NEW ACLS Pre-Course Self-Assessment
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
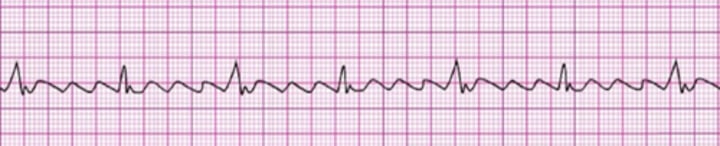
Atrial Flutter
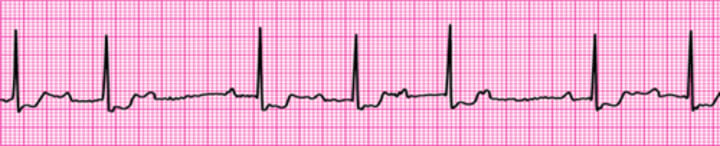
Second-degree atrioventricular block (Mobitz I Wenckebach)
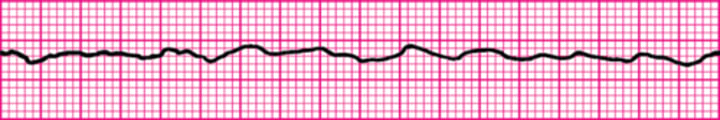
Ventricular fibrillation
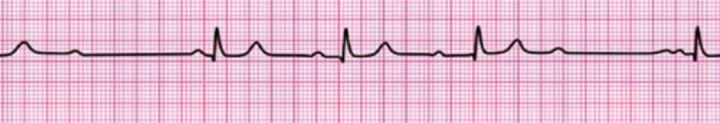
Second-degree atrioventricular block (Mobitz I Wenckebach)
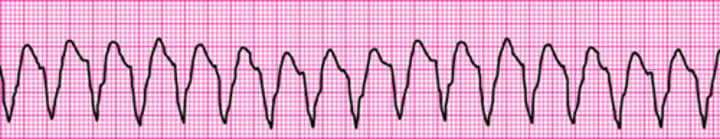
Monomorphic ventricular tachycardia
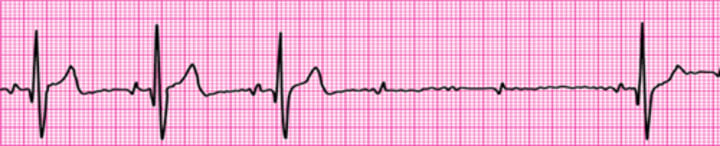
Second-degree atrioventricular block (Mobitz II block)
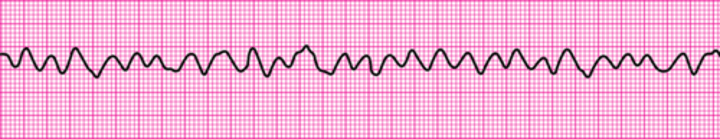
Ventricular fibrillation
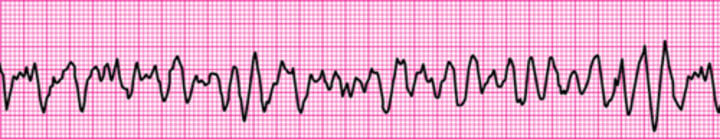
Ventricular fibrillation
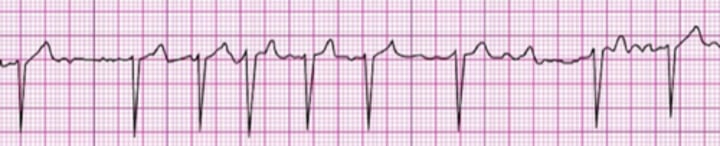
Atrial fibrillation
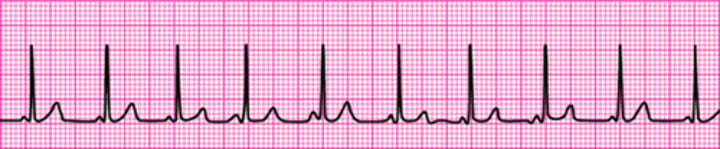
Pulseless electrical activity
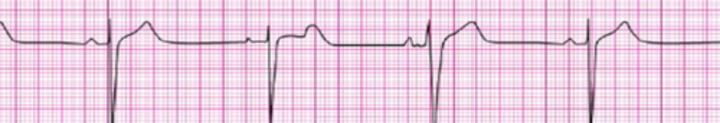
Sinus Bradycardia
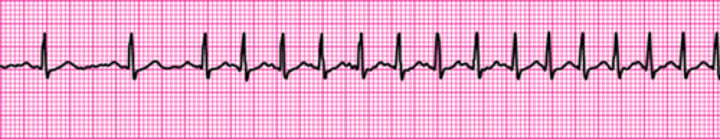
Supraventricular Tachycardia
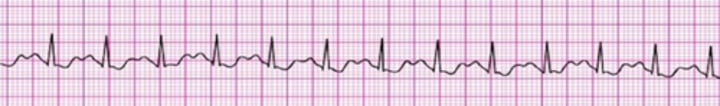
Sinus Tachycardia
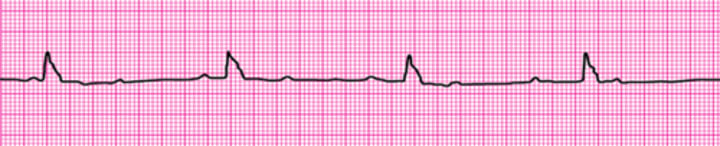
Third-degree Atrioventricular block
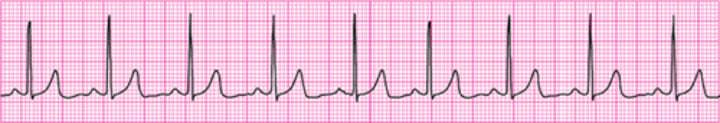
Normal Sinus Rhythm
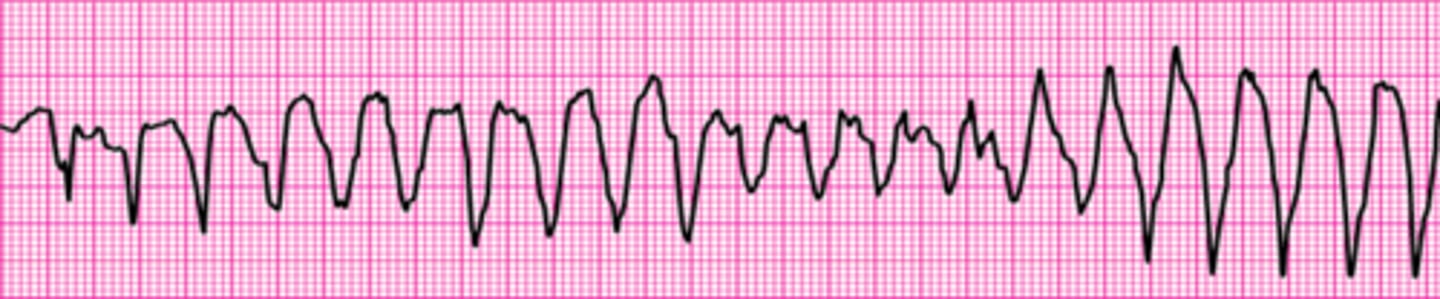
Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia
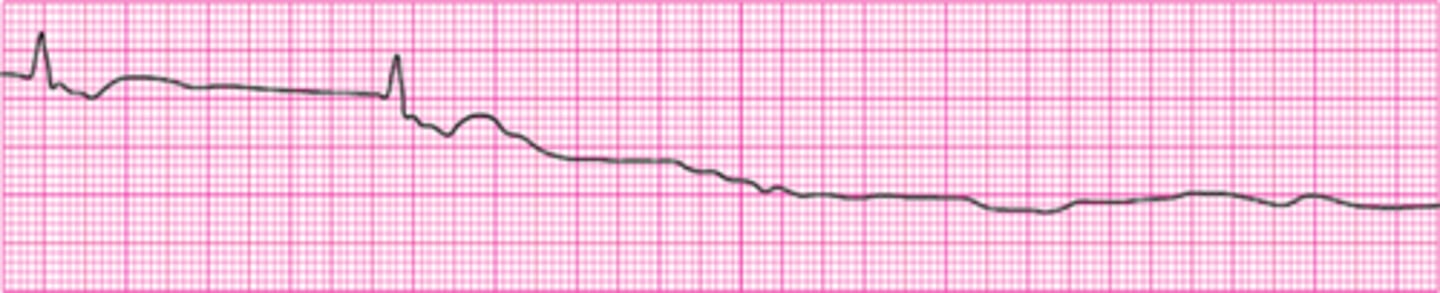
Agonal Rhythm/Asystole
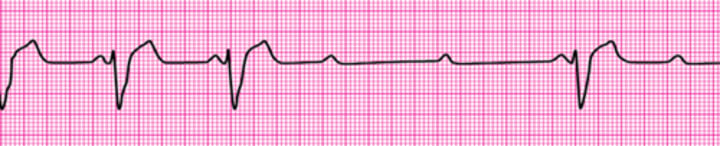
Second-degree Atrioventricular Block (Mobitz II Block)
