Arrhythmias and EKG - Pathophysiology
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
What does this refer
Are disturbances of the heart rhythm
Ranges from an occasional “missed” beat or rapid beats to severe disturbances that affect the pumping ability of the heart
Can be caused by an abnormal rate of impulse generation or an abnormal impulse conduction
Dysrhythmias
What does this refer
Atrial fib/flutter
WPW syndrome
Reentry tachycardia
Ventricular tach/fib
Tachycardia
What does this refer
Bundle branch blocks
AV node block
Bradycardia
What does this refer
“Arrhythmias, bradyarrhythmias, tachyarrhythmias”
AV block
What does this refer
What does this refer
What does this refer
What does this refer
What does this refer
What does this refer
What does this refer
What does this refer
What does this refer
What does this refer
What does this refer
Ectopic beats can be normal, particularly when generated within the atria (premature atrial contraction).
Ventricular premature contractions can also occur sporadically in the absence of myocardial disease
Ectopic activity is promoted by hypoxia and ischemia, increased sympathetic tone, hyperkalemia
Ectopic Activity Can Generate Extra Beats
What does this refer
Conduction blocks
AV node pacemaker cells are vulnerable to aging, hypoxia
Common site of partial or complete blocks of propagation—can result in bradycardia due to nonconducted beats
Focal conduction blocks contribute to reentrant arrhythmias
General Mechanisms of Arrhythmias

What does this refer to “Prolonged PR interval” look at image
Atrioventricular Block—First Degree
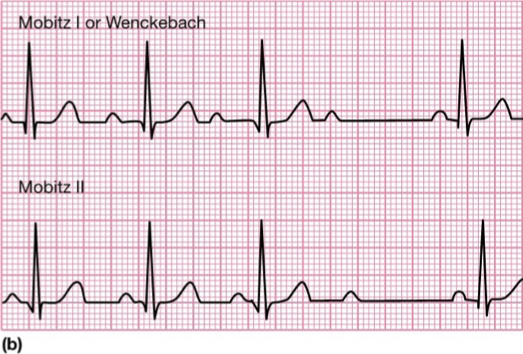
What does this refer
P waves are not all followed by QRS complex, temporary failure of AV conduction
Mobitz I shows progressive PR lengthening before nonconducted P wave
Atrioventricular Block—Second Degree
What does this refer to
