HF decomp- Heeter
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What are precipitating factors for ADHF?
(ADHF= acute decompensated heart failure)
meds
dietary non-compliance
arrhythmias
uncontrolled HTN
myocardial ischemia/infarction
anemia
endocrine abnormalities
infection
pulmonary emboli
excessive alcohol/drug use
Meds that precipitate ADHF tend to do 3 things.
promote fluid retention
negative inotropic
exhibit direct cardiotoxicity
describe meds that belong to each category?
promote fluid retention—> NSAIDs, glitazones, steroids
negative inotropic—> non-DHP CCBs, nifedipine, flecanide, sotalol, b-blockers, itraconazole
exhibit direct cardiotoxicity—> anthracyclines, amp B, clozapine, stimulants
WHAT ARE S/SX OF VOLUME OVERLOAD?
must know these
orthopnea/paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea (PND)
pitting edema
weight gain
ascites
DOE/SOB
S3 gallop
crackles in lung fields
increased BNP
positive JVD
positive HJR
WHAT ARE S/SX OF REDUCED CARDIAC OUTPUT (CO)?
must know these
(these are more nonspecific and harder to determine compared to volume overload s/sx)
fatigue
hypotension
narrow pulse pressure
pallor/cyanosis
cold extremities
prerenal AKI (increased BUN:SCr ratio)
decreased urine output (<0.5 ml/kg/hr)
altered mental status
poor appetite
Decreased renal fxn= 1st sign of decreased CO
To confirm ADHF what’s the main laboratory test/ cardiac biomarker we are going to order?
What levels confirm HF?
BNP or pro-BNP
BNP >100 pg/mL
pro-BNP >300 pg/mL
Invasive hemodynamic monitoring aka right heart catheterization… measures what 2 main things?
What does each indicate?
pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP)—> indicator of volume status
