Parasitology 12 Trematodes/Flukes
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Hermaphroditic tissue fluke morphology
Leaf-shaped, oral/ventral suckers, blind GI tract
Sheep liver fluke
intermediate host: snail
Fasciola hepatica
Intestinal fluke
first intermediate host: snail
second intermediate host: pig
Fasciolopsis buski
Liver fluke
first intermediate host: snail
second intermediate host: fish
Clonorchis sinensis
Lung fluke
first intermediate: snail
second intermediate host: crabs
Paragonimus westermani
How do humans get infected by hermaphroditic flukes?
Eating metacercariae of second intermediate host
Treatment for all hermaphroditic flukes?
Praziquantel
T/F: Hermaphroditic flukes do not multiply, so burden depends on inoculum
True
What species cause fascioliasis: bile duct block (gallstone disease) and possibly liver damage?
Fasciola hepatica, Fasciola gigantica
What is and is not effective against Fascioliasis
Triclabendazole
NOT Praziquantel
How do Fasciola spp. develop in snail tissue?
Sporocysts → rediae → cercariae
Fasciolopsiasis
what species causes it
symptoms
associations?
Fasciolopsis buski
ulcers, diarrhea, toxic reactions
ingestion of water chestnuts or fresh-water plant-fed animals
Fasciola hepatica distribution (areas with what animal)
areas with sheep/cattle
Europe, Middle East, Asia
F. gigantica distribution
Asia, Africa, Hawaii
Fasciolopsis buski distribution (areas with what animal)
areas with pigs
China, Taiwan, SE Asia, Indonesia, Malaysia, India
Where are metacercarial cysts found for Clonorchis sinensis
uncooked freshwater fish
Diagnosis of Clonorchis sinensis
eggs in stool or duodenal aspirate
egg with operculum and shoulders
T/F: When bile duct is obstructed, eggs in stool are not excreted
True
Diagnosis of Fasciola spp.
eggs in stool (big)
egg with operculum
Clonorchis distribution
Asia (SE Asia, South Asia) and non-endemic areas
How do Clonorchis develop in snail
Miracidia → Sporocysts → Rediae → Cercariae
Clonorchis disease
asymptomatic often
inflammation, intermittent obstruction of biliary ducts
acute: abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhea
chronic: cholangiocarcinoma
Clonorchis treatment
praziquantel or albendazole
Paragonimus westermani distribution
Asia/SE Asia, India, Africa
How is paragonimus westermani transmitted?
eating metacercariae cyst from undercooked crab meat
What fluke causes granulomatous reaction leading to fibrosis?
P. westermani
Symptoms Paragonimus westermani
cough, pleurisy, pulmonary pain, hemoptysis
Diagnosis of P. westermani
eggs in sputum, rarely in feces
brown eggs
operculum
How do P westermani develop in snails?
Sporocyst → Rediae → Cercariae
Where do cysts excyst in?
Duodenum
Paragonimus westermani eggs exit where?
sputum
What free-living amoeba causes primary amoebic meningoencephalitis?
Naegleria fowleri
What free-living amoeba causes granulomatous amoebic encephalitis
Balamuthia mandrillaris
Acanthamoeba spp.
What free-living amoeba cause keratitis
Acanthamoeba spp.
What species enter through offactory neuroepithelium?
Naegleria fowleri
What species enter through lower respiratory tract or through ulcerated skin?
Acanthamoeba spp. and Balamuthia mandrillaris

What species does this cyst, flagellate, and trophozoite belong to?
N. fowleri
Acute primary amebic meningoencephalitis
cause?
symptoms?
who affected?
enter how?