“favored by ischemia, sympathetic nervous system stimulation; common during myocardial infarction”
Increased automaticity
What does this refer to
Increased automaticity: favored by ischemia, sympathetic nervous system stimulation; common during myocardial infarction
Triggered activity
Reentry—facilitated by branching and converging pathways, differing rates of propagation, and ectopic foci
Mechanisms of Tachyarrhythmias
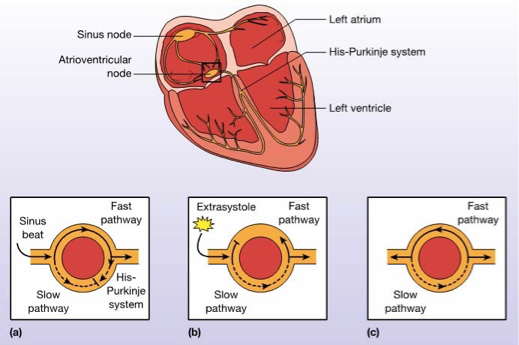
What does this refer
Sinus beat is conducted along fast pathway to bundle of His
Slow pathway has refractory section, impulse is blocked
Ectopic impulse stimulates slow pathway, travels anterograde along His–Purkinje path AND retrograde along fast pathway
Also known as “circus rhythm”
Reentry in AV nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT)
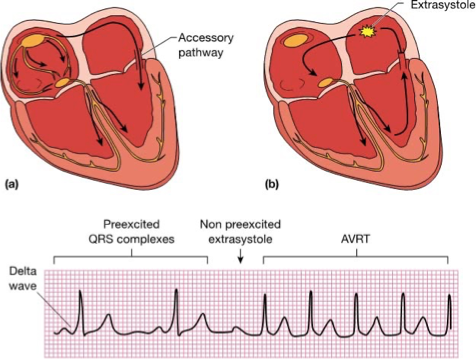
What does this refer
Accessory pathway between atria and ventricles can bypass AV node completely, setting up large reentrant circuit
