Session 1: Light Microscopy
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Most human cells are ___ in diameter
10-20 µm
Order these cells from sizes (smallest to largest)
Keratinocyte, Oocyte, Neutrophil, RBCs
1) Smallest = RBCs
2) Neutrophils
3) Keratinocyte
4) Largest = Oocyte
Limit of resolution
The minimum distance at which two objects can be distinguished (resolved) as two separate entities
Resolution is ___ proportional to wavelength
inversely
What is the practical limit of resolution for light microscopy
200nm
What is the practical limit of resolution for electron microscopy
~0.1nm
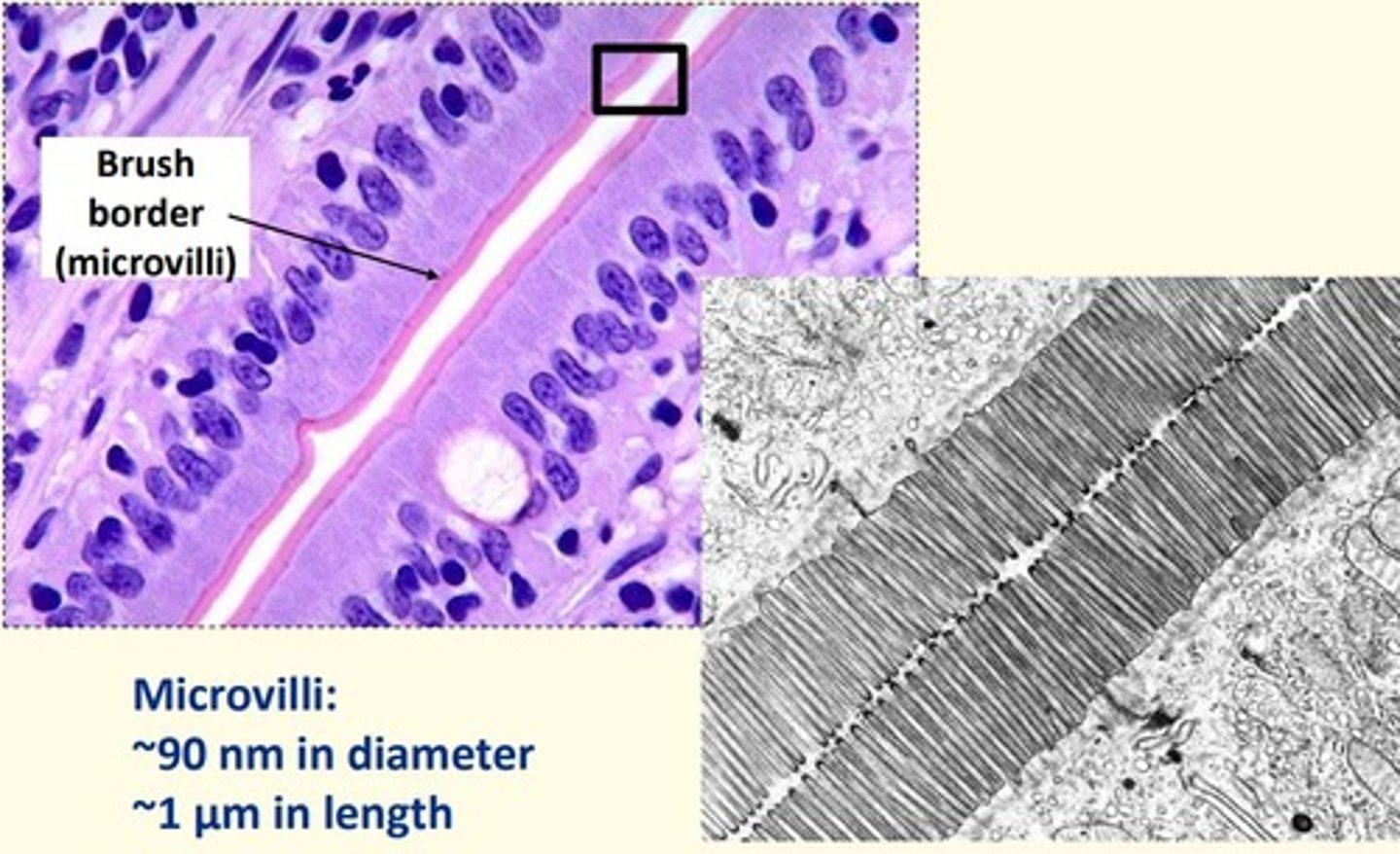
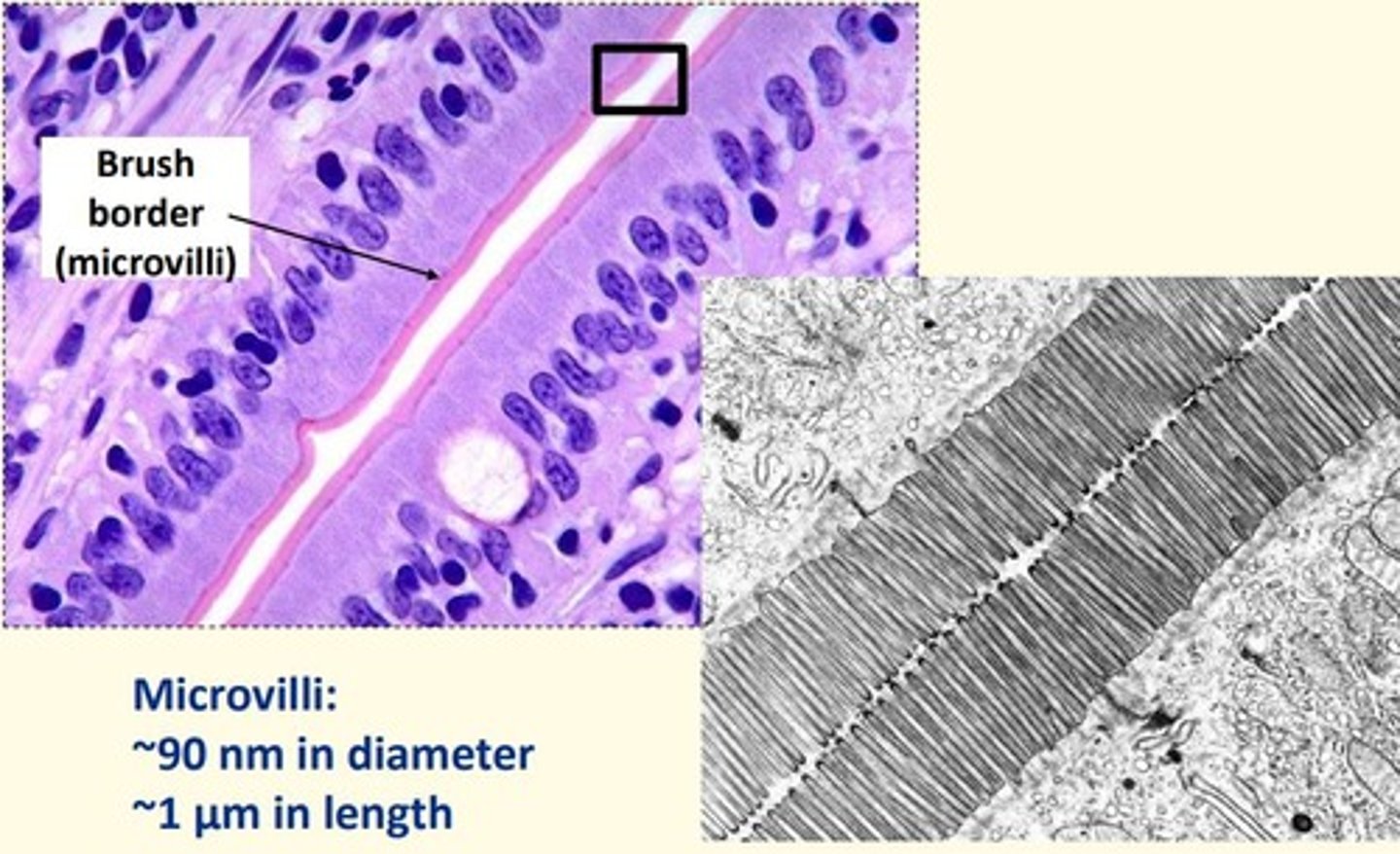
Intestinal epithelium
Value of histology in diagnosis
- Malignancies are associated with characteristic histological changes
- Benign/malignant samples differences
- Cancer 'staging' allows for effective trreatment and prognosis
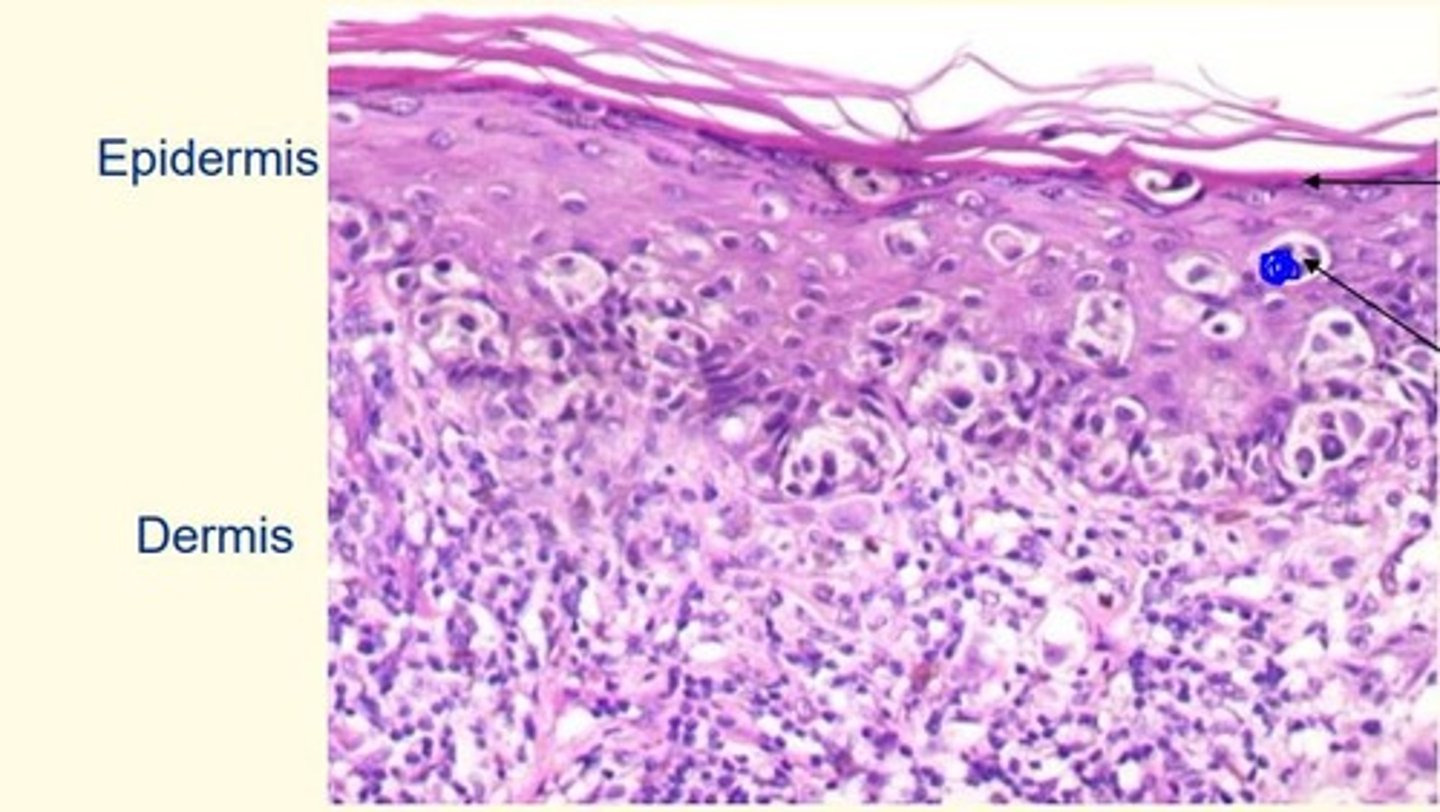
What is the arrow pointing to here. Are these cells dividing? What types of cells are they?
