3b: Properties of waves
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
1
New cards
waves
a way of transferring energy from place to place without matter by oscillations about a fixed point
2
New cards
two types of waves
- longitudinal
- transverse
- transverse
3
New cards
transverse waves
waves where the points along its length vibrate at 90 degrees to the direction of energy transfer
4
New cards
features of transverse waves
- have peaks and troughs
- vibrate 90 degrees to the direction of energy transfer
- transfer energy but not particles
- cannot move in gas
- electromagnetic waves can move in a vacuum
- constant density and pressure
- vibrate 90 degrees to the direction of energy transfer
- transfer energy but not particles
- cannot move in gas
- electromagnetic waves can move in a vacuum
- constant density and pressure
5
New cards
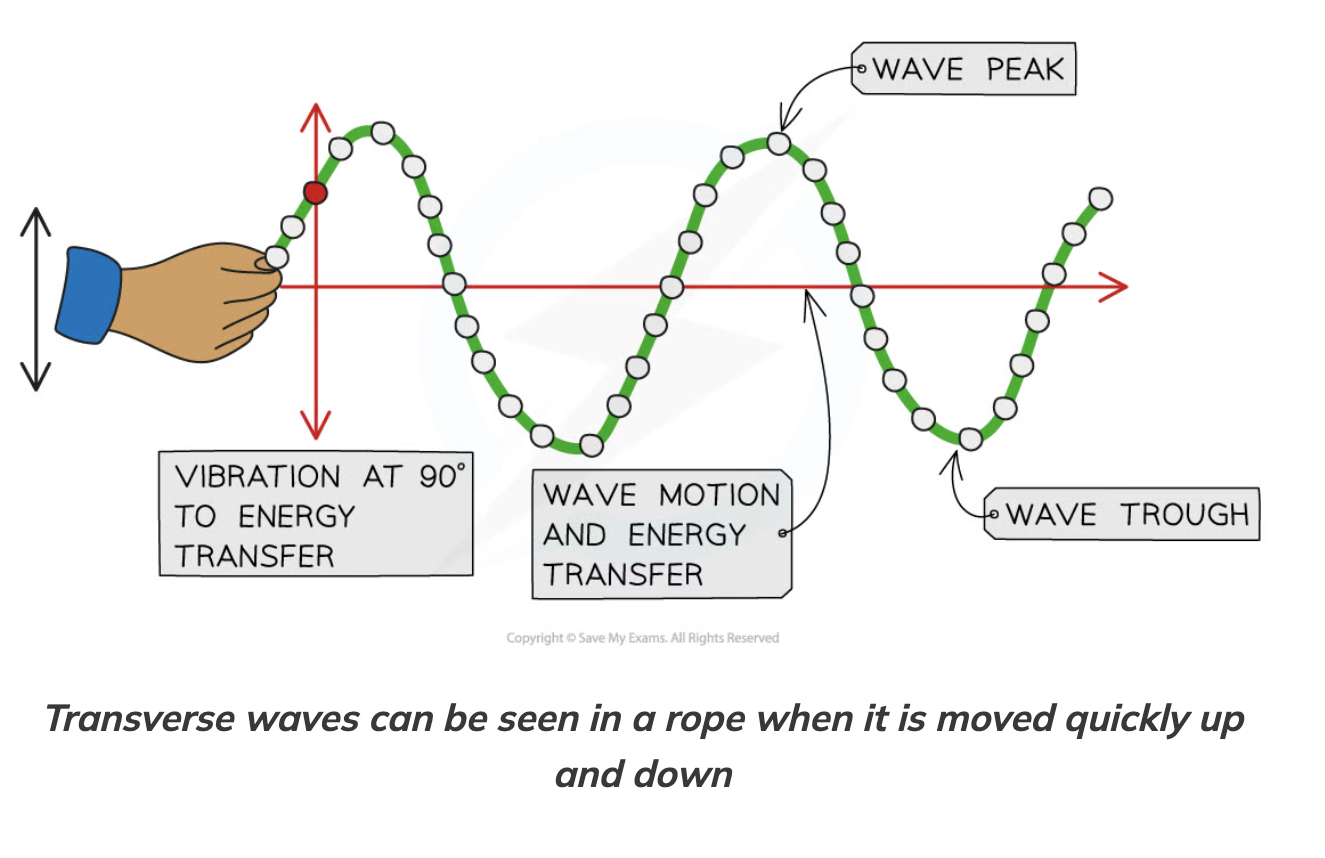
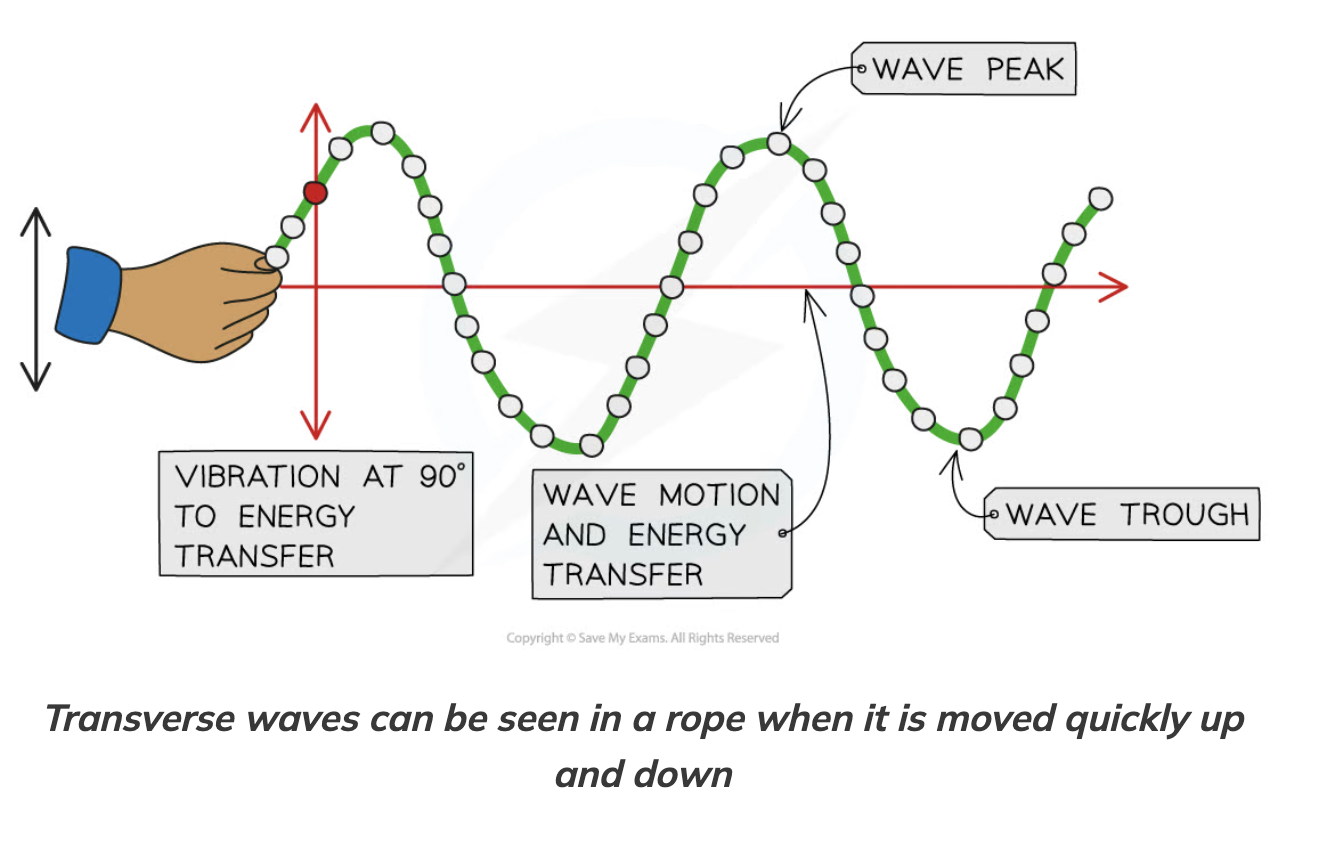
peak/crest
highest point on the wave above the rest position
6
New cards
trough
lowest point on the wave below the rest position
7
New cards
transverse waves - 4 examples
- ripples on water
- vibrations in a guitar string
- s-waves
- EM waves
- vibrations in a guitar string
- s-waves
- EM waves
8
New cards
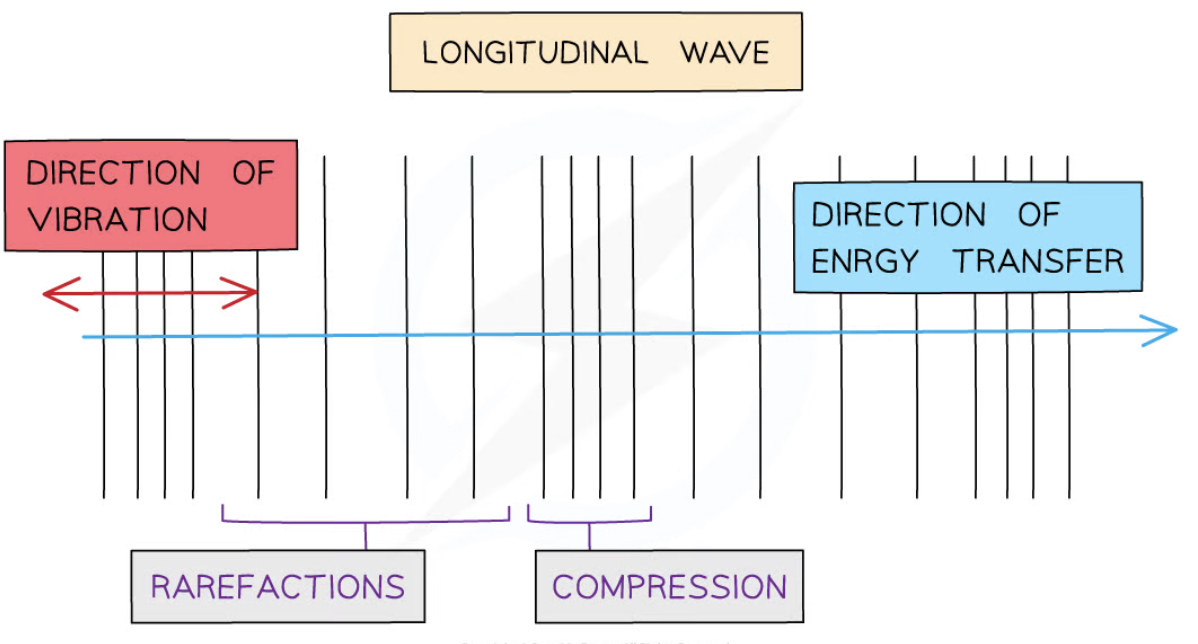
longitudinal waves
waves where the points along its length vibrate parallel to the direction of energy transfer
9
New cards
