N209 - Heart & Neck Vessels
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Diastole
2/3
What is occurring when the ventricles are relaxed & the AV valves are open? How much of the cardiac cycle does this make up?
Protodiastolic (early) filling
What is the passive filling phase (blood going down its gradient & into ventricles) of diastole?
Presystole/atrial systole/ atrial kick
What is the active filling phase (atria contracts and pushes the last amount of blood into ventricles after pressure equalizes) of diastole called?
Systole
1/3
What is occurring when blood is pumped from the ventricles & fills the pulmonary & systemic arteries? How much of the cardiac cycle does this make up?
ventricular diastole
What is occurring at the same time as atrial systole?
Isometric contraction
= ventricles contract but blood is not ejected bc all valves are closed (inc. pressure in ventricles)
Isometric relaxation
= all valves are closed & ventricles are relaxed
right side
requires less energy to pump to the pulmonary circuit than the left to systemic circuit
Which side of the heart has less pressure? Why?
S1
Sound of AV valves being forced closed (beginning of systole
Heard loudest @ the apex
S2
Sound from closure of the semilunar valves (end of systole & beginning of diastole)
Heard loudest @ the base
s3
Occurs when ventricles are resistant to filling during protodiastole immediately after S2
when AV valves open and atrial blood first pours into ventricles
= a dull, soft sound
Can be found in Pregnancy, fever; isn’t pathologic (goes away after)
s4
Occurs at end of diastole, at presystole, when ventricle resistant to filling
Atria contracts and pushed blood into the noncompliant ventricle
occurs just before S1
s4
daLUB-dub
s3
LUB-duppa
murmurs
= Gentle, blowing, swooshing sound that can be heard on chest wall
Occurs with Conditions that create turbulent blood flow & collision currents
Velocity of blood increases (flow murmur)
Viscosity of blood decreases (e.g., anemia)
Structural defects in valves (narrowed valves, regurgitant valves)
What conditions can result in murmurs?
Diastolic
What murmurs always indicate heart disease?
pulse
= a pressure wave generated by each systole pumping blood into the aorta
a smooth rapid upstroke, followed by a rounded and smooth summit, followed by a gradual downstroke.
How would you describe this pulse?

Carotid Artery
Where would you find this pulse?

Jugular veins
Which vein empties unoxygenated blood directly into superior vena cava?
Carotid
What vein in the neck are you evaluating if the pt. is sitting up?
Jugular Veins
What vein in the neck are you evaluating if the pt. is supine & slightly elevated?
Precordium
= the area directly overlying the heart and great vessels.
Pulse & BP
Extremities
Neck Vessels
Precordium
In what order would you do a regional cardiovascular assessment?
central venous pressure (CVP)
it’s efficiency as a pump
What does assessing the jugular vein tell you about the heart?
1-2 cm above the clavicle
Where should the jugular vein be visible normally?
Jugular Vein Distension (JVD)
fluid overload
What is visible in the image? Why might this have occurred?
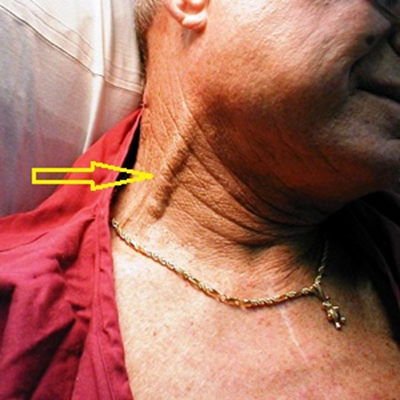
Jugular Vein
Location = lower, more lateral, under or behind the sternomastoid muscle
Quality - undulant (wavelike), w 2 visible waves per cycle
Respiration - descends during inspiration (intrathoracic pressure)
Palpable - no
Pressure - light pressure @ the base of the neck
Position of the person - drops/disappears when sitting up
Carotid Artery
Location - higher & medial to sternomastoid muscle
Quality - brisk & localized; 1 wave per cycle
Respiration - does not vary
Palpable - yes
Pressure - no change
Position of the person - unaffected
doing both can compromise blood flow to the brain
Why shouldn’t you palpate both carotids at the same time?
doing this could slow down the HR & cause syncope.
