Oceanography Lab- Final Review
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
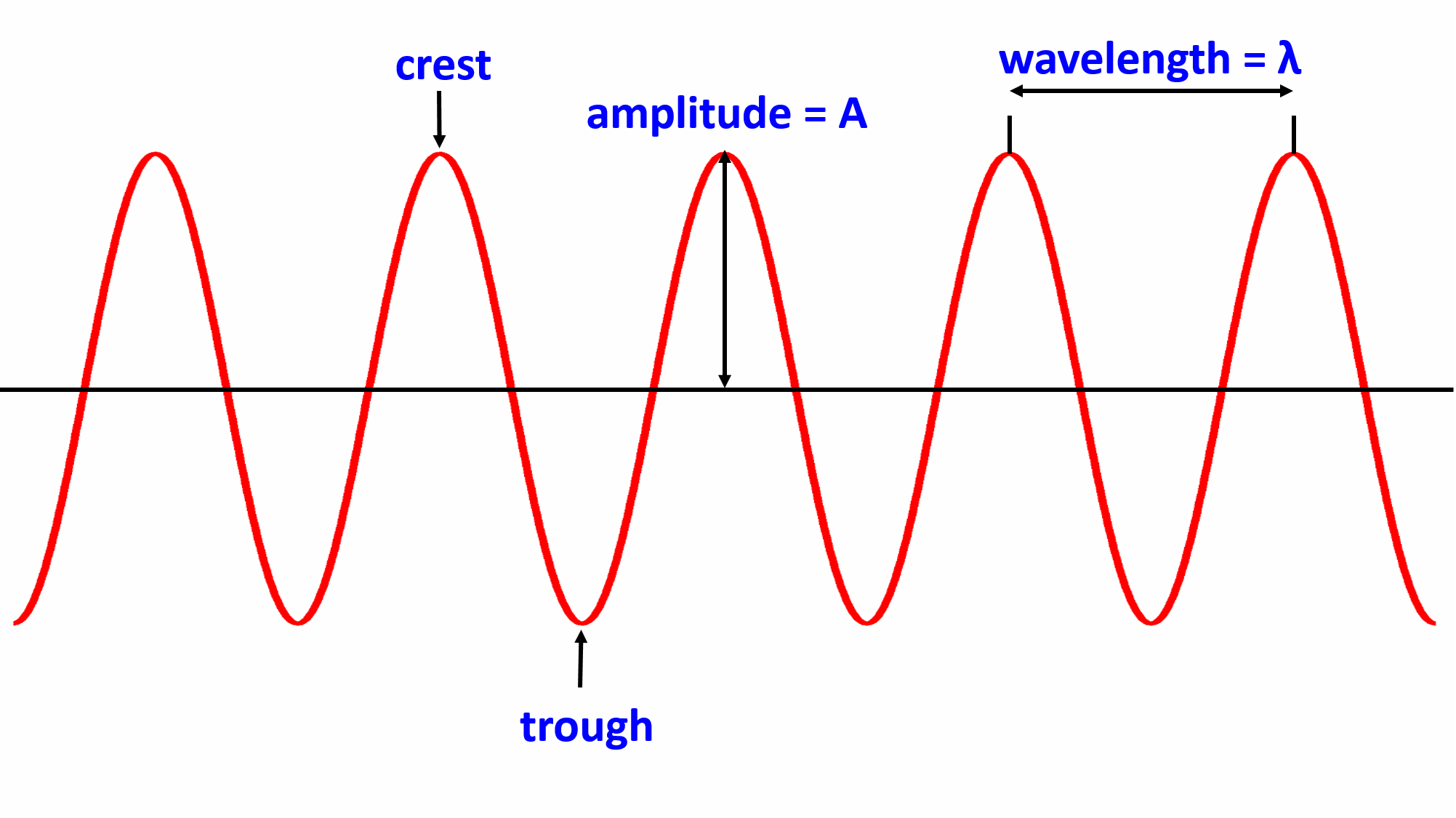
Trough
The lowest point of the wave
Crest
Highest point of a wave
Wave Period
The time it takes a wave to pass a fixed point
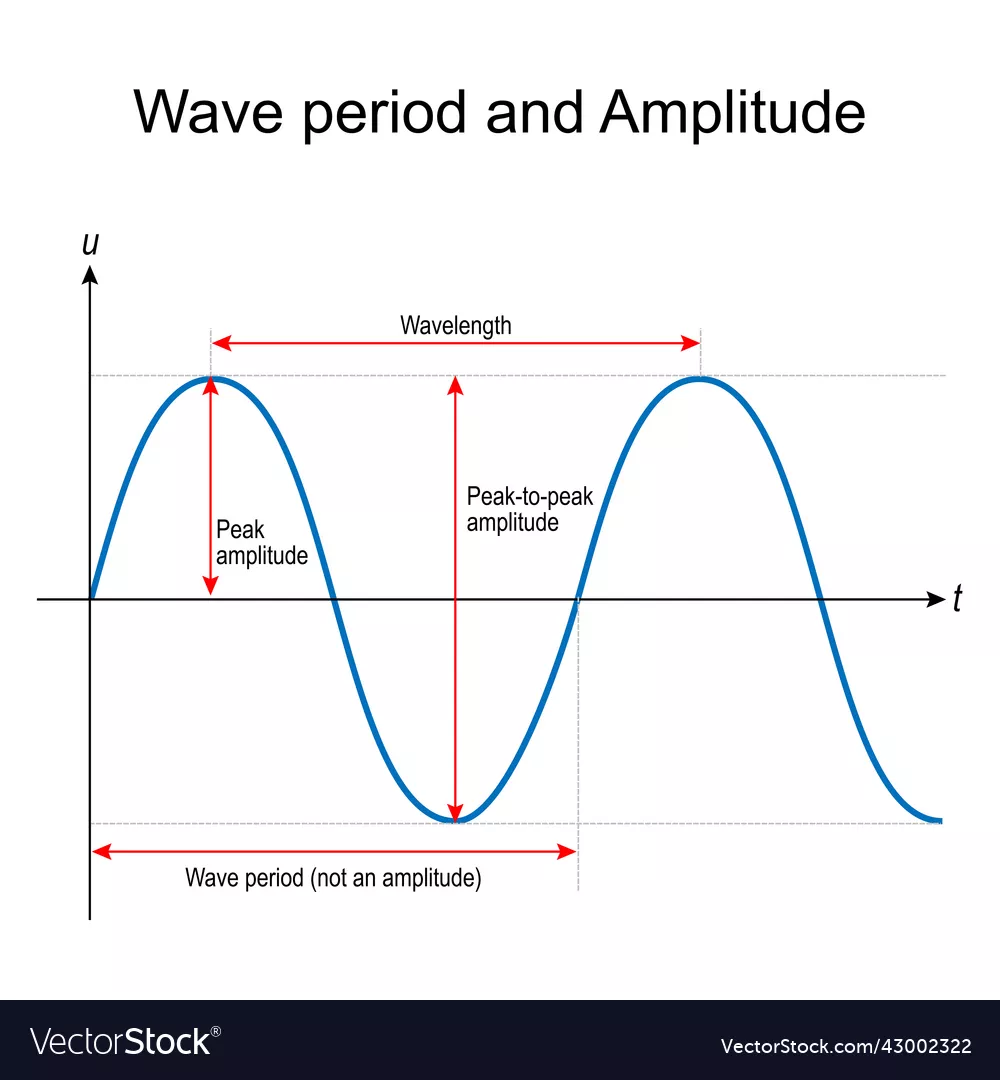