features of longitudinal waves
- have compressions and rarefactions
- parallel to direction of energy transfer
- transfer energy but not particles
- move in all 3 states of matter
- cannot move in a vacuum
- changes in density and pressure
- parallel to direction of energy transfer
- transfer energy but not particles
- move in all 3 states of matter
- cannot move in a vacuum
- changes in density and pressure
10
New cards
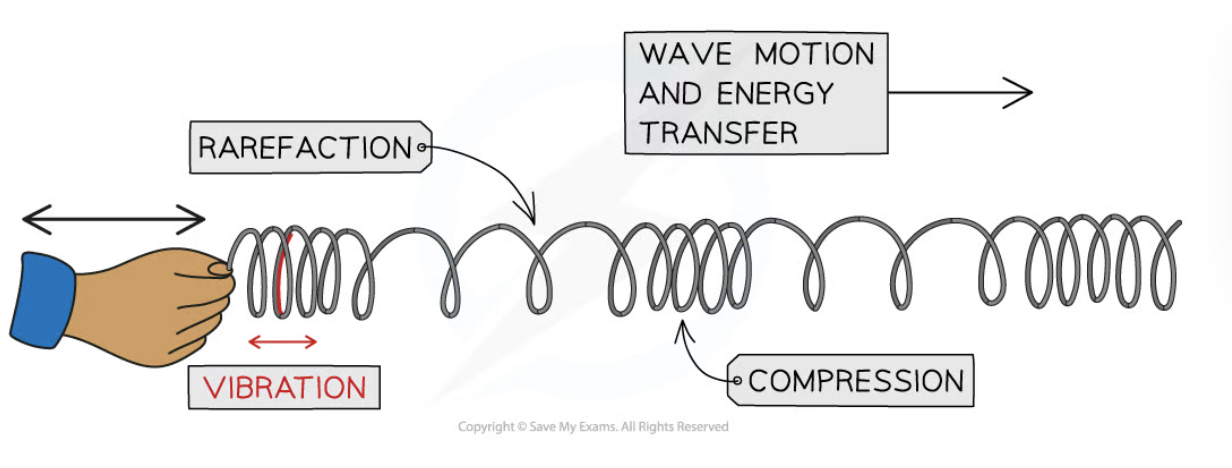
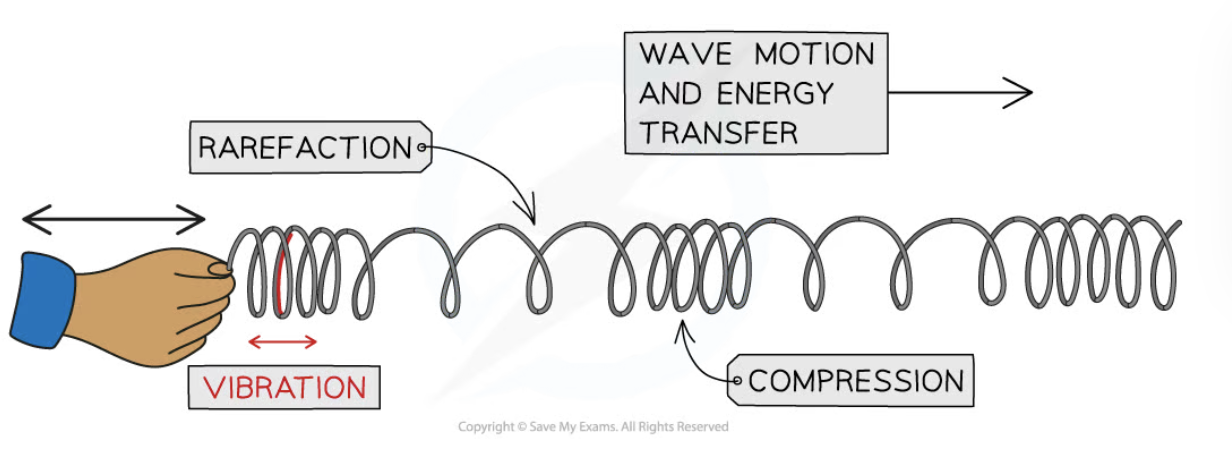
compressions
close together
11
New cards
rarefaction
far apart
12
New cards
longitudinal waves - 3 examples
- sound waves
- p-waves
- pressure waves
- p-waves
- pressure waves
13
New cards
