Oral Path Exam 1
1/258
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
259 Terms
Tumor
swelling
Neoplasm
"new growth"
true
T or F: Tumor and neoplasm are interchangeable
False (can be either benign or malignant)
T or F: Neoplasms cannot be malignant
slow growing, well encapsulated, non-invasive, well differentiated, "oma" (lymphoma exception), asymptomatic, pushing of nearby structures
What are some benign characteristics of soft tissues?
Rapid growth, invasive, poorly demarcated borders, metastasis, pain, "carcinoma"/"sarcoma"
What are some malignant characteristics of soft tissues?
True
T or F: Cancers can metastasize to the jaws and soft tissues of the oral cavity
smooth
For benign radiographic characteristics, root resorption will look...
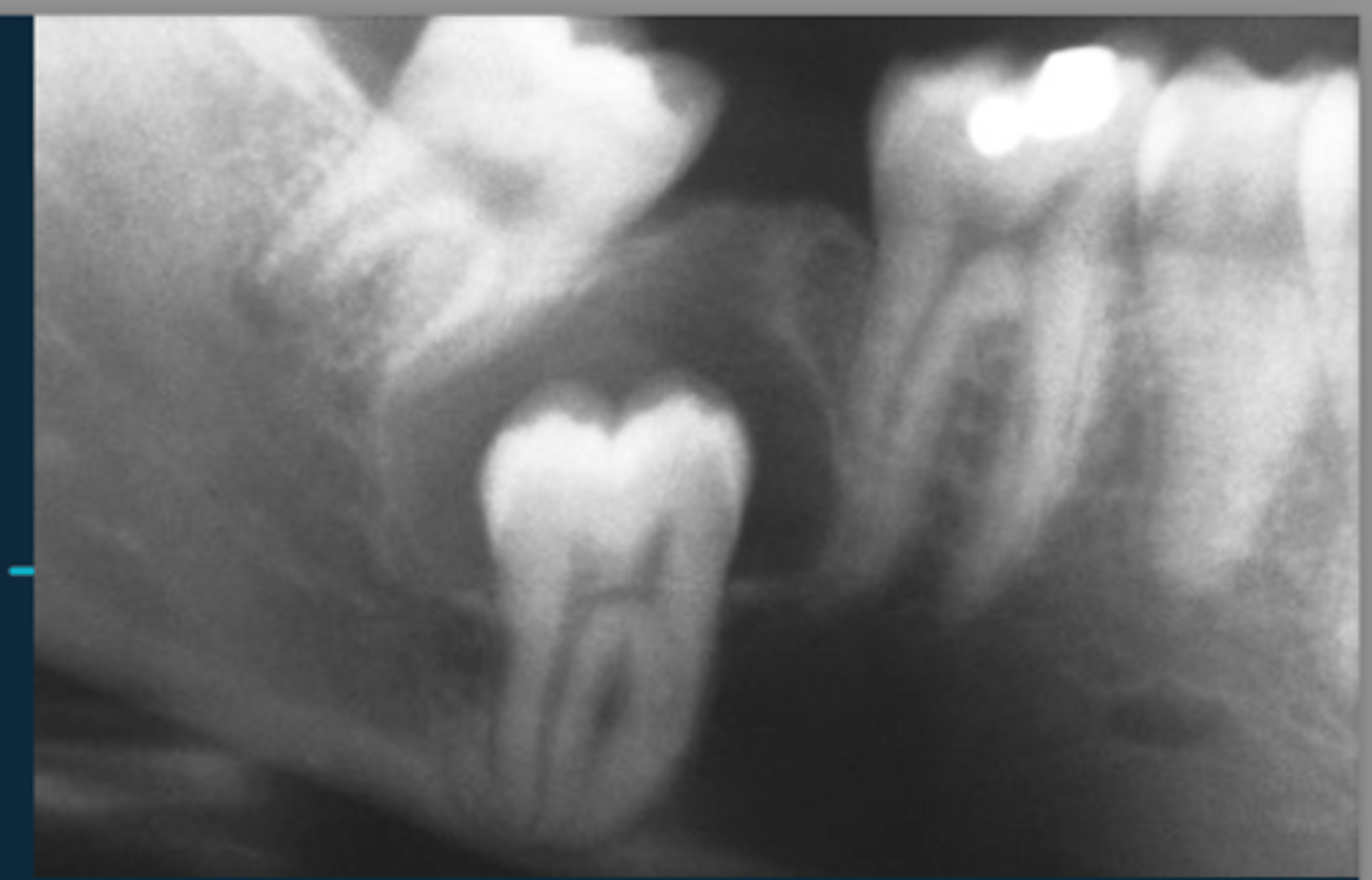
corticated, smooth borders, slow, structure displacement
What are some benign radiographic characteristics>
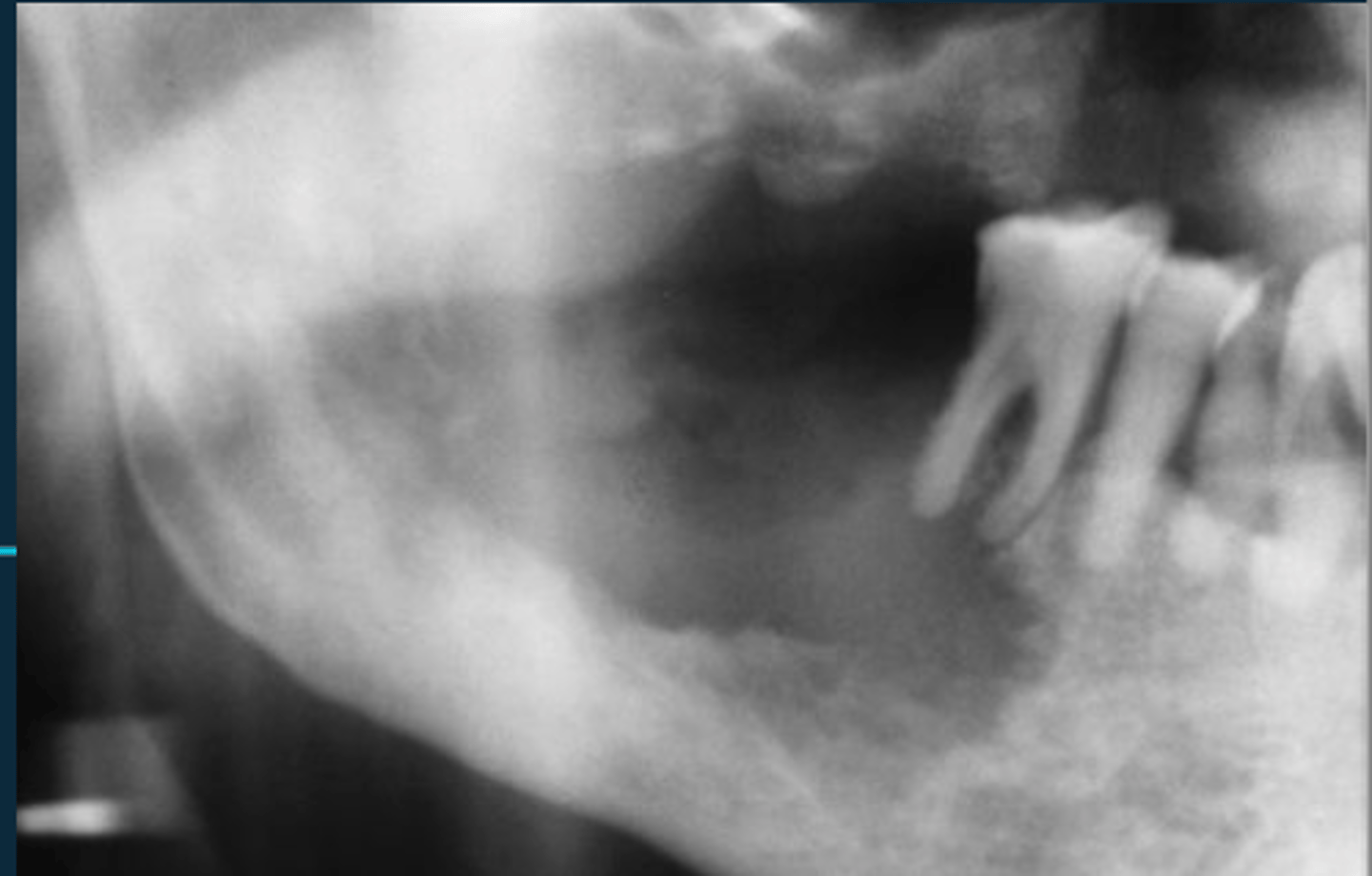
Destructive, tooth floating in air, unexplained PDL widening
What are some malignant radiographic characteristics?
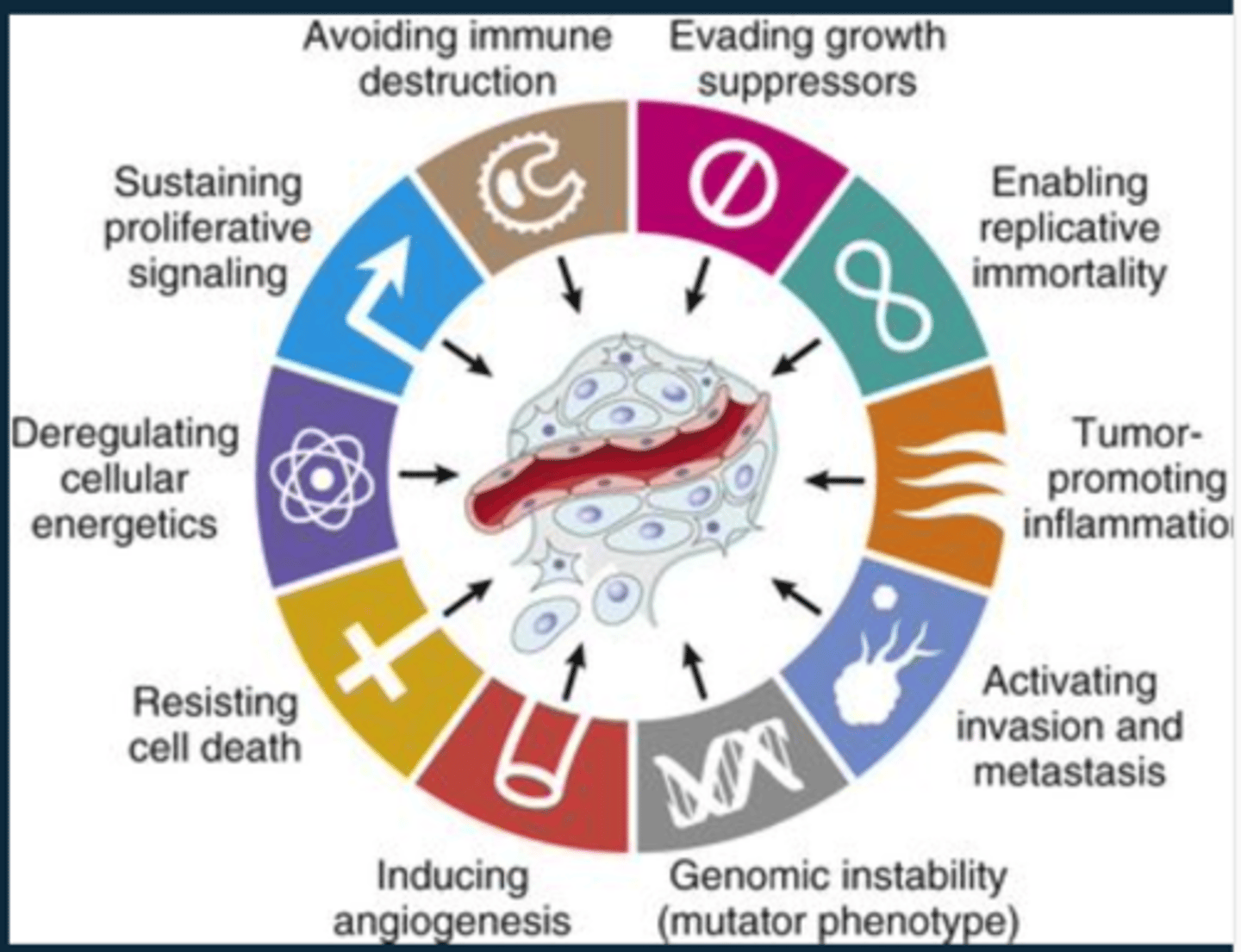
Hallmarks of cancer
Gingiva, Attached alveolar
mucosa, Mid-palatine raphe,
Dorsum tongue (anterior to CV papillae)
Salivary glands are NOT present in...
