Pre AP Biology Chapter 10
1/38
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
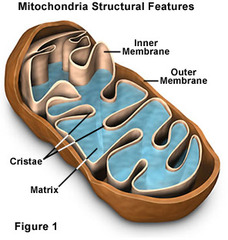
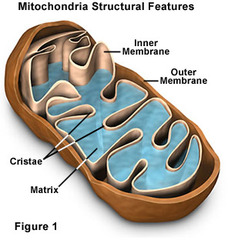
Matrix
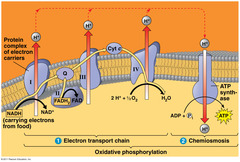
the space inside the inner membrane where the krebs cycle takes place
Intermembrane space
The space between the inner and outer membranes where H+ ions accumulate during the ETC
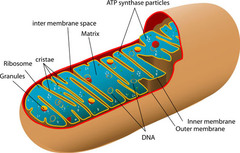
Outer mitochondrial membrane
The outer membrane of the mitochondria.
Inner Mitochondrial Membrane
The folded inner membrane of the mitochondria. The site of the ETC and ATP synthesis.
Calorie
Amount of energy needed to raise temperature 1 gram of water 1 degree C
kilocalorie
a unit of energy equal to 1,000 calories or 1 food calorie

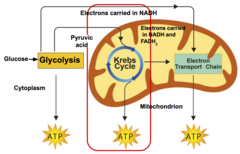
cellular respiration
the process of energy conversion that releases chemical energy stored in food in the presence of oxygen.
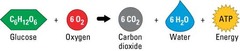
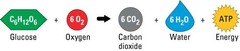
chemical formula for cellular respiration
C6H12O6 + O2 --> CO2 + H2O + ATP
aerobic
Process that requires oxygen
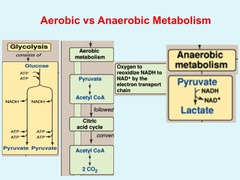
anaerobic
Process that does not require oxygen
Where do organisms get energy?
Organisms get the energy they need from food.
What is Cellular Respiration?
Cellular respiration is the process that releases energy from food in the presence of oxygen.
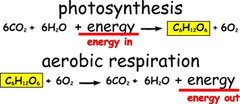
What is the relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
Photosynthesis removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, and cellular respiration puts it back. Photosynthesis releases oxygen into the atmosphere, and cellular respiration uses that energy to release energy from food.
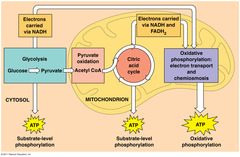
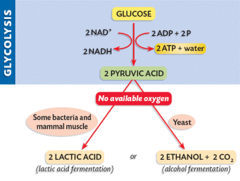
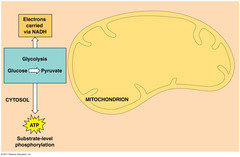
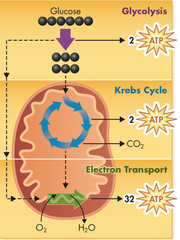
glycolysis
first step in releasing the energy of glucose, in which a molecule of glucose is broken into two molecules of pyruvic acid
location of glycolysis
cytoplasm
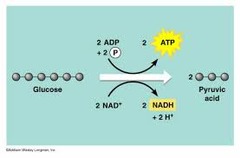
What happens during the process of glycolysis?
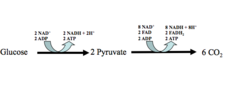
During glycolysis, 1 molecule of glucose, a 6-carbon compound, is transformed into 2 molecules of pyruvic acid, a 3-carbon compound
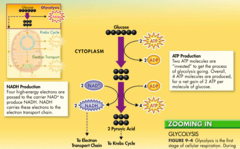
Products of glycolysis
2 pyruvate (pyruvic acid), 2 net ATP (4 total ATP), 2 NADH, 2 ADP
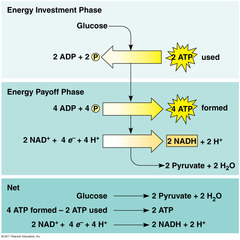
Reactants of glycolysis
glucose, 2 ATP, 2 NAD+, 4 ADP
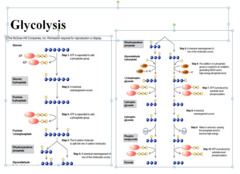
is glycolysis aerobic?