Dividing melanocytes
The top layer is the = granular layer (last living layer of the epidermis)
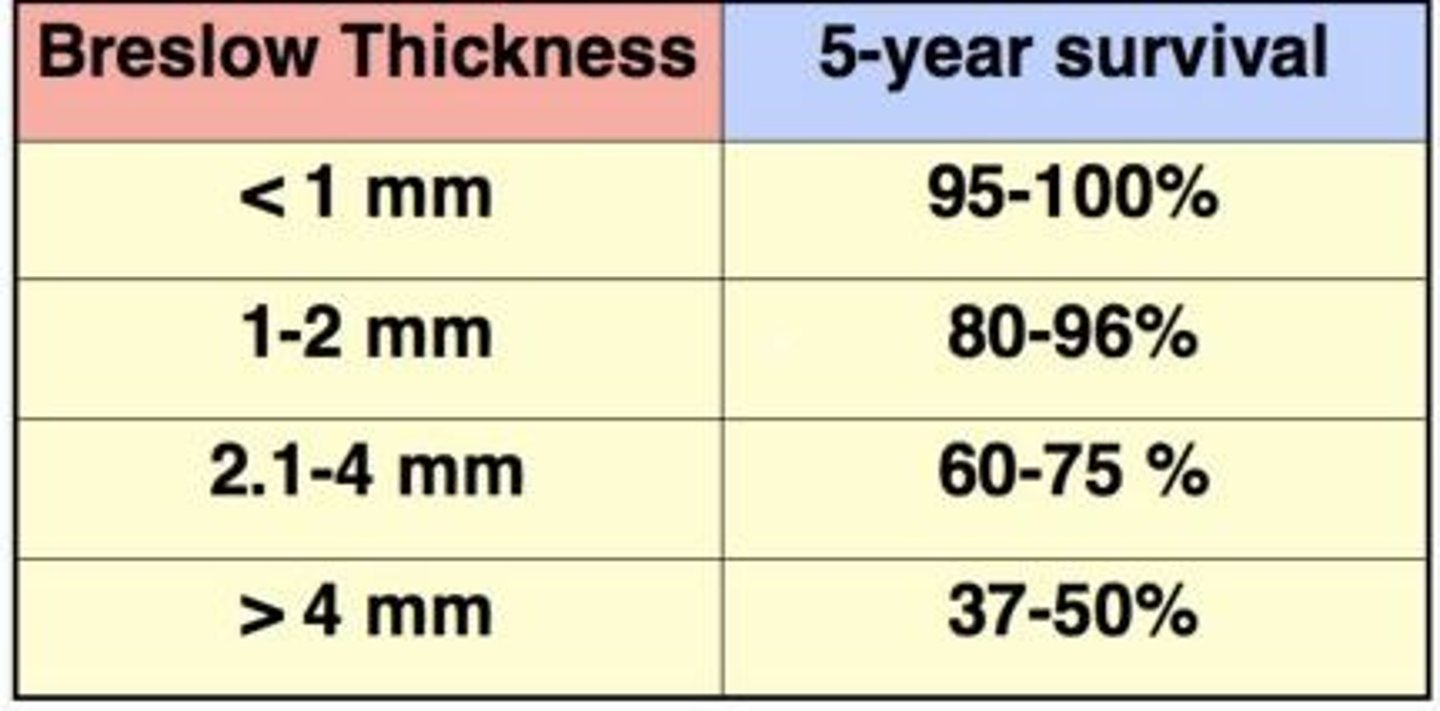
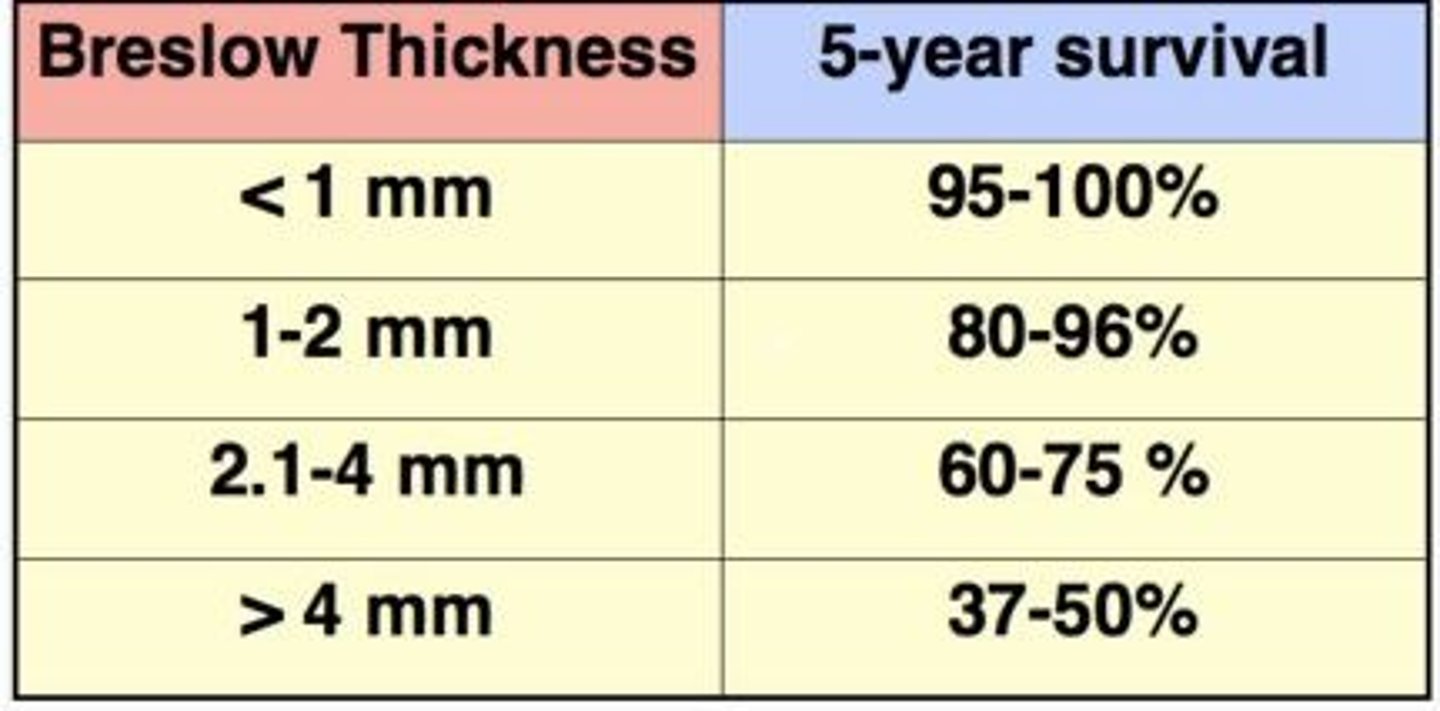
Breslow thickness
Depth of invasion of melanoma from the granular layer of the epidermis, the best predictor of 5-year survival rates
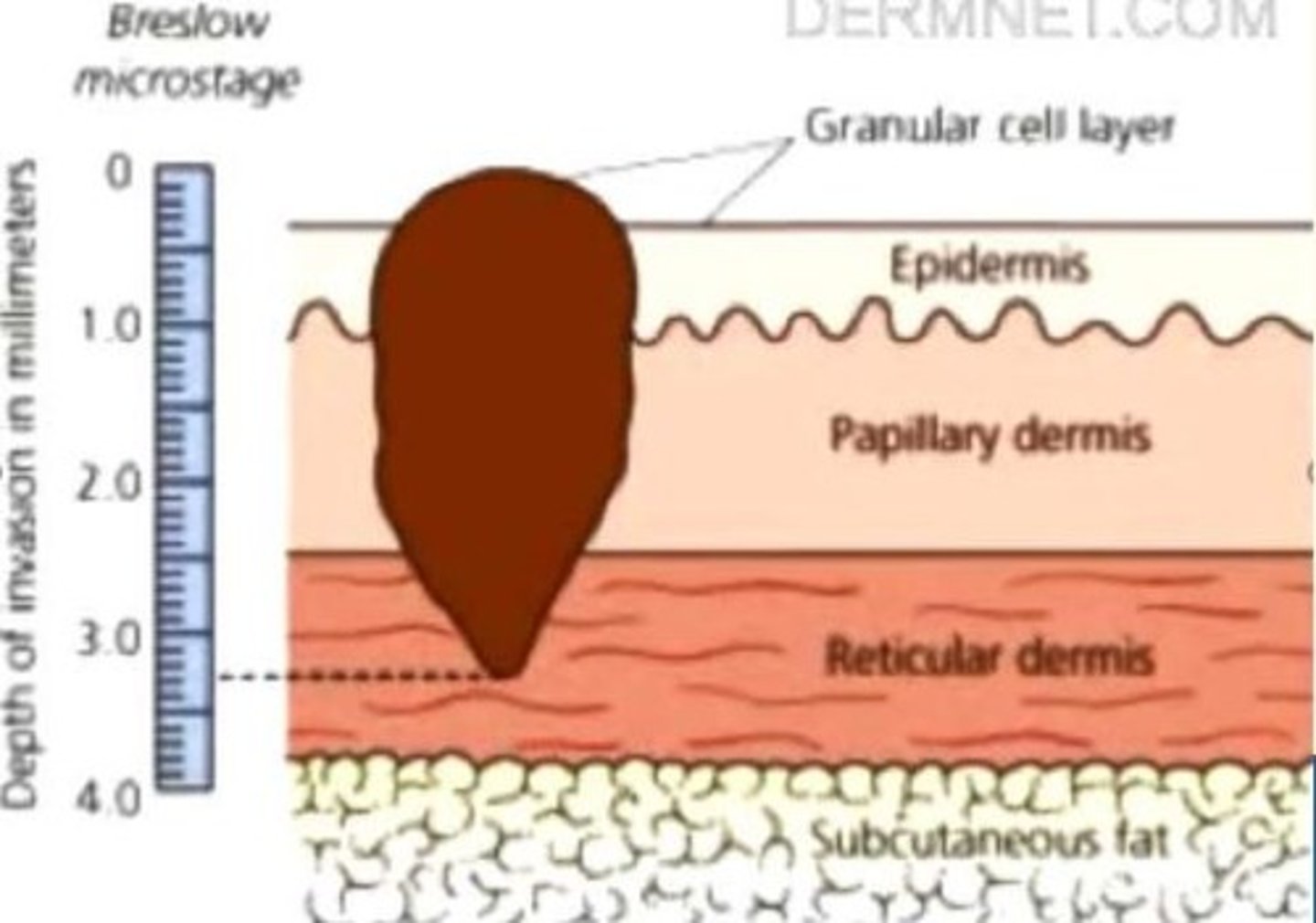
Breslow thickness <1mm
5-year survival rate
95-100%