cardiac index (CI)—> indicator of cardiac output
What is a normal PCWP? What level indicates fluid overload?
heeter said to know
PCWP > 18 mmHg= fluid overload
normal PCWP= <12 mmHg
A CI <______ ml/min/m2= poor perfusion
2.2
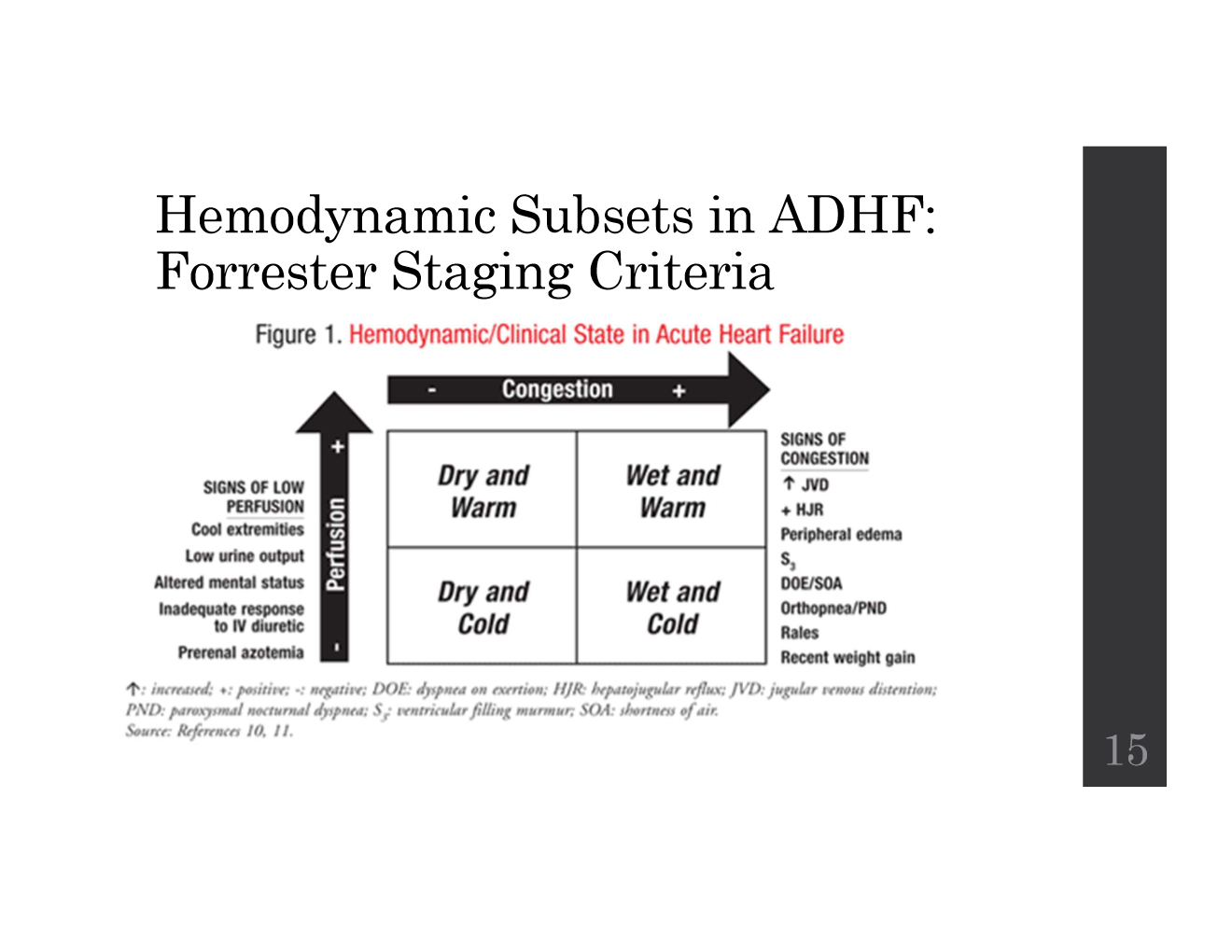
What are the two main clinical axes in Forrester staging?
What are the s/sx for each?
heeter- “know forrester staging criteria and how to stage pts.”
Congestion (Wet vs. Dry)
volume overload s/sx
Perfusion (Warm vs. Cold)
reduced CO s/sx
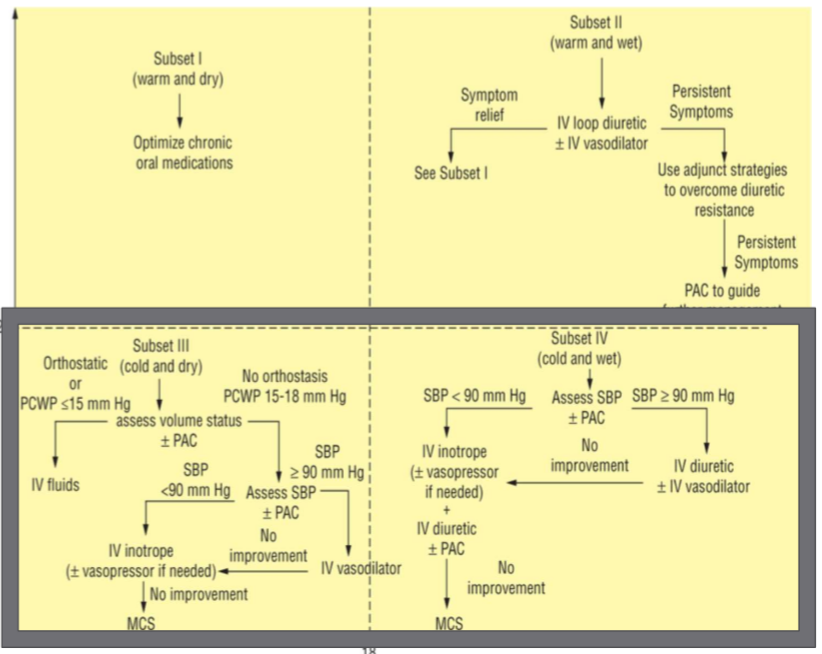
What are the 4 Forrester hemodynamic subsets?
heeter- “know forrester staging criteria and how to stage pts.”
Subset 1: Warm & Dry
Subset 2: Warm & Wet
Subset 3: Cold & Dry
Subset 4: Cold & Wet
Evaluating a pts. chronic HF tx (aka the meds they were on before being admitted to the hospital) in the acute setting is necessary.
How do we adjust the pts. diuretic when admitted?
hold at home PO dose and initiate IV loop diuretic if volume overload
Evaluating a pts. chronic HF tx (aka the meds they were on before being admitted to the hospital) in the acute setting is necessary.
How do we adjust the pts. beta blocker when admitted?
WE DO NOT WANT TO D/C THE B-BLOCKER (most of the time)
exceptions:
really really really low bp or if dose was just increased then go back down
Evaluating a pts. chronic HF tx (aka the meds they were on before being admitted to the hospital) in the acute setting is necessary.
How do we adjust the pts. ACE/ARB/MRA when admitted?
d/c if seeing kidney ADRs
Evaluating a pts. chronic HF tx (aka the meds they were on before being admitted to the hospital) in the acute setting is necessary.