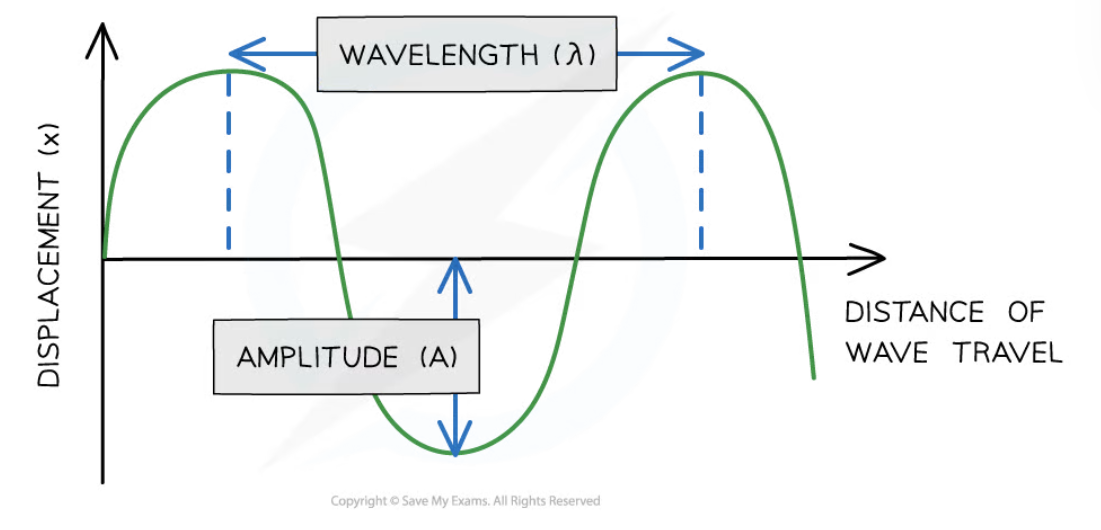
amplitude (A)
distance from the undisturbed position to the peak or trough of a wave
14
New cards
unit for amplitude
metres
15
New cards
wavelength
distance from one point on the wave to the same point on the next wave
16
New cards
wavelength - transverse waves
measured from one peak to the next peak
17
New cards
wavelength - longitudinal waves
measured from the centre of one compression to the centre of the next
18
New cards
symbol for wavelength
λ (lambda)
19
New cards
unit for wavelength
metres
20
New cards
frequency (f)
number of waves passing a point in a second
21
New cards
unit for frequency
hertz (Hz)
22
New cards
time period (T)