Without extrasystole, impulse moves anterograde between atria and ventricles—creating delta wave (early rise of QRS complex)
With ectopic beat, circus rhythm creates tachycardia
Reentry in Wolf–Parkinson–White syndrome
What does this refer
Most common chronic rhythm disturbance
No discernible P waves
Irregularly irregular QRS complexes and pulse
Associated with aging, atrial enlargement due to hypertension, heart failure, valve disorders
Common triggers: caffeine, alcohol, lung disease
Initiated by ectopic foci at junction of atria with pulmonary veins
Atrial Fibrillation
What does this refer
Inadequate cardiac output—loss of atrial “kick” completing ventricular filling, vulnerability to activity intolerance
Tachycardia shortens diastole and filling, compromises myocardial oxygenation, vulnerability to ischemia
Clot formation promoted by atrial blood stasis—major risk factor for transient ischemic attack [TIA] and stroke, managed with anticoagulants
Pathological consequences of atrial fibrillation
What does this refer
Short runs may be self-limiting
If sustained—predisposes to ventricular fibrillation
Mechanisms: increased automaticity, triggered activity, reentry
Life-threatening consequence of heart disease, ischemia, infarction
Can occur as a complication of genetic syndromes of ion channel dysfunction
Ventricular Tachycardias
What does this refer
Congenital dysfunction of fast sodium channel (SCN5A)
ECG with varying ST elevation
Potentially life-threatening, may require implanted defibrillator
Brugada Syndrome
What does this refer
Arise from genetic mutations affecting fast sodium channel or delayed potassium channel—enhancing excitability or delaying repolarization of nonpacemaker action potentials
Many subtypes with varying degrees of vulnerability to sudden death
Can precipitate the torsades de pointes form of ventricular tachycardia
Contraindication to certain medications
Long QT Syndrome