Why should you avoid excessive pressure on the carotid sinus area?
+2 (moderate)
What should the strength of the carotid be?
bruit
= blowing, swishing sound heard in blood vessels that indicates blood flow turbulence
can be artificially created if an artery is compressed
atherosclerosis
What is a bruit when auscultating the carotid a marker for?
otherwise, you’ll hear tracheal breaths.
hold your breath w the pt. so you are conscious of how long they’ve held it.
Why should you ask a pt to hold their breath when auscultating the carotid? What practice should you yourself do during this?
angle of the jaw
midcervical area
base of the neck
At what 3 places should you auscultate the carotid artery?
arrange tangential lighting to accentuate flickers of movement
How should you inspect for any pulsations on the anterior chest?
apical pulse
What is the ONLY pulse that you should visibly see on the anterior chest normally?
left midclavicular, 4th or 5th intercostal space
Where is the apical pulse located?
the base, the left sternal border and the apex
you should only feel a pulsation the apical pulse
What should you palpate on the anterior chest and what should you feel?
Retractions
= pulling of tissue with heart beats (abnormal)
Lifts
= strong, sustained outward thrusts
Heaves
= excessive thrust of larger area of the chest
NO! the sound radiates with the direction of blood flow
Should you hear the valve sounds over their anatomical position? Why or why not?
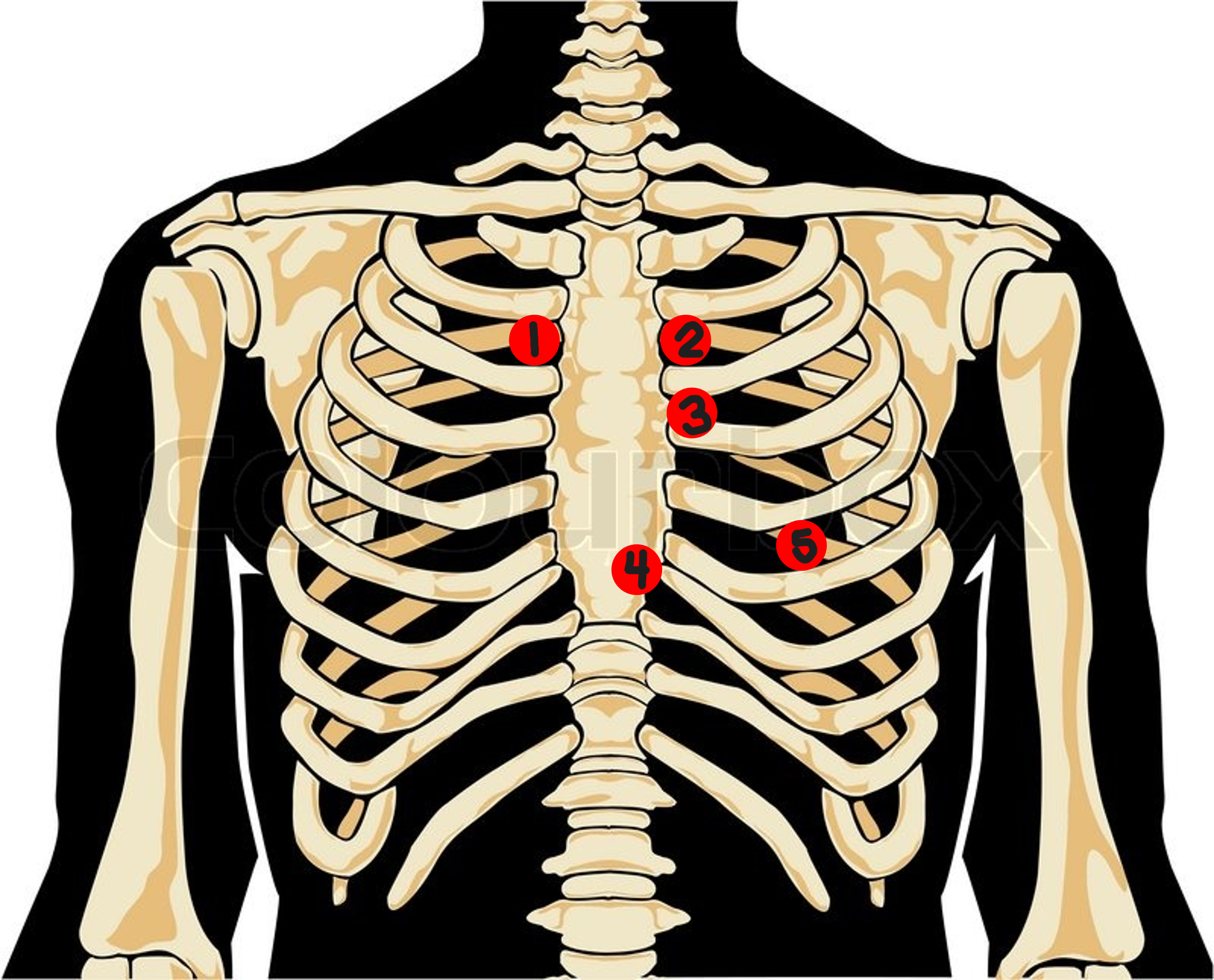
Aortic Valve Area
right 2nd interspace
#1? How would you describe this location?
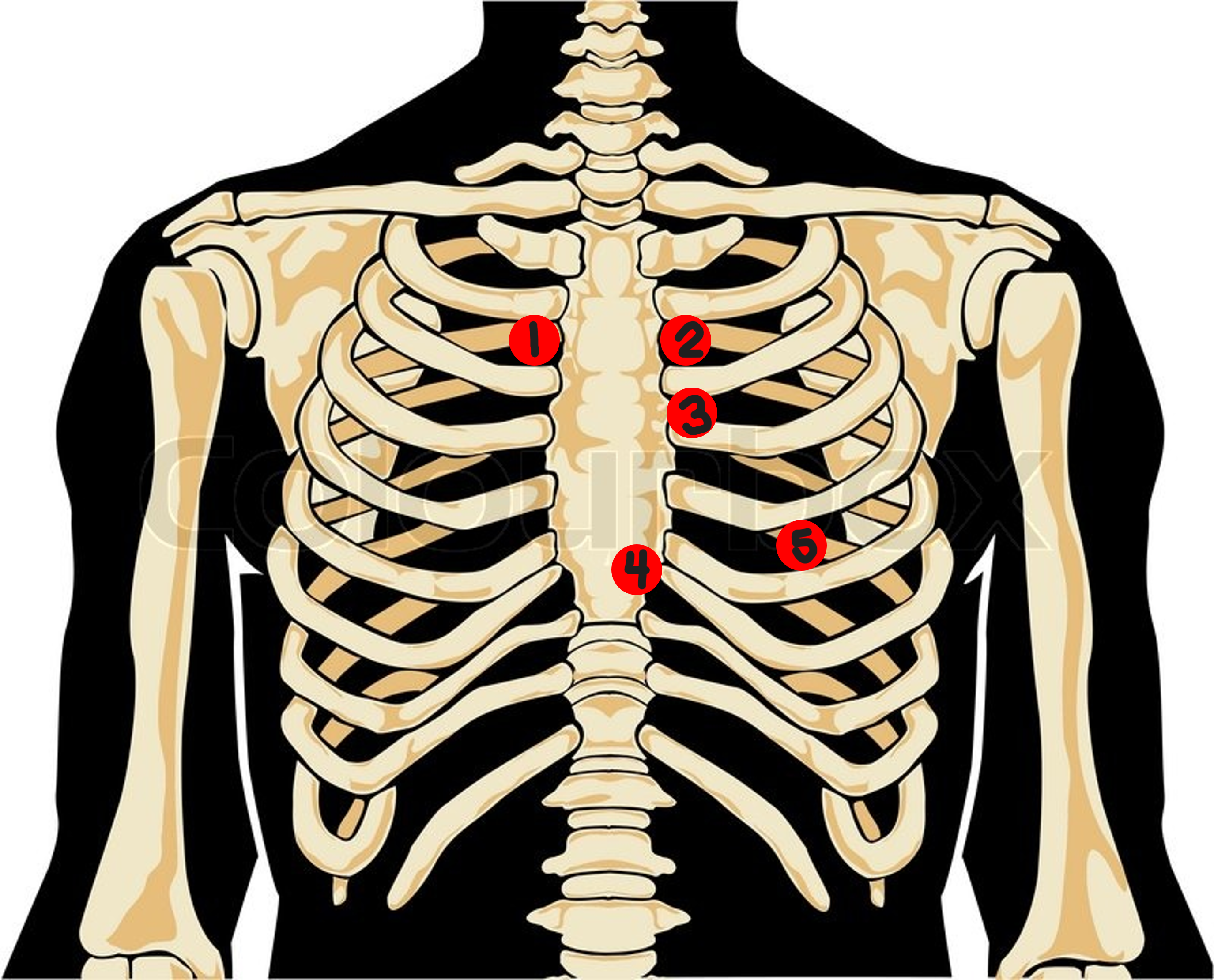