time taken for a single wave to pass a point
23
New cards
unit for time period
seconds
24
New cards
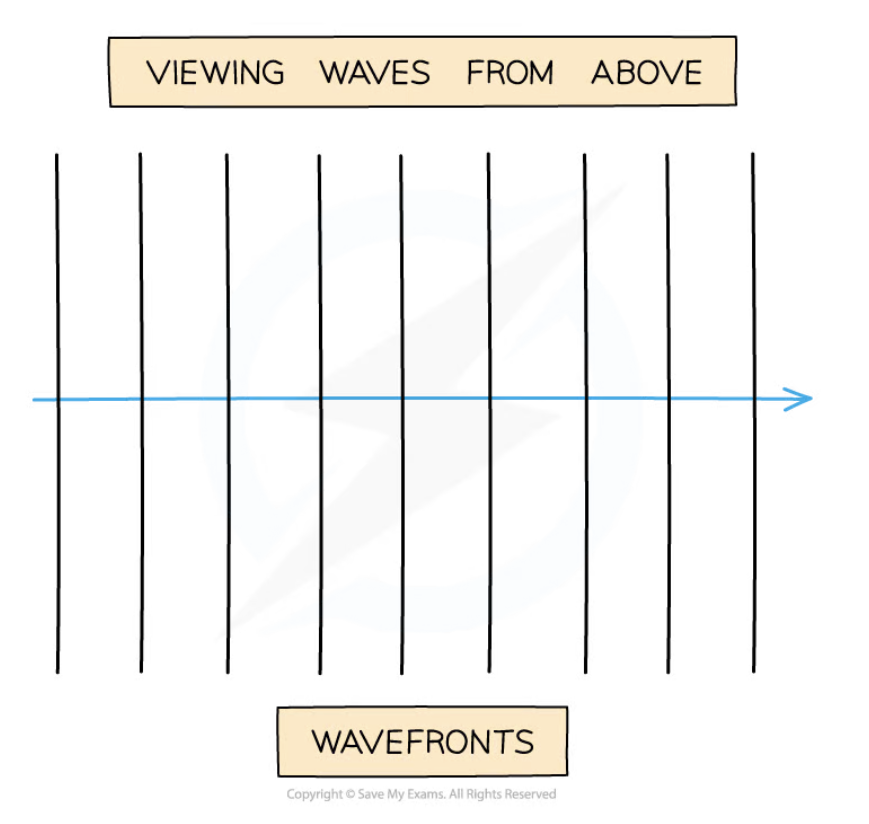
wavefronts
created by overlapping lots of different waves and represented by a line where all the vibrations are in phase and the same distance from the source
25
New cards
wavefront - ray
arrow showing the direction the wave is moving
26
New cards
wavefront - wavelength
space between each wavefront
27
New cards
wavefronts close together
short wavelength
28
New cards
wavefronts far apart
long wavelength
29
New cards
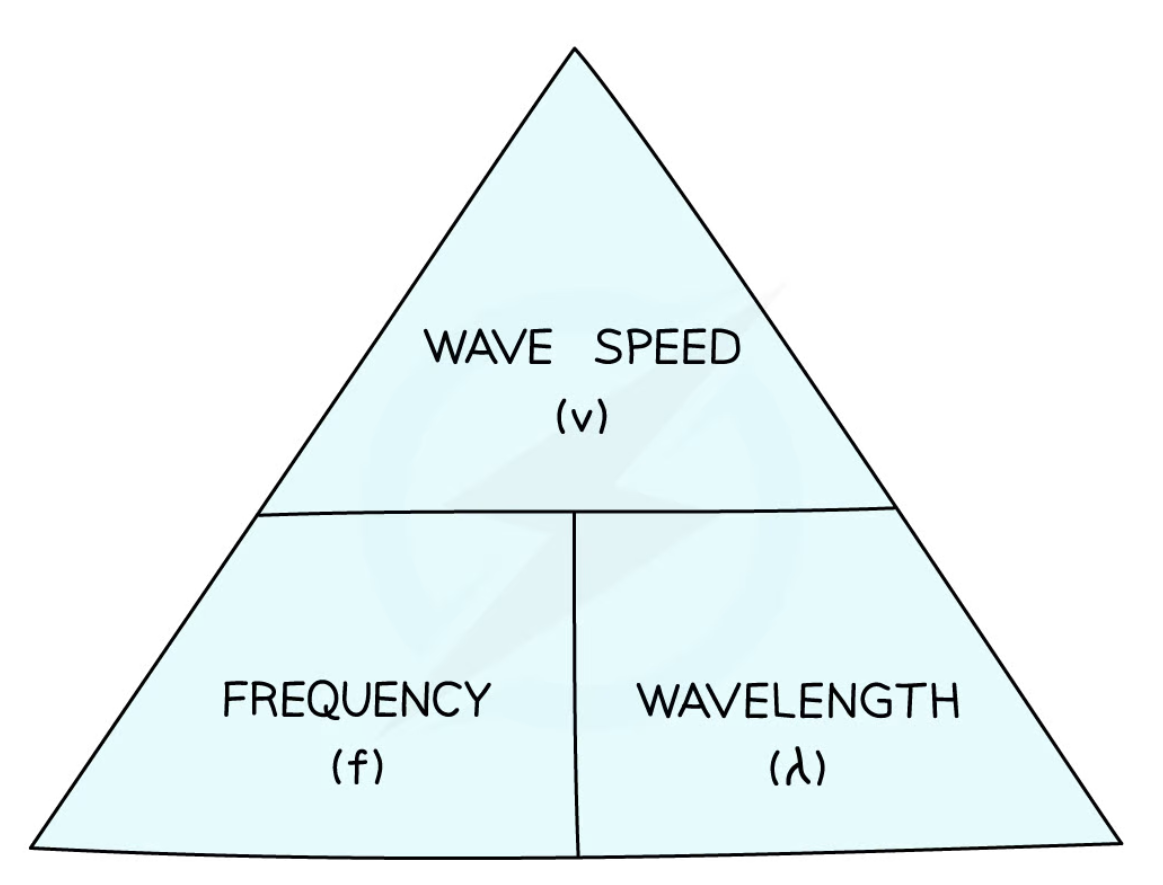
relationship between the speed, frequency and wavelength of a wave
wave speed = frequency x wavelength
30
New cards
