Chapter 5 (not done)
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
Four Primary Tissues
Connective, Epithelial, Muscle, Nervous
Epithelial tissue covers
all body surfaces (internal and external
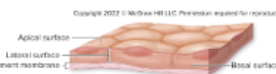
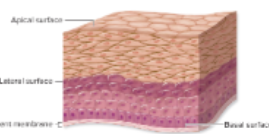
Apical surface
faces external environment [e.g. lumen of intestinal tract, air side of
lungs, line blood vessels, skin]
Basal surface
side attached to basement membrane
vasculature
blood vessels
lacking or without
“a”

Muscular Tissue

connective tissue

Nervous tissue

Epithelial tissue
Epithelia are avascular
no blood supply [within the tissue]
Epithelia are innervated
have a nerve supply
Epithelia re—-
regenerate [regrow]
Epithelial tissue Function: Protection
prevents water loss (skin)
protects underlying tissues
resists physical stress
Epithelial tissue Function: Secretion
glands produce hormones, sweat, mucus
Epithelial tissue Function: Absorption
takes up material from the environment
(e.g., circulation, digestive tract, lungs)
Epithelial tissue Function: Filtration and selective movement
filtrate formation in kidney
transporters for specific molecules (e.g., glucose, ions)
Epithelial tissue Function: Excretion (one way waste products are released
movement of CO2 from blood into alveoli
sweat contains ammonia, urea, NaCl
Epithelial tissue Function: Sensation
nerve endings in detect pain (paper cut, stomach pain)
specialized cells detect changes in internal and external environments
Examples of Sensation in Epithelial tissue
Taste and smell, Touch and vibration
Epithelial tissue Function: Immune defenses
physical barrier
some cells of immune system here [additional protective function]
Epithelia can be classified according to
cell shape of the layer closest to the environment, and number of cell layers
Simple Epithelium

Squamous Cell
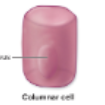
Columnar cell
Stratified Epithelium
One cell layer thick
simple epithelium
two or more cell layers thick
stratified epithelium
Pseudo
false
pseudostratified
falsely layered
Osteoblasts
build bone
Osteoclasts
Breakdown bone
Merocrine gland
secretions packaged into vesicles, released by exocytosis
e.g., Lacrimal (tear) and salivary glands
Apocrine gland
accumulates secretion in apical region of cell
apical membrane pinches off forming a vesicle containing the secretion
e.g., mammary and ceruminous glands
Holocrine gland
cell ruptures becomes part of secretion
e.g., sebaceous (oil) glands
Extensibility
a change in length [stretching]
allows stretching without breaking (~1 ½ increase
Elasticity
allows fibers return to resting length after stretching
Areolar connective tissue [all three fibers]
well vascularized
e.g., beneath skin, surrounds nerves and blood vessels
Reticular connective tissue [mostly reticular fibers]
e.g., lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, bone marrow
Dense regular - parallel collagen fibers
resistant to tension in one direction
fibroblasts between fiber bundles
little ground substance and few blood vessels
e.g., tendons and ligaments [one plane of movement]
Dense regular elastic connective tissue
mostly parallel-oriented elastic fibers
in walls of structures that stretch to perform their function,
e.g., large blood vessels near heart and certain ligaments
Dense irregular
random direction of collagen fibers) [disorganized fibers]
some open space with ground substance and some cells
strong and resists tension in all directions
e.g., dermis, fibrous sheath around bones, nerves, organs and joints
Two types of fat
white and brown
White adipose tissue
see one large lipid inclusion (triglycerides) in cytosol
cell size varies
fat storage (major energy reserve)
insulation (retains warmth)
shock absorption and protection
secretes hormones
[e.g., appetite regulation, reproduction, metabolism]
White adipose tissue
Brown adipose tissue
more in infants and children
brown color due to numerous mitochondria and rich blood supply
fat readily converted to energy to produce heat in cold temperatures amount increases in cold-acclimated adults
Chondroblasts
cells that synthesize extracellular matrix
Chondrocytes
mature, inactive chondroblasts
trapped in matrix spaces called lacunae
elastic fibers predominate
allows for flexibility and return to shape after stretching or deforming
Elastic cartilage
Liquid Connective Tissues
Blood and Lymph
Difference in fiber types is the
basis for subclassifications
hyaline, elastic and fibrocartilage
Endocrine glands
ductless and secrete products directly into interstitial fluid and bloodstream
products, usually hormones
systemic effects
[e.g., insulin and glucagon]
Exocrine glands
have ducts and release products onto an epithelial surface
(e.g., salivary and mammary glands
Serous glands
produce thin, watery fluids
[e.g. perspiration, milk, and tears]
Mucous glands
actually secrete mucin (glycoprotein), which absorbs water, forming mucus
[e.g., respiratory and digestive tracts]
Mixed glands
produce a mixture of secretions
[e.g., salivary glands –produce secretion that is both mucus and serous composition]
Goblet cells
unicellular exocrine gland, secrete mucus thick, sticky liquid that protects underlying epithelium
Examples: digestive and respiratory tract