pulmonic valve area
left 2nd interspace
#2? How would you describe this location?
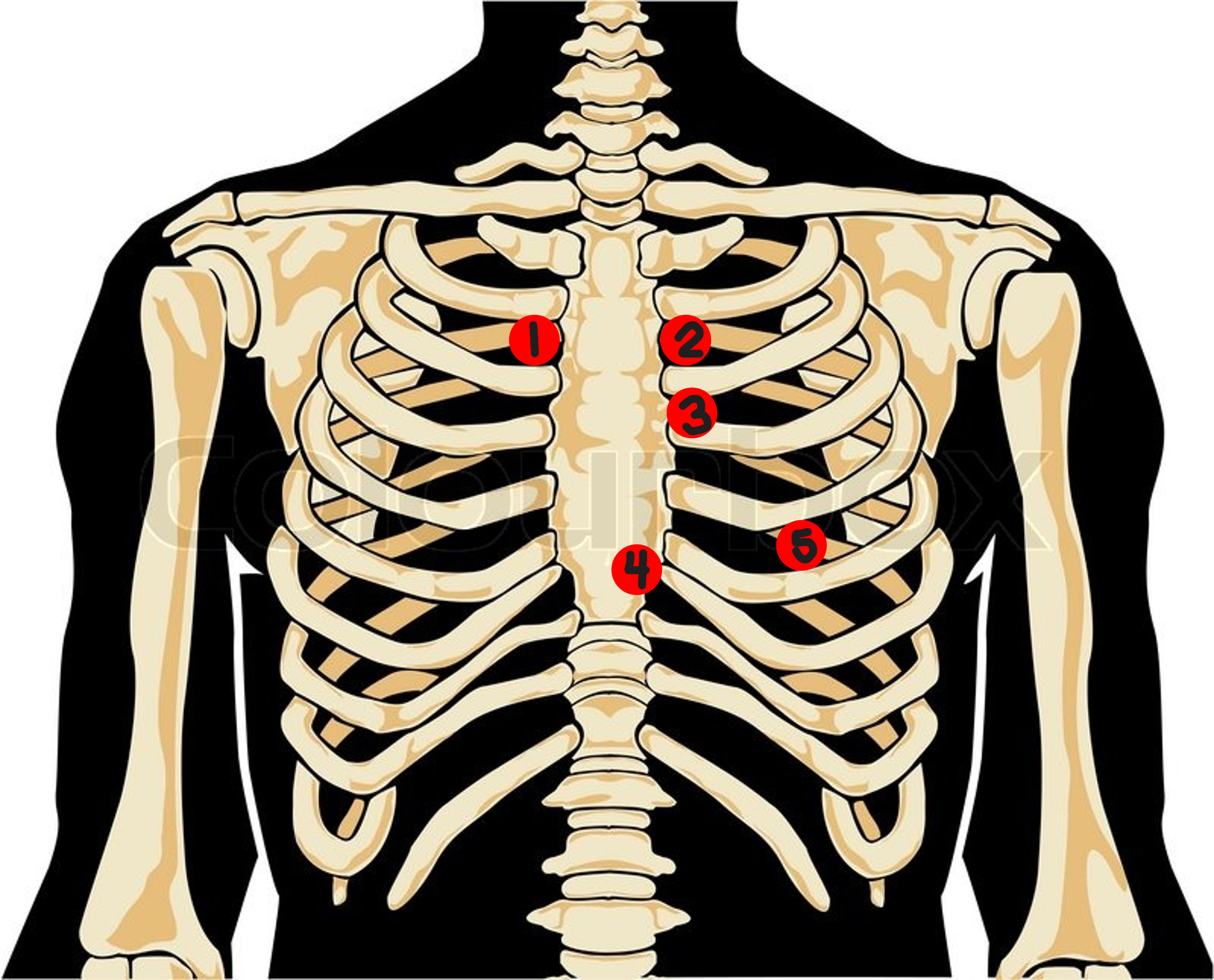
Erb’s Point
left 3rd interspace
#3? How would you describe this location?
Tricuspid Valve Area
left sternal border
#4? How would you describe this location?
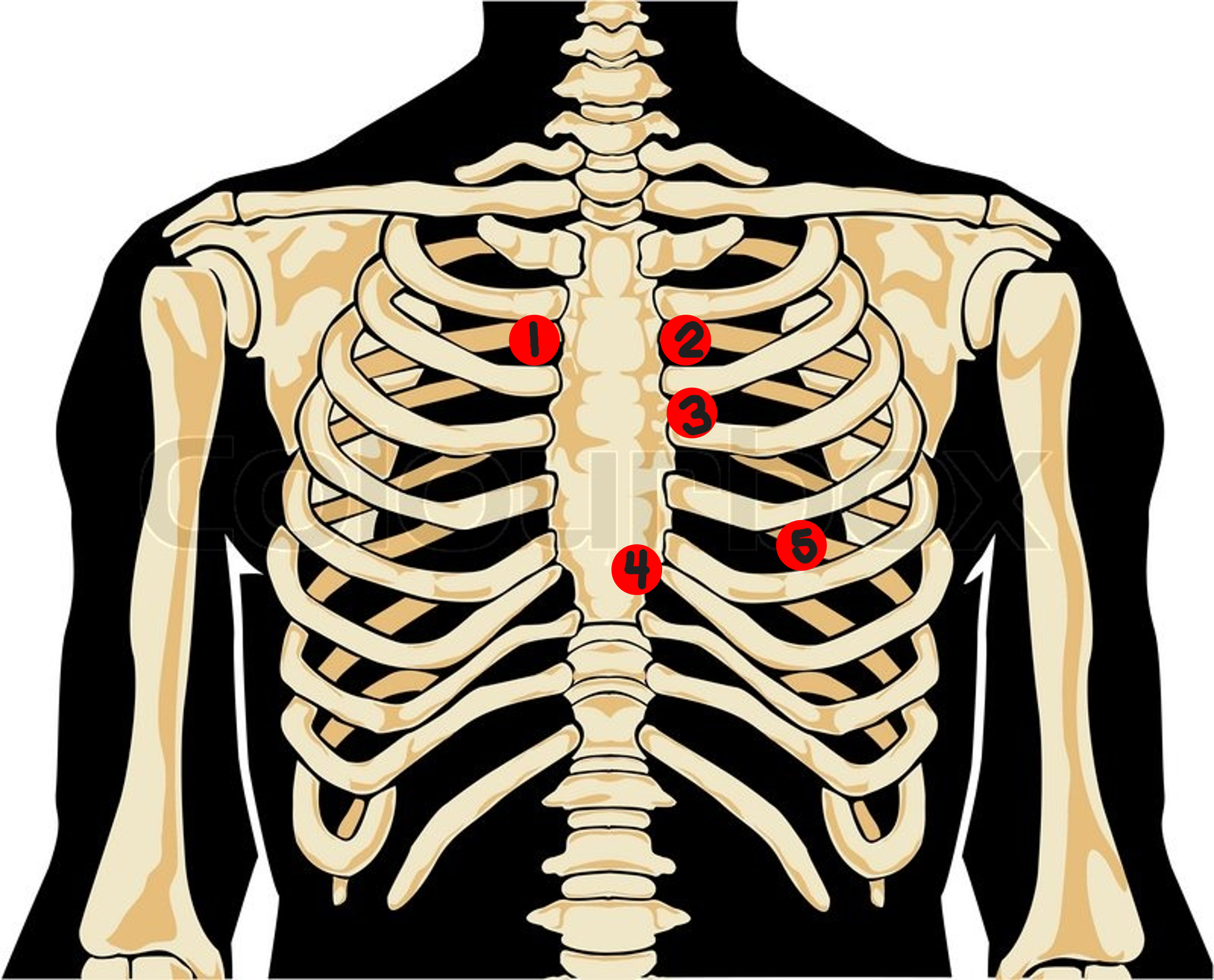
Mitral Valve Area
5th interspace, midclavicular
#5? How would you describe this location?
auscultate the apical beat while palpating the radial pulse
How would you check for pulse deficit?
left lateral recumbent
(Brings the heart closer to the chest wall)
what position is best for auscultating the heart?
Split S1
= a normal variation of asynchronous valves (hearing the mitral and tricuspid components separately)
Loud (accentuated) S1
= variation in S1 from increased velocity of blood flow