Salivary gland aplasia
rare condition where there is loss or missing of salivary gland tissue, can occur by itself or as a syndrome
Sialorrhea
excessive production of saliva
Sialadenitis
Inflammation of the salivary glands that can arise from various infectious and noninfectious causes; common culprits: mumps, S. aureus, medications, surgery, dehydration
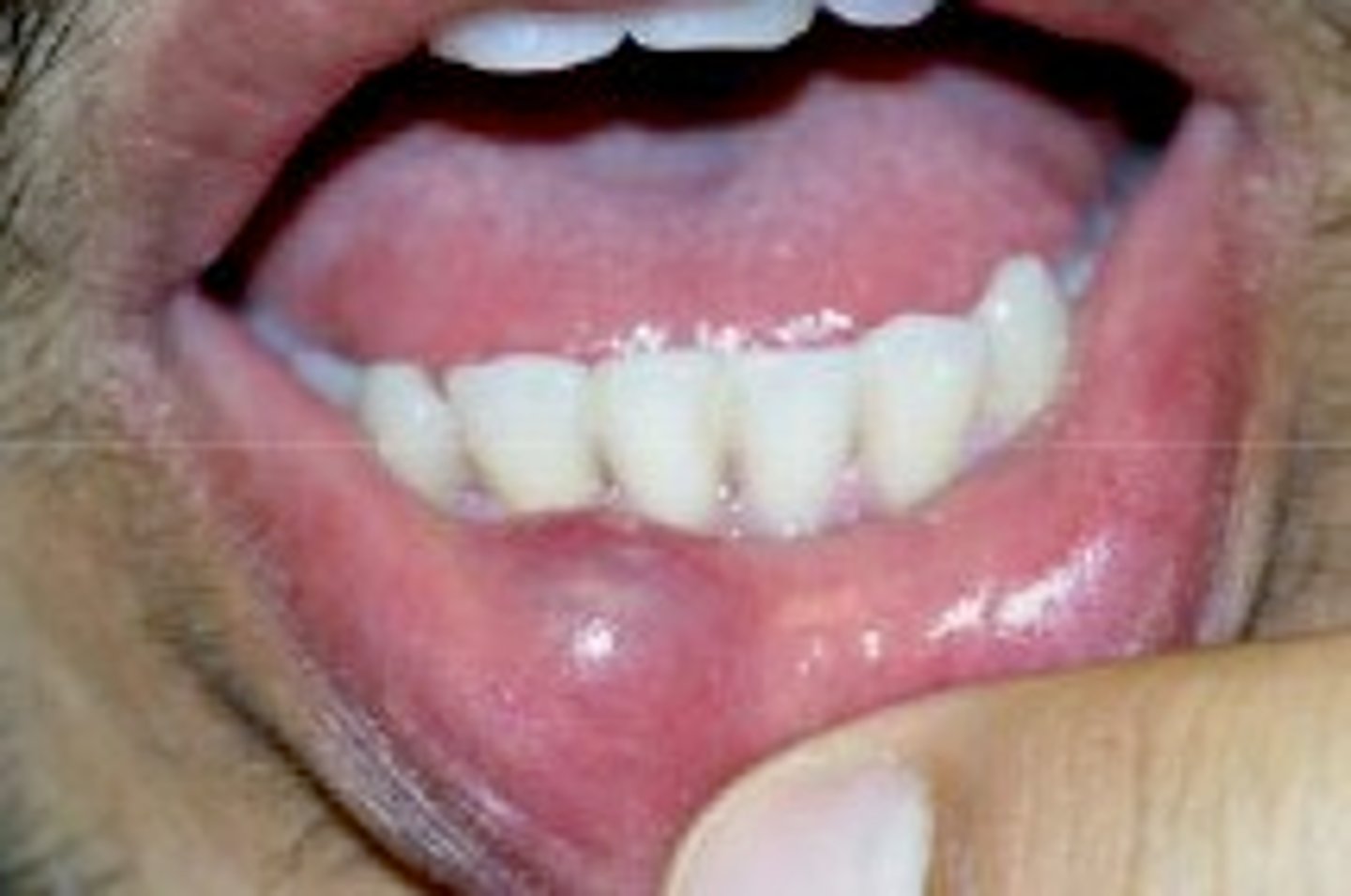
Sialadenosis
non-inflammatory enlargement of a salivary gland or glands
-causes: endocrine disorders, pregnancy, nutritional conditions, neurogenic medications