How do we adjust the pts. digoxin when admitted?
WE DO NOT WANT TO D/C DIGOXIN (most of the time)
exceptions: if pt. is experiencing digoxin toxicity or bradycardia
PRACTICE:
Which of the following medications is most important for ADHF patients to NOT to d/c when being admitted to the hospital?
SATA
a. furosemide
b. lisinopril
c. valsartan
d. metoprolol
e. digoxin
d, e
FYI: which forrester subset is the most common in pts.? (~2/3)
wet and warm
How is subset 2 aka warm and wet treated?
know this
reduce preload—> loop diuretics ± vasodilators
Preferred loop diuretic for subset 2 aka warm and wet?
furosemide
Furosemide PO: IV is ___:___.
2:1
Bumetanide PO: IV is ___:___.
1:1
Duration of action of Furosemide (Lasix)?
4-6 hrs (Lasix)
How is diuretic resistance to loop diuretics managed?
increase DOSE of loop diuretic
initiate add-on therapy with thiazide
Preferred thiazide diuretic to initiate for loop diuretic resistance?
metolazone PO
alts: hydrochlorothiazide PO, chlorothiazide PO/IV
Administration considerations with thiazide-type diuretics for loop diuretic resistance?
TAKE METOLAZONE 30 MIN BEFORE LOOP
What is the I/O (intake/output) goals when taking diuretics for subset II aka warm and wet?
heeter—> know this
>500 ml within 1st 2 hours for Scr <2.5 mg/dL
(aka we give dose, and within 1st 2hrs we should see 500 mL of urine)
When do we consider adding a vasodilator for subset 2 aka warm and wet?
refractory volume overload
acute pulmonary edema
severe HTN
basically—> works faster than diuretics to help decrease fluid overload…
What is the preferred IV vasodilator for subset 2 aka warm and wet?
Nitroglycerin (NTG)
ADRs of nitroglycerin?
tachyphylaxis and HA
What are 2 alternative vasodilators that are only used for subset 3 and 4?
nesiritide and sodium nitroprusside
Do each of the following effect arterials, venous, or both?
nitroglycerin
sodium nitroprusside
nesiritide
nitroglycerin—> venous
sodium nitroprusside—> both
nesiritide—> both + natriuresis
What is the major drawback with sodium nitroprusside?
metabolized to cyanide/thiocyanate—> potentially fatal cyanide toxicity
What is a non-pharm intervention for fluid overload?
When do we consider it?
ultrafiltration
rapid fluid removal
consider when:
diuretic resistance
worsening renal impairment following diuretics
worsening renal impairment despite IV vasodilator and/or inotrope therapy
HF is most commonly associated with
a. hypovolemic hypernatremia
b. hypovolemic hyponatremia
c. hypervolemic hyponatremia
d. hypervolemic hypernatremia
c. (effects 1 in 5 pts. hospitalized)
What vasopressin antagonists are indicated for hypervolemic/euvolemic hyponatremia in SIADH, cirrhosis, or HF?
What must the serum sodium be?
Tolvaptan
serum Na+ must be <125 mEq/L
What is the general tx approach to “cold” patients aka subset 3 and 4?
measure SBP and volume status
treat based on type of ADHF and ± hypotension
consider invasive monitoring parameters in severely ill pts.
IV vasodilators—> Nesiritide and Sodium Nitroprusside
use in select pts. with low CO
IV inotropes—> Dobutamine, Milrinone
increase CO
consider when need for temp Maintenace of end-organ perfusion in pts. with cardioshock or severely depressed CO and low SBP and can’t use IV vasodilators
bridge therapy for HF pts. for MCS or transplant
Dobutamine MOA?
non-selective beta agonist
Milrinone MOA?
inhibits PDE-3
What is the tx for subset 4 cold and wet?
SBP <90 mmHg vs. SBP ≥90?
SBP <90 mmHg—> IV inotrope ± vasopressors + IV diuretic ± PAC
SBP ≥90 mmHg —> IV diuretic ± vasodilator
What is the tx for subset 3 cold and dry?
orthostatic or PCWP ≤15 mmHg
no orthostasis or PCWP 15-18 mmHg
SBP <90 mmHg vs. SBP ≥90
orthostatic or PCWP ≤15 mmHg—> IV fluids
no orthostasis or PCWP 15-18 mmHg
SBP <90 mmHg—> IV inotrope ± vasopressor
SBP ≥90—> IV vasodilator
Tx summary FYI: