CHA101L Quiz 1
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/40
Earn XP
Last updated 11:57 PM on 1/16/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
1
New cards
Cervical enlargement
Larger part of the spinal cord (more superior) that contains sensory and motor neurons for the upper limb
2
New cards
Superior: Cervical enlargement
Inferior: Lumbosacral enlargement
Inferior: Lumbosacral enlargement
Identify
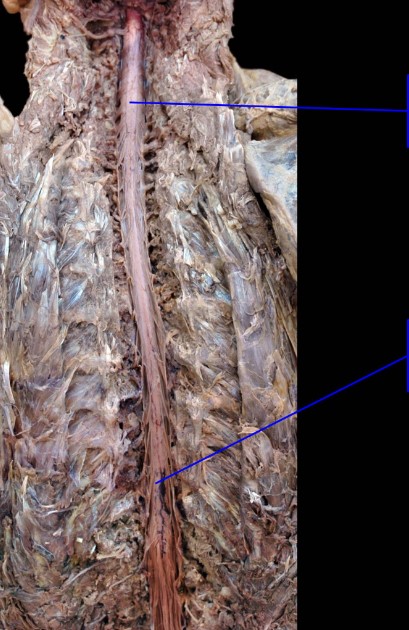
3
New cards
Lumbosacral enlargement
Larger part of the spinal cord (more inferior) that contains sensory and motor neurons for the upper limb
4
New cards
Conus Medullaris
Tapering inferior end of the spinal cord; typically found at the intervertebral disc between the L1 and L2 vertebrae
5
New cards
Conus Medullaris (tip)
Cauda equina
Filum terminale
Cauda equina
Filum terminale
Identify
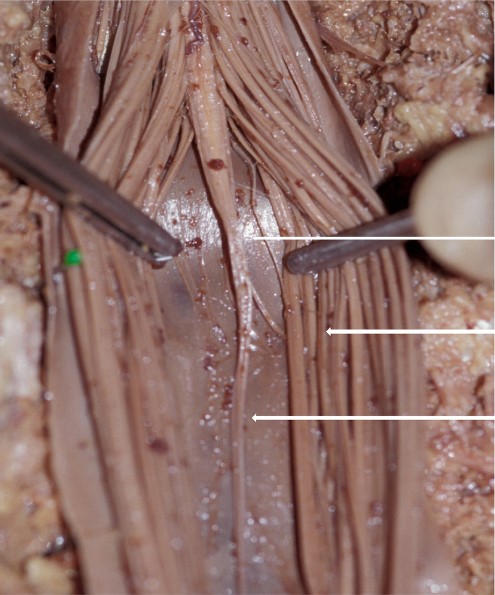

6
New cards
Dura Mater
Most superficial layer of the spinal meninges.
7
New cards
Arachnoid Mater
Spinal meninges layer deep to the dura, separated from it by a potential subdural space.
8
New cards
Pia Mater
The innermost meningeal layer, is a delicate, transparent covering. Closely invests the spinal cord and is not visible to the naked eye.
9
New cards
Epidural vs. Subdural vs. Subarachnoid
* Between the vertebrae and the dura mater
* Between the dura mater and arachnoid mater (potential space)
* Between the arachnoid mater and pia mater (filled with CSF)
* Between the dura mater and arachnoid mater (potential space)
* Between the arachnoid mater and pia mater (filled with CSF)
10
New cards
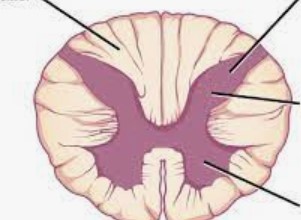
Top left: White matter
Top right: Gray matter
Right middle: Dorsal horn
Bottom Right: Ventral horn
Top right: Gray matter
Right middle: Dorsal horn
Bottom Right: Ventral horn
Identify
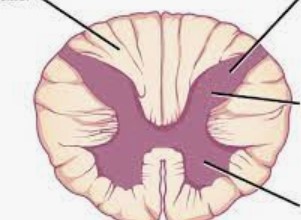
11
New cards
Dorsal rootlet
Emerge from posterior (dorsal) horns and converge to form the dorsal root
12
New cards
Ventral rootlet
Emerge from anterior (ventral) horns and converge to form the ventral root
13
New cards
Dorsal root
Before the spinal nerve, sensory only
14
New cards
Ventral root
Before the spinal nerve, motor only
15
New cards
Spinal nerve
Conversion of dorsal and ventral root, both sensory and motor
16
New cards
Dorsal root ganglion
Group of sensory neuron cell bodies, before the spinal nerve
17
New cards
Dorsal rami
Branching from spinal nerve, innervates sensory and motor information for the skin and muscles on the back.
18
New cards
Ventral rami
Branching from spinal nerve, innervates sensory and motor information to majority of the body.