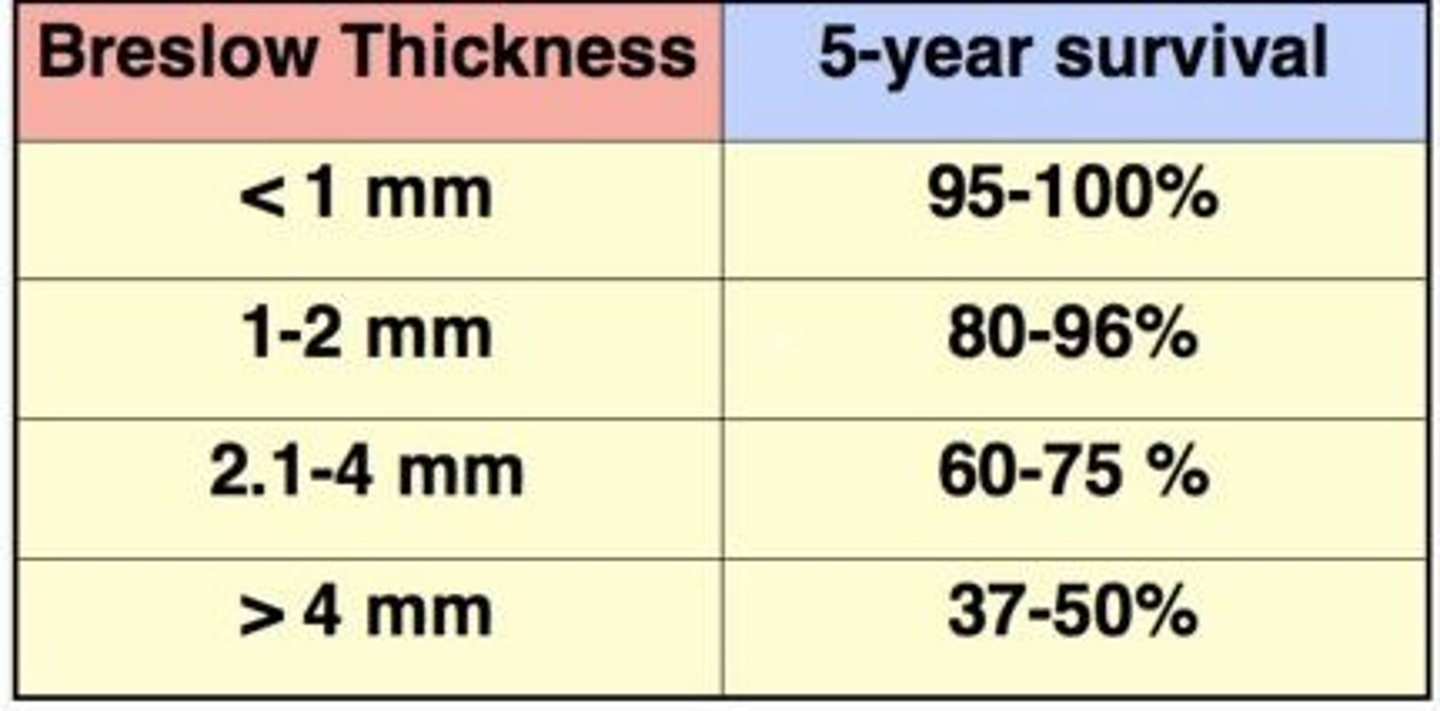
Breslow thickness 1-2mm
5-year survival rate
80-96%
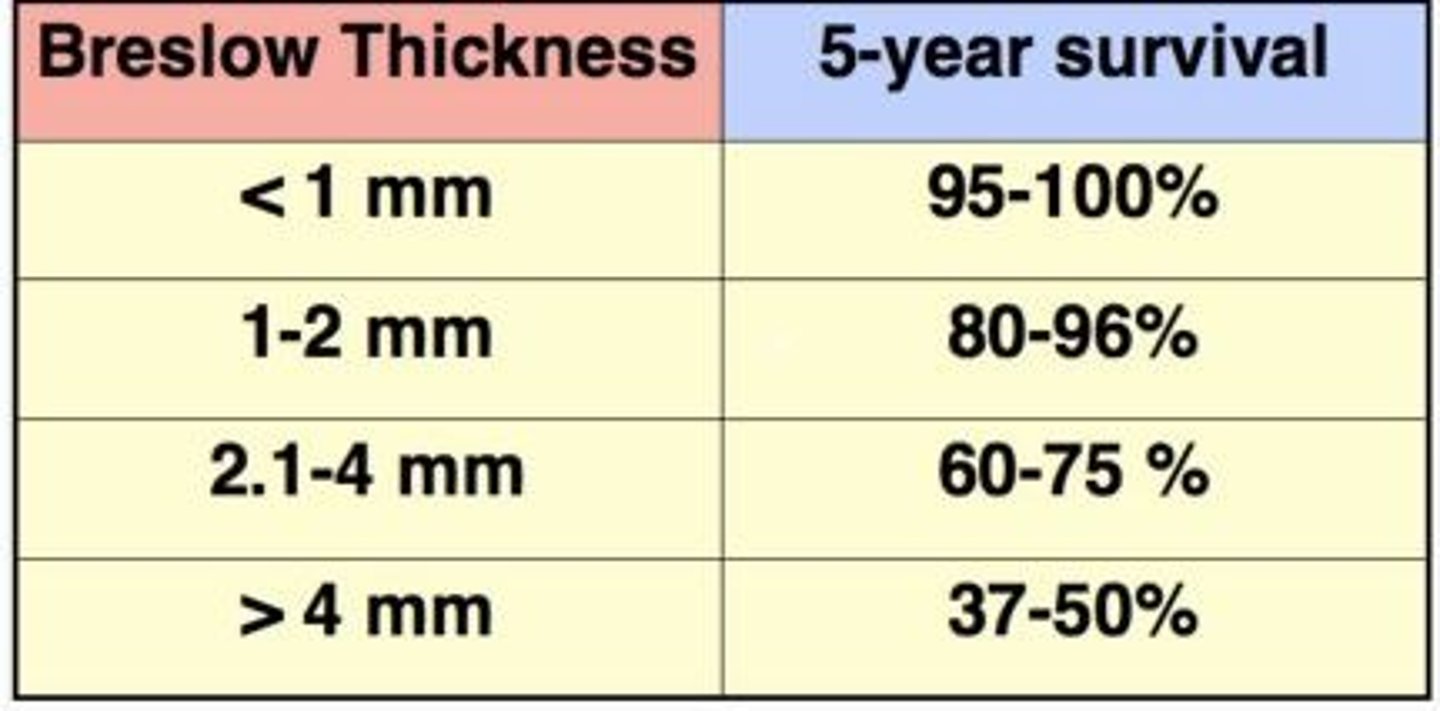
Breslow thickness 2.5mm
5-year survival rate
60-75%
2.1-4mm
Breslow thickness 4mm
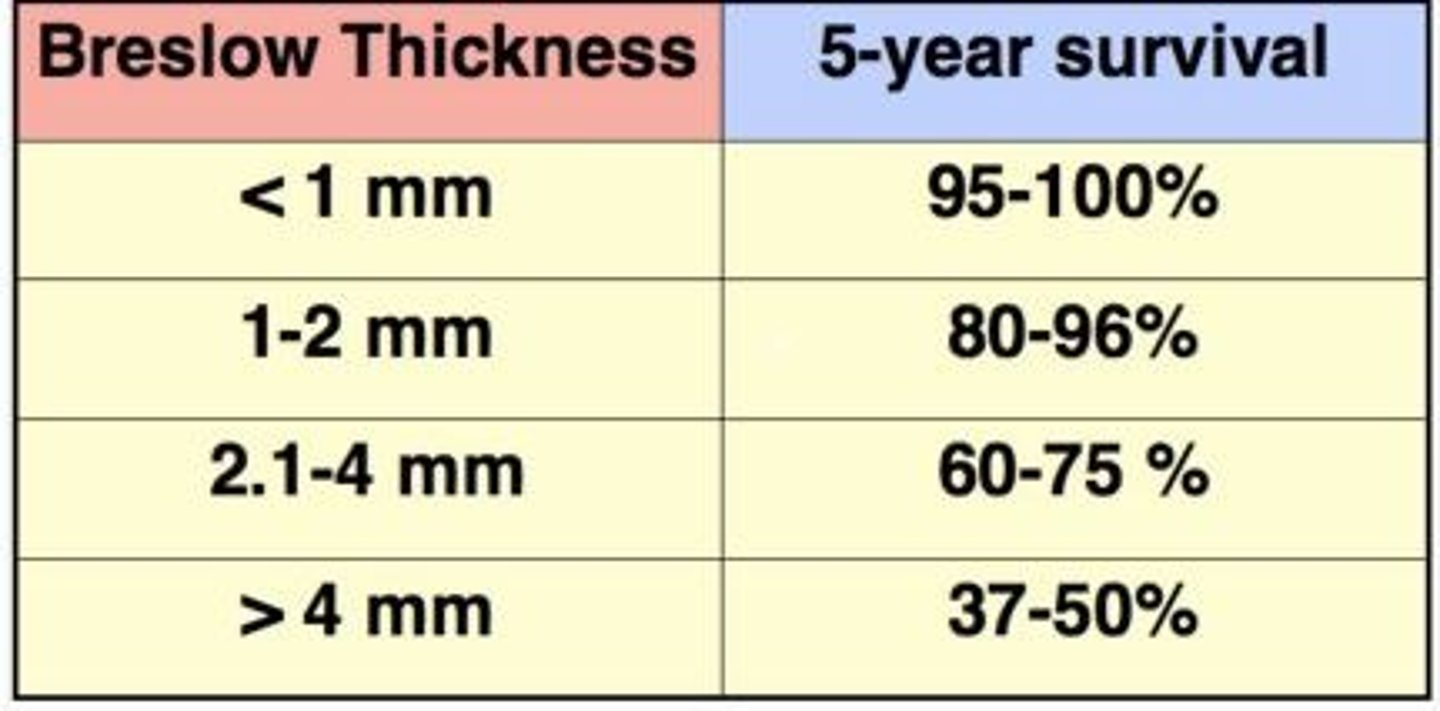
5-year survival rate
60-75%
Breslow thickness 5mm
5-year survival rate
37-50%
Describe the process of histology from biopsy to microscopy...