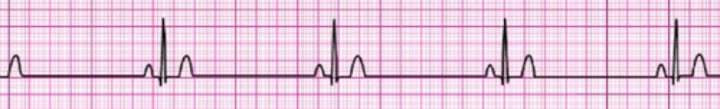
Sinus Bradycardia
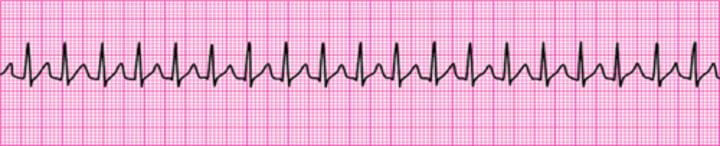
Supraventricular Tachycardia
A monitored patient in the ICU developed a sudden onset of narrow-complex tachycardia at a rate of 220/min. The patient's blood pressure is 128/58 mm Hg, the PETCO2 is 38 mm Hg, and the pulse oximetry reading is 98%. There is vascular access in the left arm, and the patient has not been given any vasoactive drugs. A 12-lead ECG confirms a supraventricular tachycardia with no evidence of ischemia or infarction. The heart rate has not responded to vagal maneuvers. What is your next action?
Administer amiodarone 300 mg IV push
Administer adenosine 6 mg IV push
Perform synchronized cardioversion at 200 J
Perform synchronized cardioversion at 50 J
Administer adenosine 6 mg IV push
You are caring for a 66-year-old man with a history of a large intracerebral hemorrhage 2 months ago. He is being evaluated for another acute stroke. The CT scan is negative for hemorrhage. The patient is receiving oxygen via nasal cannula at 2 L/min, and an IV has been established. His blood pressure is 180/100 mm Hg. Which drug do you anticipate giving to this patient?
Aspirin
rtPA
Glucose (D50)
Nicardipine
Aspirin
A patient is in pulseless ventricular tachycardia. Two shocks and 1 dose of epinephrine have been given. Which drug should be given next?
Epinephrine 3 mg
Lidocaine 0.5 mg/kg