19
New cards
Dermatome
Strip of skin innervated by one spinal nerve.
20
New cards
Myotome
Group of muscles innervated by one spinal nerve.
21
New cards
Nerve plexus
Network of nerves coming from ventral or dorsal rami
22
New cards
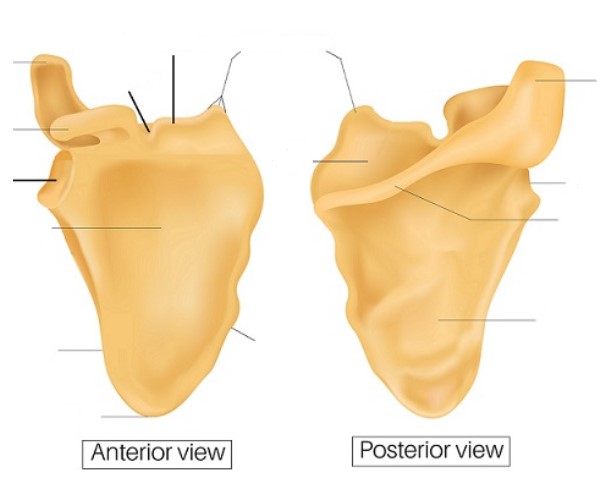
Left side: acromion, Coracoid process, glenoid cavity, subscapular fossa, lateral border, inferior angle
Right side: acromion, lateral angle, spine, infraspinous fossa
Middle (start left middle then move down, 5 total): scapular notch, superior border, superior angle, supraspinous fossa, medial border
Right side: acromion, lateral angle, spine, infraspinous fossa
Middle (start left middle then move down, 5 total): scapular notch, superior border, superior angle, supraspinous fossa, medial border
Identify
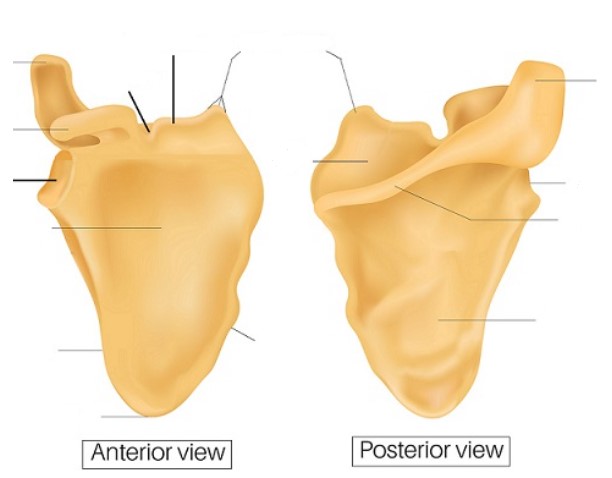
23
New cards
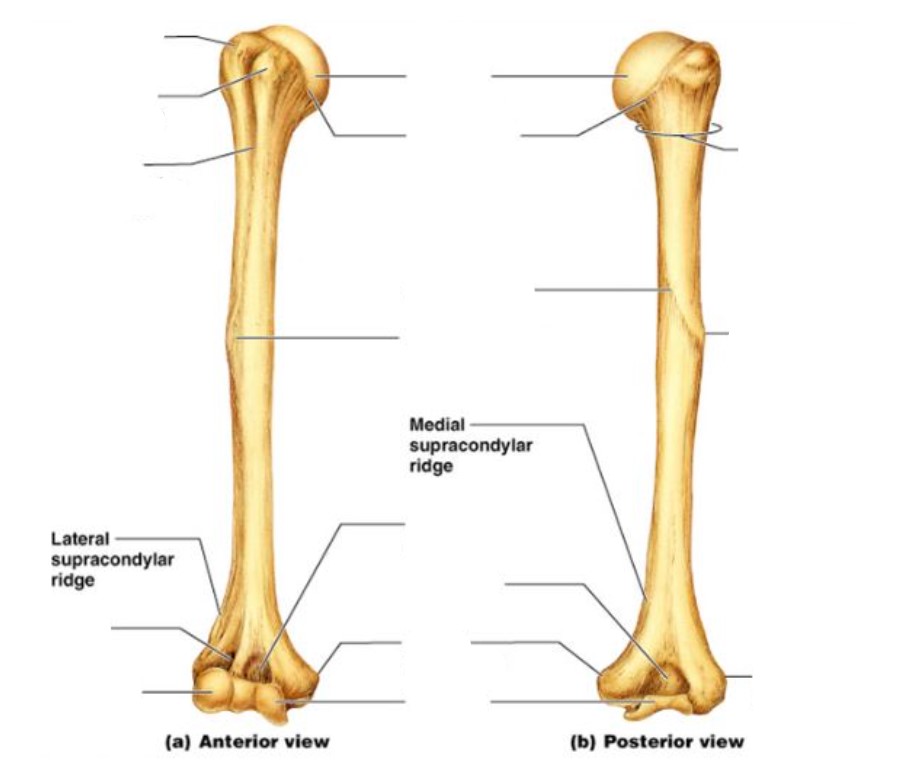
Left side: Greater tubercle, lesser tubercle, intertubercular groove, radial fossa/groove, capitulum
Right side: Surgical neck, deltoid tuberosity, lateral epicondyle
Middle: Head, anatomical neck, radial groove, deltoid tuberosity, coronoid fossa, olecranon fossa, medial epicondyle, trochlea