Xerostomia
dry mouth, can note bubbles at the base of tongue where saliva pools
-causes: metabolite loss, iatrogenic, local factors, systemic
Xerostomia
bacterial sialadenitis
Sialadenosis
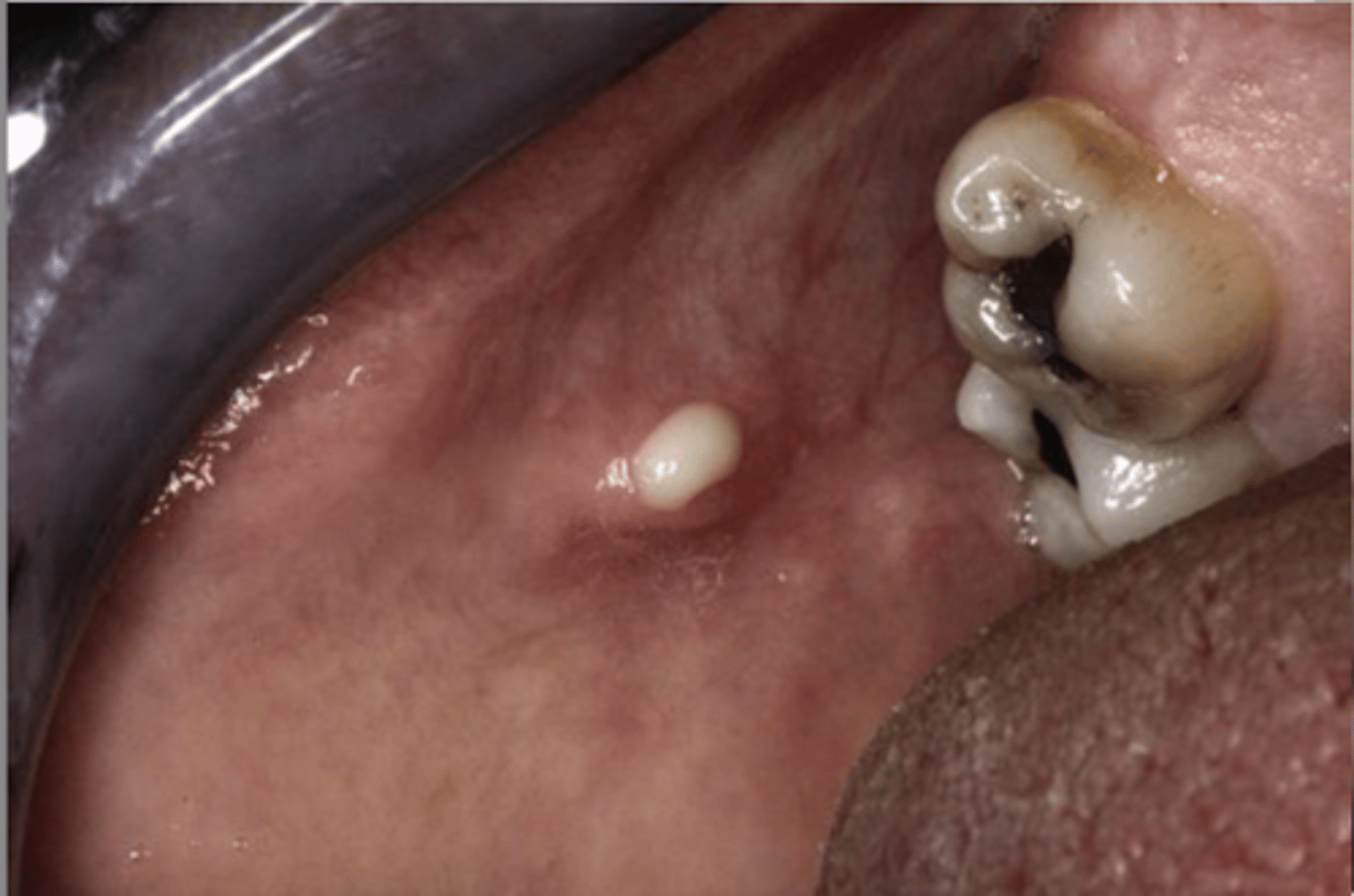
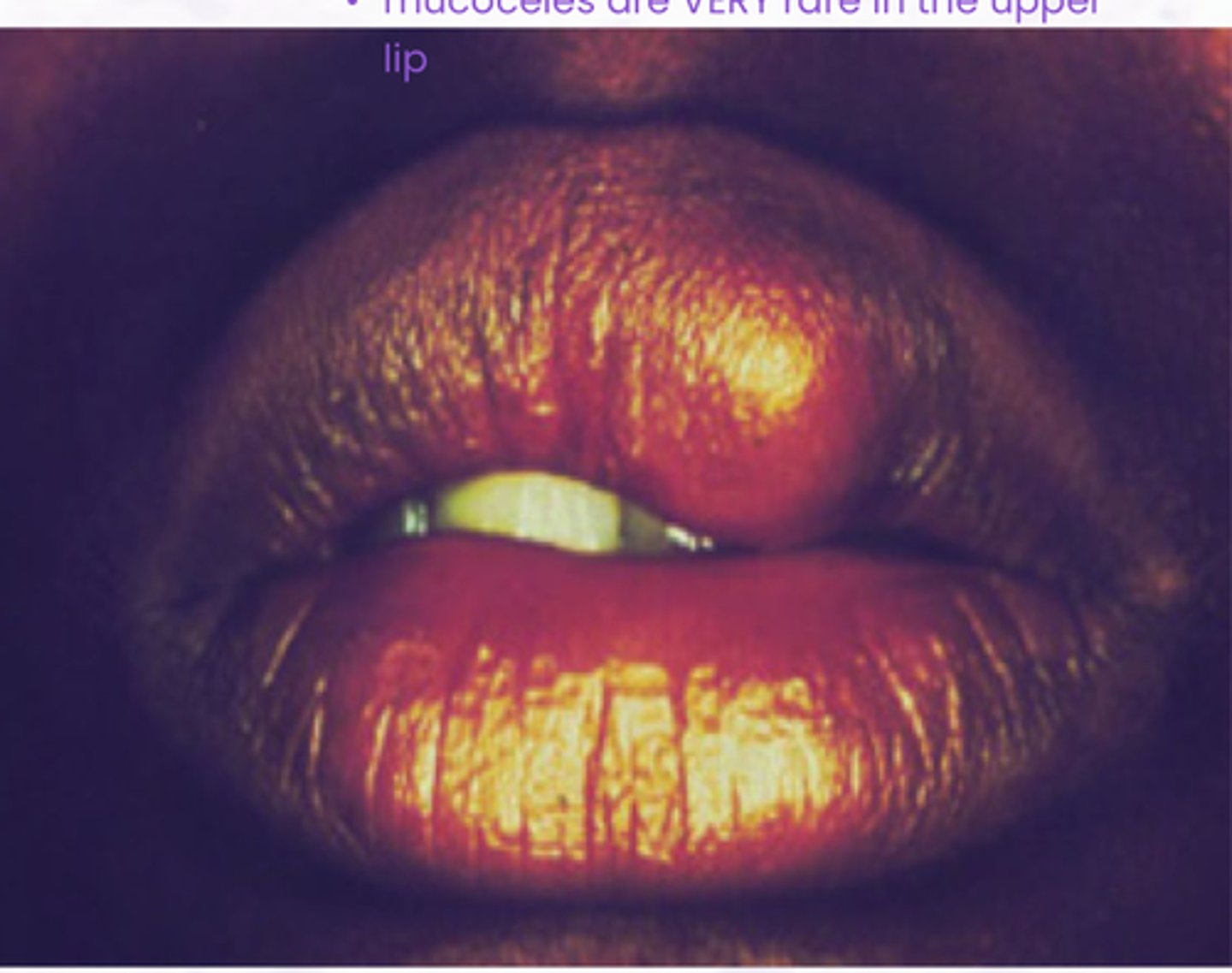
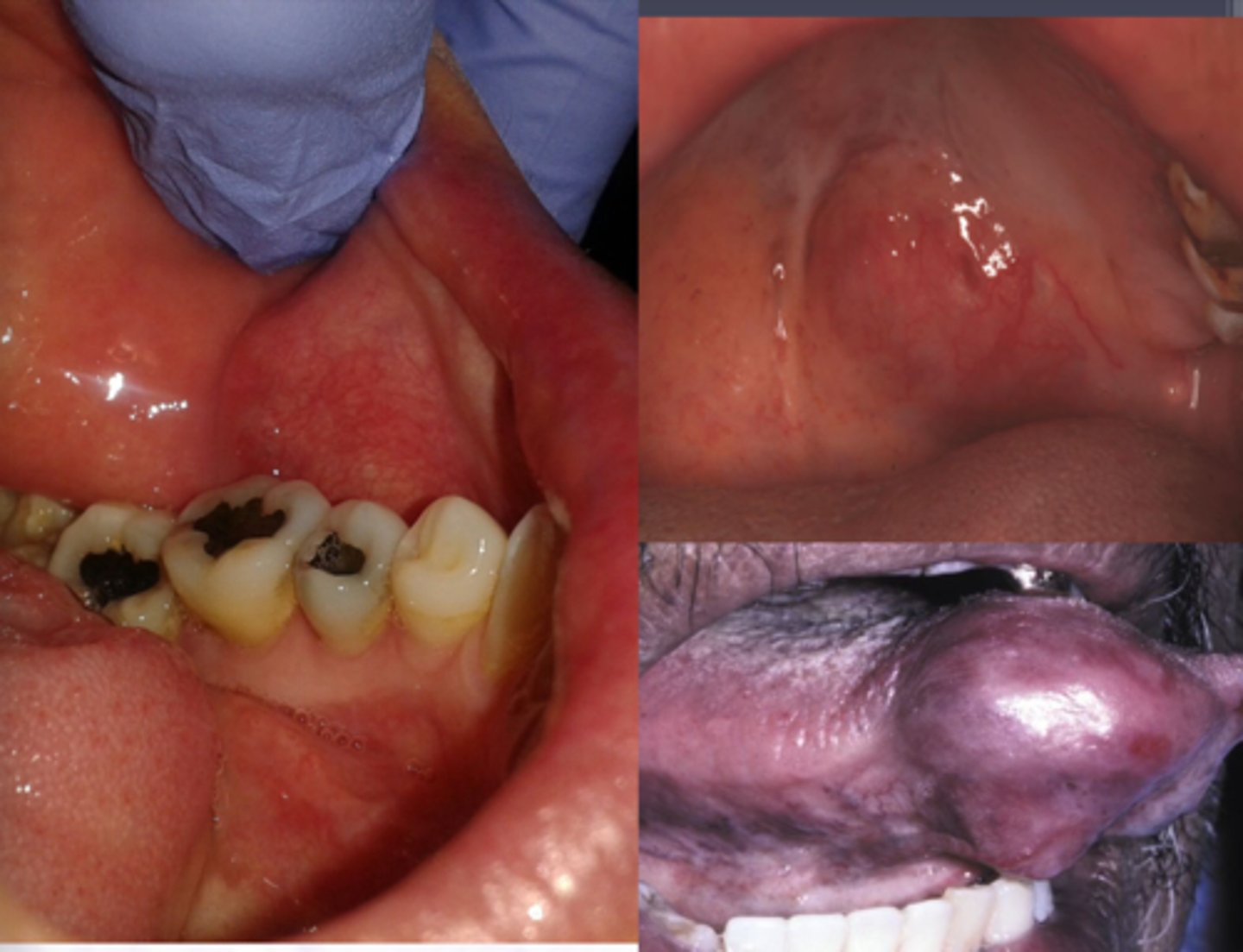
Mucocele
Damage or severing of salivary gland duct, Not a true cyst
Mucocele
what is one of the most common oral ST enlargements?
false ( they do: rupture, drainage,
reforming)