Amiodarone 300 mg
Adenosine 6 mg
Amiodarone 300 mg
A patient with possible STEMI has ongoing chest discomfort. What is a contraindication to nitrate administration?
Heart rate less than 90/min
Use of a phosphodiesterase inhibitor within the previous 24 hours
Anterior wall myocardial infarction
Systolic blood pressure greater than 180 mm Hg
Use of a phosphodiesterase inhibitor within the previous 24 hours
A patient is in cardiac arrest. High-quality chest compressions are being given. The patient is intubated, and an IV has been started. The rhythm is asystole. What is the first drug/dose to administer?
Dopamine 2 to 20 mcg/kg per minute IV/IO
Atropine 1 mg IV/IO
Epinephrine 1 mg IV/IO
Atropine 0.5 mg IV/IO
Epinephrine 1 mg IV/IO
A patient is in refractory ventricular fibrillation. High-quality CPR is in progress. One dose of epinephrine was given after the second shock. An antiarrhythmic drug was given immediately after the third shock. You are the team leader. Which medication do you order next?
Epinephrine 1 mg
A second dose of the antiarrhythmic drug
Epinephrine 3 mg
Sodium bicarbonate 50 mEq
Epinephrine 1 mg
Which intervention is most appropriate for the treatment of a patient in asystole?
Atropine
Transcutaneous pacing
Defibrillation
Epinephrine
Epinephrine
A patient with sinus bradycardia and a heart rate of 42/min has diaphoresis and a blood pressure of 80/60 mm Hg. What is the initial dose of atropine?
