HST History, Vital Signs and Physical Exam
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
136 Terms
Blood pressure is measured with a
sphygmomanometer
_____ hypertension occurs as a result of other conditions such as kidney or heart disease
secondary
Primary or _____ hypertension is hypertension without identifiable cause
essential
The standard unit for measuring blood pressure is mm of ____
mercury
When evaluating for orthostatic hypotension, if the pulse rate increases more than 10 bpm or if the blood pressure drops more than points this is documented as a positive ____
Tilt test
You should insert a rectal thermometer _____ for children
½-1 inches
You should insert a rectal thermometer _____ for adults
1 ½ inches
To take the tympanic temperature in an adult pull the pinna
Up and back
To take the tympanic temperature in a child pull the pinna
Down and back
Height should be recorded to the nearest
¼ inch
Auscultatory Gap
Period of diminished or absent sounds during Phase 2
(Often a sign of hypertension & can lead to falsely low systolic BP or falsely high diastolic BP)
What is the interview technique?
P: Provoke or Palliative
Q: Quantity or Quality
R: Region or Radiation
S: Severity Scale
T: Timing
Cheif Complaint
Subjective statement made by the patient describing the most significant signs or symptoms
Anthropometric measurement
Noninvasive quantitive measurements of the body. etc: height, weight, head circumference, BMI, and skinfold thickness
Differential diagnosis
Determining the correct diagnosis when two or more diagnosis are possible
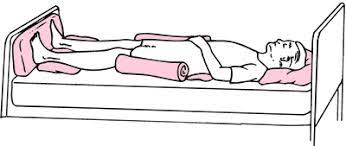
What position is this?
Supine
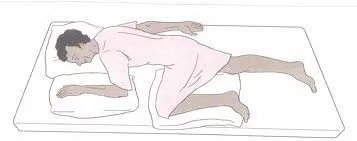
What position is this?
Sims’
The process of listening to body sounds
Auscultation
A forecast of the probably outcome and course of a disease
Prognosis
Tapping or striking the body to determine location, size and denstiny of a body structure or organ
Percussion
The visual examination of the patient’s entire body and overall appearance
Inspection
Repeating back what the patient says in your own words
Restatement
Objective information that can be detected by a person other than the affected person
Sign
Abbreviation for history is:
H/O
The SOAP method of documentation is short for:
S-Subjective, O-Objective, A-Assessment, P-Plan
WNL is short for:
Within normal limits
NKA is short for:
No known allergies
A body temperature above normal
Febrile
CC is short for:
Chief complaint
Type of drape often utilized for proctologic exams/a sterile body sheet with a hole or "window" that exposes the incision site
Fenestrated drape
Instruments to better examine the nasal cavity
Penlight and Nasal speculum
Pressure at phase 1 of Korotkoff sounds
Systolic
Exam position to evaluate the back and feet
Prone
Temperature at the armpit
Axillary
Pressure at phase 5 of Korotkoff sounds
Diastolic
Absence of respirations
Apnea
Rapid breathing
Tachypnea
Heart points to the right side of the chest
Dextrocardia
Machine that measures both pulse and Oxygen saturation
Pulse Oximeter
Process of measuring
Mensuration
physical exam by touching
Palpation
What materials are required for evaluation of the ears and hearing
Otoscope and audiometer
Systematic moving of a patient’s body parts for exam purposes
Manipulation
Slow heart rate
Bradycardia
What instrument is needed for an exam of the female genitalia
Vaginal speculum
The blood pressure cuff should be what distance above the elbow
1 Inch
The sounds heard while checking blood pressure
Korotkoff sounds
Subjective information provided by the patient, not observable or measurable
Symptom
Primary condition for when a patient is receiving care. Abbreviated DX:
Diagnosis
Your patient needs to have the front of the body examined but is short of breath and can’t sit unsupported, what is a good alternative position?
Fowler’s
If a female patient is unable to get in the lithotomy position because of severe arthritis, what is an alternative position?
Dorsal Recumbent
How long after eating and drinking should you wait to check an oral temperature
15 minutes
An exceptionally high fever
Hyperpyrexia
Pulse that feels like it leaps out then quickly disappears
Bounding pulse
A fast pulse
Tachycardia
Crackling sounds that indicate fluid in the lungs
Rales
The instrument that amplifies body sounds
Stethoscope
Low blood pressure that results from moving from a lying to sitting or standing position
Orthostatic or postural hypotension
Deep snoring or rattling breathing sounds associated with parietal obstruction of airways
Rhonchi
To take the tympanic temperature in a child, pull the pinna:
Down and back
What are the three body meadurements for infants
Length, width, and head circumference
Height should be recorded to the nearest
¼ Inch
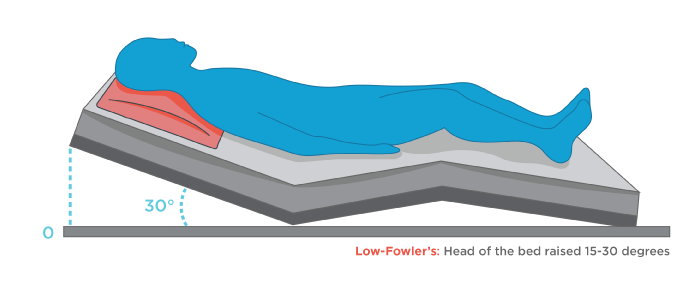
What position is this?