T or F: Mucocele do not fluctuate in size
Mucocele
• Granulation tissue
• Spilled mucin
• Inflamed salivary gland tissue
upper lip
What location is the LEAST common site for mucoceles?
excision, removal of adj salivary gland tissue
What are the treatments for a Mucocele
True
T or F: A Salivary Duct Cyst is a True Cyst
Epithelial lining
A true cyst has what type of lining?
Salivary Duct Cyst
Mimic mucoceles in
appearance
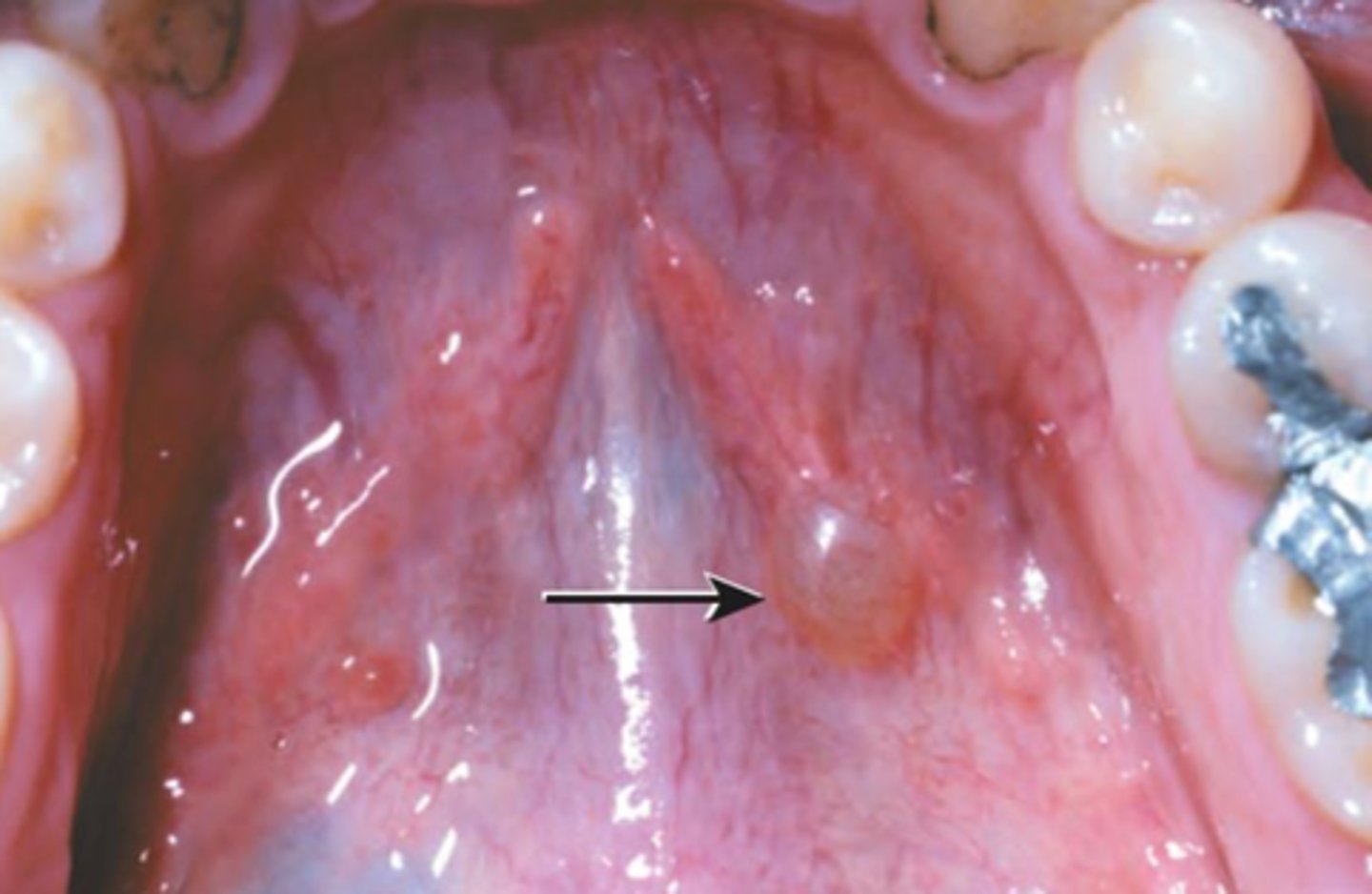
Major and minor salivary glands
Where is the site for Salivary Duct Cyst?