0.1 mg
1 mg
3 mg
0.5 mg
1 mg
A patient with STEMI has ongoing chest discomfort. Heparin 4000 units IV bolus and a heparin infusion of 1000 units per hour are being administered. The patient did not take aspirin because he has a history of gastritis, which was treated 5 years ago. What is your next action?
Give enteric-coated aspirin 325 mg rectally
Give aspirin 162 to 325 mg to chew
Give enteric-coated aspirin 75 mg orally
Give clopidogrel 300 mg orally
Give aspirin 162 to 325 mg to chew
A 57-year-old woman has palpitations, chest discomfort, and tachycardia. The monitor shows a regular wide-complex QRS at a rate of 180/min. She becomes diaphoretic, and her blood pressure is 80/60 mm Hg. Which action do you take next?
Seek expert consultation
Perform electrical cardioversion
Establish IV access
Obtain a 12-lead ECG
Perform electrical cardioversion
A patient is in refractory ventricular fibrillation and has received multiple appropriate defibrillation shocks, epinephrine 1 mg IV twice, and an initial dose of amiodarone 300 mg IV. The patient is intubated. Which best describes the recommended second dose of amiodarone for this patient?
150 mg IV push
1 to 2 mg/min infusion
300 mg IV push
1 mg/kg IV push
150 mg IV push
A patient has sinus bradycardia with a heart rate of 36/min. Atropine has been administered to a total dose of 3 mg. A transcutaneous pacemaker has failed to capture. The patient is confused, and her blood pressure is 88/56 mm Hg. Which therapy is now indicated?
Adenosine 6 mg
Epinephrine 2 to 10 mcg/min
Normal saline 250 mL to 500 mL bolus
Atropine 1 mg
Epinephrine 2 to 10 mcg/min
A patient is in cardiac arrest. Ventricular fibrillation has been refractory to an initial shock. If no pathway for medication administration is in place, which method is preferred?
Endotracheal tube
Central line
External jugular vein
IV or IO
IV or IO
A patient is in cardiac arrest. Ventricular fibrillation has been refractory to a second shock. Which drug should be administered first?
Epinephrine 1 mg IV/IO
Lidocaine 1 mg/kg IV/IO
Atropine 1 mg IV/IO
Sodium bicarbonate 50 mEq IV/IO
Epinephrine 1 mg IV/IO
A patient has a rapid irregular wide-complex tachycardia. The ventricular rate is 138/min. He is asymptomatic, with a blood pressure of 110/70 mm Hg. He has a history of angina. What action is recommended next?
Performing synchronized cardioversion
Giving lidocaine 1 to 1.5 mg IV bolus
Giving adenosine 6 mg IV bolus
Seeking expert consultation
Seeking expert consultation
In which situation does bradycardia require treatment?
Diastolic blood pressure greater than 90 mm Hg
12-lead ECG showing a normal sinus rhythm
Hypotension
Systolic blood pressure greater than 100 mm Hg
Hypotension
What is the indication for the use of magnesium in cardiac arrest?
Shock-refractory monomorphic ventricular tachycardia
Ventricular tachycardia associated with a normal QT interval
Shock-refractory ventricular fibrillation
Pulseless ventricular tachycardia-associated torsades de pointes
Pulseless ventricular tachycardia-associated torsades de pointes
You arrive on the scene with the code team. High-quality CPR is in progress. An AED has previously advised "no shock indicated." A rhythm check now finds asystole. After resuming high-quality compressions, which action do you take next?
Perform endotracheal intubation
Call for a pulse check
Insert a laryngeal airway
Establish IV or IO access
Establish IV or IO access
A 35-year-old woman has palpitations, light-headedness, and a stable tachycardia. The monitor shows a regular narrow-complex QRS at a rate of 180/min. Vagal maneuvers have not been effective in terminating the rhythm. An IV has been established. Which drug should be administered?
Epinephrine 2 to 10 mcg/kg per minute
Lidocaine 1 mg/kg
Atropine 0.5 mg
Adenosine 6 mg
Adenosine 6 mg
A 62-year-old man suddenly experienced difficulty speaking and left-sided weakness. He meets initial criteria for fibrinolytic therapy, and a CT scan of the brain is ordered. Which best describes the guidelines for antiplatelet and fibrinolytic therapy?