It is anaerobic as it does not require the presence of oxygen.
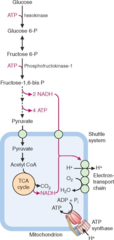
What happens during the Kreb's cycle?
During the Krebs cycle, pyruvic acid is broken down into carbon dioxide in a series of energy-extracting reactions.
How does the electron transport chain use high energy electrons from glycolysis and the Kreb's Cycle?
The electron transport chain uses the high energy electrons from glycolysis and the Kreb's Cycle to synthesize ATP from ADP
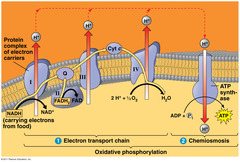
How much ATP does cellular respiration generate?
Together, glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain release about 36 molecules of ATP per molecule of glucose.
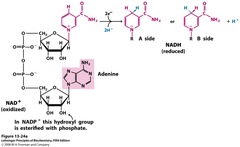
NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide)
an organic molecule that serves as an electron carrier by accepting a pair of high energy electrons and a hydrogen ion, becoming NADH
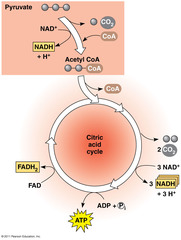
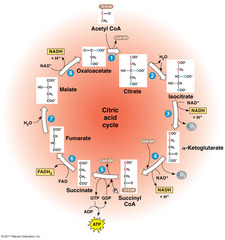
Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle)
second stage of cellular respiration, in which pyruvic acid is broken down into carbon dioxide in a series of energy-extracting reactions
matrix
the innermost compartment of the mitochondrion and the site of the Krebs cycle reactions
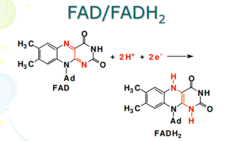
FAD (flavin adenine dinucleotide)
An energy carrier that accepts electrons from the Kreb's cycle and feeds them into the electron transport chain
Location of the Kreb's Cycle
mitochondrial matrix
Reactants of Krebs Cycle
pyruvic acid, NAD+, ADP, FAD
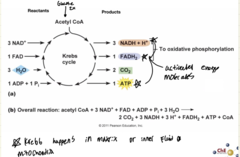
Products of Kreb's Cycle
CO2, NADH, FADH2, ATP
Waste product of cellular respiration
carbon dioxide (CO2)
Fermentation
Process by which cells make ATP via glycolysis in the absence of oxygen
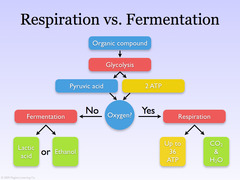
How do organisms generate energy when oxygen is not available?
In the absence of oxygen, fermentation releases energy from food molecules by producing ATP.
How does the body produce ATP during different stages of exercise? (for short quick burst of energy)
the body uses ATP already in muscles as well as ATP made by lactic acid fermentation
How does the body produce ATP during different stages of exercise? (for exercise longer than about 90 seconds)
cellular respiration is the only way to generate a continuous supply of ATP
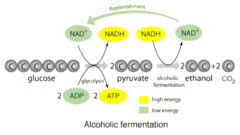
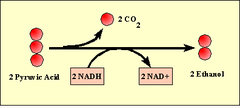
alcoholic fermentation
anaerobic process in which cells convert pyruvic acid into carbon dioxide and ethyl alcohol; carried out by many bacteria and fungi such as yeasts
lactic acid fermentation
The conversion of pyruvate to lactate with no release of carbon dioxide.
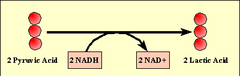
reactants of fermentation
pyruvic acid and NADH
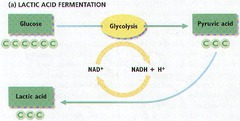
products of lactic acid fermentation
NAD+ and lactic acid
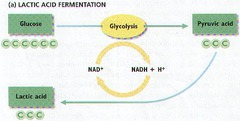
products of alcoholic fermentation
Alcohol, CO2, NAD+