Ranula
Resembles frogs
underbelly, Less common type of mucocele
sublingual, submandibular gland
a ranula involves which gland?
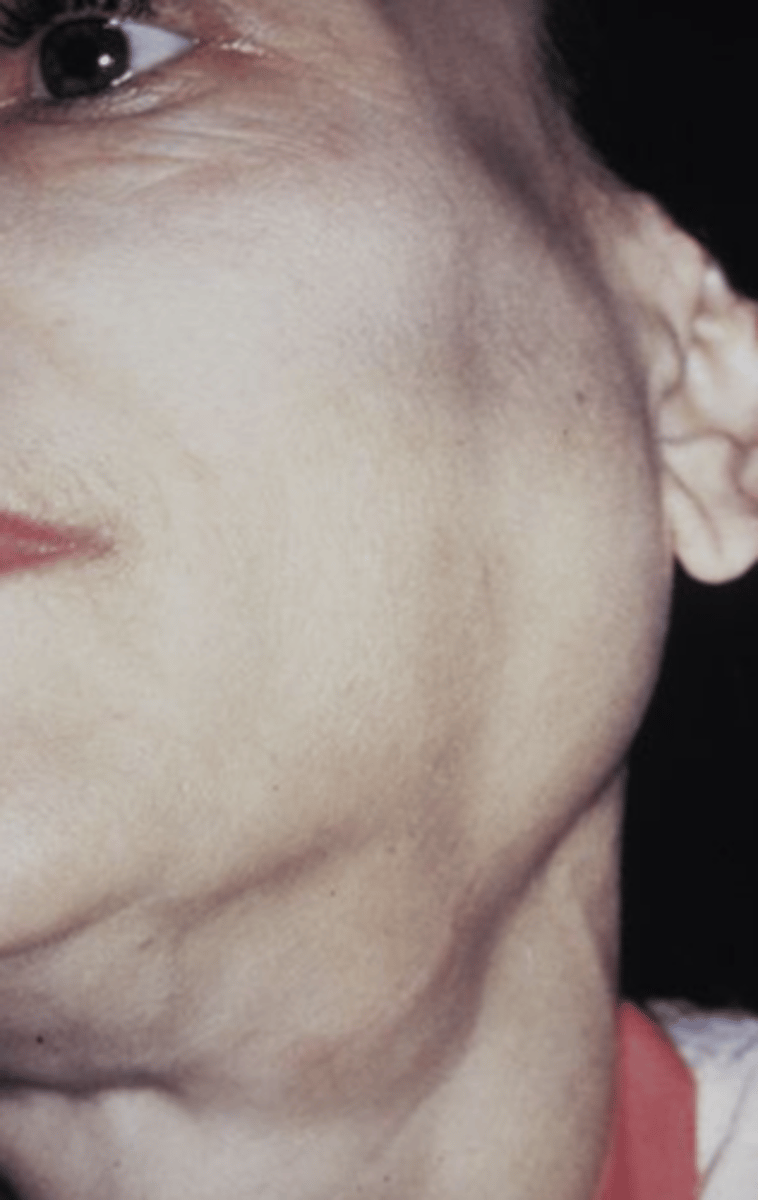
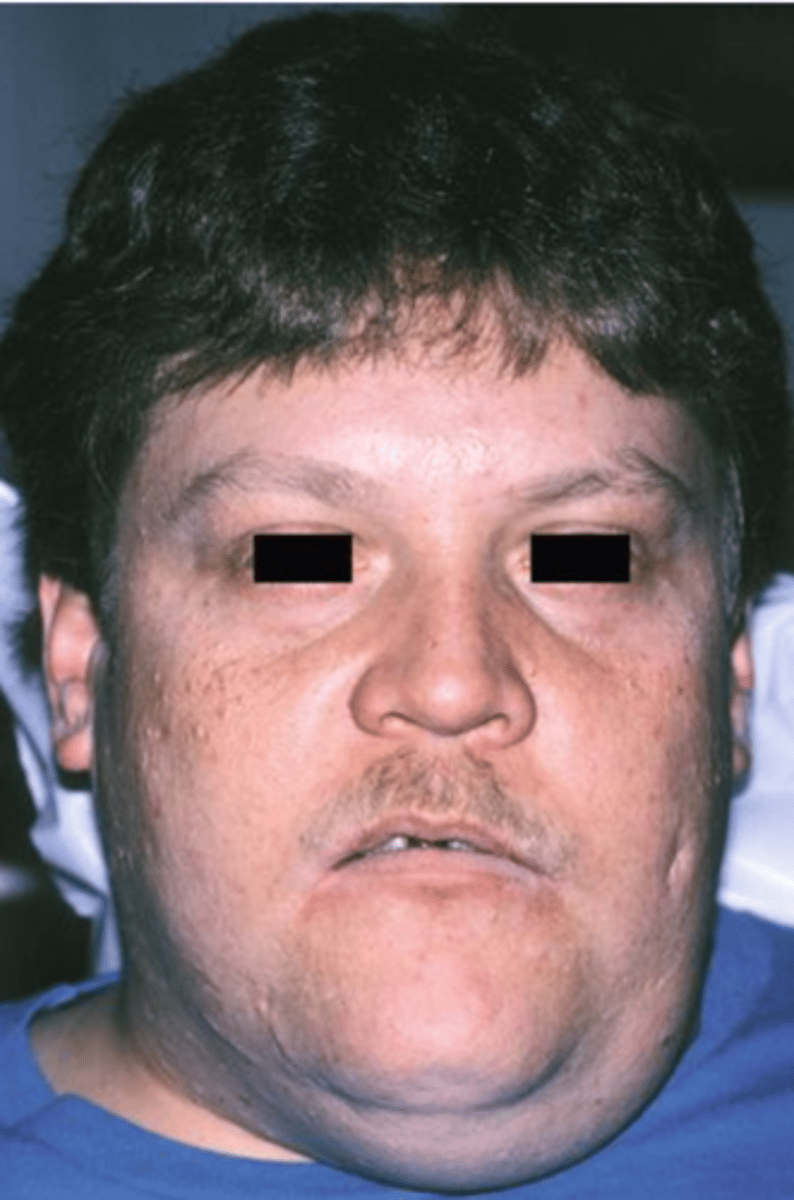