Give aspirin 120 mg and clopidogrel 75 mg orally
Give aspirin 162 to 325 mg to be chewed immediately
Give heparin if the CT scan is negative for hemorrhage
Hold aspirin for at least 24 hours if rtPA is administered
Hold aspirin for at least 24 hours if rtPA is administered
How often should you switch chest compressors to avoid fatigue?
About every 2 minutes
About every 4 minutes
About every 5 minutes
About every 3 minutes
About every 2 minutes
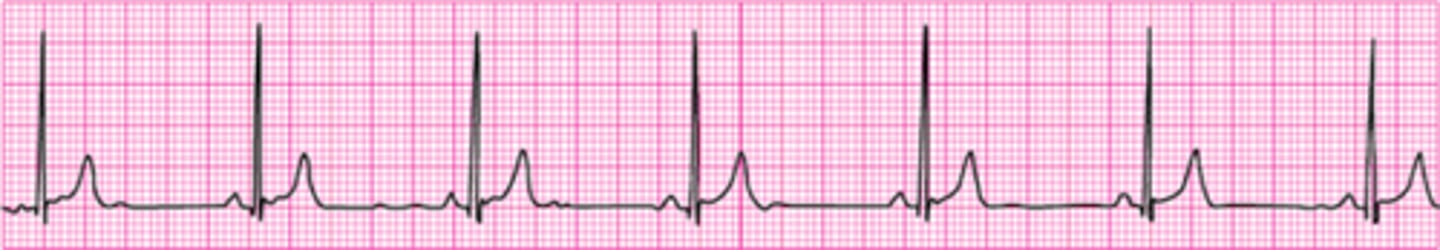
Your patient is a 56-year-old woman with a history of type 2 diabetes who reports feeling dizzy. She is pale and diaphoretic. Her blood pressure is 80/60 mm Hg. The cardiac monitor documents the rhythm shown here. She is receiving oxygen at 4 L/min by nasal cannula, and an IV has been established. What do you administer next?
Dopamine at 2 to 10 mcg/kg per minute
Morphine sulfate 4 mg IV
Atropine 1 mg IV
Glucose 50% IV push
Atropine 1 mg IV
What action minimizes the risk of air entering the victim's stomach during bag-mask ventilation?
Ventilating as quickly as you can
Ventilating until you see the chest rise
Squeezing the bag with both hands
Delivering the largest breath you can
Ventilating until you see the chest rise
How does complete chest recoil contribute to effective CPR?
Reduces the risk of rib fractures
Allows maximum blood return to the heart
Reduces rescuer fatigue
Increases the rate of chest compressions
Allows maximum blood return to the heart
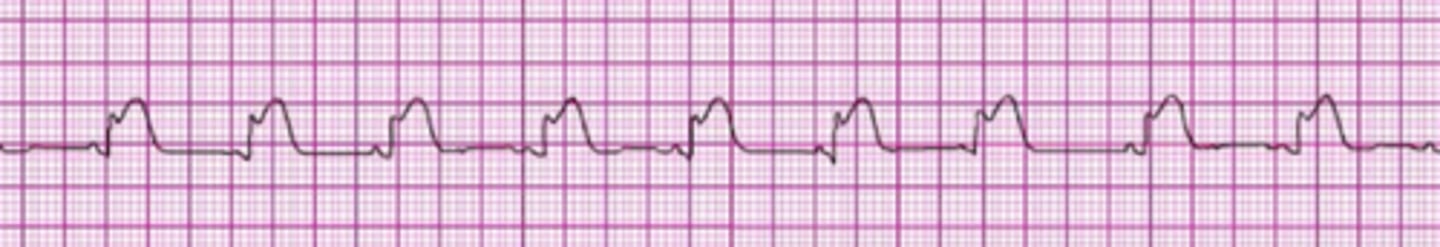
A patient's 12-lead ECG is transmitted by the paramedics and shows a STEMI. When the patient arrives in the emergency department, the rhythm shown here is seen on the cardiac monitor. The patient has resolution of moderate (5/10) chest pain after 3 doses of sublingual nitroglycerin. Blood pressure is 104/70 mm Hg. Which intervention is most important in reducing this patient's in-hospital and 30-day mortality rate?
Reperfusion therapy
Nitroglycerin administration
Application of transcutaneous pacemaker
Atropine administration
Reperfusion therapy
Which action is likely to cause air to enter the victim's stomach (gastric inflation) during bag-mask ventilation?