Semi-Fowler’s
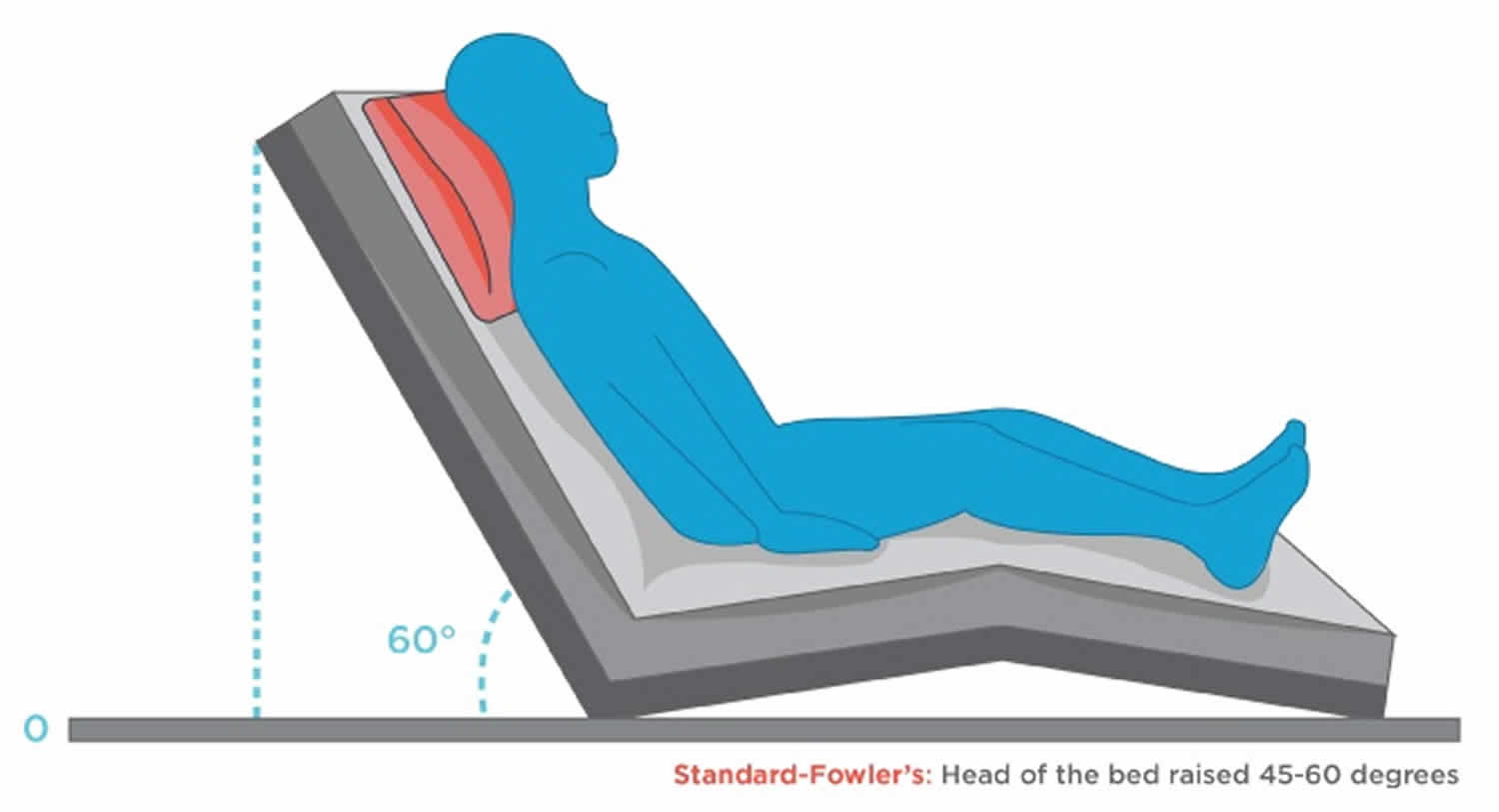
What position is this?
High-Fowler’’s
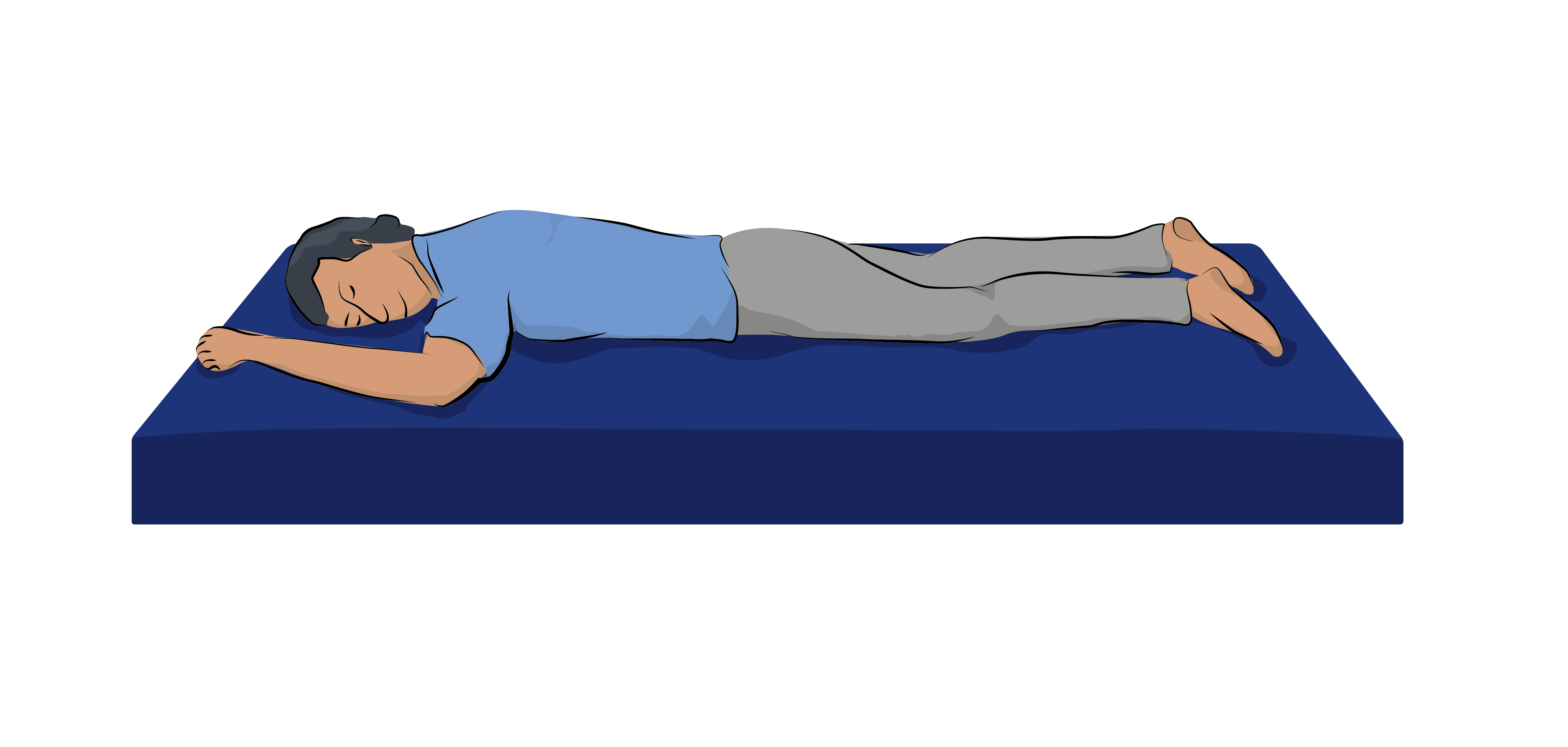
What position is this?
Prone
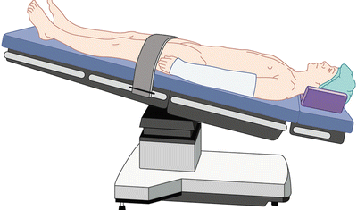
What position is this?
Trendelenberg
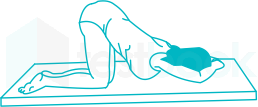
What position is this?
Knee Chest
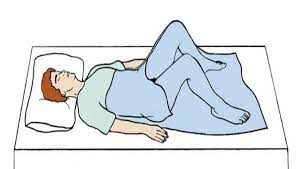
What position is this?
Dorsal Recumbent
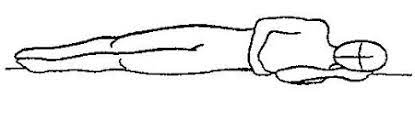
What position is this?
Lateral Recumbent
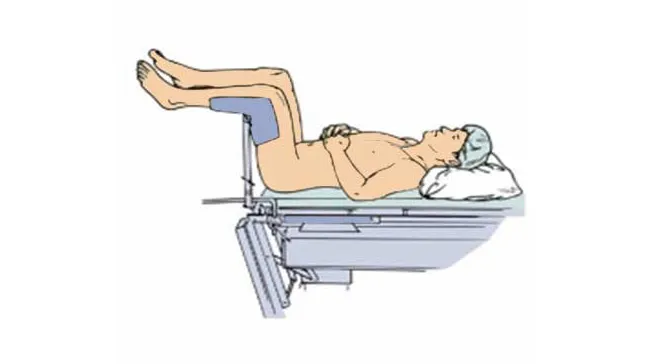
What position is this?
Lithotomy
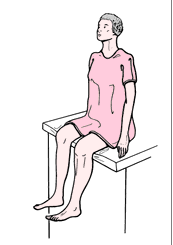
What position is this?
Sitting