Plunging Ranula
Dissects through mylohyoid
▫ Swelling in the neck
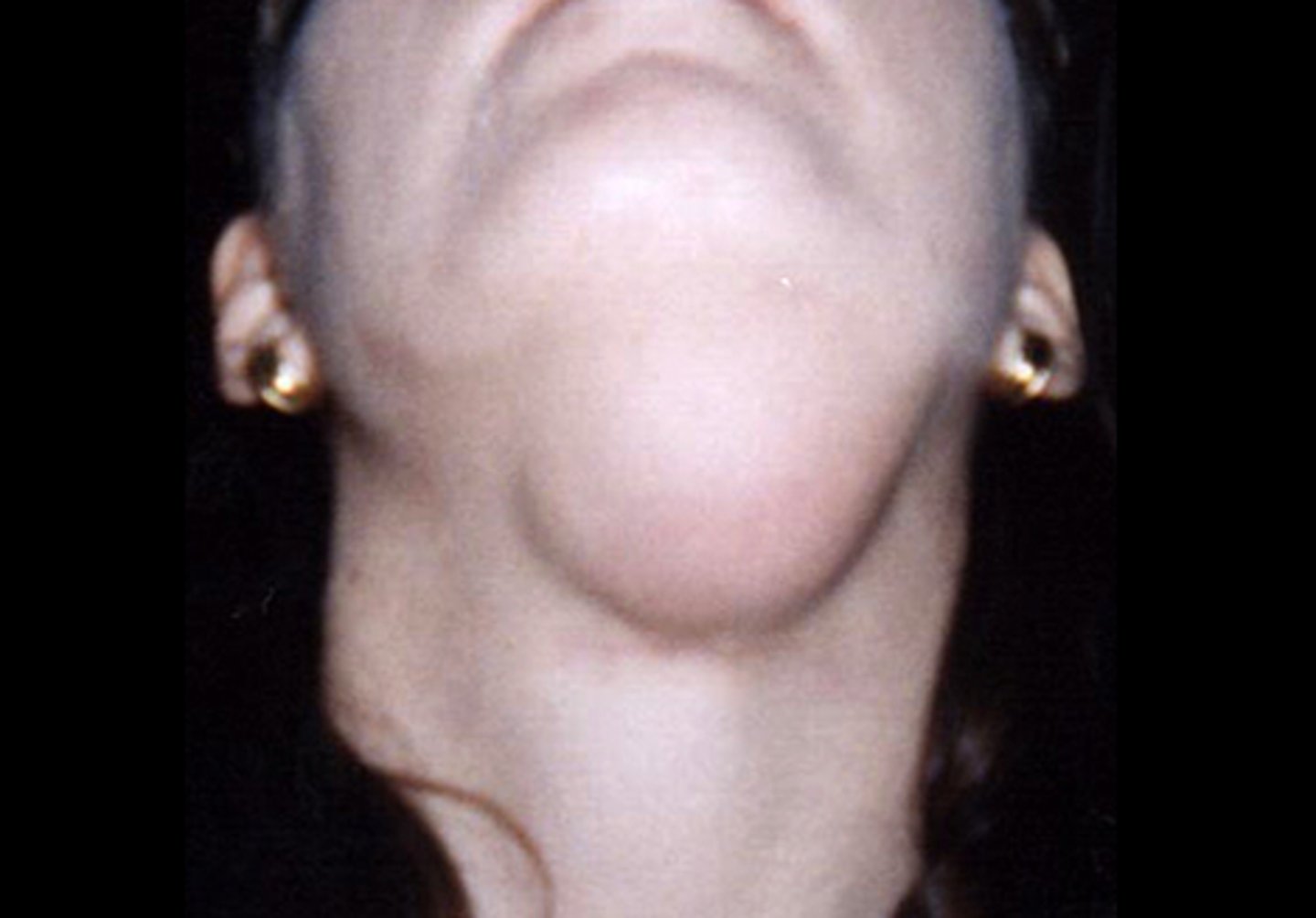
Marsupialization, Removal of feeder gland
What are some treatments for Ranulas?