Wavelength
The distance from trough or crest to crest
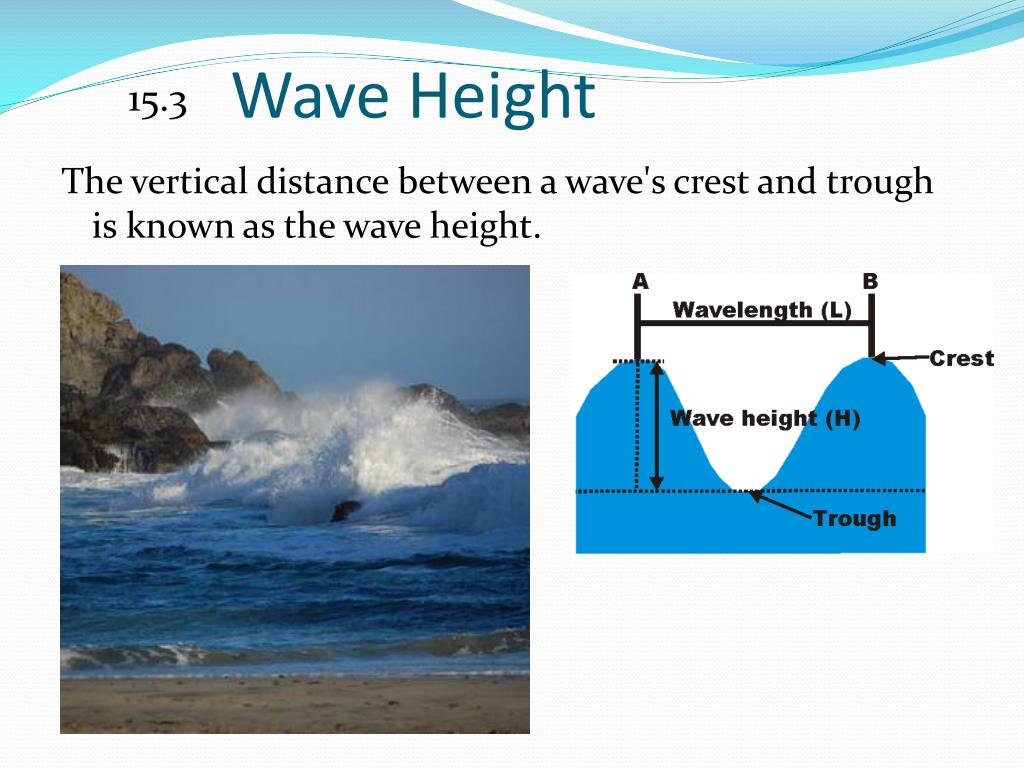
Wave height
The distance between the crest and the trough
Amplitude
Half of wave height; calm sea level to crest or trough
Water Depth
The distance between the calm sea floor to the ocean floor