1) Biopsy = collection of tissue sample
2) Fixation = chemical preservation of tissue
3) Embedding/processing = dehydration and solidification of tissue
4) Sectioning = cutting of solifided tissue with microtome
5) Staining = colouring of tissue section
6) Viewing/analysis = microscopic viewing of stained tissue
Biopsy
Removal of a small piece of tissue for microscopic examination
Smear biopsy locations
Cervix
Buccal cavity
Curettage biopsy location
Endometrial lining of uterus
Direct incision biopsy location
Skin
Mouth
Larynx
Needle biopsy location
Brain
Breast
Liver
Kidney
Muscle
Endoscopic biopsy location
Lung
Intestine
Bladder
Transvascular biopsy location
Heart
Liver
Fixation
Macromolecules are cross-linked, cellular structure is preserved.
Prevents autolysis or putrefaction.
Give some examples of fixatives
Glutaraldehyde
Formaldehyde
Alcohol
Embedding is carried out at what temperature?
56 degrees celsius
Dehydration is carried out in what solution?
Ethanol (70-100%)
Biopsy is impregnated with and embedded in what solution?
Paraffin wax
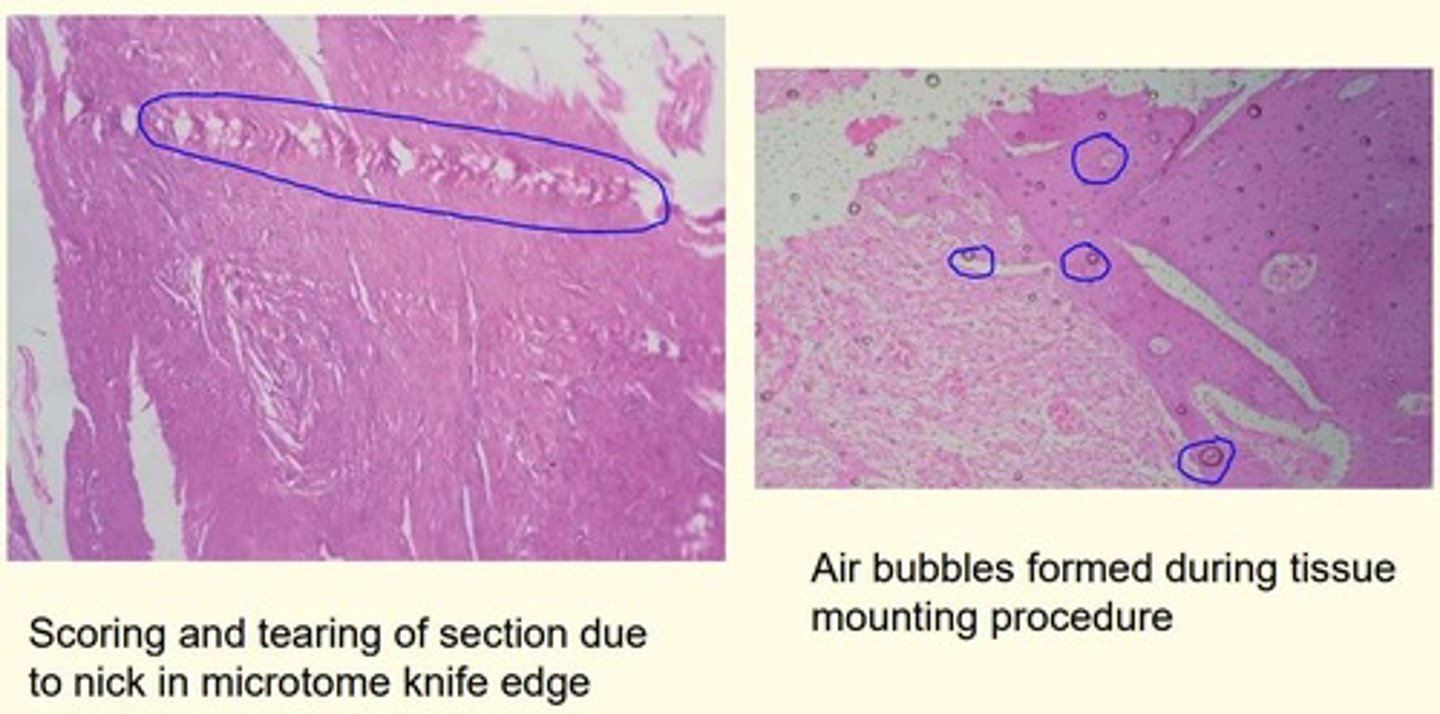
Give an example of two ways artefacts can be formed due to errors in tissue processing process?
1) Scoring and tearing of section = due to nick in microtome knife edge
2) Air bubble formation = during tissue mounting procedure
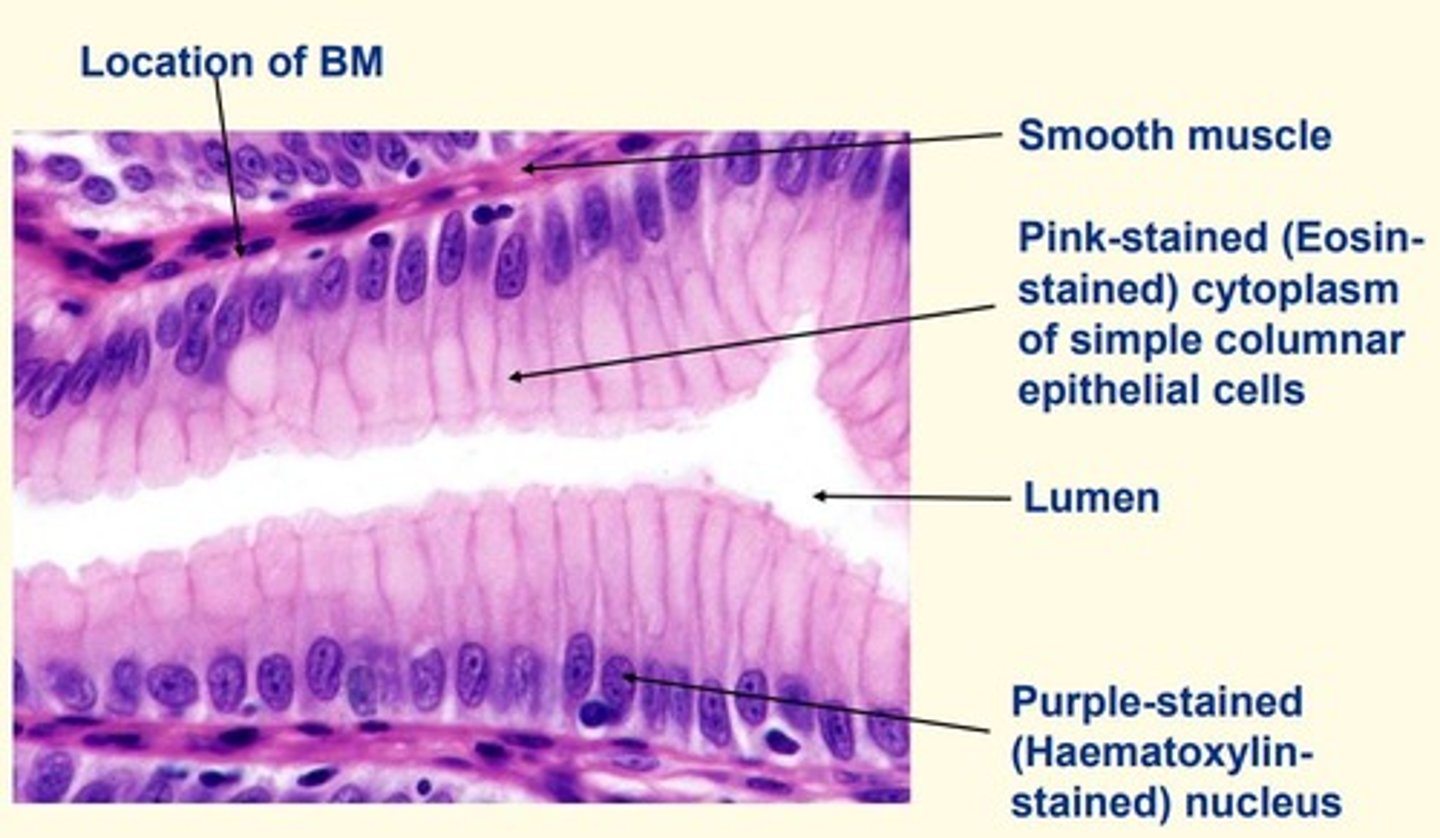
Haematoxylin
- Basic dye
- Stains acidic components of cells purple/blue
- Stains nucleolus/r-RNA purple/blue
Eosin
- Acidic dye
- Stains basic components of cells pink
- Stains cytoplasmic proteins and extracellular proteins (collagen) pink
Gastric pit of the stomach (stained with H&E)
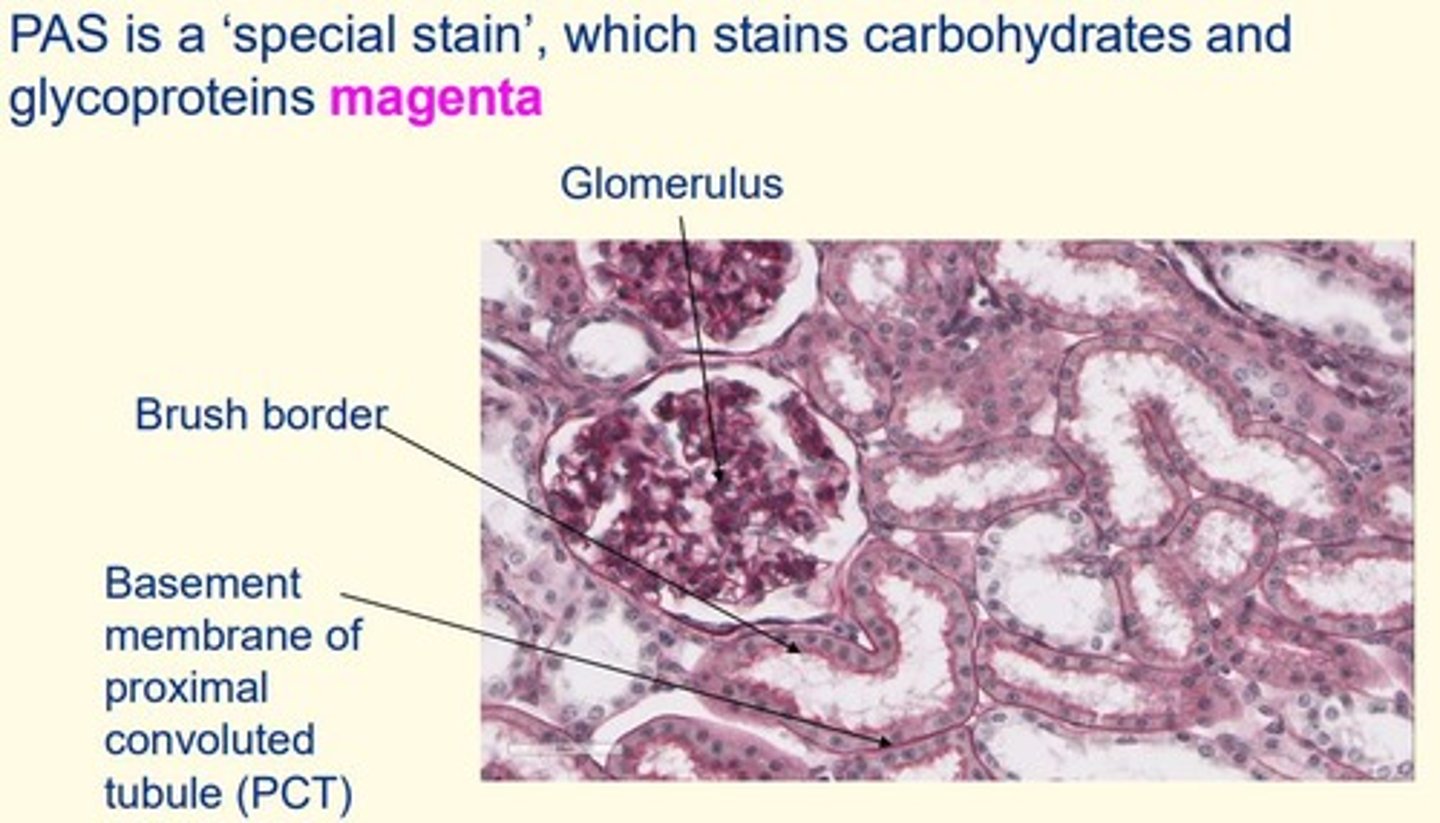
Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS)
