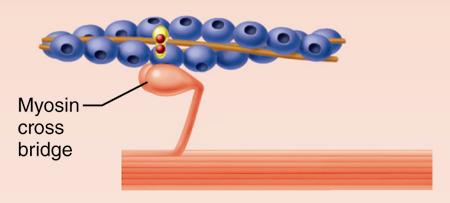
Which selection best describes the initial event in contraction?
Calcium binds actin to myosin to begin the cross bridge cycle.
Tropomyosin binds to myosin heads and actin bridges with tropomyosin.
Myosin heads bind to the newly exposed myosin-binding sites on actin to form cross bridges.
The myofilaments slide closer together.
Myosin heads bind to the newly exposed myosin-binding sites on actin to form cross bridges.
Match the following
1) Cistern
2) Voltage-sensitive tubule protein
3) Myosin
4) T Tubule
5) Troponin

Put the following in order of the correct occurrence of the excitation-contraction coupling
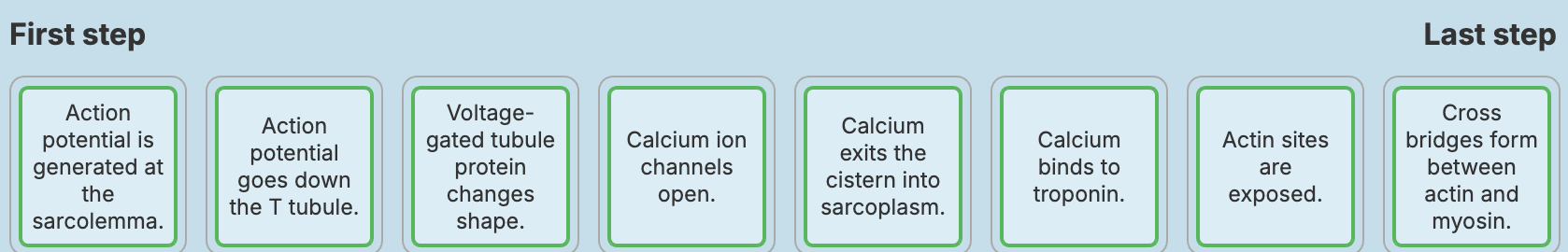
Coupling begins with an action potential after the arrival of ACh and graded potentials, and it ends before ?
cross bridge cycling.
Which of the following choices best summarizes excitation-contraction coupling?
A series of events in which an action potential triggers the release of chemical messengers
A series of events in which an electrical stimulus is conveyed to a muscle fiber to enact contraction
A series of events in which actin binds myosin to enact contraction
A series of events in which calcium gradients are used to convey a signal to the muscle fiber to enact contraction
A series of events in which an electrical stimulus is conveyed to a muscle fiber to enact contraction
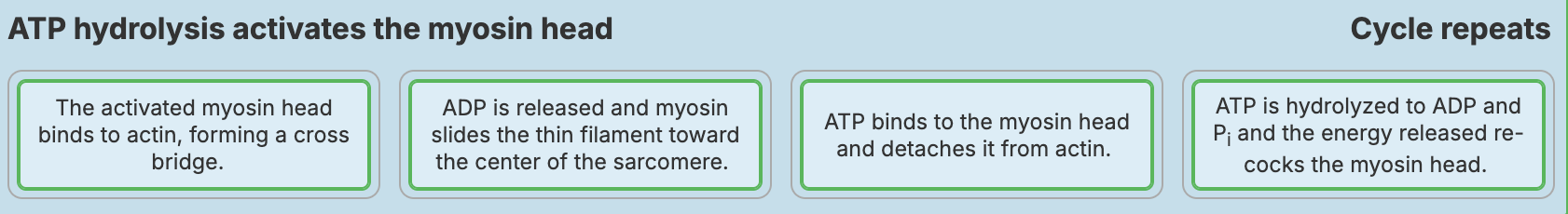
The cross bridge cycle starts when _________.
acetylcholine diffuses away from the synaptic cleft
Ca2+ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum binds to tropomyosin
Ca2+ is actively transported into the sarcoplasmic reticulum
Ca2+ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum binds to troponin
ATP binds to troponin and is hydrolyzed to ADP and Pi

Place the steps that occur during a single cross bridge cycle in the correct order from left to right.