Celerity
Waves speed or how fast it moves (wavelength/ wave period)


A Progressive wave
Moves through the water column

Longshore Trasport
The transportation of sand parallel to the coast (when waves hit the coast at an angle perpendicular to the shoreline)
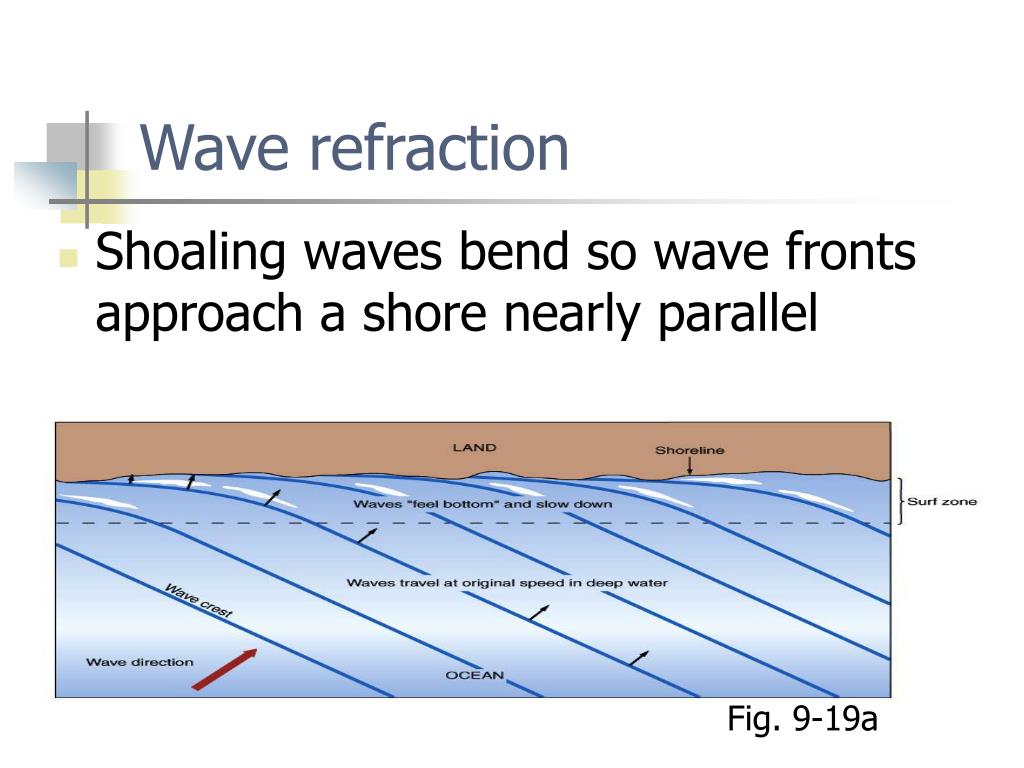
Wave refraction
When waves hit a manmade structure (causes more sediment transportation)

