1.4 Energy ⚡
1/72
Earn XP
Description and Tags
GCSE CCEA Specification GCSE Physics Double Award Science, Triple Award Science Unit 1: Motion, Force, Moments, Energy, Density, Kinetic Theory and Radioactivity
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Work (energy)
measure of energy transferred from one store to another
Work (forces)
force causes a displacement of the object
The equation linking work, force and distance (in the direction of the force)
work = force * distance
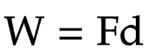
Unit for energy and work
Joules (J)
Unit for force
Newtons (N)
Unit for distance
Metres (m)
Equivalent of 1J
1J = 1Nm
e.g lifting a (1N) apple 1m
Alternative unit for work done by a force
Newton-metre (Nm)
Effect of doing work against friction
rise in the temperature of the object
Power
rate at which energy is transferred or work is done
The equation linking power, energy transferred and time
power = energy ÷ time
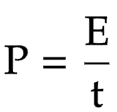
Unit for power
Watts (W)
Unit for time
Seconds (s)
One watt is equal to
1W = 1 J/s
The equation linking power, work done and time
power = work done ÷ time
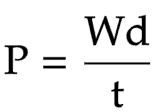
how is work done affected by kinetic energy
to stop object, same amount of energy is required
Link between gravitational potential energy and kinetic energy
Gravitational potential energy at the top = kinetic energy at the bottom
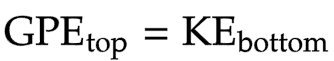
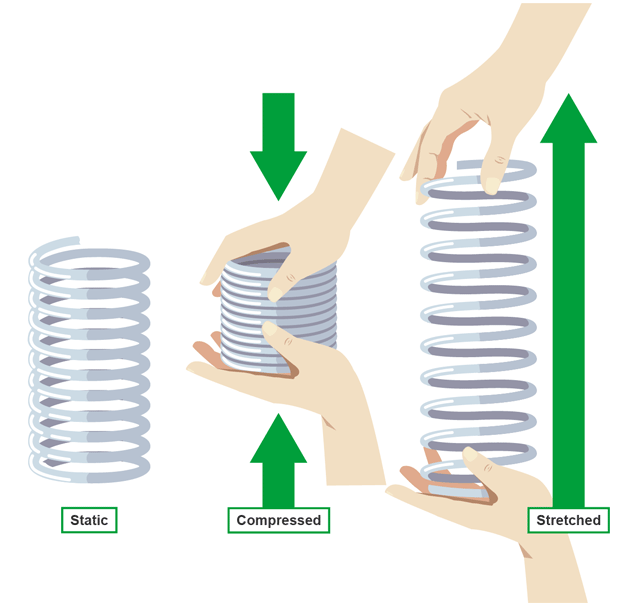
Elastic potential energy