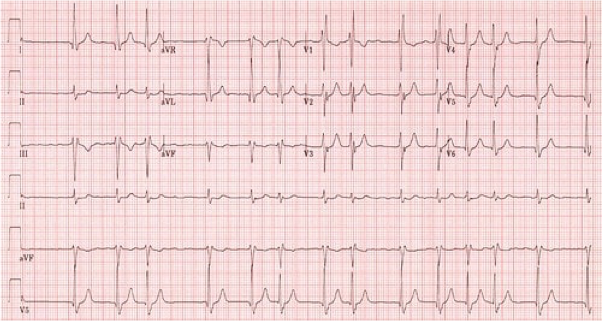
What does this refer to
Atrial fibrillation (Irregularly irregular rhythm, absent P waves)
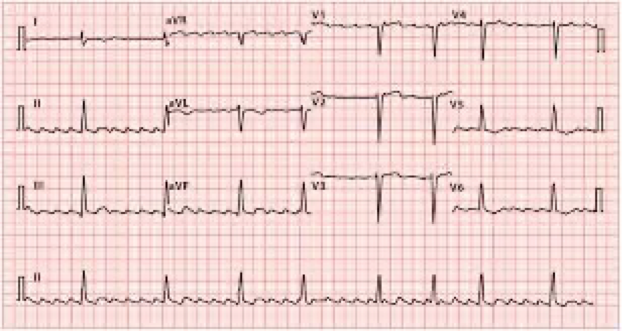
What does this refer “Sawtooth flutter waves, typically regular”
Atrial flutter
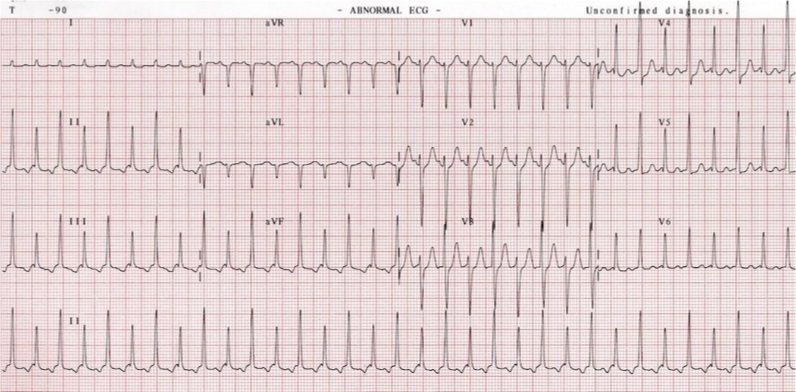
What does this refer to “narrow QRS, rapid rhythm”
Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT)
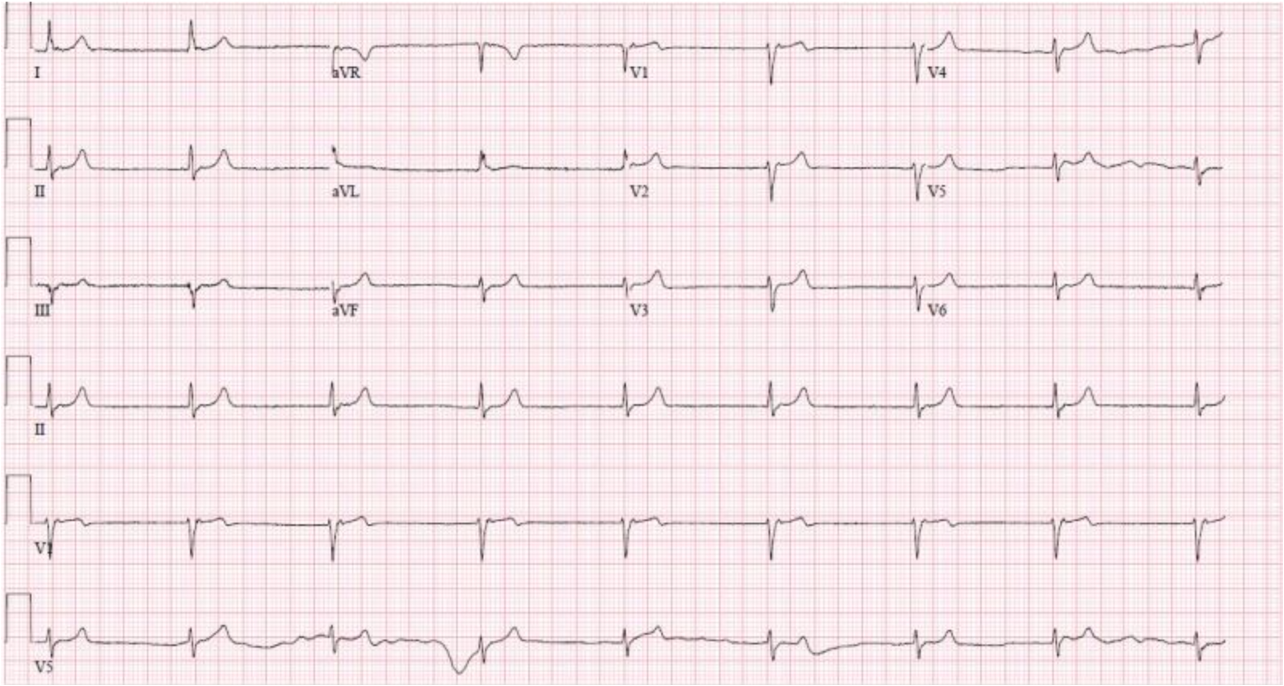
What does this refer “Originating near the AV node, absent or inverted P waves”
Junctional Rhythms
What does this refer
“PVCs, Ventricular Tachycardia, Ventricular Fibrillation”
Ventricular Dysrhythmias
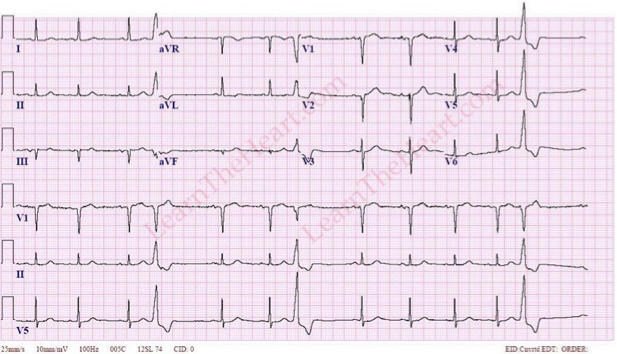
What does this refer “Wide and bizarre QRS complexes”
Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCs)
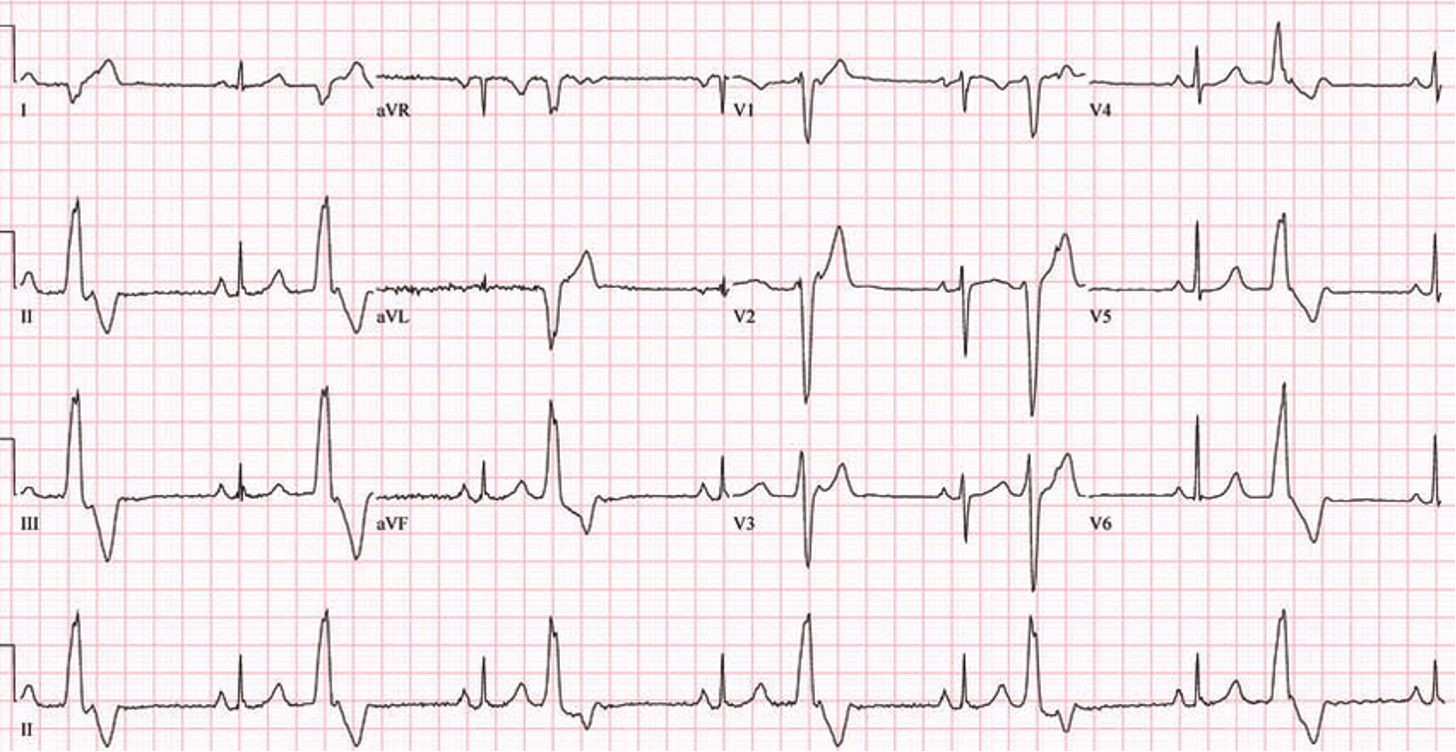
What does this refer “PVCs alternating with sinus beats”
Ventricular Bigeminy
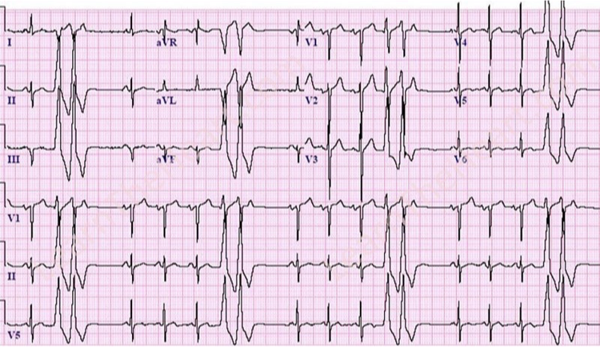