- Stains carbohydrates and glycoproteins magenta
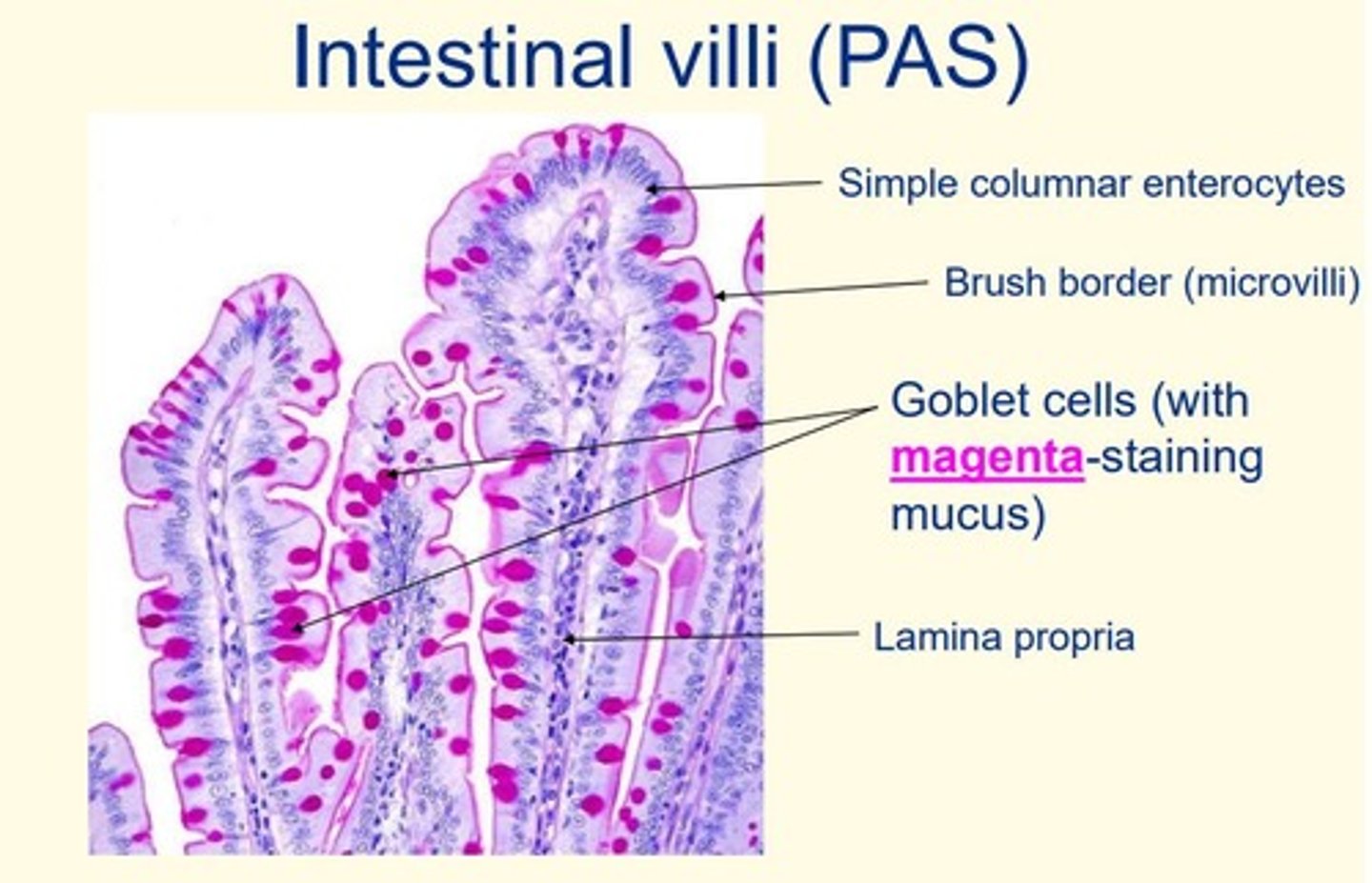
Intestinal villi stained with Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS)
Note = the goblet cells are stained magenta (due to mucus)
Viewing and analysis in clinical settings - tools used and two examples
High-throughout digital slide scanners and image analysis softwares commonly used in clinical settings
- Aperio AT2
- Leica

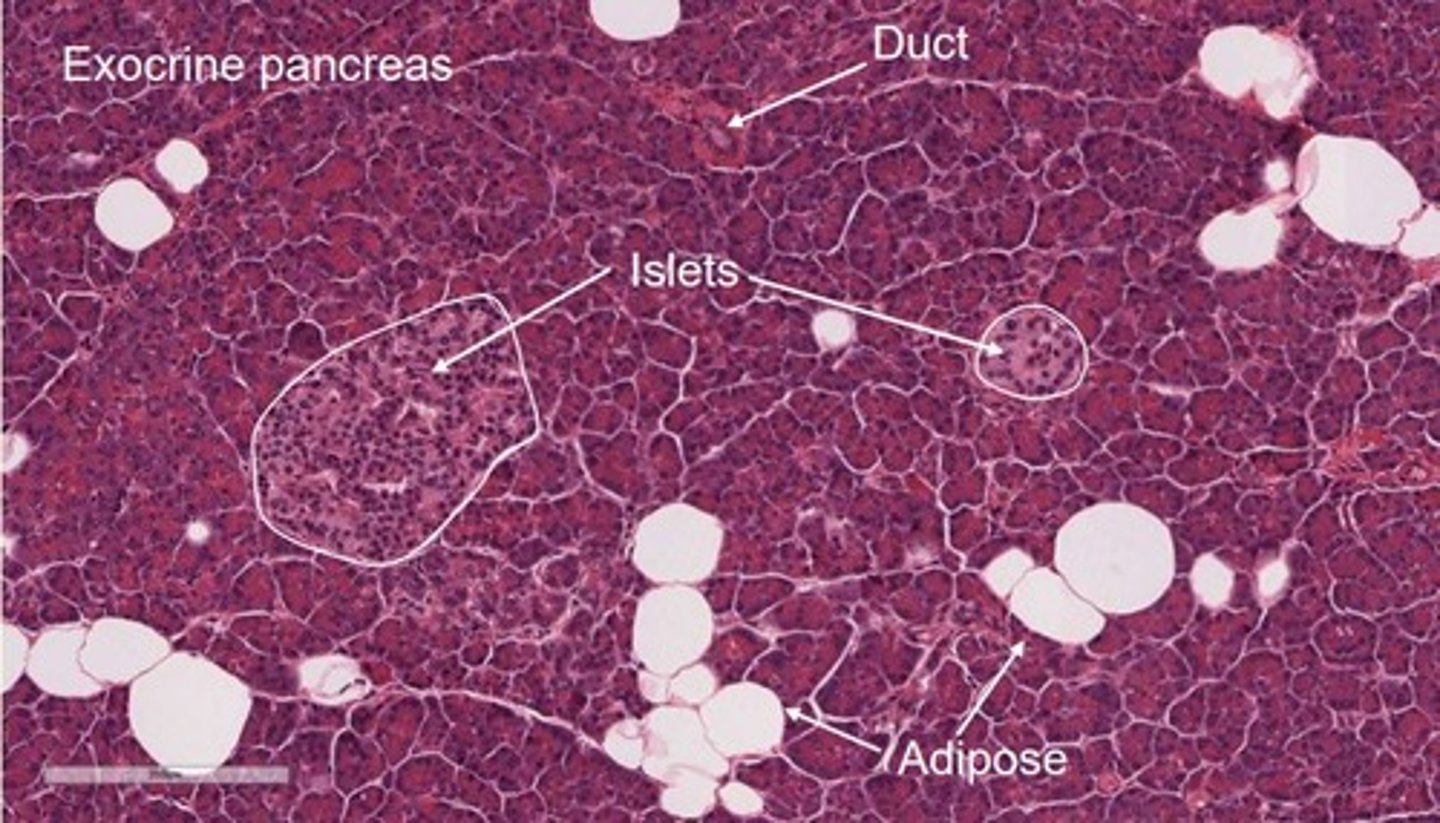
H&E stained pancreas
Heterochromatin
- Highly condensed/tightly packed chromatin/DNA
- Transcriptionally SILENT/inactive
- Intense haematoxylin staining
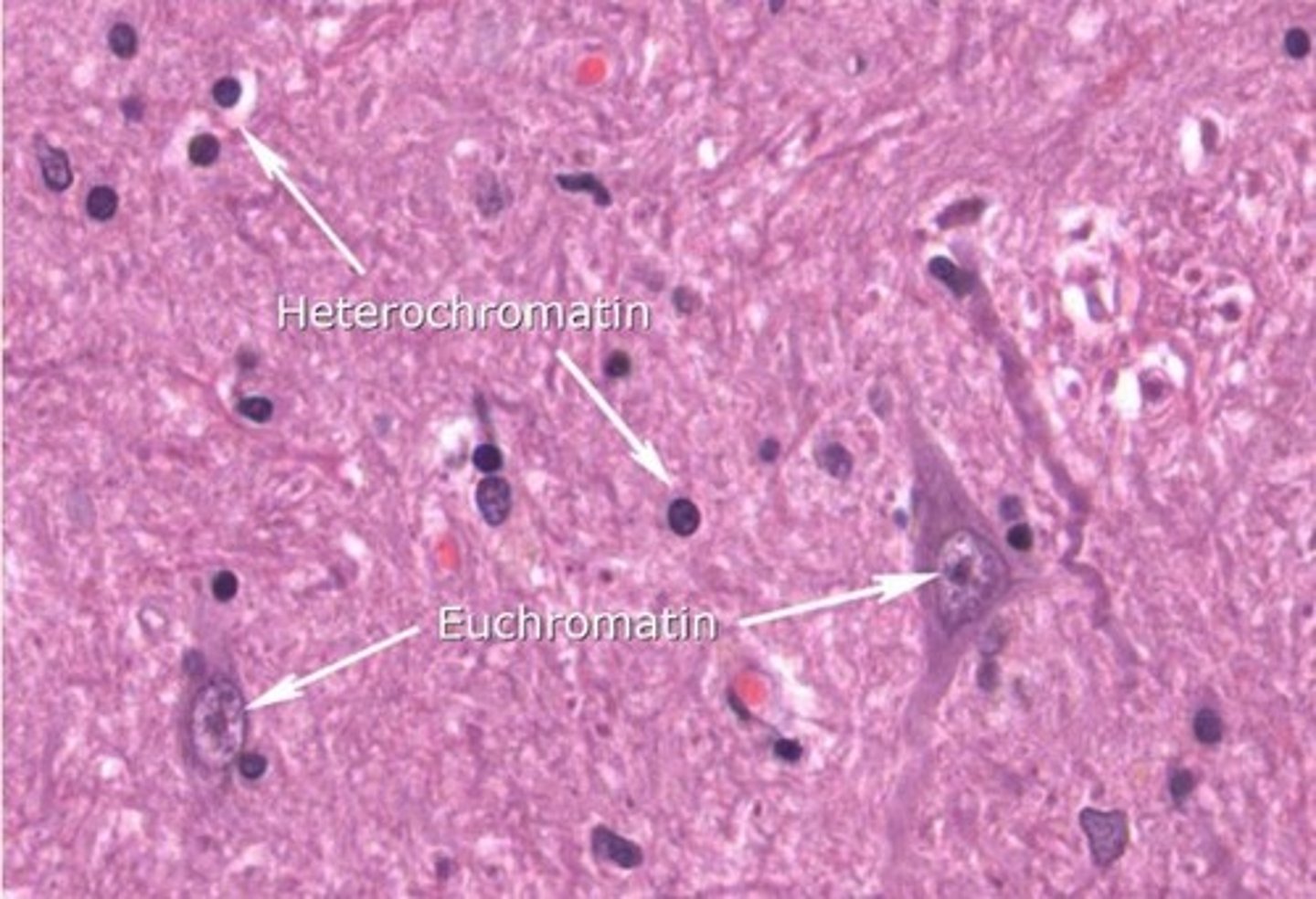
Euchromatin
- Less condensed form of chromatin/looser
- Transcriptionally ACTIVE
- Mostly found at periphery of nucleus/nucleolus
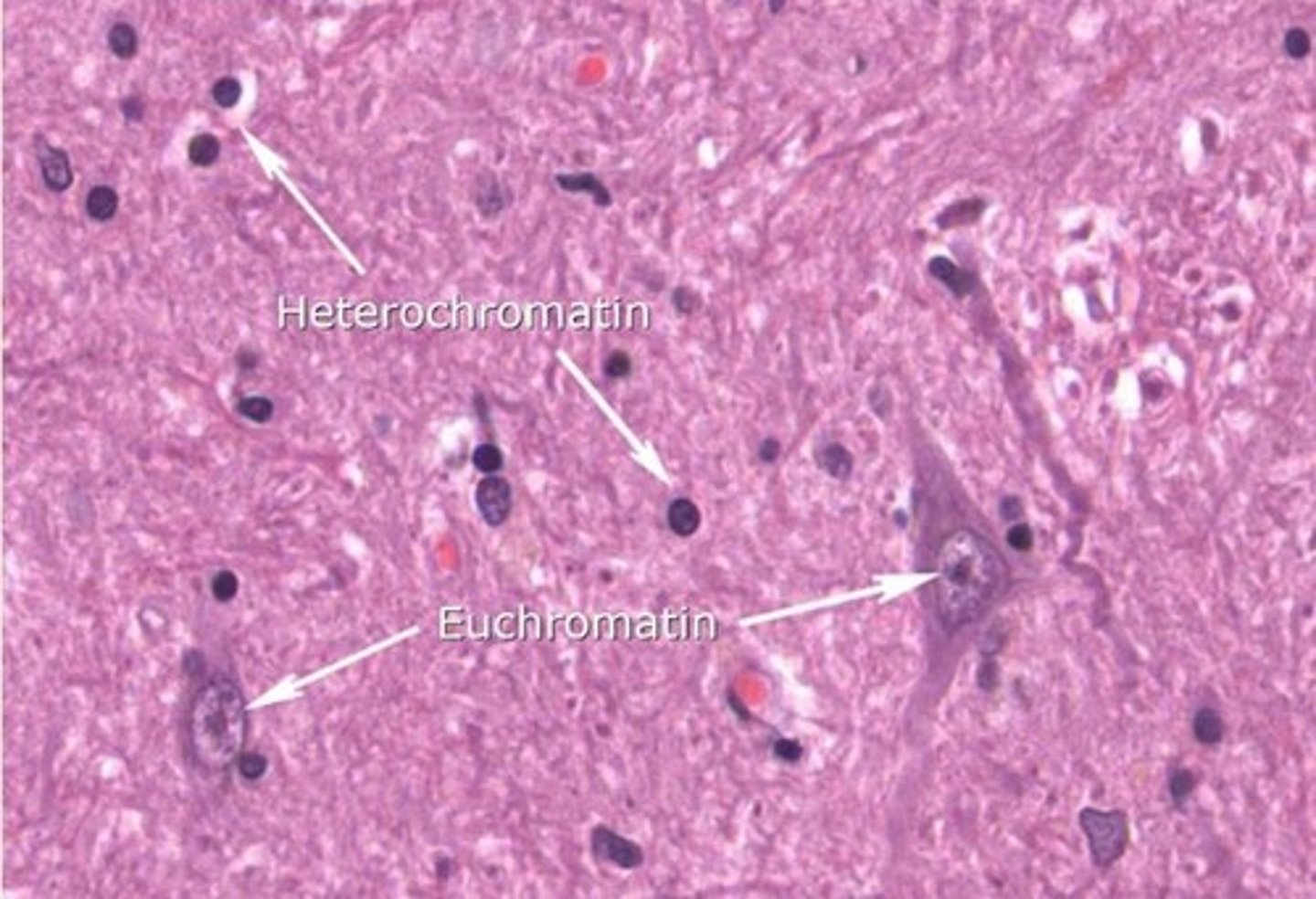
Where are Nissl bodies found?
