Electric Circuits
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Current (I)
Rate at which charge carriers pass through a cross-sectional area of a wire
Drift Velocity
Average velocity of charge carriers due to an electric field
Why do charged particles drift?
Electric Potential difference
Conventional current moves in the _______ flow of the charges.
Positive
Real current follows the flow of ____________ charge carriers.
Negative
Current flows on a _________ _______.
Closed Path
What must be present so current is able to flow?
Potential Difference
Electrical Resistance
Measure of how much an onject resists the flow of charge
Resistivity
Property of a material that describes how much that material resists the flow of electrical charge
What happens to potential difference (V) as current increases?
Increases
What happens to current as resistance increases?
Decreases
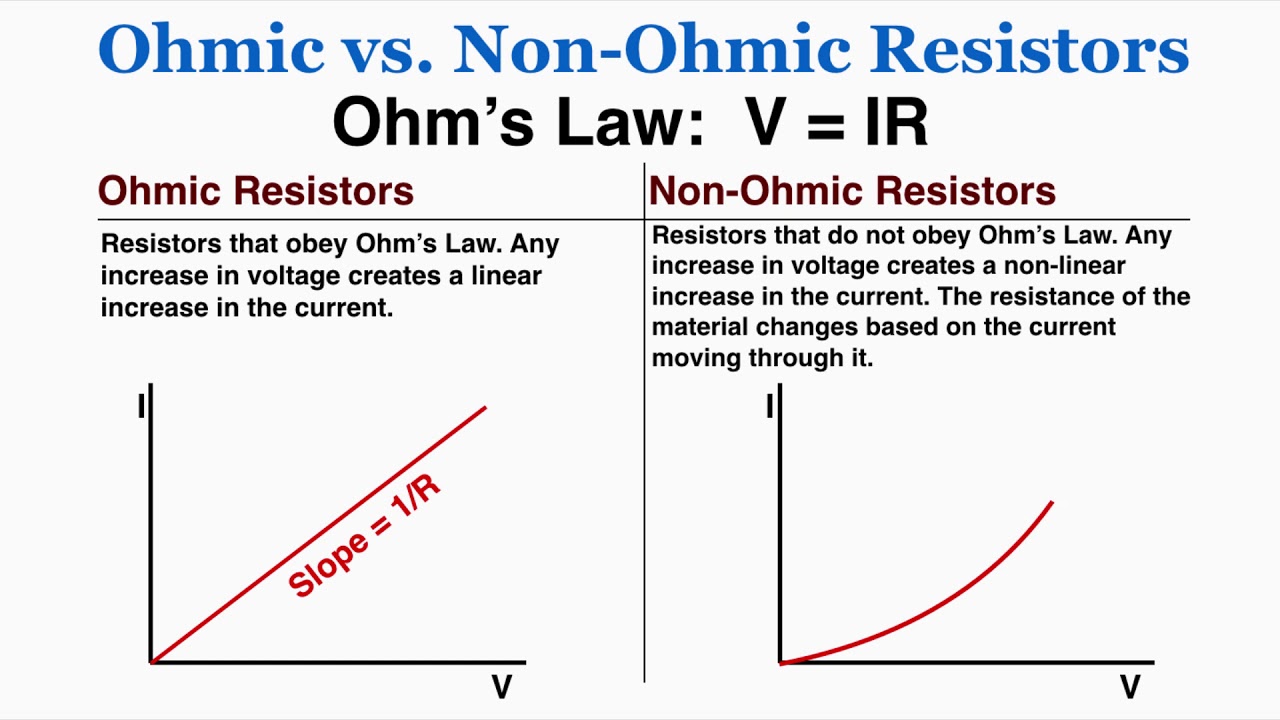
What is an ohmic circuit?
It follows Ohm’s Law.
Power
Rate at which work is done
Equations of Power
P = IV
P = I2 R
P = V2R
The brighter the light bulb the more ______ is dissipating.
Power; More Power = More Brightness
What remains the same in a series circuit?
Current
When resistors are added to a series circuit, what happens to the resistance of the entire circuit?
Increases
When resistors are added to a parallel circuit, what happens to the resistance of the entire circuit?
Decreases
What remains the same in a parallel circuit?
Voltage
Internal Resistance of a Battery Equation

Voltermeters
Measure the potential difference between any two points in a circuit
How must voltmeters be connected?
In Parallel
Ammeter
Measure the current at a specific point in a circuit
How must voltmeters be connected?
In series with the element of which the current is being measured
Kirchoff’s Loop Rule
The sum of the potential differences across all the circuit elements must be equal to 0
What happens when we are moving in the opposite direction that the current is moving?
Increase in potential difference
Kirchoff’s Junction Rule
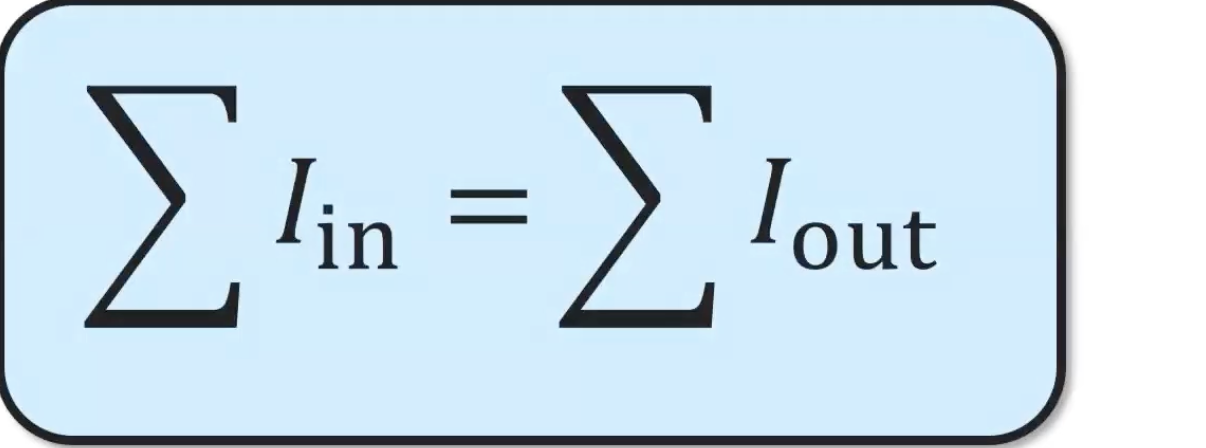
After a capacitor has been charging for a long time, what will the potential difference (V) be.
Zero