due to exercise, fever, anemia & pulmonary stenosis
Split S2
= normal variation heard @ the end of inspiration in some people
inspiration separates the timing of the semilunar valves closing.
Fixed split
= abnormal S2 split that is unaffected by respirations & always present
Midsystolic click
= extra systolic sound from mitral valve prolapse; tensing of valve leaflets and chordae tendinea create the click
Aortic prosthetic valve sounds
= extra systolic sound from mechanical aortic ball-in-cage prosthetics
Ejection Click
= extra systolic sound that is a result of the SL valves opening at the start of ejection in the presence of aortic & pulmonary stenosis
Pericardial Friction Rub
= Extra diastolic sound from inflammation of the pericardium; high-pitched and scratchy
Summation Sound
= Extra diastolic sound when both s3 and s4 are present (quadruple rhythm)
Mitral Prosthetic Valve Sound
= Extra diastolic sound from the opening of the ball-in-cage mitral prosthetic
newborns transition from fetal to pulmonic circulation (can take time for shunts from fetal circulation to close)
Why don’t murmurs in the immediate newborn period necessarily indicate congenital heart disease?
Poor weight gain
developmental delay
persistent tachycardia
tachypnea
dyspnea on exertion (DOE)
cyanosis
clubbing
What are signs that may indicate heart disease in children?
sinus arrythmia
What characterizes rhythm of a child’s HR?
because their SBP gradually rises with age
Why does the pulse pressure (diff. b/t diastolic and systolic) widen in OA?
Orthostatic hypotension
= drop in BP when rising to sit or stand