Ventilating too quickly
Providing a good seal between the face and the mask
Giving breaths over 1 second
Providing just enough volume for the chest to rise
Ventilating too quickly
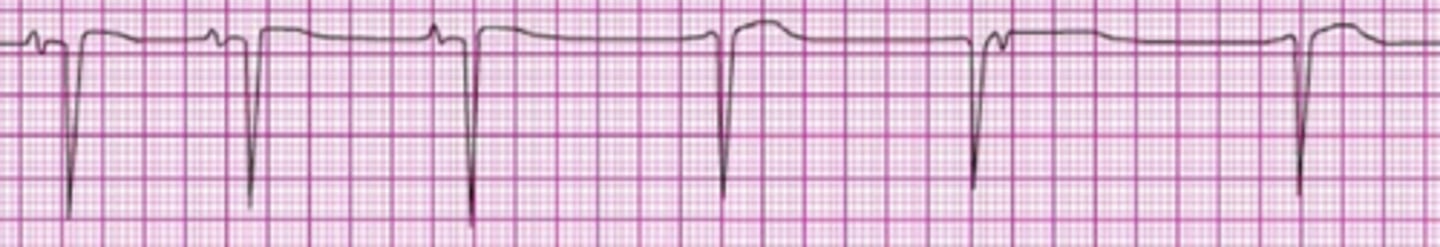
A patient becomes unresponsive. You are uncertain if a faint pulse is present. The rhythm shown here is seen on the cardiac monitor. An IV is in place. Which action do you take next?
Start high-quality CPR
Begin transcutaneous pacing
Administer epinephrine 1 mg IV
Administer atropine 1 mg
Start high-quality CPR
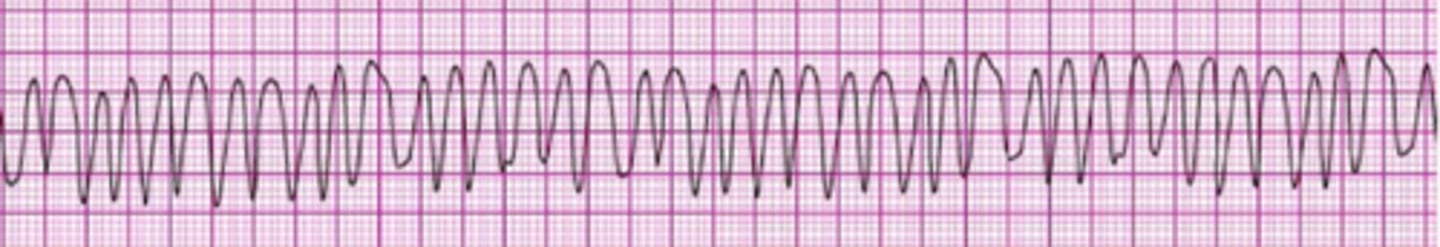
A patient has been resuscitated from cardiac arrest. During post-ROSC treatment, the patient becomes unresponsive, with the rhythm shown here. Which action is indicated next?
Perform synchronized cardioversion
Repeat amiodarone 300 mg IV
Give lidocaine 1 to 1.5 mg/kg IV
Give an immediate unsynchronized high-energy shock (defibrillation dose)
Give an immediate unsynchronized high-energy shock (defibrillation dose)
What is the maximum interval for pausing chest compressions?
10 seconds
20 seconds
25 seconds
15 seconds
10 seconds
Which action should you take immediately after providing an AED shock?
Prepare to deliver a second shock
Resume chest compressions
Check the pulse rate
Start rescue breathing
Resume chest compressions
Your patient is not responsive and is not breathing. You can palpate a carotid pulse. Which action do you take next?
Apply an AED
Obtain a 12-lead ECG
Start an IV
Start rescue breathing
Start rescue breathing
You arrive on the scene to find CPR in progress. Nursing staff report the patient was recovering from a pulmonary embolism and suddenly collapsed. Two shocks have been delivered, and an IV has been initiated. What do you administer now?