Spilling breaker
Shallow or gentle slope
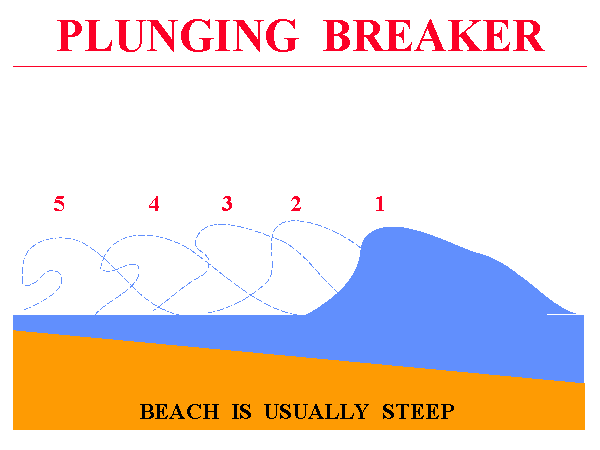
Plunging breaker
Moderate beach slope
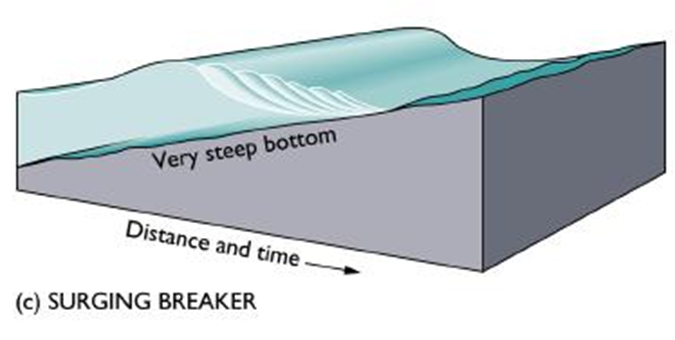
Surging breaker