when an object is squashed it stores energy and is released when it returns
The equation linking kinetic energy, mass and speed
kinetic energy = 0.5 * mass * velocity squared
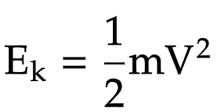
Unit for mass
Kilograms (kg)
Unit for speed or velocity
Metres per second (m/s)
The equation linking gravitational potential energy, mass, gravity and height
gavitational potential energy = mass * gravity * height
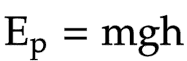
Unit for gravitational field strength
Newtons per kilogram (N/kg)
Unit for height
Metres (m)
Efficiency
how good device is at transferring total energy supplied (input) to useful energy stores (output)
The equation linking efficiency and energy
Efficiency = useful output energy transfer ÷ total input energy transfer
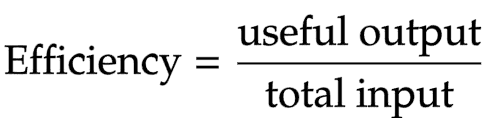
The equation linking efficiency and power
Efficiency = useful power output ÷ total power input
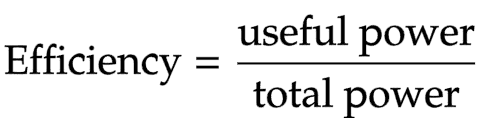
Why can't you have an efficiency greater than 1 or 100%
would break the law of conservation of energy as energy is being created
Reasons devices waste energy
Friction between moving parts
Heat due to electrical resistance
Unwanted sound or light
Ways to improve efficiency
Lubricate mechanical to reduce friction between moving parts
Insulate heating to reduce dissipation of thermal energy
Energy resource
useful supply or store of energy
Non-renewable
sources used at a higher rate than can be replaced so will eventually run out (finite)
Examples of non-renewable resources
Fossil fues (coal, crude oil, natural gas)