Transcutaneous pacing
Endotracheal intubation
Epinephrine 1 mg IV
Atropine 0.5 mg IV
Epinephrine 1 mg IV
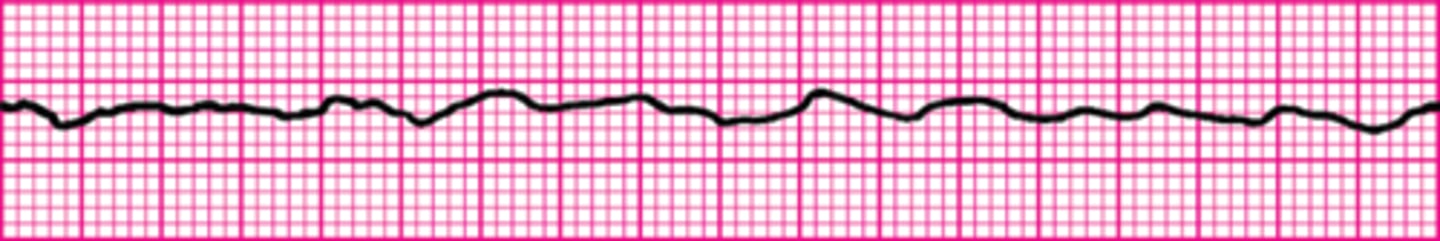
A patient was in refractory ventricular fibrillation. A third shock has just been administered. Your team looks to you for instructions. What is your next action?
Resume high-quality chest compressions
Give amiodarone 300 mg IV
Check the carotid pulse
Give atropine 1 mg IV
Resume high-quality chest compressions
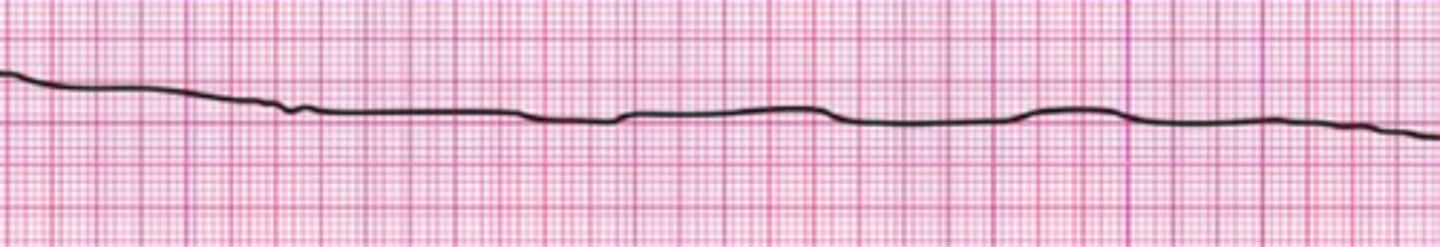
A 45-year-old woman with a history of palpitations develops light-headedness and palpitations. She has received adenosine 6 mg IV for the rhythm shown here, without conversion of the rhythm. She is now extremely apprehensive. Her blood pressure is 128/70 mm Hg. What is the next appropriate intervention?
Perform synchronized cardioversion
Perform unsynchronized cardioversion
Administer adenosine 12 mg IV
Perform vagal maneuvers
Administer adenosine 12 mg IV
What is the recommended depth of chest compressions for an adult victim?
At least 3 inches
At least 2.5 inches
At least 1.5 inches
At least 2 inches
At least 2 inches
You are the code team leader and arrive to find a patient with CPR in progress. On the next rhythm check, you see the rhythm shown here. Team members tell you that the patient was well but reported chest discomfort and then collapsed. She has no pulse or respirations. Bag-mask ventilations are producing visible chest rise, and IO access has been established. Which intervention would be your next action?
Intubation and administration of 100% oxygen
Epinephrine 1 mg
Dopamine at 10 to 20 mcg/kg per minute
Atropine 1 mg
Epinephrine 1 mg
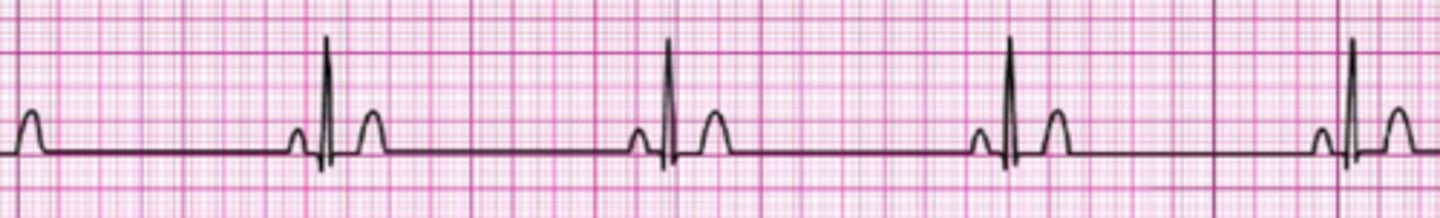
After initiation of CPR and 1 shock for ventricular fibrillation, this rhythm is present on the next rhythm check. A second shock is given, and chest compressions are resumed immediately. An IV is in place, and no drugs have been given. Bag-mask ventilations are producing visible chest rise. What is your next intervention?
Give epinephrine 1 mg IV/IO
Administer 3 sequential (stacked) shocks at 320 J (monophasic defibrillator)
Intubate and administer 100% oxygen
Give amiodarone 300 mg IV/IO
Give epinephrine 1 mg IV/IO
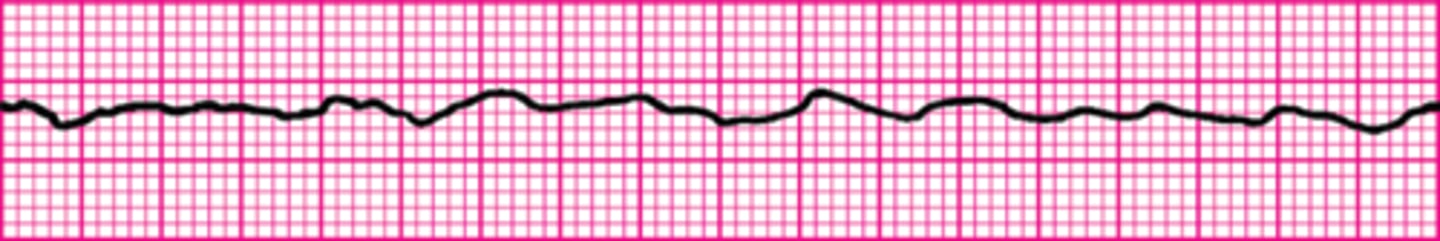
A 35-year-old woman presents with a chief complaint of palpitations. She has no chest discomfort, shortness of breath, or light-headedness. Her blood pressure is 120/78 mm Hg. Which intervention is indicated first?
Adenosine 3 mg IV bolus
Metoprolol 5 mg IV and repeat if necessary
Vagal maneuvers
Adenosine 12 mg IV slow push (over 1 to 2 minutes)
Vagal maneuvers
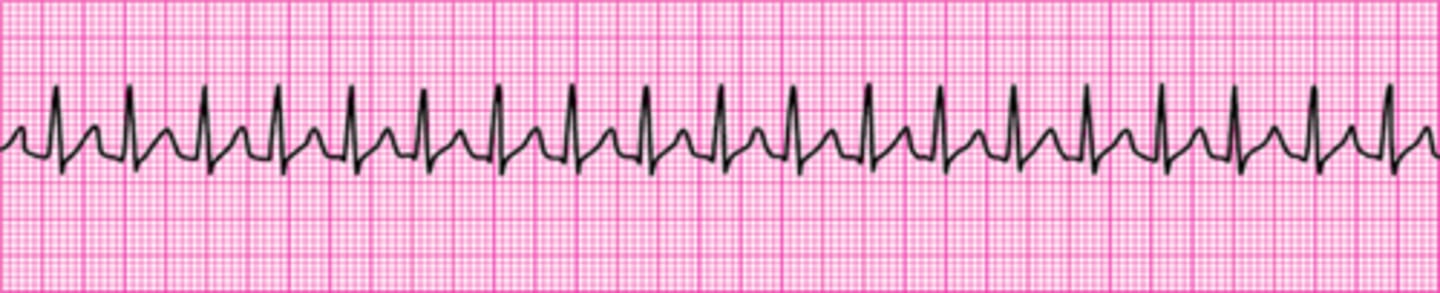
You are providing bag-mask ventilations to a patient in respiratory arrest. How often should you provide ventilations?
Every 6 seconds
Every 12 seconds
Every 14 seconds
Every 10 seconds
Every 6 seconds
What is the recommended compression rate for high-quality CPR?
70 to 80 compressions per minute
100 to 120 compressions per minute
50 to 20 compressions per minute
90 to 100 compression per minute
100 to 120 compressions per minute