Abundant in large nerve cells such as motor neurones
Nissl bodies
RER and free ribosomes in neurons = sites of protein synthesis
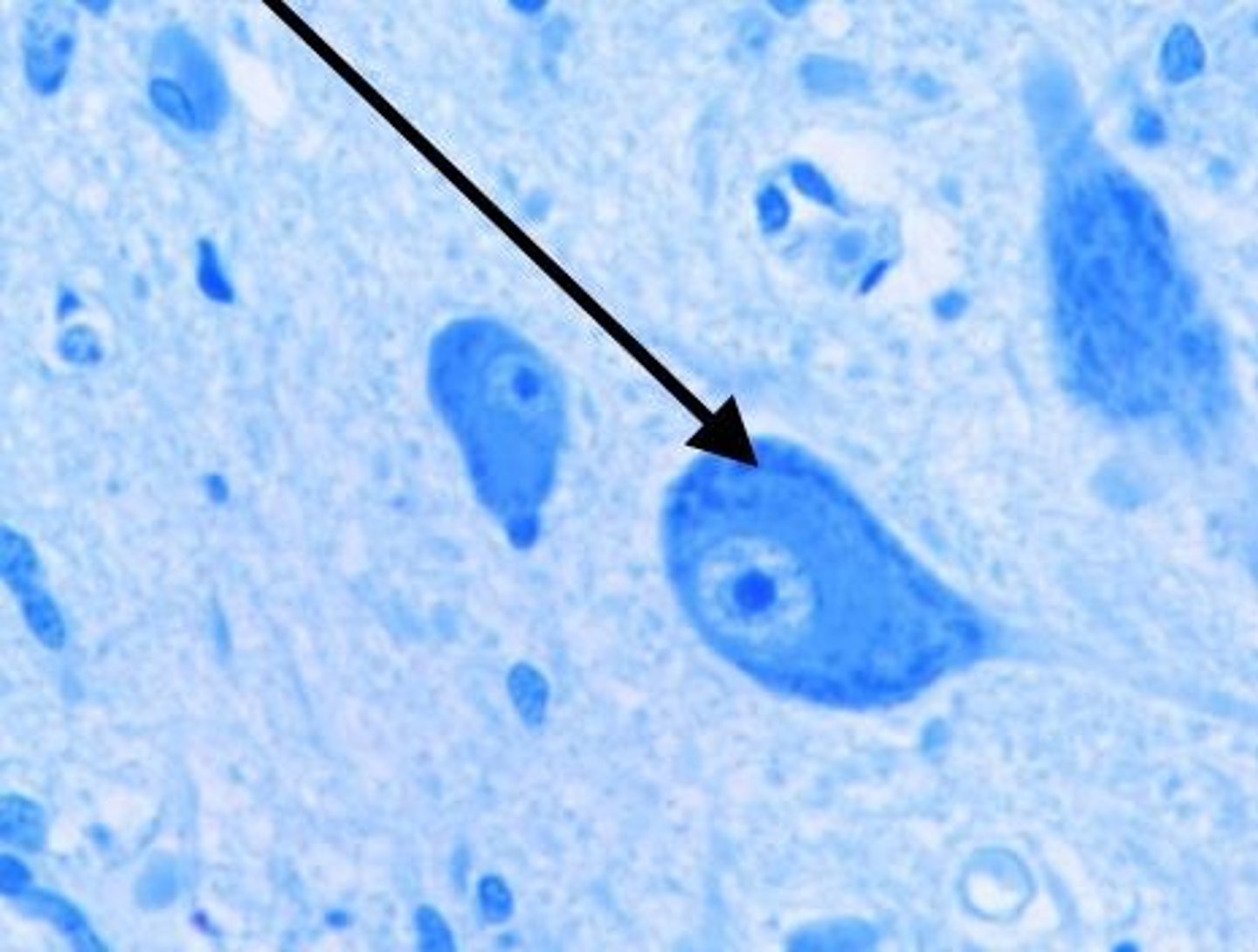
What factors must be considered when taking histological sections?
- Planes of section = region of interest may lie in a different plane
- Shape of cell being sectioned = e.g., RBC is biconcave
Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) stains are useful for revealing structures such as...
Basement membrane
Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) stains are useful for revealing what pathologies?
Diabetes
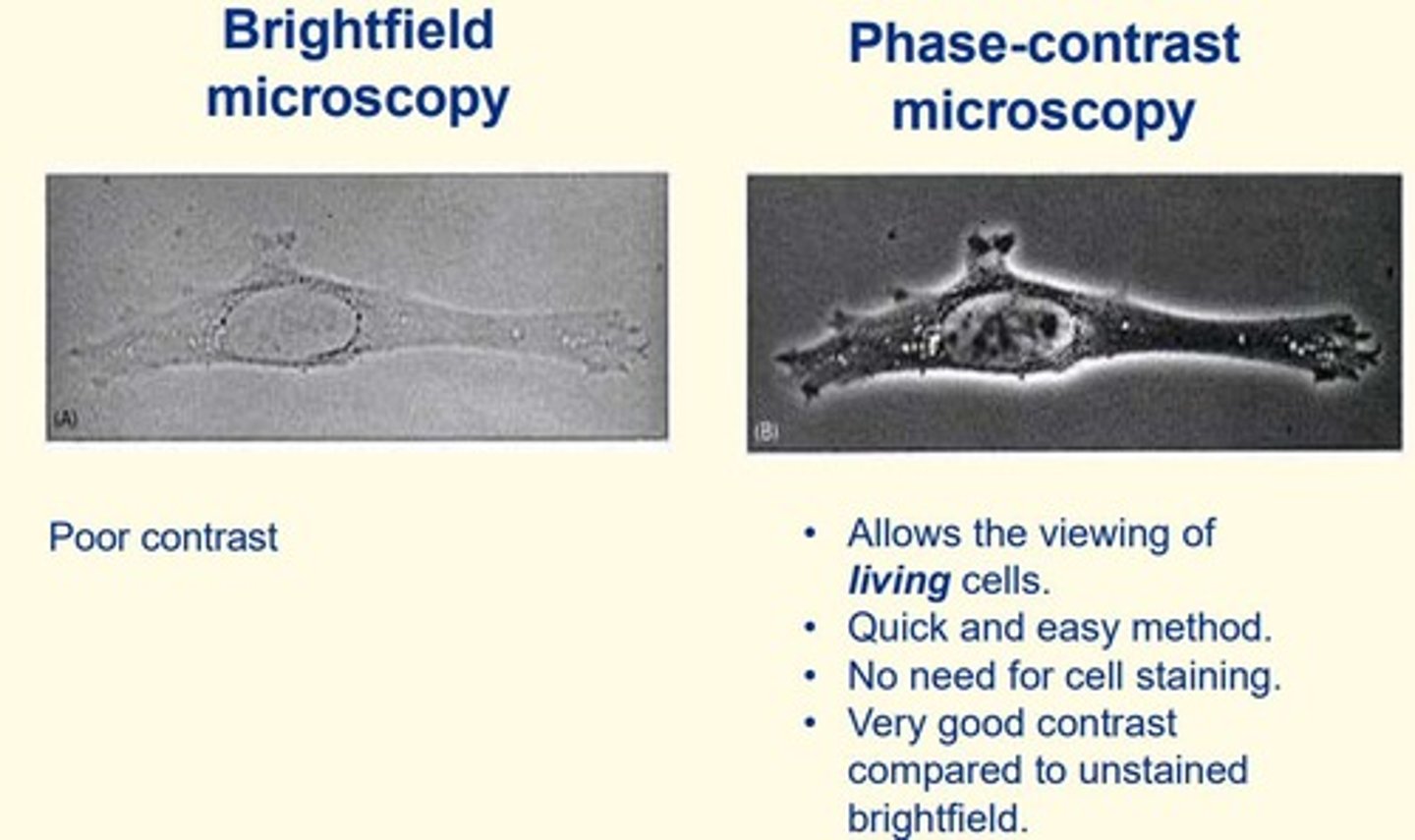
Phase-contrast microscopy
- Allows examination of living cells
- Quick and easy method
- No need for cell staining (cells unstained)
- Very good contrast compared to unstained brightfield microscopy
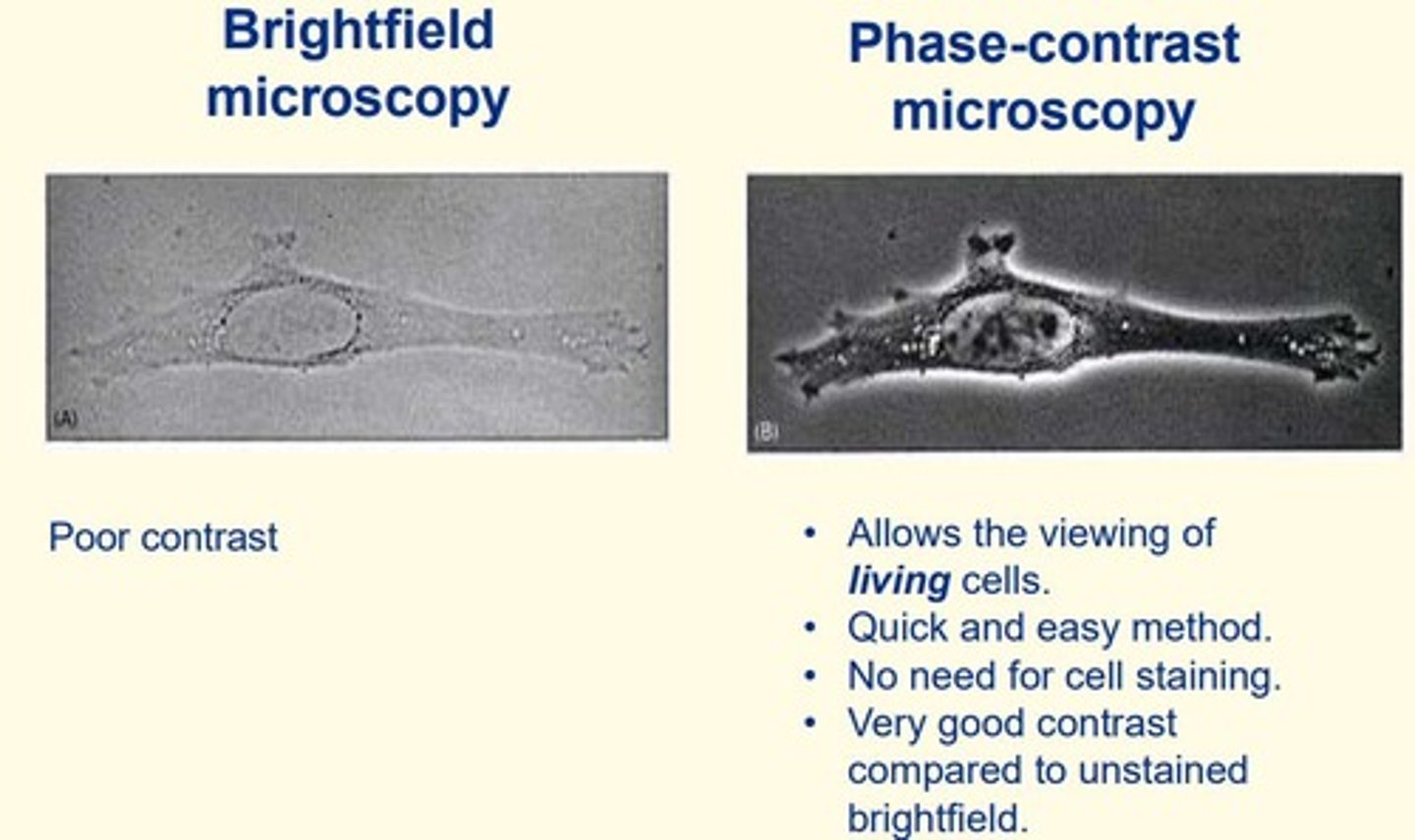
Brightfield microscopy
- Objects are dark and the field is light; can be used to observe unstained microorganisms
- Poor contrast
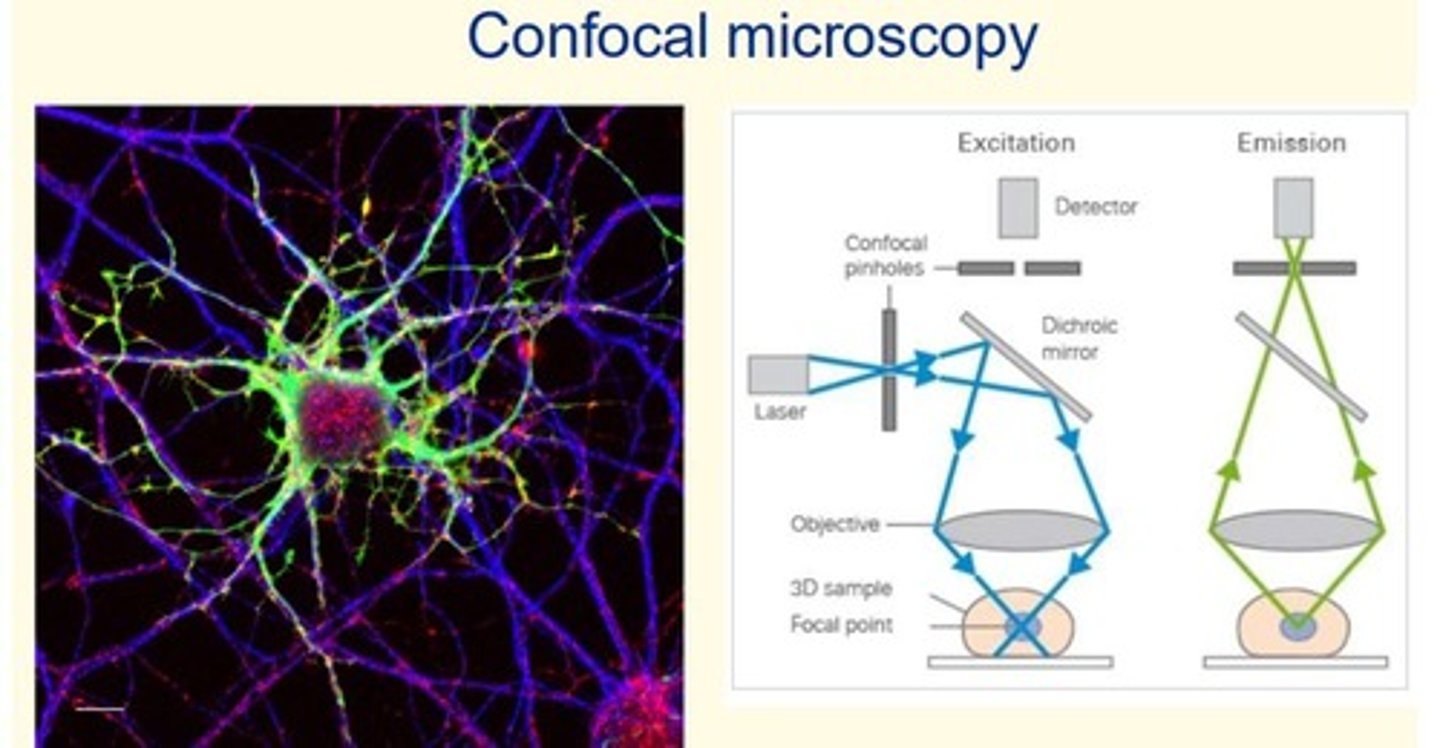
Confocal microscopy
- High resolution images with no out-of-focus light
- Stain specific proteins with fluorescent dyes/fluorescently-tagged antibodies = many applications
- 3D image construction
Darkfield microscopy
- Light objects are visible against a dark background
- Similar set-up to Brightfield
- Useful for diagnosing Treponema palliudum (syphilis)
- Useful for detecting Vibrio cholerae (cholera) in stool sample
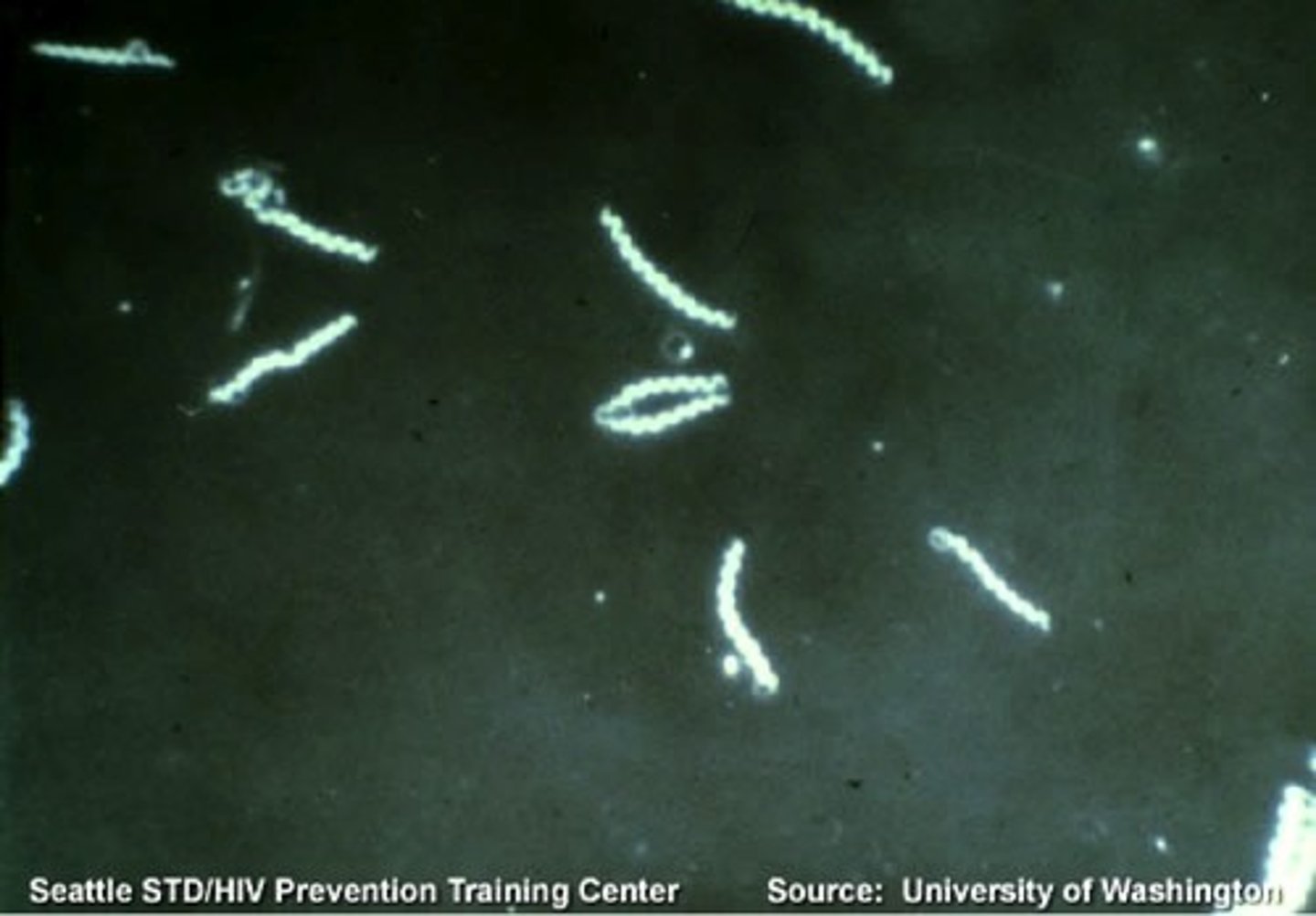
What two conditions is darkfield microscopy useful for identifying?
1) Treponema pallidum = syphilis
2) Vibrio cholerae = cholera
Why is it necessary to preserve fresh tissue? Give the most appropriate answer.
a) To preserve nucleic acids