nuclear fuels (uranium, plutonium)
Finite
has a limited number of uses before it runs out
Renewable
Energy sources that are replenished as they are being used so will not run out
Examples of renewable resources
Bio-fuels, solar, wind, geothermal, wave, tidal, hydroelectric
Advantages of wind energy
renewable energy resource
no fuel costs
No harmful polluting gases are produced
disadvantages of wind energy
noisy and may spoil the view for people living near them
amount of electricity generated depends on the strength of the wind
If there is no wind, there is no electricity
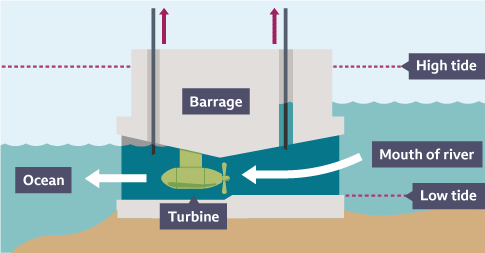
Advantages of wave, tide and falling water energy
renewable energy resources and there are no fuel costs
no harmful polluting gases are produced
Tidal barrages and hydroelectric power stations are very reliable and easily switched on
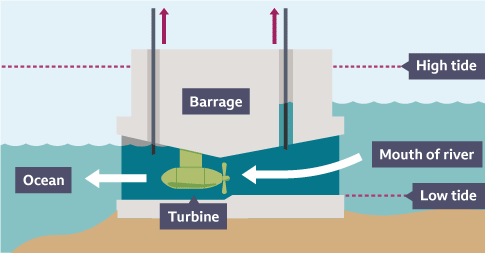
Disadvantages of wave, tide and falling water energy
difficult to make machines big enough to produce large amounts
tidal barrages destroy places where birds and fish live
hydroelectricity dams flood farmland and push people from their homes
rotting vegetation underwater releases methane, which is a greenhouse gas
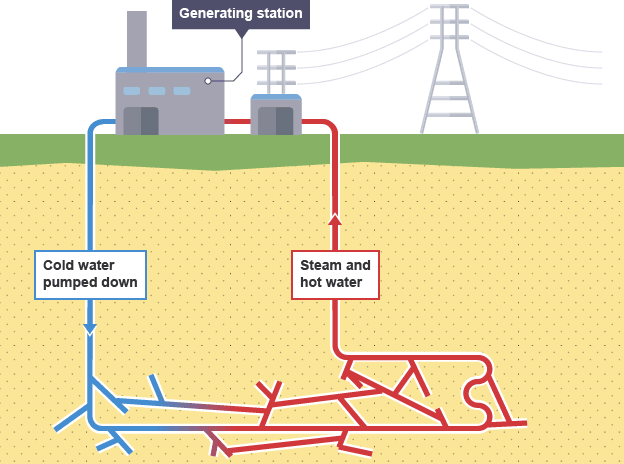
Advantages of geothermal energy
a renewable energy resource and there are no fuel costs
no harmful polluting gases are produced
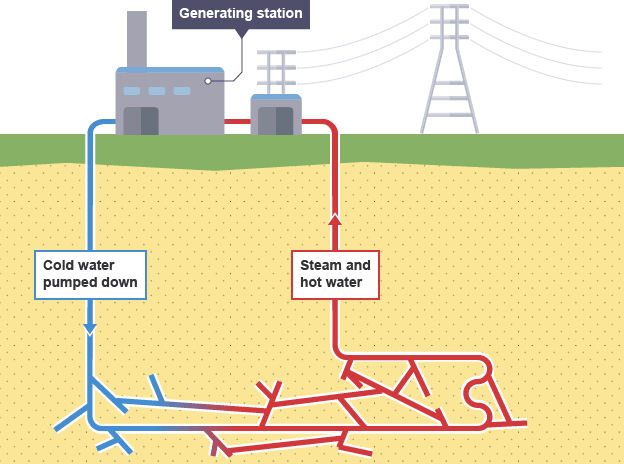
Disadvantages of geothermal energy
most places don’t have suitable areas where geothermal energy can be exploited
