Understanding Stimulus Control and Behavior Modification - Chapters 7,9,10 & 11
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Antecedent Stimulus
A trigger that happens before a behavior and effects whether it will get reinforced.
Situation-Specific Reinforcement
Reinforcement given only in certain situations, making the behavior stronger when those situations occur.
Stimulus Control
When a behavior is more likely to happen in the presence of a specific cue because of past reinforcement
SD (Discriminative Stimulus)
A signal that tells you reinforcement is available for a behavior.
SΔ (S-delta)
A signal that reinforcement won't happen for a behavior
Stimulus Discrimination Training
Reinforcing behavior in presence of SD only.
Three-Term Contingency
Antecedent, behavior, consequence relationship.
Stimulus Generalization
When a behavior happens with things that are similar to the original cue.
Stimulus Class
Group of stimuli evoking the same response.
Conditional Discrimination
Discrimination outcome depends on another stimulus.
Stimulus Equivalence
Different stimuli perceived as equivalent.
Symmetry in Equivalence
Matching A to B implies matching B to A.
Transitivity in Equivalence
Learning A=B and B=C implies A=C.
Successive Approximations
Small steps resembling the final target behavior.
Differential Reinforcement
Reinforcing only specific behaviors among variations.
Extinction in Shaping
Stops reinforcement of previously reinforced behaviors.
Conditioned Reinforcer
Stimulus that gains value through association with primary reinforcers.
Prompt
Stimulus to increase likelihood of correct behavior performance.
Response Prompt
Assistance from another's behavior to elicit correct response.
Verbal Prompt
Using spoken instructions to guide behavior.
Gestural Prompt
Using gestures to indicate the correct behavior.
Modeling Prompt
Demonstrating desired behavior for imitation.
Physical Prompt
Physically guiding the learner to perform behavior.
Within-Stimulus Prompt
Changing characteristics of the SD for clarity.
Extrastimulus Prompt
Adding a stimulus to the SD to aid response.
Least-to-Most Prompting
Starting with minimal prompts, increasing as needed.
Most-to-Least Prompting
Beginning with maximum assistance, decreasing over time.
Fading of Response Prompts
Slowly reducing help until the behavior is done on its own.
Fading with Least-to-Most Prompting
Increasing prompt intensity if learner does not respond.
Fading with Most-to-Least Prompting
Decreasing assistance as learner gains proficiency.
Fading of Stimulus Prompts
Gradually reducing the prominence of prompts.
Constant Prompt Delay
Fixed wait time before giving a prompt.
Progressive Prompt Delay
Increasing wait time before providing a prompt.
Discrimination Training
Teaching when to use specific behaviors based on stimuli.
Topography of Behavior
Physical form or shape of a behavior.
Behavior Modification
Systematic approach to changing behavior patterns.
Prompt Delay Procedure
Strategy to enhance learning through timed prompts.
Stimulus Prompts
Cues added to enhance learning through highlighting.
Fading
Gradual reduction of prompts as skills improve.
Echoic
Verbal behavior repeating another's spoken words.
Tact
Naming or labeling objects in the environment.
Mand
Requesting something based on a need.
Intraverbal
Responding verbally to another person's speech.
Stimulus-Response Chain
Sequence where each behavior cues the next.
Task Analysis
Breaking down complex tasks into smaller steps.
Backward Chaining
Teaching last step first, then preceding steps.
Forward Chaining
Teaching first step first, then subsequent steps.
Total Task Presentation
Teaching entire task at once, not stepwise.
Graduated Guidance
Reducing physical assistance as independence grows.
Written Task Analysis
Step-by-step written instructions for task completion.
Chaining Procedure
Method for teaching tasks broken into steps.
Prompting
Providing cues to assist in task performance.
Behavior Chain
Linked behaviors where one triggers another.
Differential Reinforcement and Shaping
In shaping, differential reinforcement involves reinforcing behaviors that are closer to the target behavior while withholding reinforcement for earlier approximations.
Generalization vs. Discrimination
Generalization occurs when a behavior occurs in response to stimuli similar to the SD. Discrimination occurs when a behavior occurs only in response to the SD and not similar stimuli.