b) All answers are correct
c) Prevent putrefaction
d) Preserve proteins
e) Maintain structure
b) All answers are correct
Why is it difficult to cut thin sections of fresh tissue? Give the most appropriate answer.
Select one:
a. Fresh tissue will blunt the microtome blade too quickly
b. Fresh tissue is too bloody
c. Fresh tissue is too fibrous to cut consistently
d. Fresh tissue is soft and will lose its integrity as the microtome blade passes through it
d) Fresh tissue is soft and will lose its integrity as the microtome blade passes through it
Which two of the following methods allow for the effective sectioning of tissues?
a. Heating
b. Embedding in a solid medium such as wax or plastic
c. Formalin fixation
d. Freezing (cryopreservation)
e. Clearing in xylene
f. Drying
b) Embedding in a solid medium such as wax or plastic
d) Freezing (cryopreservation)
Why is it difficult to infuse fresh tissue with wax?
Cells are mainly water, which doesn't mix with wax
Why might you wish to stain histological sections with haematoxylin and eosin?
a) To allow long-term storage
b) To preserve structure
c) To identify specific proteins
d) Thin tissues are translucent and must be stained to reveal structure
d) Thin tissues are translucent and must be stained to reveal structure
On which component of cells do fixatives primarily act?
Select one:
a) The cytoskeleton
b) Nucleic acids
c) Lipids
d) The plasma membrane
e) Proteins in general
e) Proteins in general
What is the most commonly used dehydrating agent?
Select one:
a) Formaldehyde
b) Wax
c) Xylene
d) Alcohol
e) Eosin
d) Alcohol
Order these cells from smallest to largest...
Keratinocytes
Neutrophils
RBCs
Oocytes
Smallest: RBC
Neutrophils
Keratinocytes
Largest: Oocytes