unit for wave speed
m/s
31
New cards
relationship between frequency and time period
frequency = 1/ timeperiod
32
New cards
1 kHz to Hz
1 kHz = 1000 Hz
33
New cards
doppler effect
change in wavelength and frequency of a wave emitted by a moving source
34
New cards
doppler effect - wave source moving towards the observer
- observed frequency increases
- observed wavelength decreases
- observed wavelength decreases
35
New cards
doppler effect - wave source moving away from the observer
- observed frequency decreases
- observed wavelength increases
- observed wavelength increases
36
New cards
reflection
a wave hits a boundary between two media and does not pass through, but instead stays in the original medium

37
New cards
refraction
a wave passes a boundary between two different transparent media and undergoes a change in direction
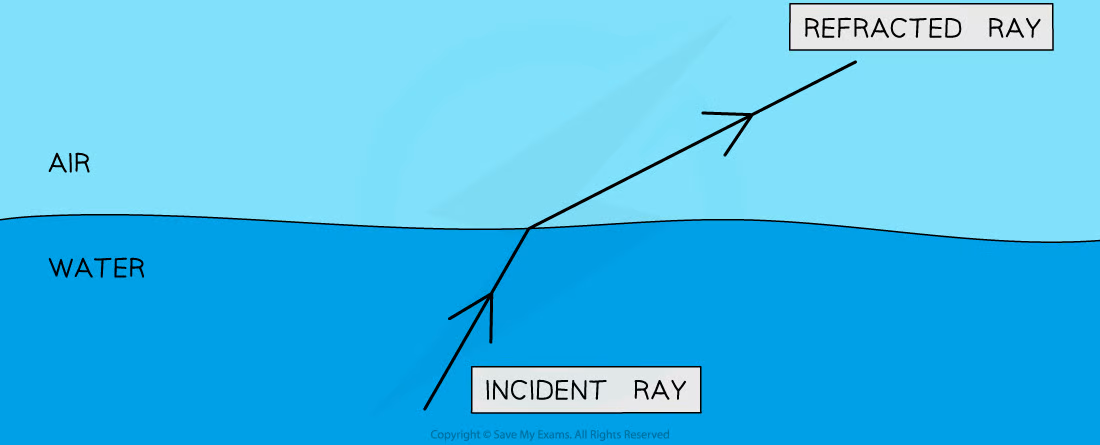
38
New cards
sound waves
vibration of air molecules
39
New cards
what happens to a sound wave when it comes into contact with a solid
vibrations transfer to the solid
40
New cards
are sound waves longitudinal or transverse
longitudinal
41
New cards
reflection of sound waves
echo
42
New cards
electromagnetic waves
transverse waves that transfer energy from the source of the waves to an absorber
43
New cards
properties of EM waves
- transverse
- travel through a vacuum at the same speed
- travel through a vacuum at the same speed