Right side: Surgical neck, deltoid tuberosity, lateral epicondyle
Middle: Head, anatomical neck, radial groove, deltoid tuberosity, coronoid fossa, olecranon fossa, medial epicondyle, trochlea
Identify
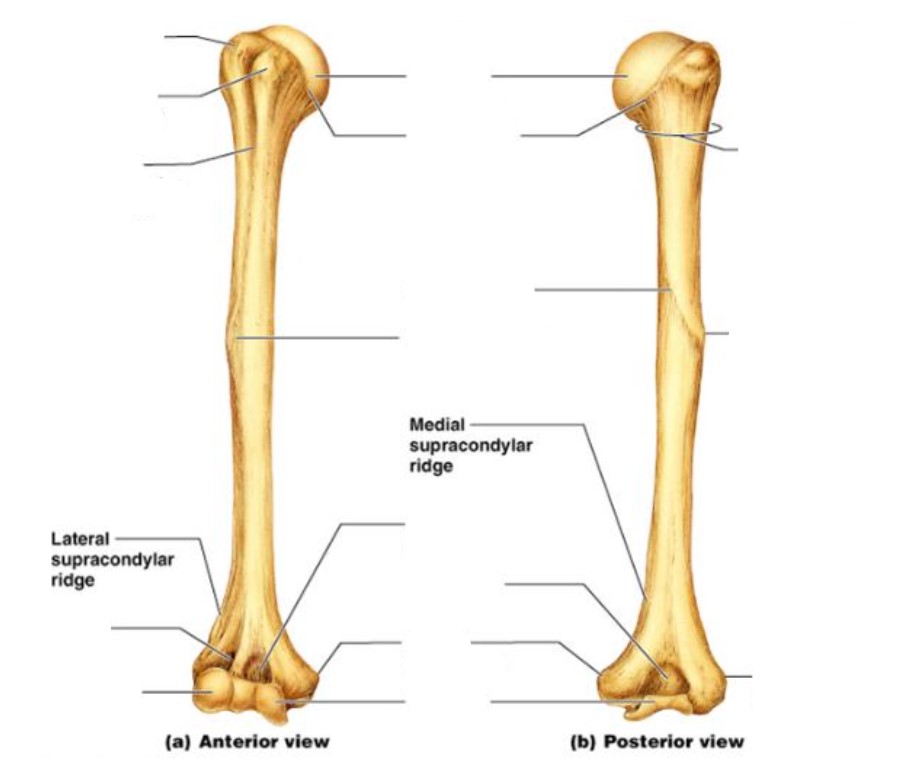
24
New cards
Anatomical and clinical importance of the surgical neck of the humerus
* Most common place for fracture
* Axillary nerve and posterior humeral circumflex branch of axillary artery are both at risk of being damaged if fracture occurs
* Axillary nerve and posterior humeral circumflex branch of axillary artery are both at risk of being damaged if fracture occurs
25
New cards
Anatomical and clinical importance of the radial (spiral) groove of the humerus
* Where the radial nerve and deep brachial artery runs through
* Any compression on that radial nerve can cause wrist drop
* Any compression on that radial nerve can cause wrist drop
26
New cards
Wrist drop
Compression of the radial nerve, which innervates many of the extensor muscles of the wrist, causing the flexor muscles to act unopposed.