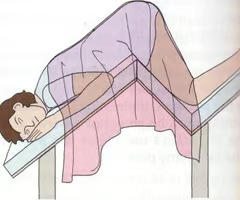
What position is this?
Proctologic
Proctologic position is also known as
Jackknife
Instrument(s) used to examine the eyes/vision
Opthalmascope
Instrument(s) used to examine the ears/hearing
Otoscope
Instrument(s) used to examine the nose & sinus
Penlight/Nasal speculum
Instrument(s) used to examine the chest & lungs
Stethoscope
Instrument(s) used to examine the Heart
Stethocope/Percussion
Instrument(s) used to examine the mouth & throat
Tongue depressor
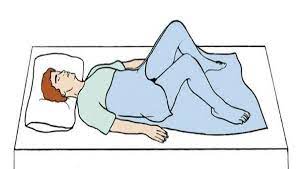
What position is this?
Dorsal Recumbent
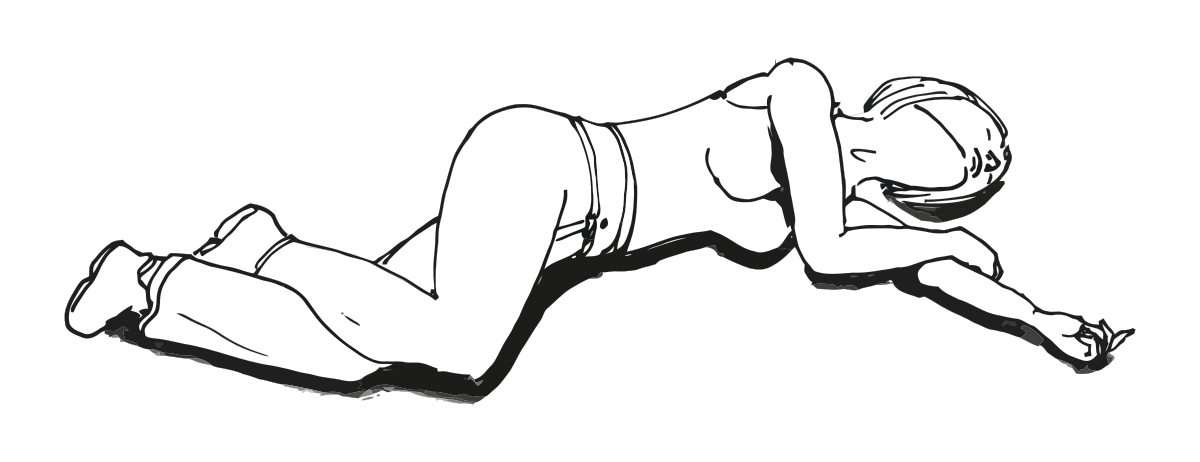
What position is this?