What does this refer to “sinus rhythm with pairs of PVC’s”
Couplets
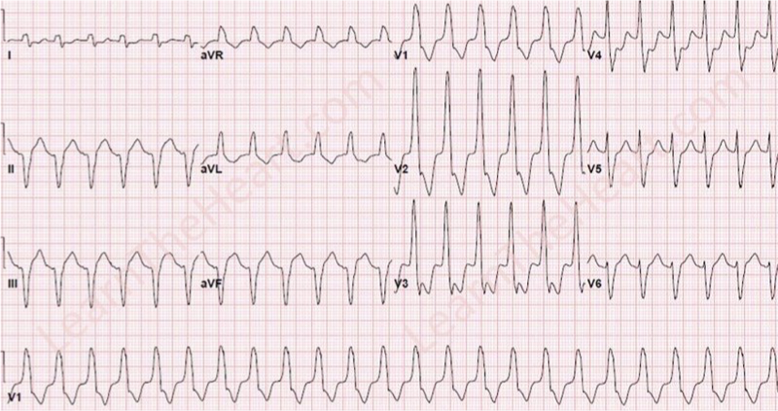
What does this refer to “rapid, wide QRS complexes”
Ventricular Tachycardia (VTach)
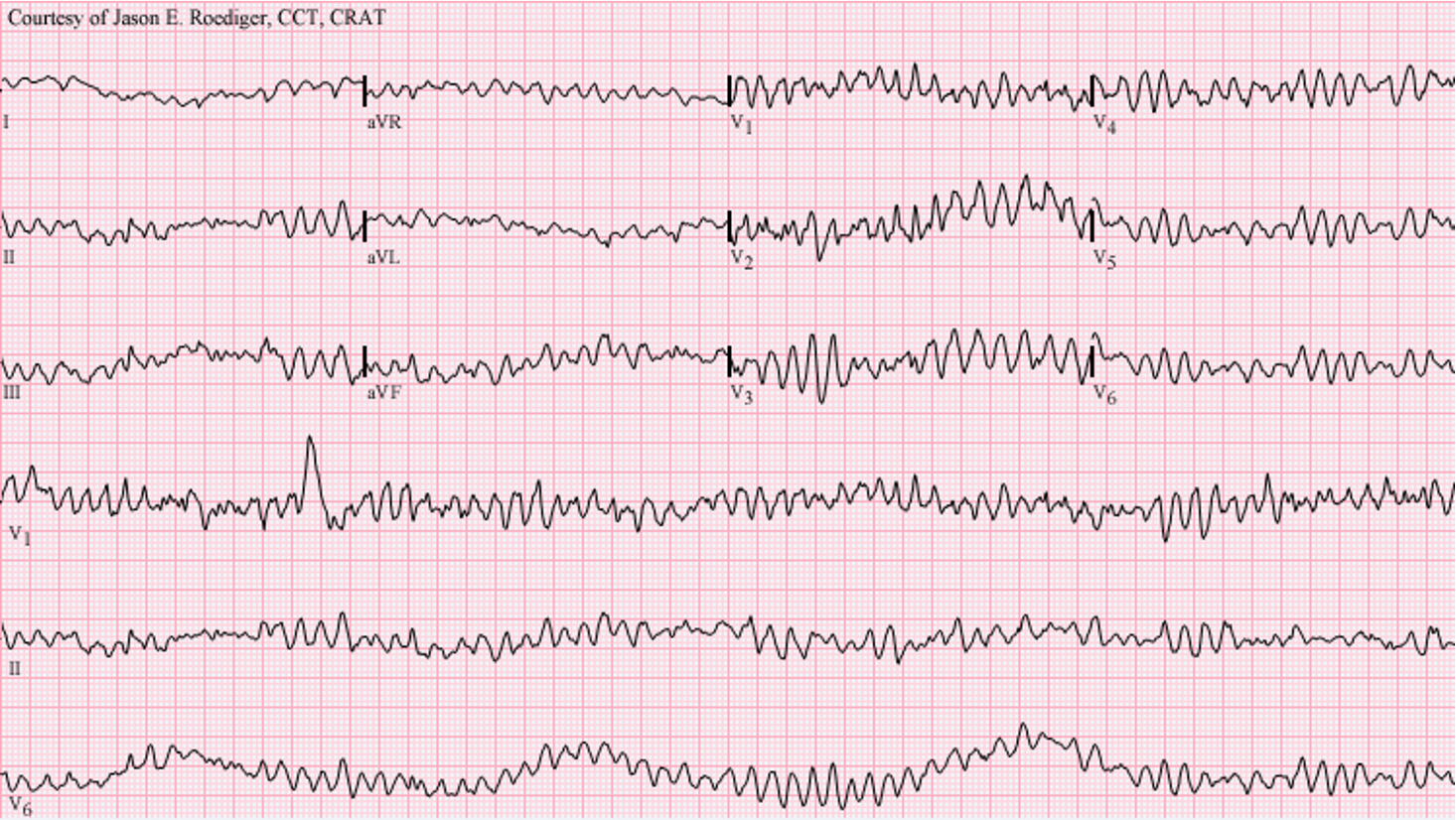
What does this refer to “Chaotic, irregular waveform with no organized QRS”
Ventricular Fibrillation (VFib)
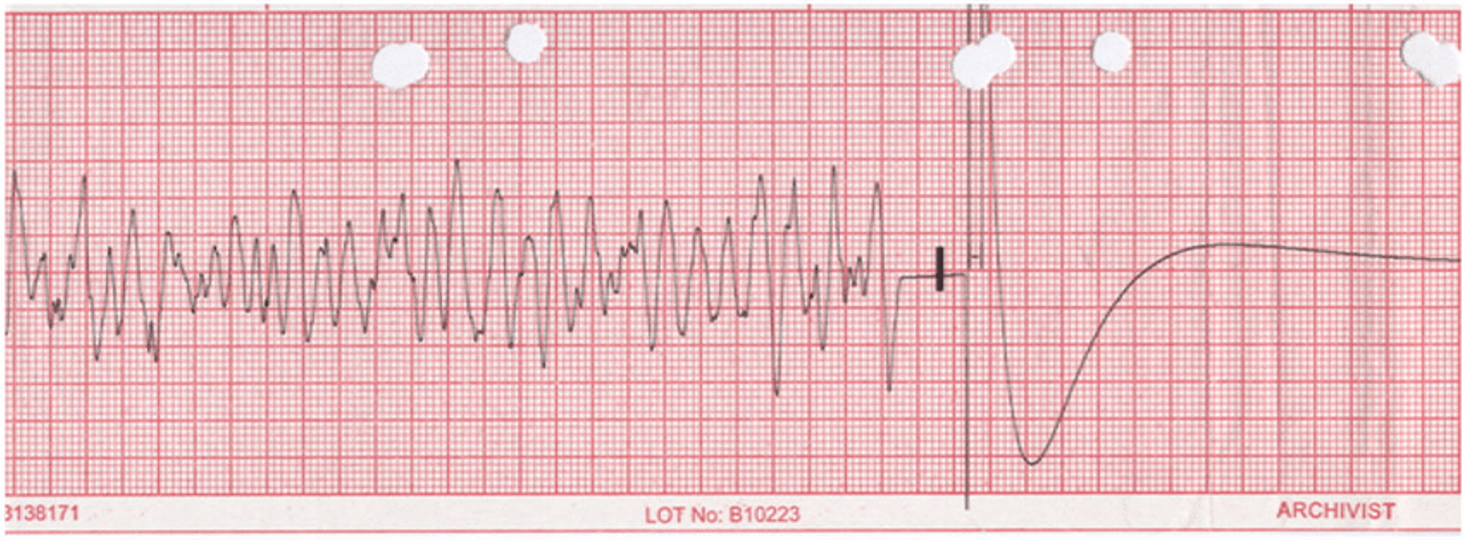
What does this refer to
Ventricular fibrillation to asytole
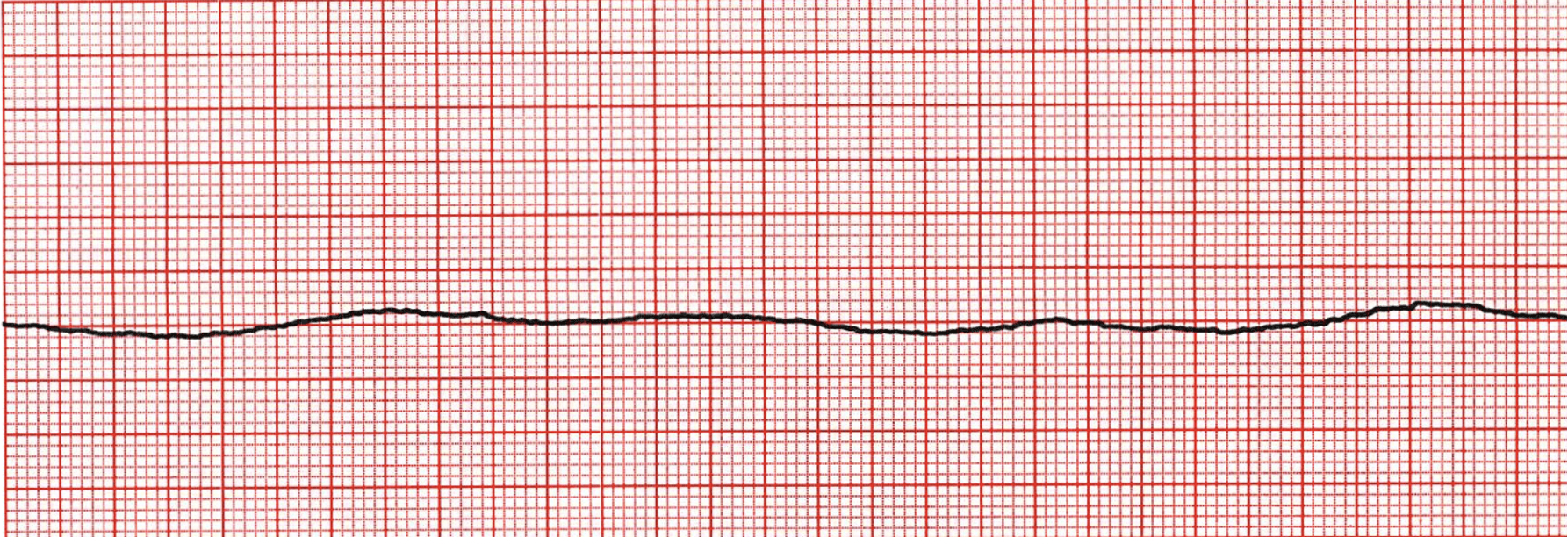
What does this refer to “Flatline- no electrical activity”
Asystole
What does this “First, Second (Mobitz I & II), and Third-degree AV blocks”
Heart blocks overview
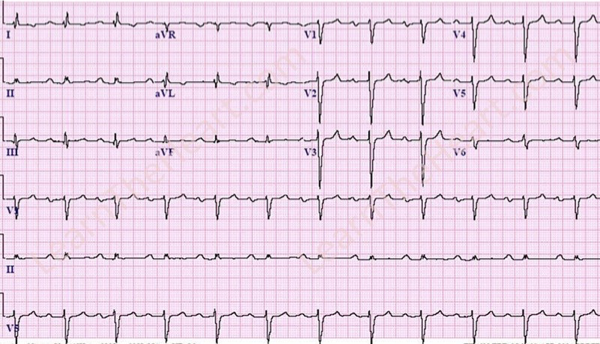
What does this refer to “Prolonged PR interval, all impulses conducted”
First-Degree AV Block
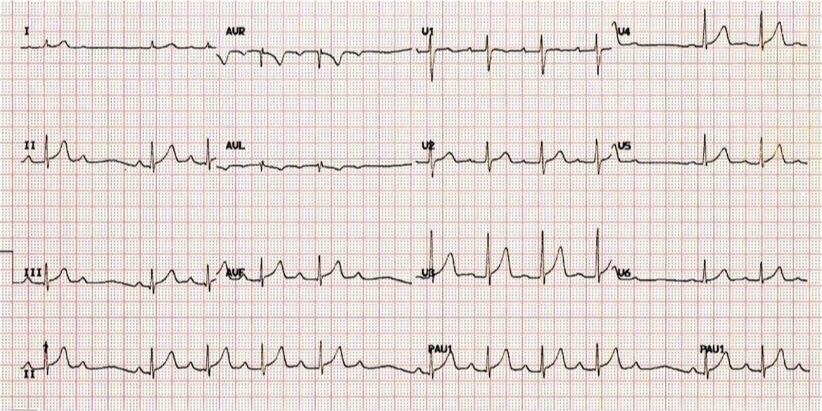
What does this refer to “Progressive PR prolongation then dropped beat”
Second-Degree AV Block Type I

What does this refer to “Dropped beats without PR prolongation”