Naegleria fowleri
severe headache + meningeal signs; fever, vomit, neurological deficit
immunocompetent kids and young adults
contaminated fresh water
enter brain via olfactory mucosa
Granulomatous amebic encephalitis
cause
symptoms
who affected
enter how
Acanthamoeba or Balamuthia spp
headaches, neurological deficit, altered mental status
immunisuppressed people
hematogenous spread from respiratory tract or ulcerated skin
can be fulminant
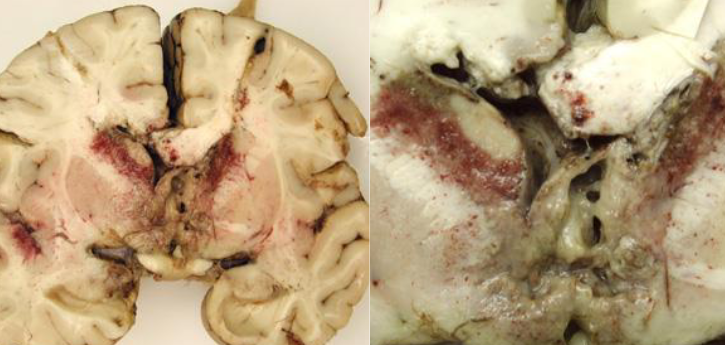
What is this
Granulomatous amebic encephalitis
Keratitis
caused by
symptoms
risks
Acanthamoeba spp.
corneal ulcers
contact lens users more at risk if poor hygiene
Naegleria diagnosis
CSF wet mount of giemsa stain
usually autopsy
Acanthamoeba/Balamuthia diagnosis
stained smear of biopsies (brain, skin, cornea)
corneal scrapings
Do N. fowleri form cysts in human tissues?
No
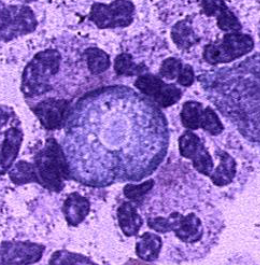
What is this
N. fowleri trophozoite
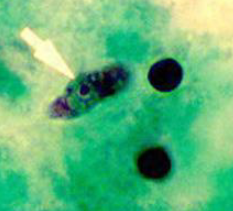
What is this
N. fowleri trophozoite
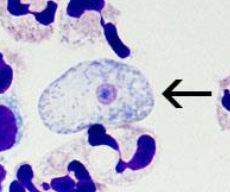
What is this?
N. fowleri trophozoite
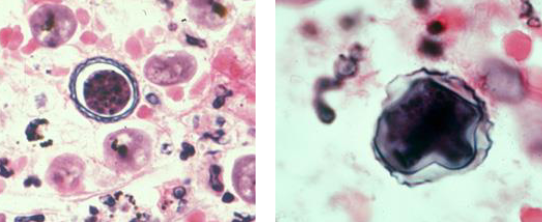
What is this?
can be found in brain, skin, eyes, lungs
Acanthamoeba cysts
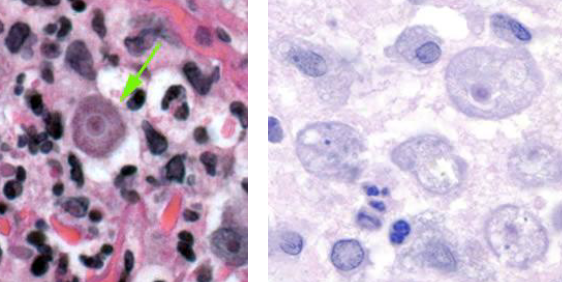
What is this?
no flagellated
pleomorphic
Acanthamoeba trophozoites
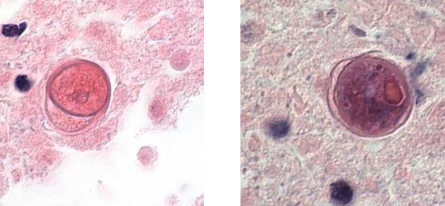
What is this?
Balamuthia mandrillaris cyst
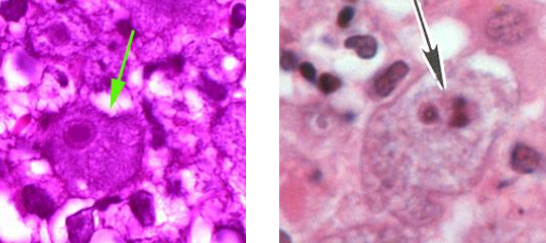
What is this?
no flagellated
Balamuthia mandrillaris trophozoite
Treatment for N. fowleri? Is it successful?
IV + amphotericin B in large doses; people rarely survive
Why is it that almost no one survives GAE?
Acanthomeba spp and Balamuthia are resistant against amphotericin B