Steep slope
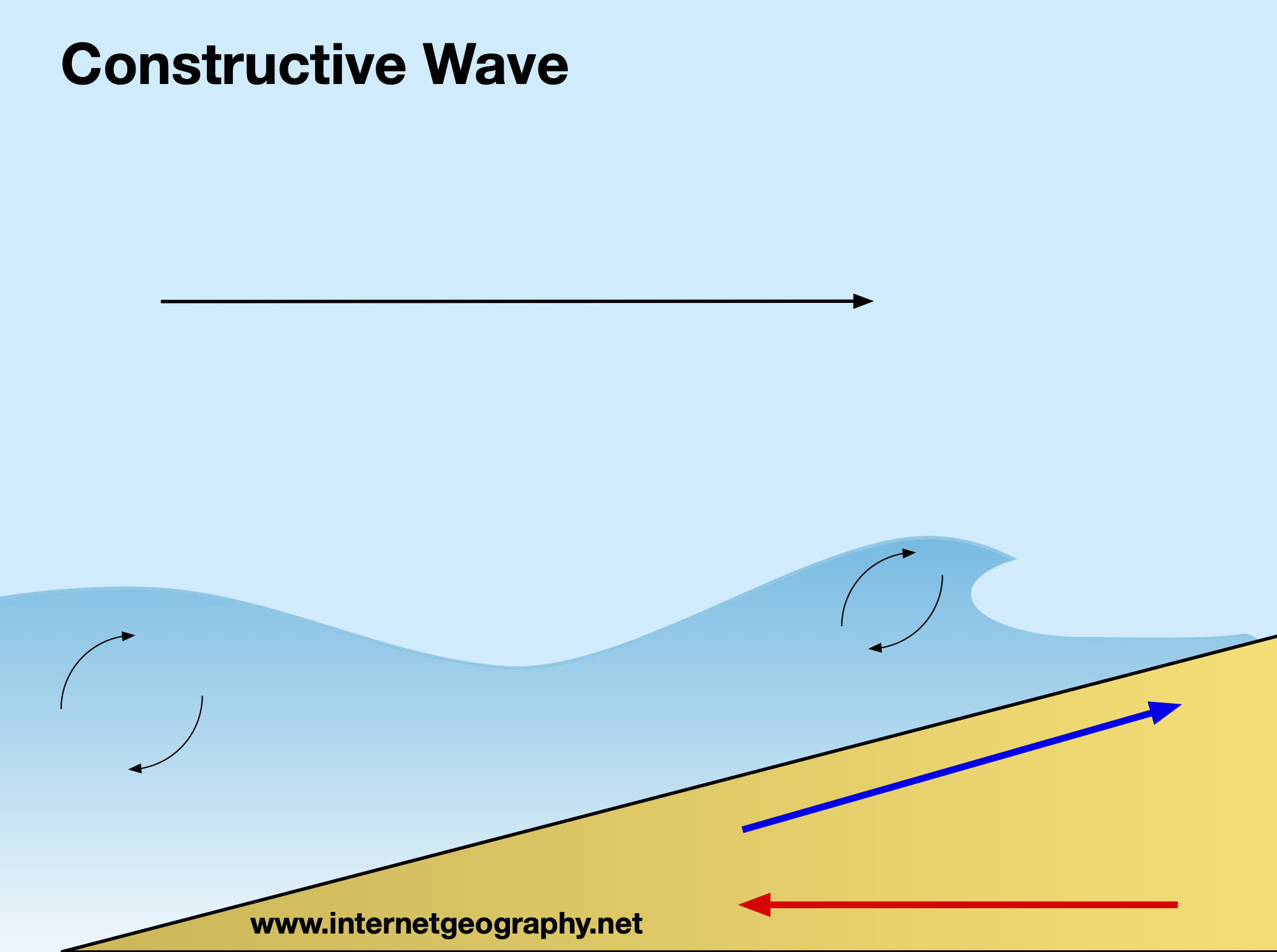
Constructive waves
Builds the beach up
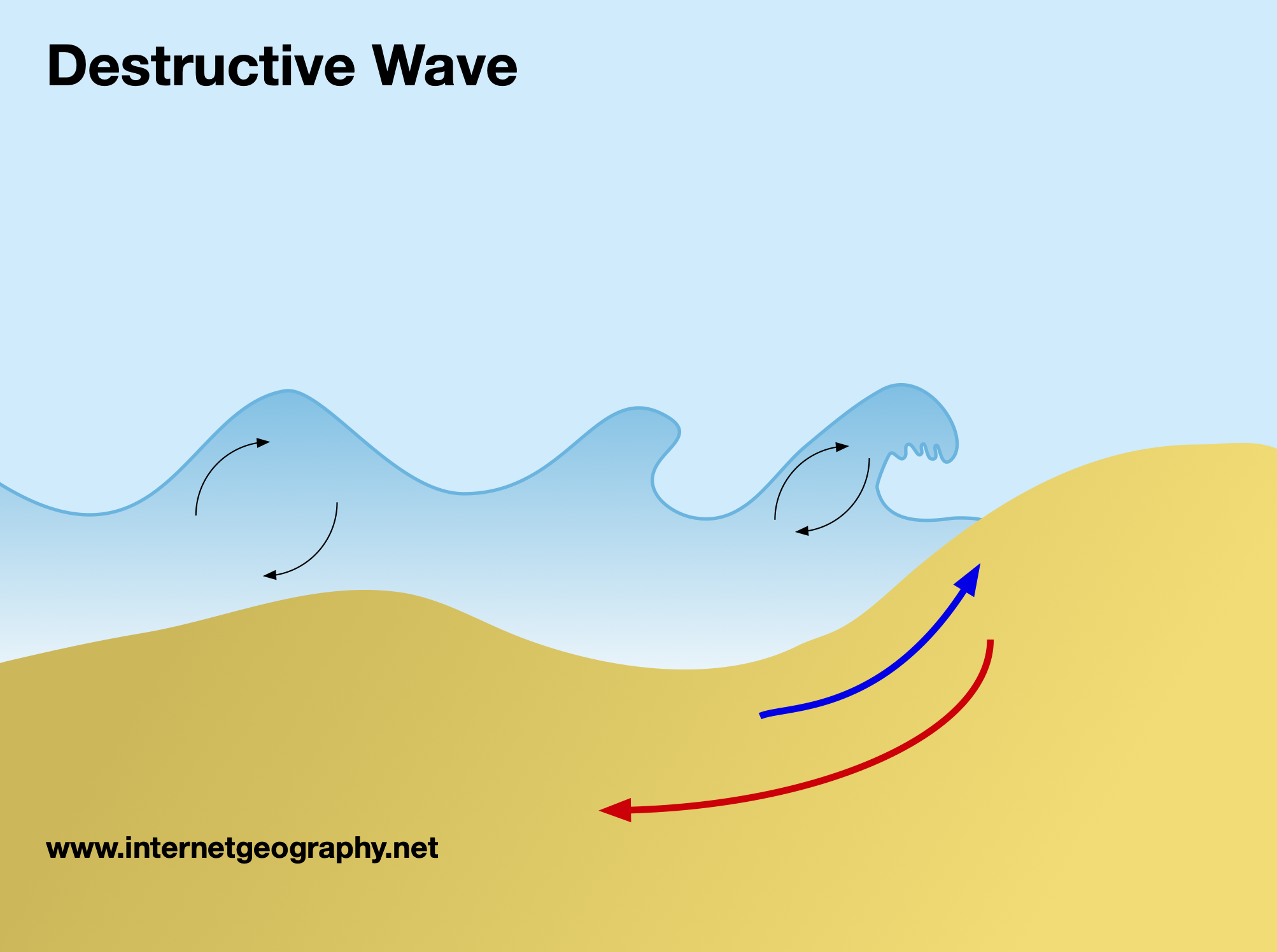
Destructive waves
Makes the beach erode