Advantages of solar energy
renewable energy resource and there are no fuel costs
no harmful polluting gases are produced
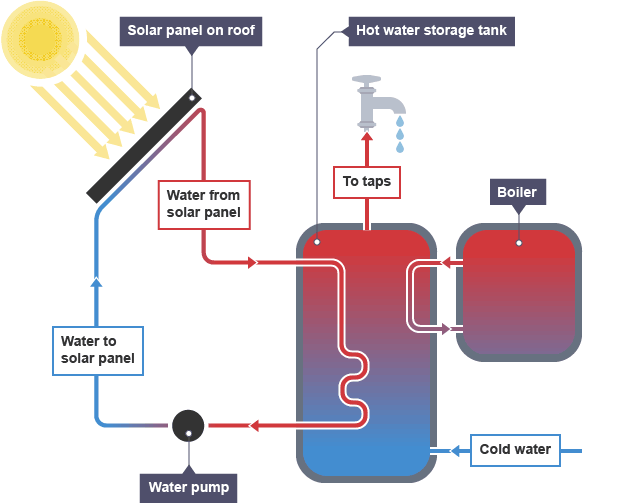
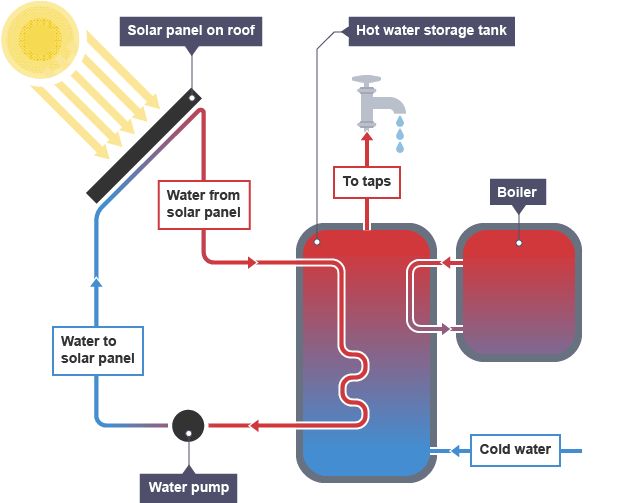
Disadvanages of solar energy
only produce hot water in sunny climates, cooler areas need to be supplemented with a conventional boiler
warm water can be produced on cloudy days but do not work at night
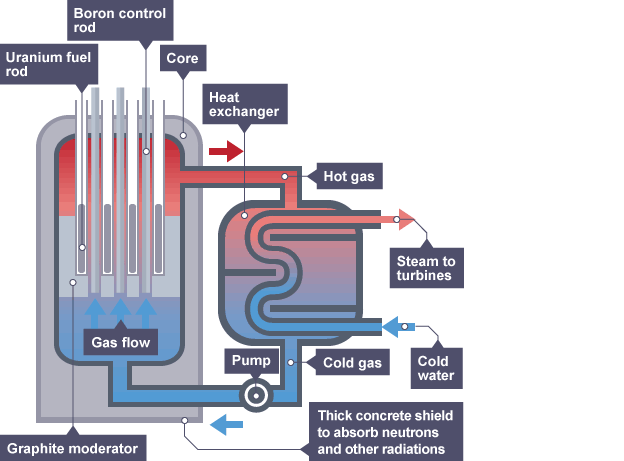
Advantages of nuclear power
do not emit greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide
do not emit gasses such as sulphur dioxide
1 kg of nuclear fuel produces millions of times more energy than 1 kg of coal
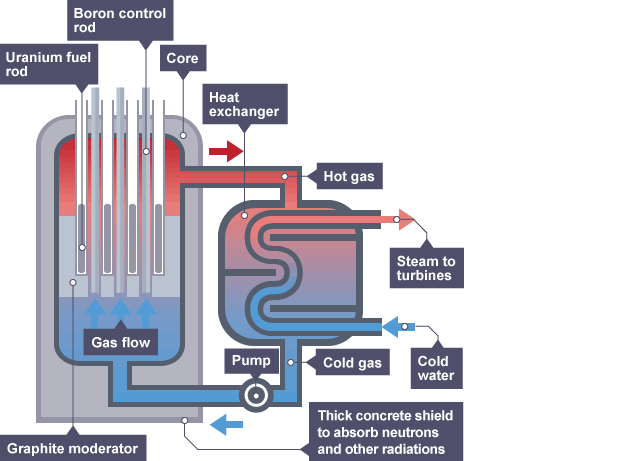
Disadvantages of nuclear power
fuels used for fission (uranium ore) are non-renewable since they wont last forever
if there is an accident, large amounts of radioactive material could be released into the environment
waste remains radioactive and hazardous for thousands of years, so must be stored safely
decommissioning power plants is extremely expensive
Fossil fuels
Fuels formed from the remains of living organisms (coal, crude oil, natural gas)
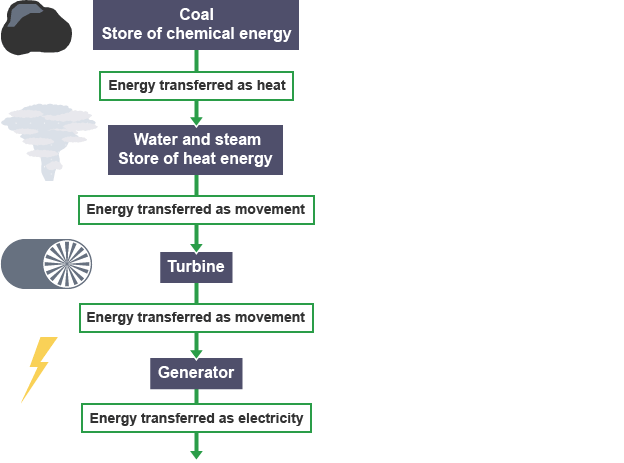
Advantages of fossil fuels
relatively cheap and easy to obtain- may not always be the case
infrastructure is designed to run using fossil fuels
Disadvantages of fossil fuels
non-renewable so supply is limited and will run out
Coal and oil release sulphur dioxide gas when burned, causing breathing problems and acid rain