27
New cards
Deltoid
* Origin: lateral 1/2 of clavicle, acromion, scapular spine
* Insertion: deltoid tuberosity
* Main actions (on arm): abduction (15-90), can help with all actions except adduction
* Innervation: axillary
* Insertion: deltoid tuberosity
* Main actions (on arm): abduction (15-90), can help with all actions except adduction
* Innervation: axillary
28
New cards
Pectoralis major
* Origin: medial 1/2 of clavicle, sternum, ribs 1-6
* Insertion: intertubercular groove of humerus (lateral)
* Main actions (on arm): adduction, flexion, medial rotation
* Innervation: medial and lateral pectoral
* Insertion: intertubercular groove of humerus (lateral)
* Main actions (on arm): adduction, flexion, medial rotation
* Innervation: medial and lateral pectoral
29
New cards
Latissimus dorsi
* Origin: spinous process of thoracic, lumbar, and sacral vertebrae, iliac crest
* Insertion: intertubercular groove of humerus
* Main actions (on arm): adduction, extension, medial rotation
* Innervation: thoracodorsal
* Insertion: intertubercular groove of humerus
* Main actions (on arm): adduction, extension, medial rotation
* Innervation: thoracodorsal
30
New cards
Teres major
* Origin: inferior angle of scapula
* Insertion: intertubercular groove of humerus (medial)
* Main actions (on arm): adduction, medial rotation
* Innervation: lower subscapular
* Insertion: intertubercular groove of humerus (medial)
* Main actions (on arm): adduction, medial rotation
* Innervation: lower subscapular
31
New cards
Coracobrachialis
* Origin: coracoid process
* Insertion: medial side of humeral shaft
* Main actions (on arm): flexion, adduction
* Innervation: musculocutaneous (pierces the muscle)
* Insertion: medial side of humeral shaft
* Main actions (on arm): flexion, adduction
* Innervation: musculocutaneous (pierces the muscle)
32
New cards
Supraspinatus
* Origin: supraspinous fossa of scapula
* Insertion: greater tubercle of humerus
* Main actions (on arm): abduction (0-15)
* Innervation: suprascapular
* Insertion: greater tubercle of humerus
* Main actions (on arm): abduction (0-15)
* Innervation: suprascapular
33
New cards
Infraspinatus
* Origin: infraspinous fossa of the scapula
* Insertion: greater tubercle of humerus
* Main action (on arm): lateral rotation, adduction
* Innervation: suprascapular
* Insertion: greater tubercle of humerus
* Main action (on arm): lateral rotation, adduction
* Innervation: suprascapular
34
New cards
Teres minor
* Origin: lateral border of scapula
* Insertion: greater tubercle of humerus
* Main actions (on arm): lateral rotation, adduction
* Innervation: axillary
* Insertion: greater tubercle of humerus
* Main actions (on arm): lateral rotation, adduction
* Innervation: axillary
35
New cards
Subscapularis
* Origin: subscapular fossa
* Insertion: lesser tubercle of humerus
* Main actions (on arm): medial rotation, adduction
* Innervation: upper and lower subscapular
* Insertion: lesser tubercle of humerus
* Main actions (on arm): medial rotation, adduction
* Innervation: upper and lower subscapular
36
New cards
Trapezius
* Origin: occipital bone, spinous processes of C7-T12
* Insertion: lateral 1/3 of clavicle, scapular spine, acromion
* Main actions (on scapula): retraction, medial and lateral rotation, elevation, depression, extension of neck
* Innervation: cranial nerve XI
* Insertion: lateral 1/3 of clavicle, scapular spine, acromion
* Main actions (on scapula): retraction, medial and lateral rotation, elevation, depression, extension of neck
* Innervation: cranial nerve XI
37
New cards
Rhomboid minor
* Origin: spinous processes of C7 and T1
* Insertion: medial border of the scapula at the base of the scapular spine
* Main actions (on scapula): retraction, medial rotation
* Innervation: dorsal scapular
* Insertion: medial border of the scapula at the base of the scapular spine
* Main actions (on scapula): retraction, medial rotation
* Innervation: dorsal scapular
38
New cards
Rhomboid major
* Origin: spinous processes of T2-T5
* Insertion: medial border of the scapula below the scapular spine
* Main actions (on scapula): retraction, medial rotation
* Innervation: dorsal scapular
* Insertion: medial border of the scapula below the scapular spine
* Main actions (on scapula): retraction, medial rotation
* Innervation: dorsal scapular
39
New cards
Levator scapulae
* Origin: transverse process of C1-C4
* Insertion: medial border of the scapula above the scapular spine
* Main actions (on scapula): elevation, medial rotation
* Innervation: dorsal scapular
* Insertion: medial border of the scapula above the scapular spine
* Main actions (on scapula): elevation, medial rotation
* Innervation: dorsal scapular
40
New cards
Pectoralis minor
* Origin: ribs 3-5
* Insertion: coracoid process of scapula
* Main actions (on scapula): protraction, scapular stabilization
* Innervation: medial pectoral
* Insertion: coracoid process of scapula
* Main actions (on scapula): protraction, scapular stabilization
* Innervation: medial pectoral
41
New cards
Serratus anterior
* Origin: lateral surface of ribs 1-8
* Insertion: anterior surface of medial border of scapula
* Main actions (on scapula): lateral rotation, protraction, holds scapula against ribcage
* Innervation: long thoracic
* Insertion: anterior surface of medial border of scapula
* Main actions (on scapula): lateral rotation, protraction, holds scapula against ribcage
* Innervation: long thoracic