Second-Degree AV Block Type II
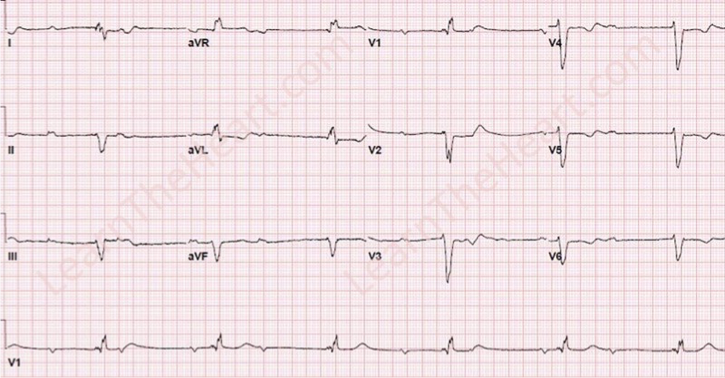
What does this refer to “Complete dissociation between atria and ventricles”
Third-degree AV block
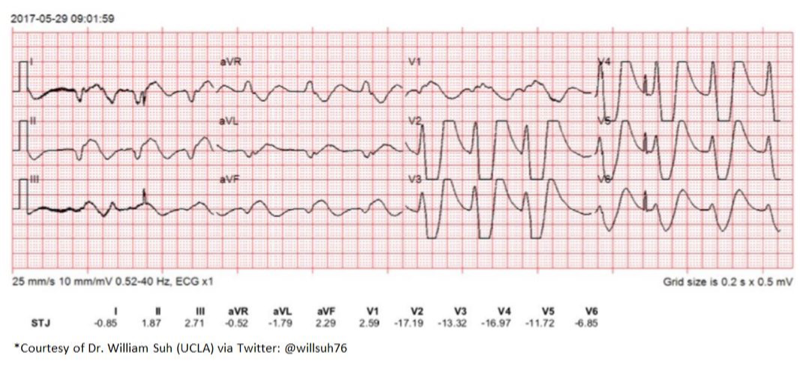
What does this refer to Electrical activity without mechanical contraction
Pulseless Electrical Activity (PEA)
What does this refer to
Special vascular system picks up excess fluid and returns it to the venous circulation.
Moving lymphocytes and leukocytes between different components of hte immune system is another important function
Has lymph nodes an vessels
Valves allow one way flow
Lymphatic veins and venules
Right lymphatic duct
Thoracic duct
Both duct drain into the subclavian
Afferent and efferent lymphatic vessels
Lymphatic System
What carries lymph to the nodes
Afferent vessels
What carries lymph away from the nodes
efferent
What is a spontaneous impulse generation from a source outside the SA node
Ectopy