release carbon dioxide when burned, adds to the greenhouse effect and increases global warming
Reliable (energy resource)
an energy resource that can supply enough energy to meet demand at predictable times
Examples of reliable resources
Fossil fuels, nuclear fuels, bio-fuels, tidal, hydroelectric and geothermal
Atmospheric pollution
Carbon dioxide from burning fossil/ bio fuels
sulfur dioxide from burning coal
Carbon neutral
Burning bio-fuels releases same amount of carbon dioxide as crops absorbed for photosynthesis
Closed system
a system (group of objects) with no net change to the total energy
Law of conservation of energy
Energy can be transferred usefully, stored or dissipated, but cannot be created or destroyed
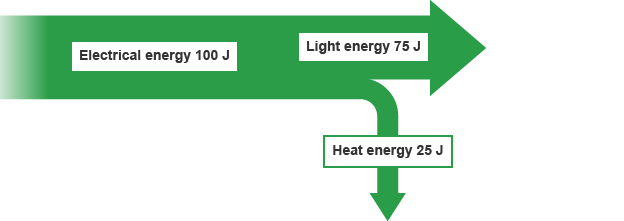
Useful energy transfer
energy is transferred to useful stores we want
Wasted energy transfer
energy transferred to useless stores we don't want, usually dissipates as heat
Dissipate
energy spreads out and is transferred to less useful energy stores, releasing heat
Insulate
reduce wasted energy by reducing amount of heat that transferred to surroundings
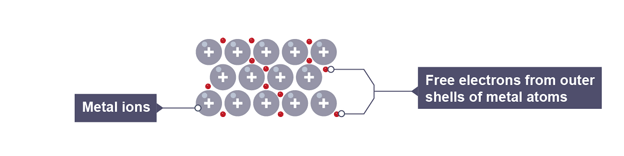
Thermal conductor
allows charge or heat to pass through it easily
free electrons absorb heat, causing them to move faster
they collide with metal atoms and transfer kinetic energy
this causes the atoms to vibrate faster
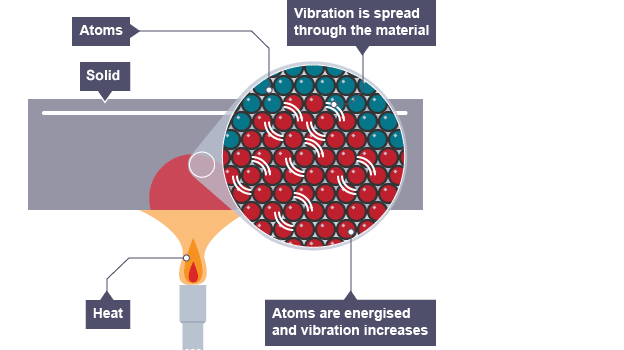
Thermal insulator
does not allow charge or heat to pass through it easily
have no free electrons so atoms absorb heat directly
vibrations pass from atom to atom through the solid
the process is much slower
Thermal conductivity
how well a material conducts energy when it is heated
Conduction
transferred through solid
vibrating particles collide and transfer energy to one another
conductors have fast and free electrons which pass the energy very quickly
slow process
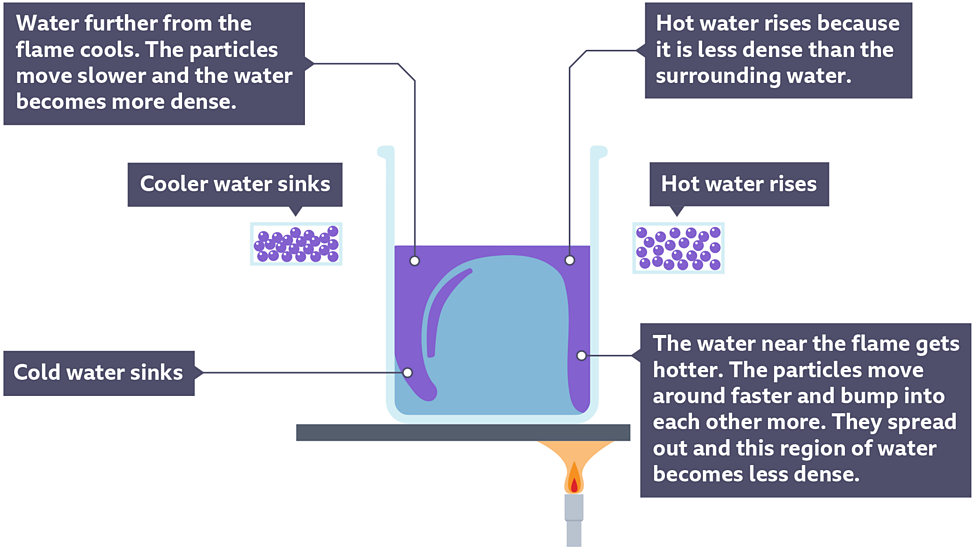
Convection
transferred through fluids (particles can move)
particles with lots of heat energy move to take place of those with less heat energy
Radiation
transferred from a hot object to cold
no particles involved so can take place in vacuum
object emitting infrared (heat) radiation
dull, matte, or rough dark surface
good absorber and emitter of heat but will cool quicker
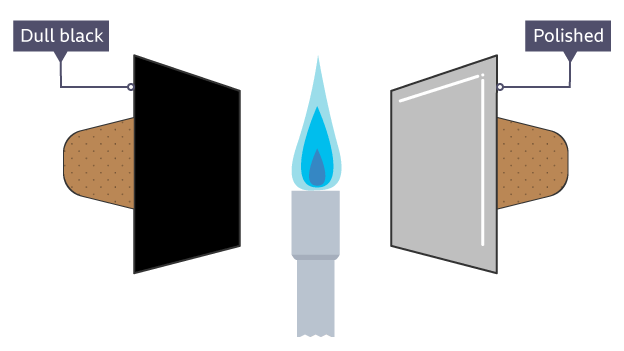
shiny light surface
poor absorber and emitter of heat but will cool slower
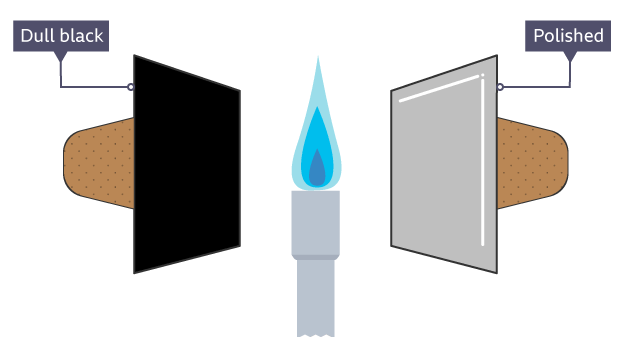
how is heat loss caused in the home
mainly conduction and convection
examples of insulating materials
air, fibreglass, mineral wool
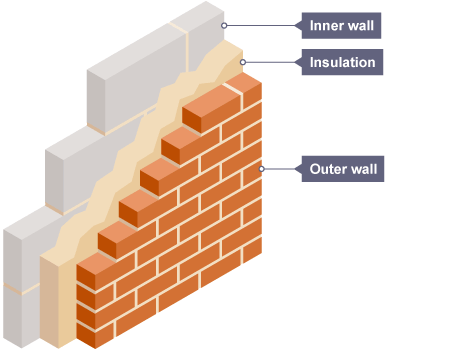
cavity wall insulation
gap between wall is filled with insulating material
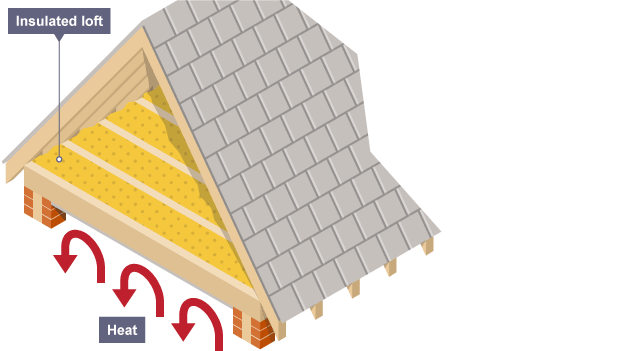
loft insulation
thick layer insulating material reduces heat transfer through the ceiling by trapping air between fibres
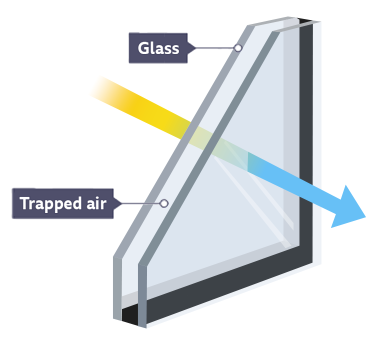
double glazed windows
gap between two panes of glass contains air or gas insulator
Energy forms
chemical
heat
electrical
sound
light
magnetic
strain/ elastic energy
kinetic
gravitational potential