Lateral Recumbent
Instrument(s) used to examine the male genitalia
gloves
Instrument(s) used to examine the rectum
gloves, lubricant
Instrument(s) used to examine the neurologic system
Penlight, relfex hammer, or verbal questions
Normal rectal temperature
98.9°-109.1°
Normal oral temperature
97.8°-99.1°
Normal axillary temperature
96.6°-98°
Formula to convert °C to °F
°F=(°Cx9/5)+32
Normal adult pulse rate
60-100 BPM
Normal child pulse rate
80-130 BPM
Normal adult respiratory rate
12-18 RR
Normal adult systolic blood pressure
Less than 120
Normal adult diastolic blood pressure
Less than 80
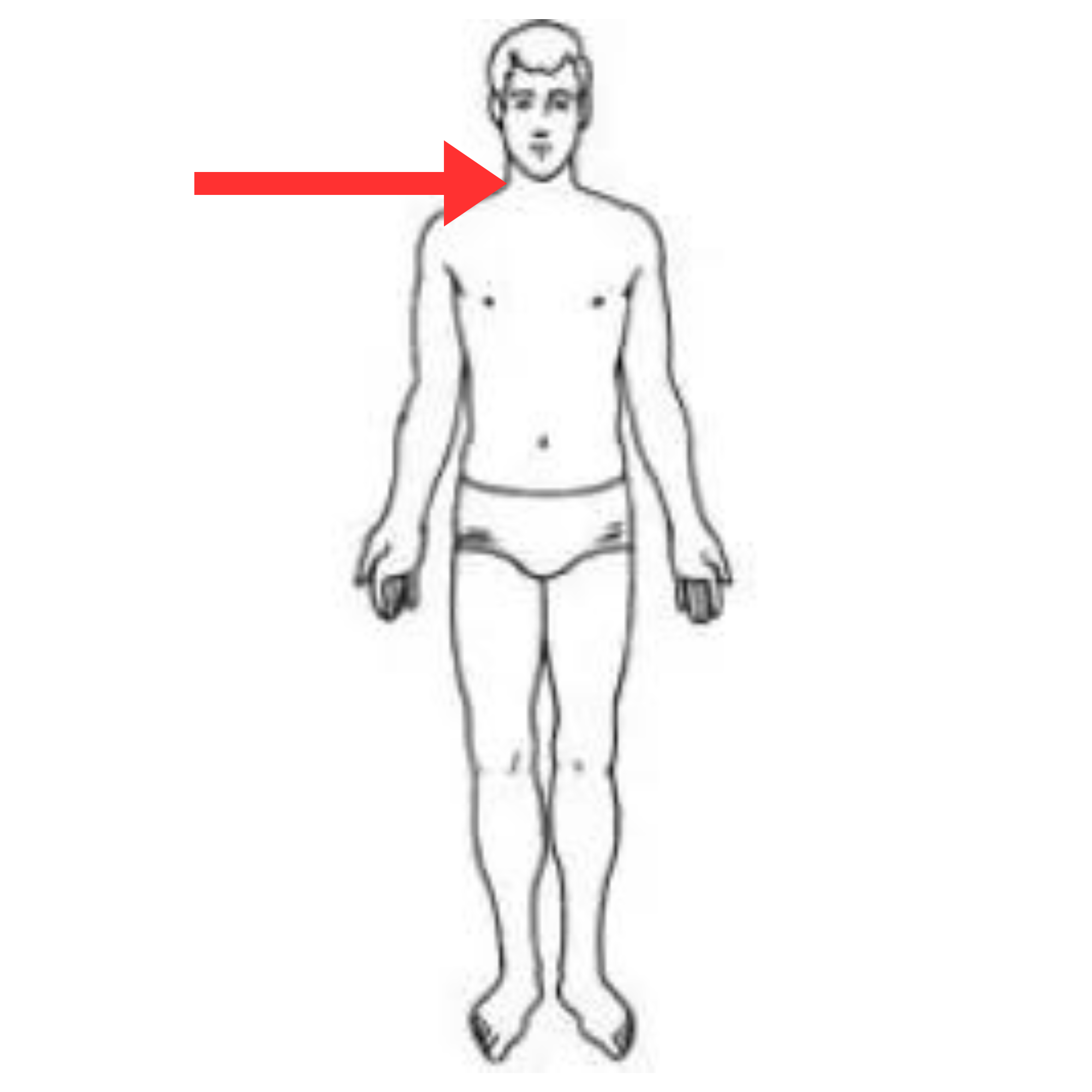
What is this pulse site
Carotid