Prompting and Fading
Prompt cues given to encourage a correct response. Fading is the gradual removal of prompts as the behavior becomes more reliable in response to the SD.
Shaping
Gradually reinforcing small steps that lead to the final behavior
How does extinction play a role in shaping?
Extinction plays a role in shaping by no longer reinforcing earlier behavior once a closer step to the target behavior is reached.
Stimulus generalization graph
A graph that shows a behavior spreads to similar cues, with the response getting weaker as the cues become less like the original one (SD).
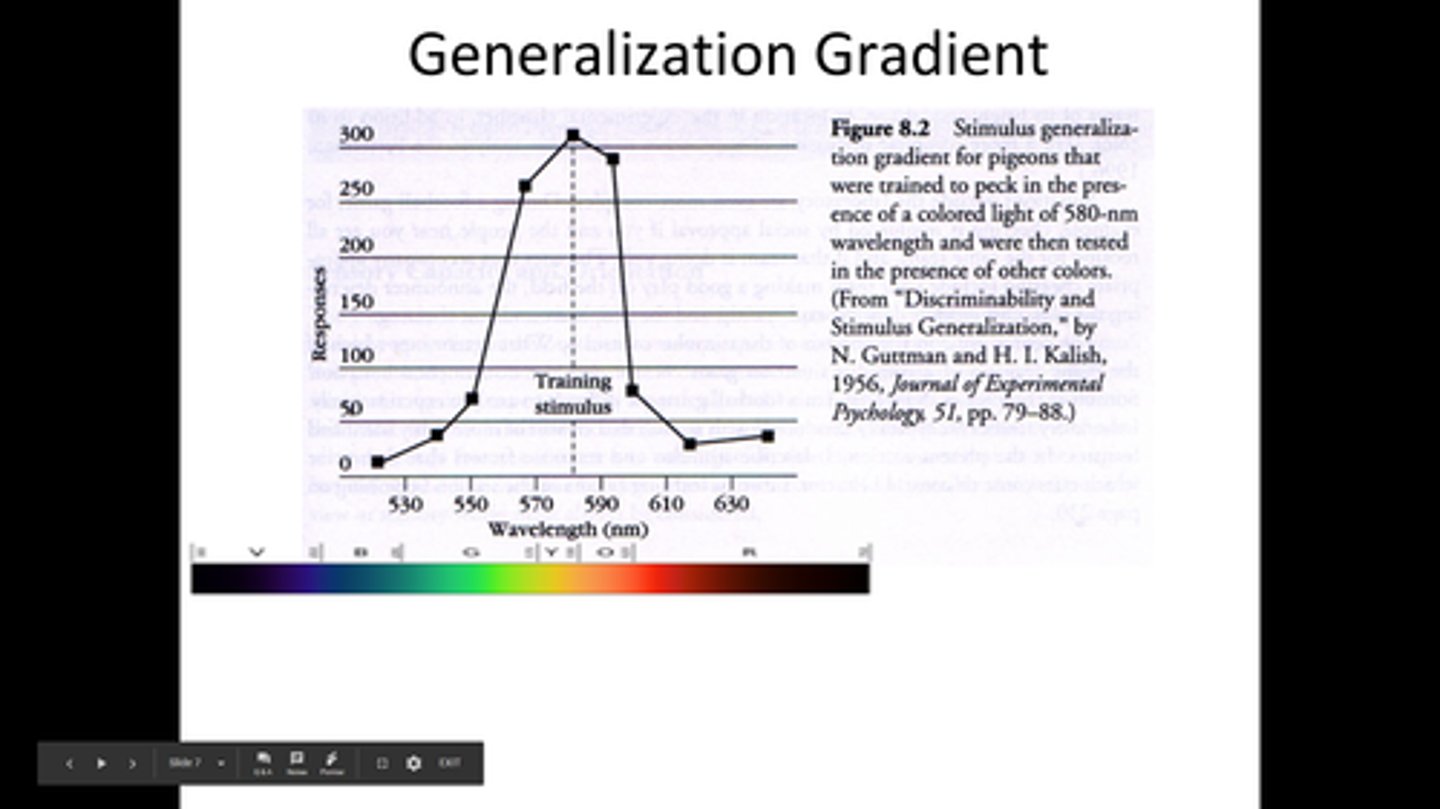
Stimulus discrimination graph
A graph that shows a behavior happens more with a specific cue (SD) and less with others (SΔ), showing a clear distinction between the stimuli.