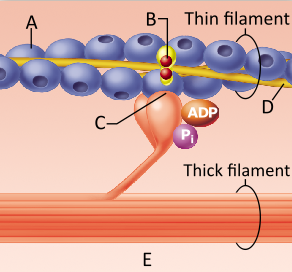
Which protein is indicated by the letter A?
troponin
actin
myosin
keratin
actin
_____ is the chief component of the thin myofilaments. It is made of a set of globular proteins attached in a chain.
Actin
Which of the following occurs during the relation phase of a muscle twitch?
a) Release of ACh into the synaptic cleft
b) Binding of Ca2+ to thin filaments
c) active transport of Ca2+ into the SR
d) Depolarization of T tubules
Actin
Increased contractile force due to recruitment results from?
a) Stimulation of muscle by increasing numbers of activated somatic motor neurons
b) Increasing frequency of muscle fiber stimulation by somatic motor neurons
c) Electrical signals traveling from one muscle fiber to adjacent fibers
d) increasing the amplitude of action potentials arriving at the neuromuscular junction along somatic motor neurons
a) Stimulation of muscle by increasing numbers of activated somatic motor neurons
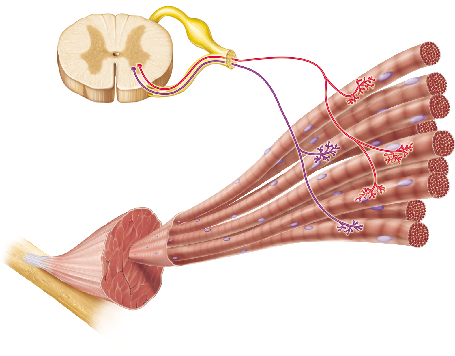
Each neuron shown in this figure innervates a group of muscle fibers. What is the term for a group of muscle fibers and the single neuron that innervates them?
neuromuscular junction
sarcomere
motor unit
fascicle
motor unit
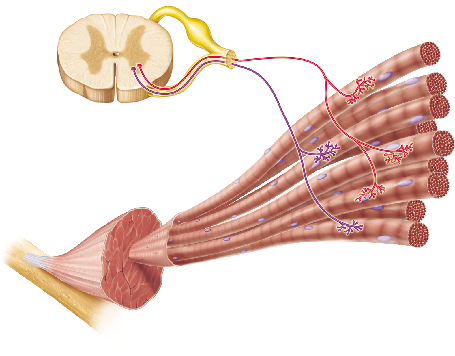
If both of the neurons in the figure were activated, more muscle fibers would contract than if either neuron alone were active. This mechanism for control of the force of muscle contraction is known as __________.
wave summation
recruitment
tetanus
excitation-contraction coupling
recruitment
Recruitment refers to the increased force generated by the activation of increasing numbers of _____ units.
motor
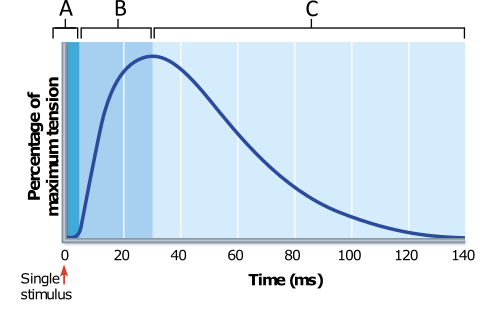
In which phase in the figure would the net movement of
Ca2+ INTO the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) be greatest?
C
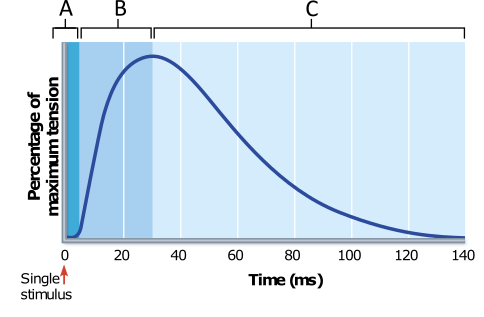
What result would be expected if an additional stimulus, equal in intensity to the first, were to be applied to the muscle at the 60 millisecond (ms) time point?
The muscle would quickly return to the fully relaxed state of minimum tension.
The muscle would increase in tension to a level greater than that measured at the beginning of phase C.
Tension would increase to the same maximum force measured at the beginning of phase C.
The tension exerted by the muscle would continue to decrease, but at a significantly slower rate than observed without the second stimulus.
The muscle would increase in tension to a level greater than that measured at the beginning of phase C.
A muscle that is lengthening while it produces tension is performing a(n) __________ contraction.
concentric
eccentric
isometric
maximal
eccentric
We use _______ contractions to lower objects (such as lowering a book from the shelf or lowering the barbell during a bench press).
eccentric
Muscle tone is ________.
the ability of a muscle to efficiently cause skeletal movements
a state of sustained partial contraction
the condition of athletes after intensive training
the feeling of well-being following exercise
a state of sustained partial contraction
which of the following is expected to occur during the recovery period following exercise?
a) ATP is synthesized anaerobically
b) Pyruvate is converted to lactate
c) Oxygen levels in muscle tissue decrease
d) Glycogen is formed from glucose
d) Glycogen is formed from glucose
What ATP regeneration pathway is used first during skeletal muscle contraction?
aerobic respiration
anaerobic glycolysis
breakdown of stored glycogen
direct phosphorylation of ADP by creatine phosphate
direct phosphorylation of ADP by creatine phosphate
Which of the following statements is NOT true regarding ATP production in muscles during periods of prolonged energy use, such as exercise?
Prolonged activity requires the use of aerobic pathways for ATP regeneration.
As your blood sugar drops at any time during prolonged activity, glycogen stores in your muscles can be broken down to supply a glucose source.
In the absence of oxygen, creatine phosphate can drive aerobic respiration pathways for a few minutes.
In the absence of oxygen, anaerobic pathways provide minimal ATP regeneration for less than a minute.
In the absence of oxygen, creatine phosphate can drive aerobic respiration pathways for a few minutes.
During vigorous exercise, there may be insufficient oxygen available to completely break down pyruvic acid for energy. As a result, the pyruvic acid is converted to ________.
lactic acid
a strong base
stearic acid
hydrochloric acid
lactic acid
Which of the following explains the decreased contractile force generated by the stretched muscle?
a) The stretched muscle fibers are less sensitive to stimulation by ACh
b) Stretching of myofibrils within the muscle fibers decreases the overlap between thin and thick myofilaments
c) AP’s weaken as they travel increasing distances along stretched muscle fibers
d) Muscle fibers begin to separate from each other within the stretched muscle
b) Stretching of myofibrils within the muscle fibers decreases the overlap between thin and thick myofilaments
which of the following is NOT a characteristic of fast glycolytic fibers?
a) White appearance
b) Relatively large fiber diameter
c) Depend on blood-delivered nutrients
d) Powerful contraction but quick fatigue
c) Depend on blood-delivered nutrients
Which of the following factors influence the velocity and duration of muscle contraction?
length of muscle fibers activated
muscle fiber size
frequency of stimulation
load placed on the muscle
load placed on the muscle
Speed (velocity) of shortening is a function of load and muscle-fiber type. Contraction is fastest when the load on the muscle is zero; a ______ load results in a slower contraction and a shorter duration of contraction.
greater
Which muscle fiber type is best suited for endurance activities, such as long-distance jogging?
fast oxidative fibers
slow oxidative fibers
slow glycolytic fibers
fast glycolytic fibers
slow oxidative fibers
____ _______ fibers are best suited for endurance activities because they produce ATP aerobically and are fatigue-resistant.
Slow oxidative
The force of a muscle contraction is NOT affected by __________.
the number of muscle fibers stimulated
the frequency of the stimulation
the amount of ATP stored in the muscle cells
the size of the muscle fibers stimulated
the degree of muscle stretch
the amount of ATP stored in the muscle cells
The longer a muscle is when it starts contracting, the more tension it can generate in the contraction.
True
False
False
In a bedridden patient recovering from a badly fractured femur, disuse atrophy in the thigh muscles is caused by _________.
decreased ability of muscle cells to produce ATP, resulting in decreased ability of the muscles to contract
decreased ability to synthesize acetylcholine in the neurons that innervate the thigh muscles
decreased synthesis of muscle proteins and/or increased breakdown of muscle proteins
none of the above
decreased synthesis of muscle proteins and/or increased breakdown of muscle proteins
Muscle tissue grows and heals in response to stress. Without the stress of exercise and normal daily activities, muscle tissue _______?
degenerates
Which of the following statements accurately describes a similarity between smooth and skeletal muscles?
a) Initiation of contraction in both smooth and skeletal muscle contraction depends on invalid expression binding to troponin
b) Both smooth muscle and skeletal muscle are striated
c) Both smooth muscle and skeletal muscle are arranged in longitudinal and circular layers
d) Both smooth muscle and skeletal muscle contain thin and thick myofilaments
d) Both smooth muscle and skeletal muscle contain thin and thick myofilaments
What feature of smooth muscle allows it to stretch without immediately resulting in a strong contraction?
smooth muscle tone
low energy requirements
stress-relaxation response
slow, prolonged contractile activity
stress-relaxation response
Which of the following is true?
Smooth muscle lacks the thin and thick filaments characteristic of skeletal muscle.
Skeletal muscle lacks the coarse connective tissue sheaths that are found in smooth muscle.
Skeletal muscle fibers tend to be shorter than smooth muscle fibers.
Skeletal muscle fibers contain sarcomeres; smooth muscle fibers do not.
Skeletal muscle fibers contain sarcomeres; smooth muscle fibers do not.
Which type of muscle is found in the body wall of hollow organs?
unitary smooth muscle
skeletal muscle
multi unit smooth muscle
cardiac muscle
unitary smooth muscle
Smooth muscle is generally classified as either unitary smooth muscle or multi unit smooth muscle. The type of muscle found in the walls of most hollow organs is?
unitary smooth muscle.
The mechanism of contraction in smooth muscle is different from skeletal muscle in that ________.
actin and myosin interact by the sliding filament mechanism
the site of calcium binding site differs
ATP energizes the sliding process
the trigger for contraction is a rise in intracellular calcium
the site of calcium binding site differs
An entire skeletal muscle is surrounded by __________.
perimysium
epimysium
endomysium
tendon sheath
sarcolemma
epimysium