Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 8- Joints
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/86
Earn XP
Description and Tags
There are (Second/third word is ____) because it would be confusing to have more than 1 of the same answer if both options come up in a question. It's ball AND socket, not ball & socket
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
1
New cards
The 2 main functions of joints are to…
Give the skeleton mobility
Hold the skeleton together
Hold the skeleton together
2
New cards
The 3 structural classifications of joints are…
Fibrous, cartilaginous, and synovial
3
New cards
Fibrous joints are ____ (Movement)
Immovable
4
New cards
A common example of a fibrous joint is…
Suture
5
New cards
Cartilaginous joints are ________ ____ (__Movement)
Slightly movable
6
New cards
If the order of the bones is as follows, what is the order of flexibility from LEAST to MOST?
Hinge, Pivot, Plane, Saddle, Ball and Socket, Condyloid (2 pairs will be in the same category)
Hinge, Pivot, Plane, Saddle, Ball and Socket, Condyloid (2 pairs will be in the same category)
2, 2, 1, 3, 4, 3
7
New cards
If the order of the bones is as follows, what is the order of flexibility from LEAST to MOST?
Saddle, Ball and Socket, Hinge, Plane, Condyloid, Pivot (2 pairs will be in the same category)
Saddle, Ball and Socket, Hinge, Plane, Condyloid, Pivot (2 pairs will be in the same category)
3, 4, 2, 1, 3, 2
8
New cards
A common cartilaginous joint is…
Ribs connecting to the sternum
9
New cards
Synovial joints are __ ____ (Movement)
Freely movable
10
New cards
The 6 types of synovial joints are…
Hinge, Pivot, Ball and Socket, Saddle, Condyloid, and Gliding
11
New cards
In fibrous structural joints, the bones are joined by (dense regular) __ ____
Fibrous tissues
12
New cards
In fibrous structural joints, there is no __ __
Joint cavity
13
New cards
In cartilaginous joints, articulating bones are united by ___
Cartilage
14
New cards
The pubic symphysis is an example of a ______ joint
Cartilaginous
15
New cards
Bones in ____ joints are separated by a fluid-containing joint cavity
Synovial
16
New cards
The function of articular cartilage and synovial fluid is…
Reduce friction
17
New cards
The function of synovial cavities is to…
Hold fluid
18
New cards
The function of fibrous capsules and reinforcing ligaaments is to…
Support the joint
19
New cards
The function of synovial membranes is…
Produce synovial fluid
20
New cards
____ are sacs lined with synovial membranes and containing synovial fluid.
Bursae
21
New cards
Bursae are common where ligaments, muscles, skin, tendons, or bones ________ together. (At ____ joints)
Rub, complex
22
New cards
The two muscle attachments across a joint are….
Origin and insertion
23
New cards
The origin in a joint is the attachment to the ____ bone
Immovable
24
New cards
The insertion in a joint is the attachment to the _____ bone
Movable
25
New cards
Tendons connect ___ to bone.
Muscle
26
New cards
Ligaments connect ____ to bone.
Bone
27
New cards
Flexion is the bending movement that ____ the angle of the joint.
Decreases
28
New cards
Extension is the reverse of flexion, where the joint angle is ____.
Increased
29
New cards
Dorsiflexion is the _____ movement of the foot. (Superior/inferior)
Superior
30
New cards
Plantar flexion is the _____ movement of the foot. (Superior/inferior)
Inferior
31
New cards
Abduction is movement ___ from the midline (frontal plane). (Away/toward)
Away
32
New cards
Adduction is movement ____ toward the midline (frontal plane). (Away/toward)
Toward
33
New cards
Circumduction is movement that describes a ____ in space.
Cone
34
New cards
____ is the turning of a bone around its own long axis.
Rotation
35
New cards
The first two vertebrae (C1 + C2) is an example of a ___ ___.
Rotation joint
36
New cards
The radius and _____ is an example of a rotation joint.
Ulna
37
New cards
Supination is the turning of the palm ____. (Up/down)
Up
38
New cards
Pronation is the turning of the palm ____. (Up/down)
Down
39
New cards
Inversion is the ___ movement of the foot. (Medial/lateral)
Medial
40
New cards
Eversion is the _____ movement of the foot. (Medial/lateral)
Lateral
41
New cards
Protraction is a ____ movement. (Forward/back)
Forward
42
New cards
Retraction is a ____ movement. (Forward/back)
Back
43
New cards
Elevation is a(n) _____ movement. (Upward/downward)
Upward
44
New cards
Depression is a(n) ____ movement. (Upward/downward)
Downward
45
New cards
Opposition is the movement of the ____ alone.
Thumb
46
New cards
Plane joints are the ____ flexible synovial joint.
Least
47
New cards
The articular surfaces in plane joints are essentially ____.
Flat
48
New cards
Plane joints are _____ joints.
Nonaxial/non-angular
49
New cards
Intercarpal and intertarsal joints are examples of ____ joints.
Plane
50
New cards
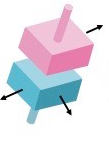
This is an example of a ___ _____ (Second word is joint)
Plane joint
51
New cards
Motion in hinge joints is along a ______ _____.__
Single joint
52
New cards
Hinge joints (_____) permit flexion and extention only.
Uniaxial
53
New cards
The humerus-ulna joint AND the knee are examples of ____ joints.
Hinge
54
New cards
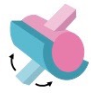
This is an example of a _____ _______ (__Second word is joint)
Hinge joint
55
New cards
In a pivot joint, the rounded end of one bone ____ into a “sleeve” or ring of another.
Protrudes
56
New cards
Rotation/___axial movement is allowed at pivot joints.
Uni
57
New cards
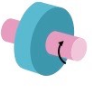
This is an example of a __ ____ (Second word is joint)
Pivot joint
58
New cards
The bones C1 + C2 AND the radioulnar joint are examples of ____ joints.
Pivot
59
New cards
An ____ surface of one bone fitting into a depression of another bone is an example of a ____ joint.
Open, condyloid
60
New cards
Condyloid joints are _____, meaning they permit all angular movements
Biaxial
61
New cards
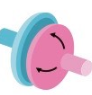
This is an example of a ______ _____ (Second word is joint)
Condyloid joint
62
New cards
The radiocarpal (wrist) and metcarpophalangeal (1st knuckle) joints are examples of ____ joints.
Condyloid
63
New cards
Saddle joints are similar to condyloid joints, but allow ____ movement. (Greater/lesser)
Greater
64
New cards
Saddle joints are __axial
Bi
65
New cards
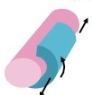
This is an example of a _____ _____ (Second word is joint)
Saddle joint
66
New cards
In ___ joints, each articular surface has both a concave and a convex surface.
Saddle
67
New cards
The carpometacarpal joint of the _____ is an example of a ___ ____ (Second word is joint)
Thumb, saddle joint
68
New cards
Ball and socket joints are the _____ flexible joints.(Most/least)
Most
69
New cards
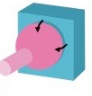
This is an example of a ____ ___ ______ _______(Fourth word is joint)
Ball and socket joint
70
New cards
____axial joints permit the most freely moving synovial joints.
Multi
71
New cards
The joint with the scapula and _____ is an example of a ball and socket joint.
Humerus
72
New cards
The joint with the _____ and acetabulum is an example of a ball and socket joint.
Femur
73
New cards
In ball and socket joints, the spherical head of one bone articulates with the _____ of another bone.
Socket
74
New cards
The shoulder has more movement than the hip because the head of the femur is ___ into the acetabulum than the head of humerus is in the ______ fossa.
Deeper, glenoid
75
New cards
Together, the femur, fibula, tibia, and patella make up the ____.
Knee
76
New cards
The knee allows flexion, ______, and some rotationext
Extension
77
New cards
There are _____ joints in one surrounded by a single joint
_____. **These are the femoropatellar joint, and the lateral and medial tibiofemoral joints.**
_____. **These are the femoropatellar joint, and the lateral and medial tibiofemoral joints.**
Three, cavity
78
New cards
The _CL is more likely to be damaged than the other ligament from a lateral force.
M
79
New cards
If you are hit from the lateral side of your leg, the ___ will be cushioned by the ligaments in the knee, but the ___ will have no cushioning and will tear. The same would happen with a force from the medial side of the leg.
LCL, MCL
80
New cards
The ______ cruciate ligament (ACL) prevents _____
Anterior, hyperextension
81
New cards
The ACL and PCL _____ at the knee joint. (Hint: X)
Cross
82
New cards
The medial and lateral meniscuses (menisci) act as _____.
Cushions
83
New cards
Flexion and extension occur on the _____ plane
Saggital
84
New cards
Adduction and abduction occur on the ____ plane.
Frontal
85
New cards
The MCL is _____(more/less) likely to be damaged than the LCL is.
More
86
New cards
The ACL is ____(more/less) ______ to be damaged than the PCL. (Two words)
More likely
87
New cards
Bursa will _____(Always/Not Always) be found at a synovial joint
Not always