Summer beaches
Builds up beaches

Winter beaches
Erodes beaches
Where are the low nutrients located
At the top
What is the formula for photosynthesis
CO2+H20+nutrients+light—> C6H1206+02
What uses photosynthesis
Used by plants and phytoplankton
What do phytoplankton go through?
Photosynthesis
What is the formula for respiration (consumes oxygen)
C6H12O6+O2—>H2O+CO2+nutrients+energy
What do zooplankton go through
Respiration
Limitations of Primary Production (Phytoplankton)
Grazing
Light
Nutrients
What does d and l stand for in d/l (multiple length by 2 before dividing )
depth and wavelength
What are the requirements for shallow water
< 0.05 (less than 0.05)
What are the requirements for intermediate water waves
Between 0.05
As you go down
There is more nutrients and less photosynthesis
At the surface the nutrients are
Low in concentration because the light gets through the water column and consumes the nutrients
What were the nutrients in lab 10
Nitrate, Phosphate, Silica, and Ammonium
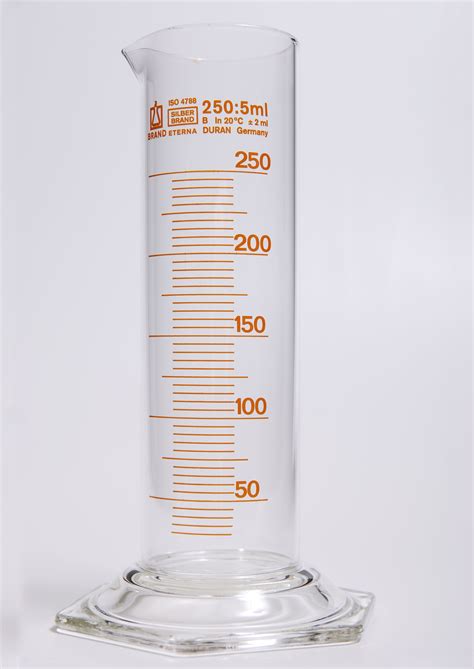