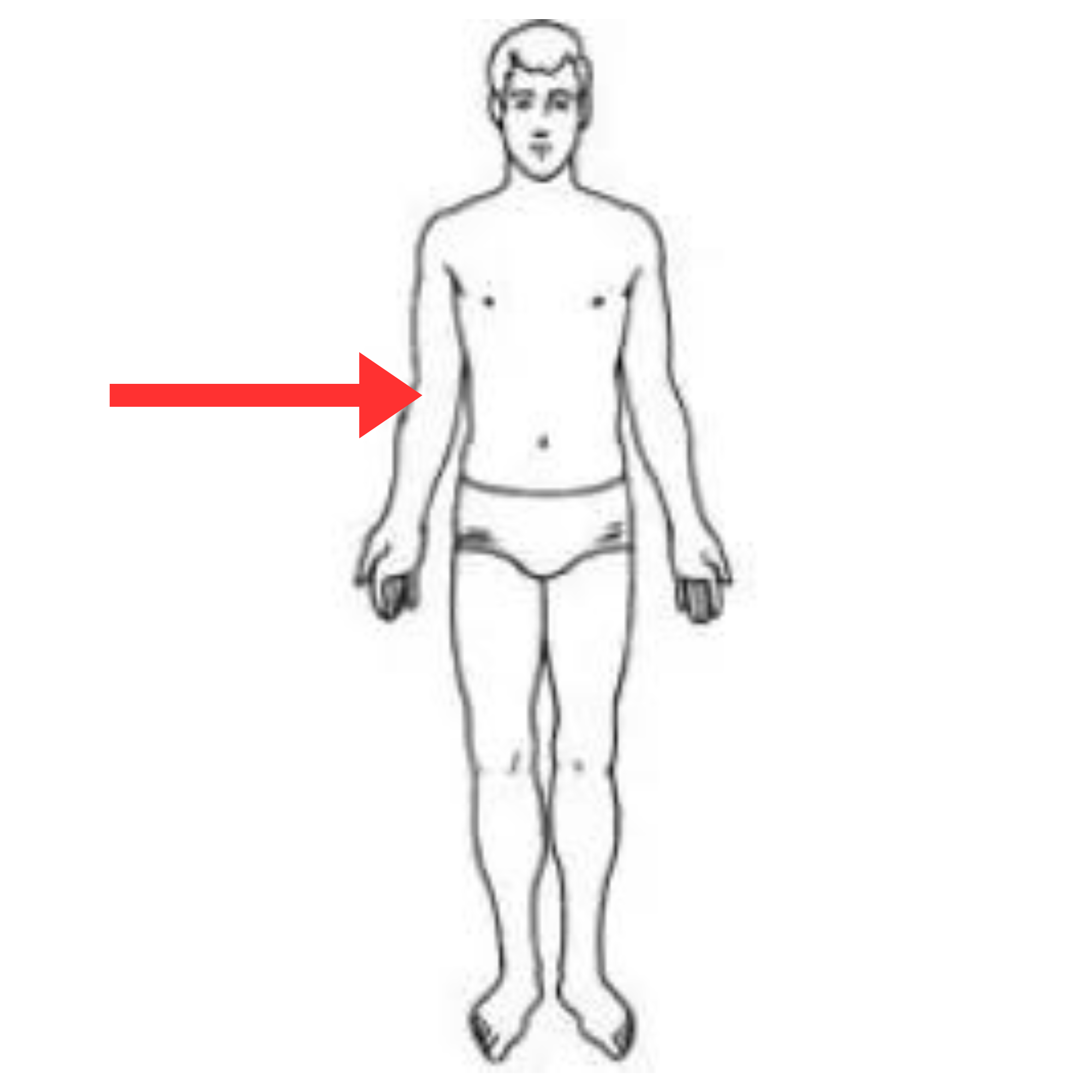
What is this pulse site
Brachial
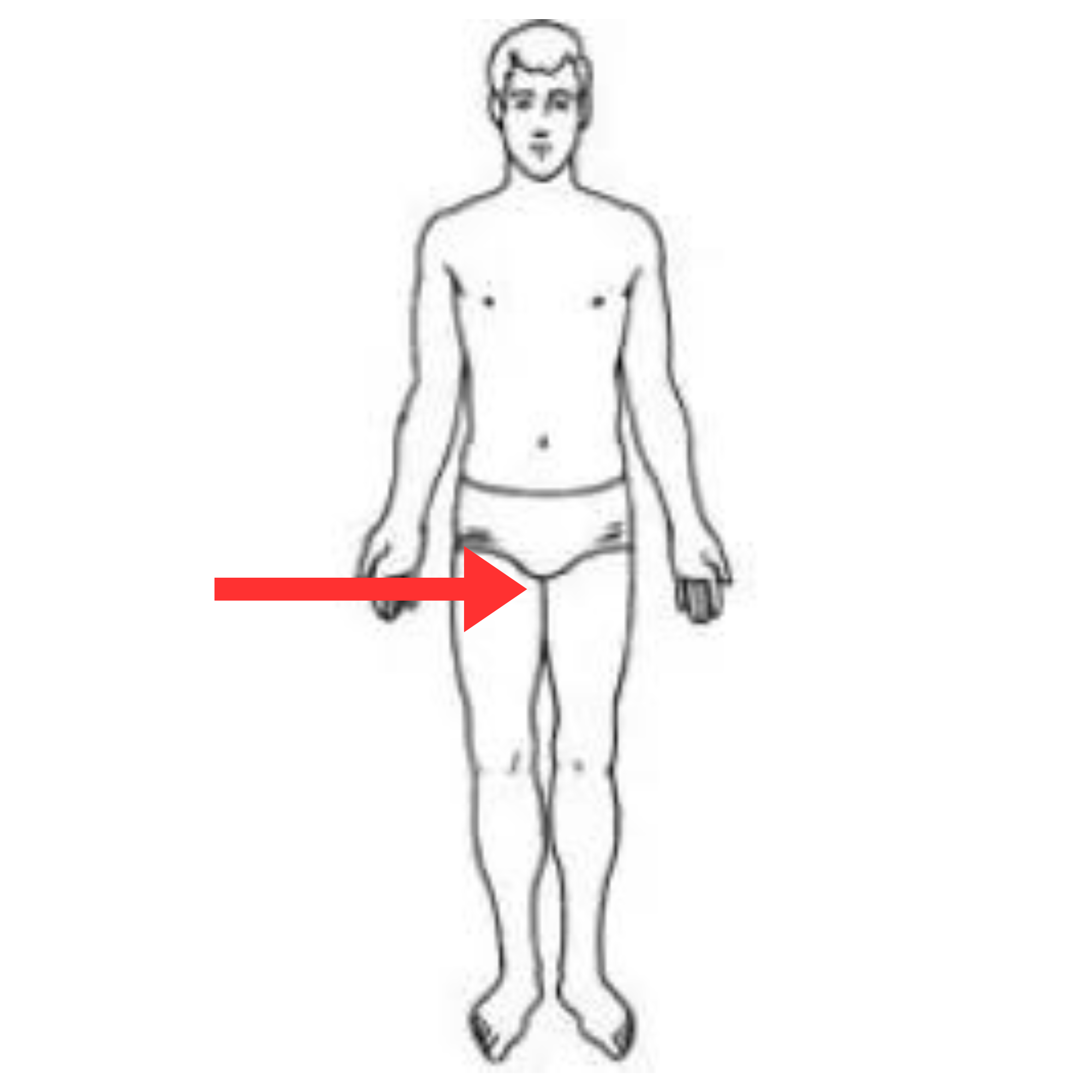
What is this pulse site
Femoral
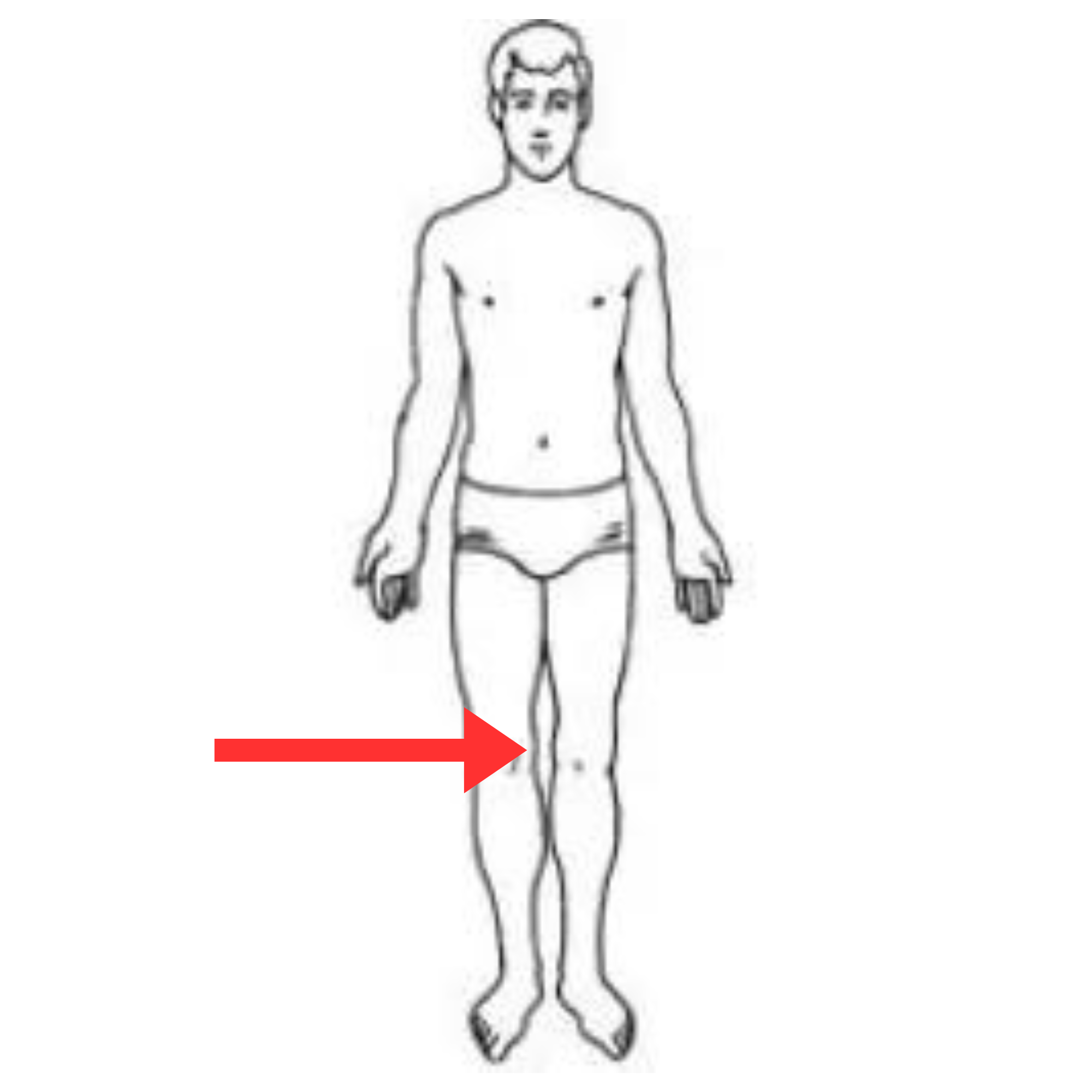
What is this pulse site
Popliteal