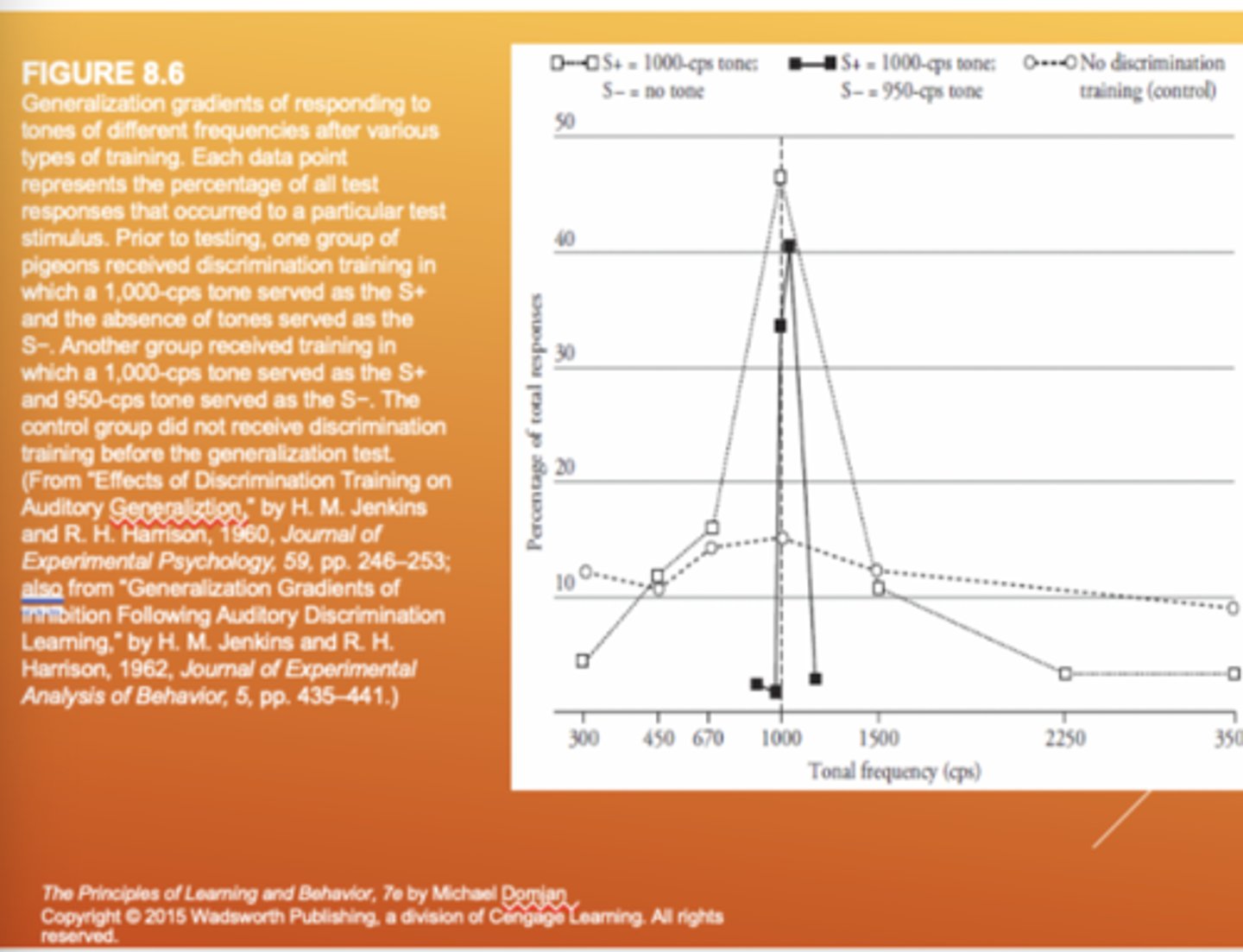
Applications of Shaping
Animal Training, Spelling, Voice Elevations, Teaching Self Care
Prompt fading
Behavioral Chain
Stimulus-response chain