What equipment did we use in lab 10
Test tubes, Beaker, granulated cylinder and

Plankton (producing)
Its movement is controlled by the tide
What is a Phytoplankton
Primary producer, get eaten by zooplankton
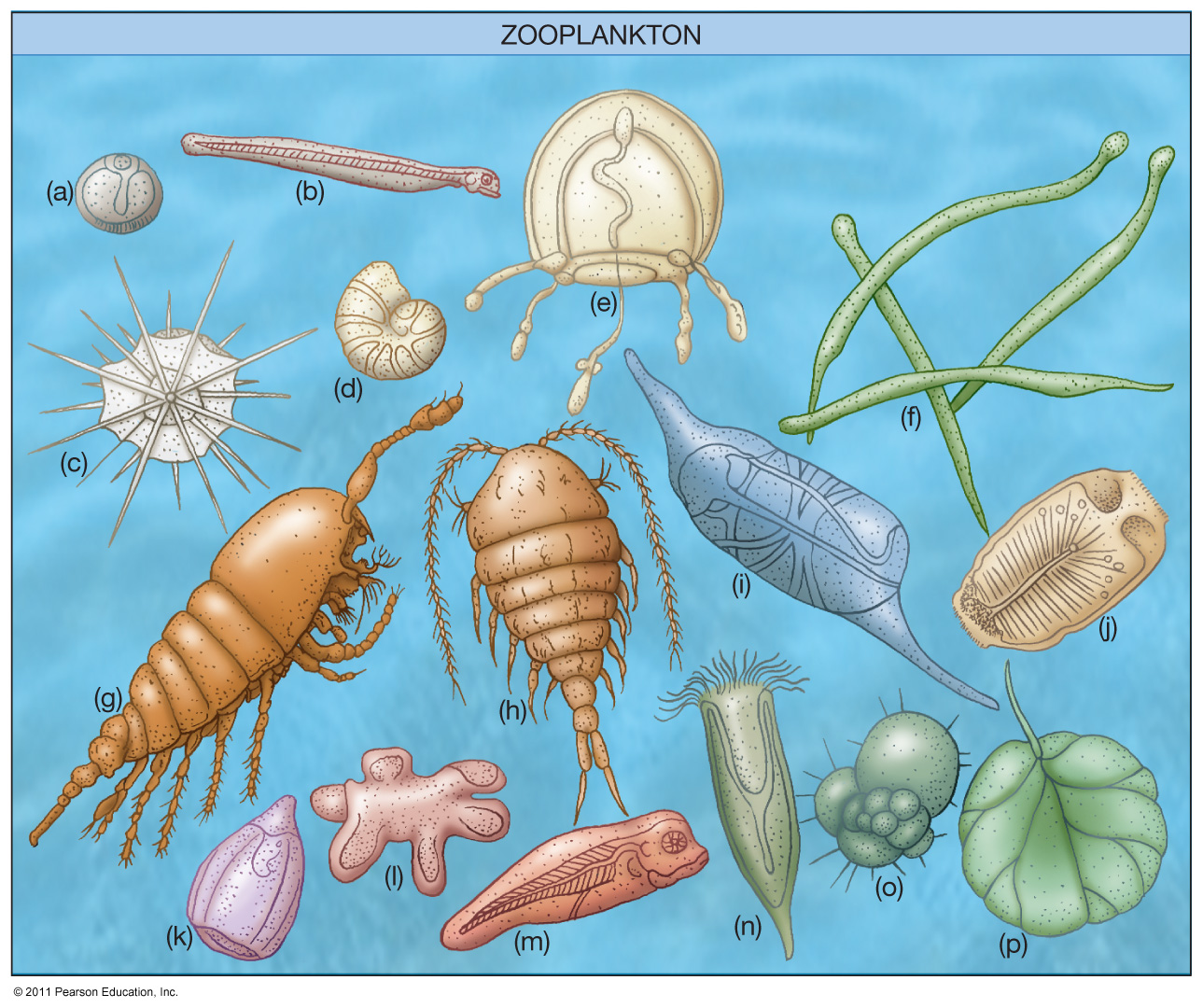
What are Zooplankton(eating)
Get energy from eating phytoplankton and respiration
Why are nutrients depleted at the surface?
Because of the sunlight
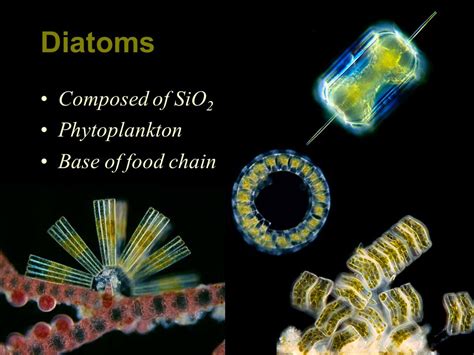
What are Diatoms
Use silica for there shell
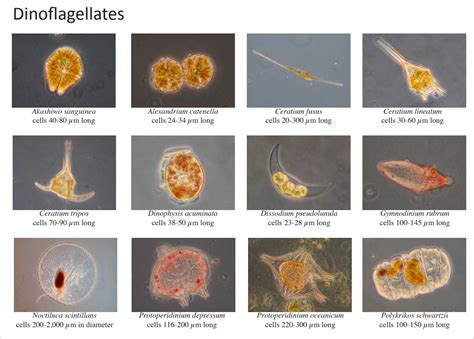
What are Dinoflagellates
Red tides and big algal blooms

What are Meroplankton (form of zooplankton)
only plankton for part of their life

What are Holoplankton (form of zooplankton)
They are plankton ALL the time and float with the tides

What causes plankton blooms
An excess in nutrients and sunlight

Where can phytoplankton be found
In the photic zone
Folsom Planton Spliter

External sources of nutrients
Rivers, runoff and fertilizer

Epifauna (an example is an Mollusca)
Epi means top, on top of the sediment
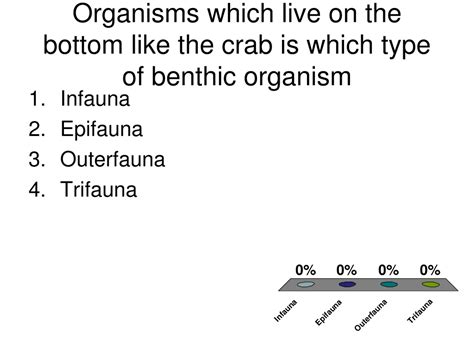
Infauna
Inside the sediment (an example is a Mollusca)
Which organism was most abundant in lab 12
Anthropoda