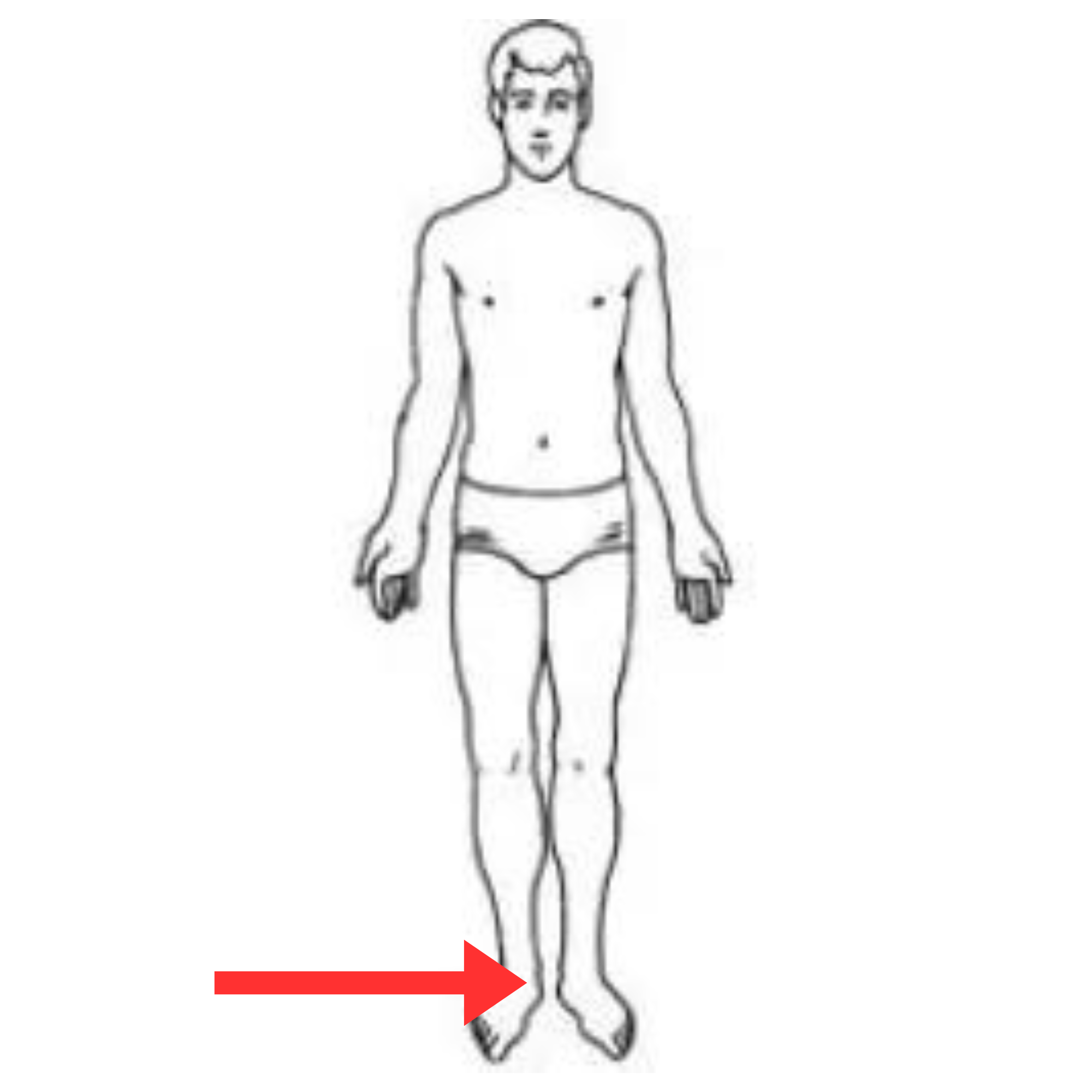
What is this pulse site
Posterior tibial artery
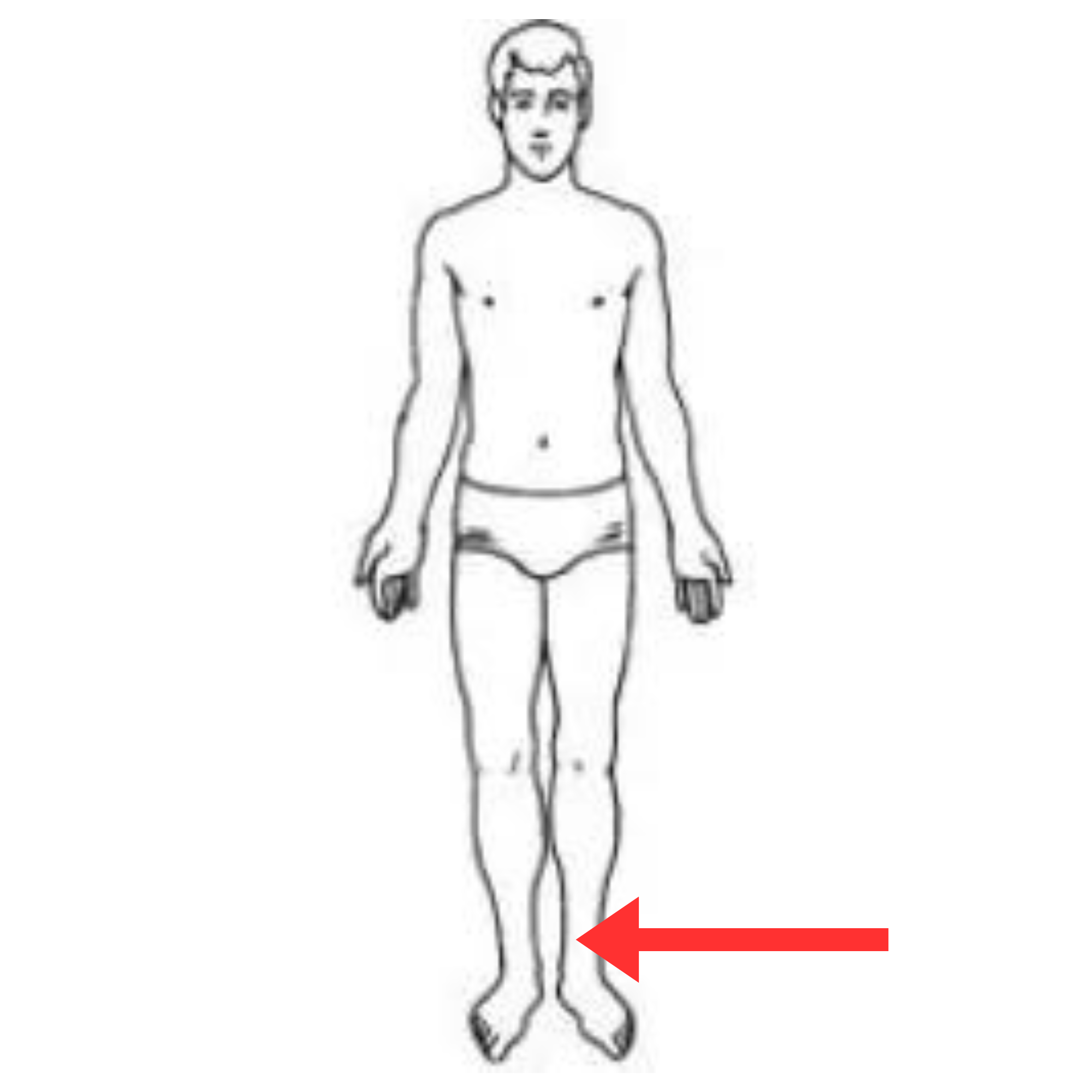
What is this pulse site
Dorsalis pedis artery
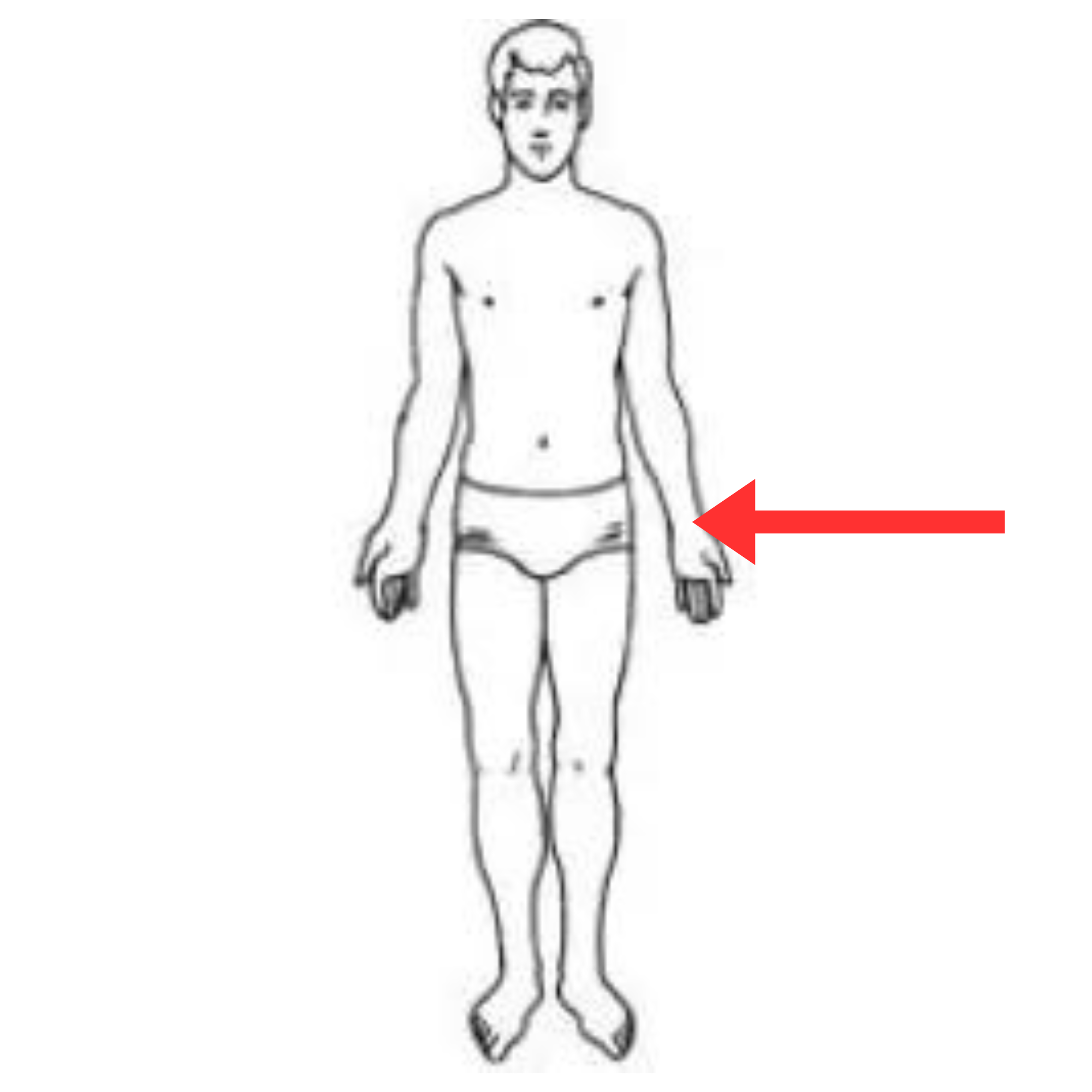
What is this pulse site
Radial