Benthic Grab
Takes a bite out of the seafloor

Trawl Net
There Towing a net along the sea floor

There is a plankton bloom if
Greater than 1,00,000 blooms
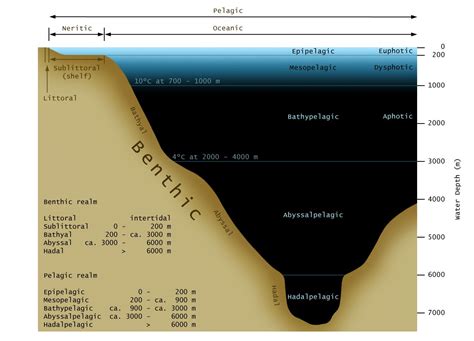
Benthic means
Bottom— organisms located on the bottom and they lack spines

Sessile
Stuck in one place
CTD
Conductivity, temperature and depth
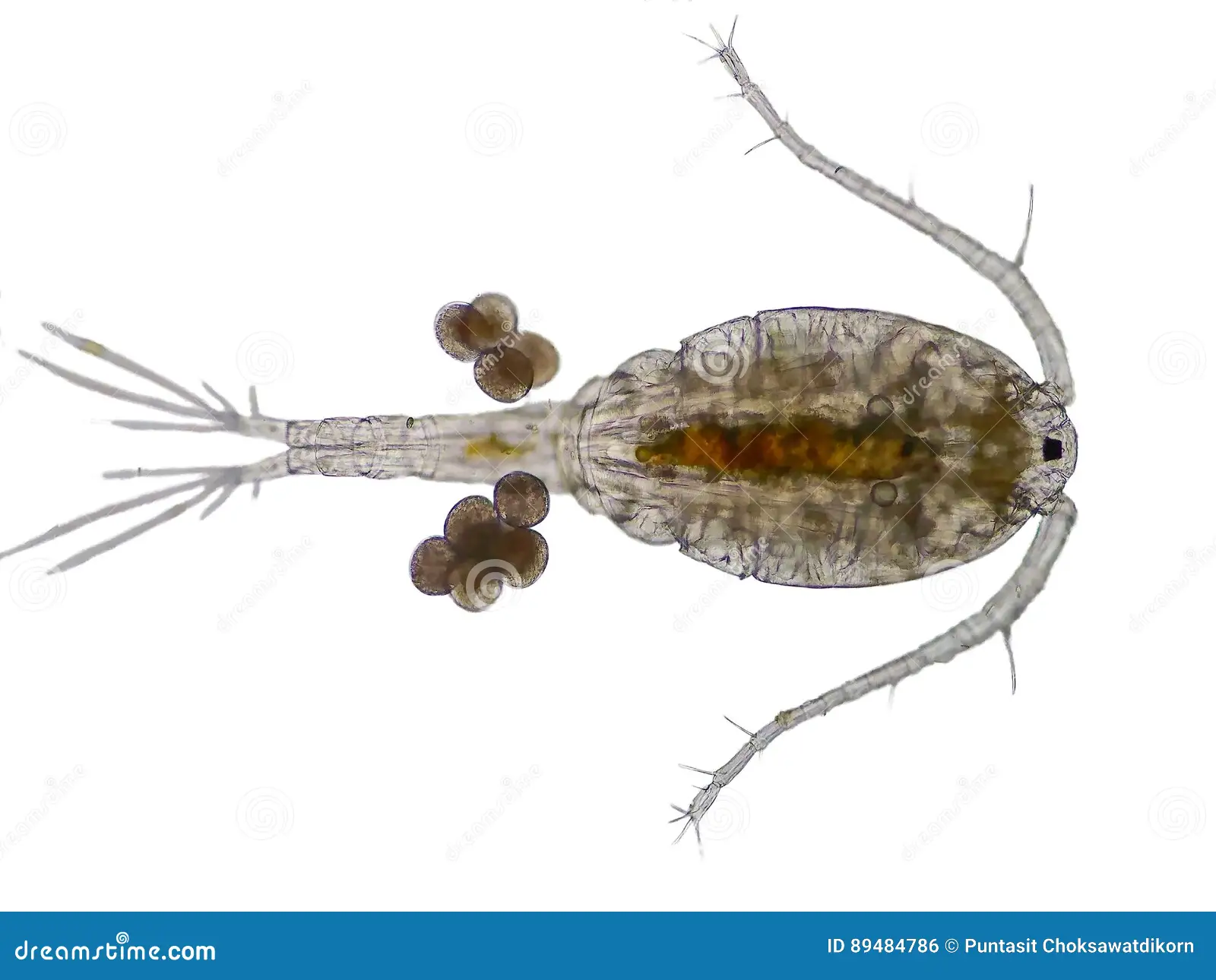
Bonus Question: What is this called
A copepod