Sialolith
Deposits of calcium salts in the salivary gland/ duct, Decreased salivary flow OR increased viscosity
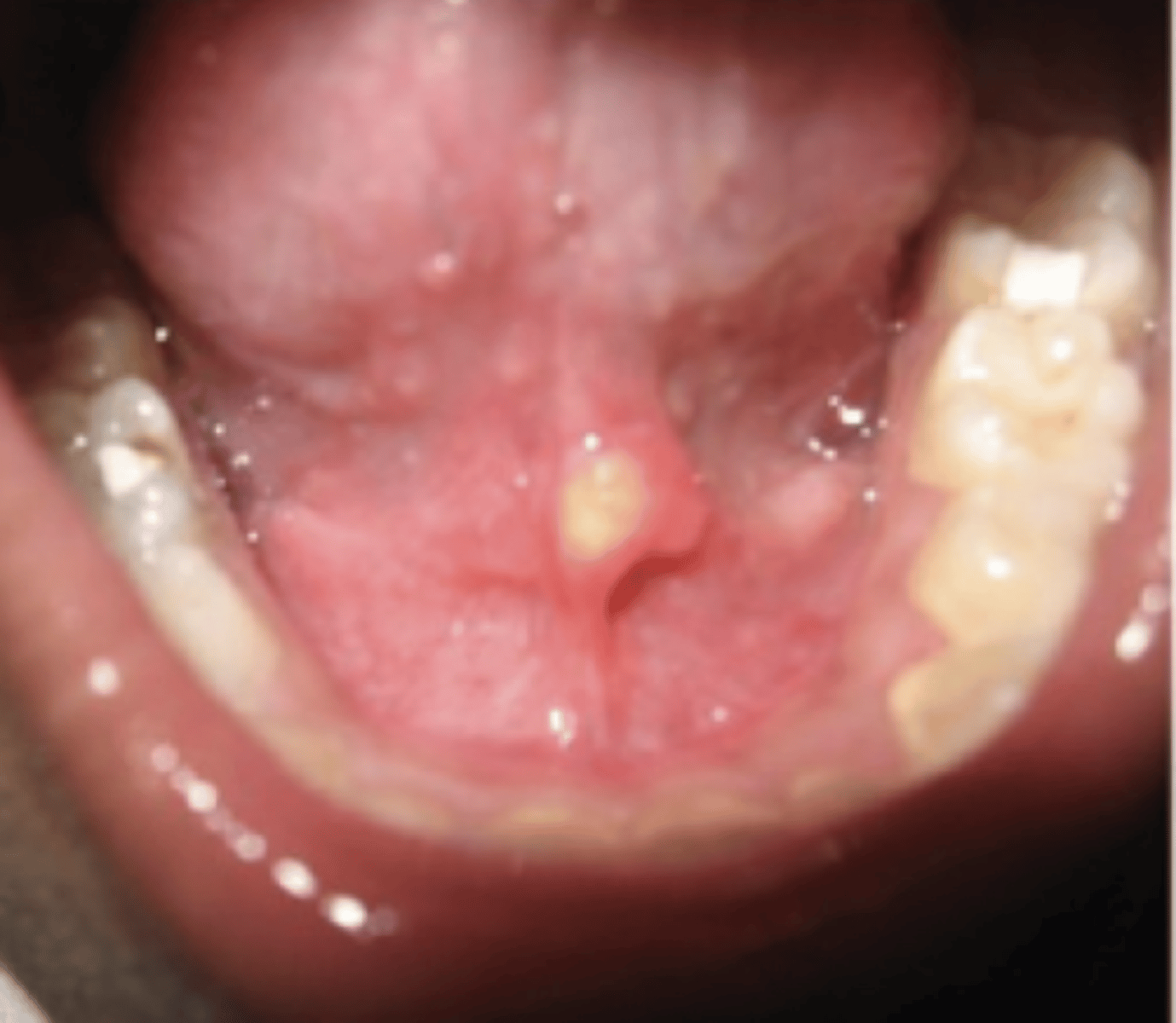
submandibular
Sialolith most common in which gland?
Sialolith
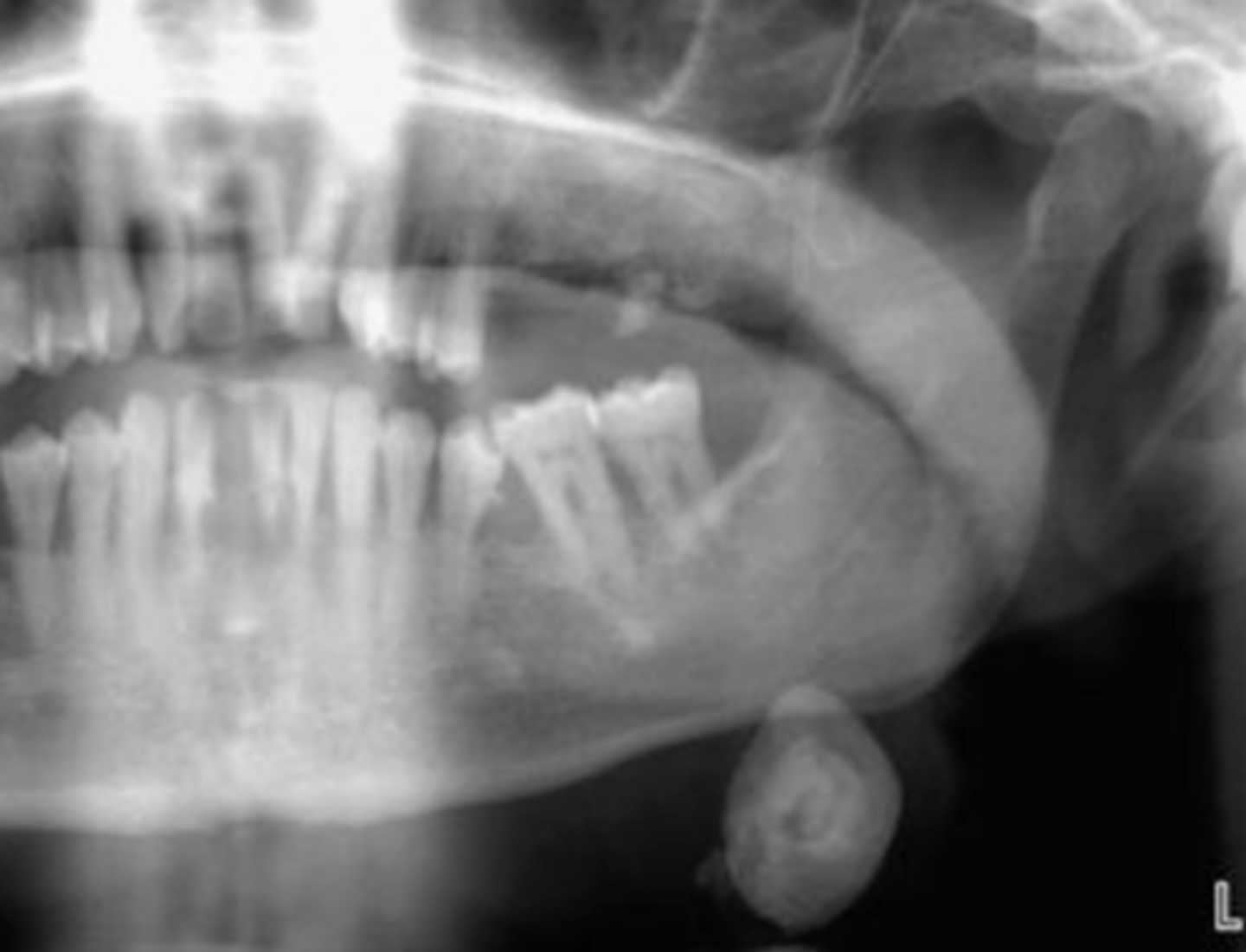
Sialolith
Calcified mass, Surrounded by inflamed and fibrotic salivary glands
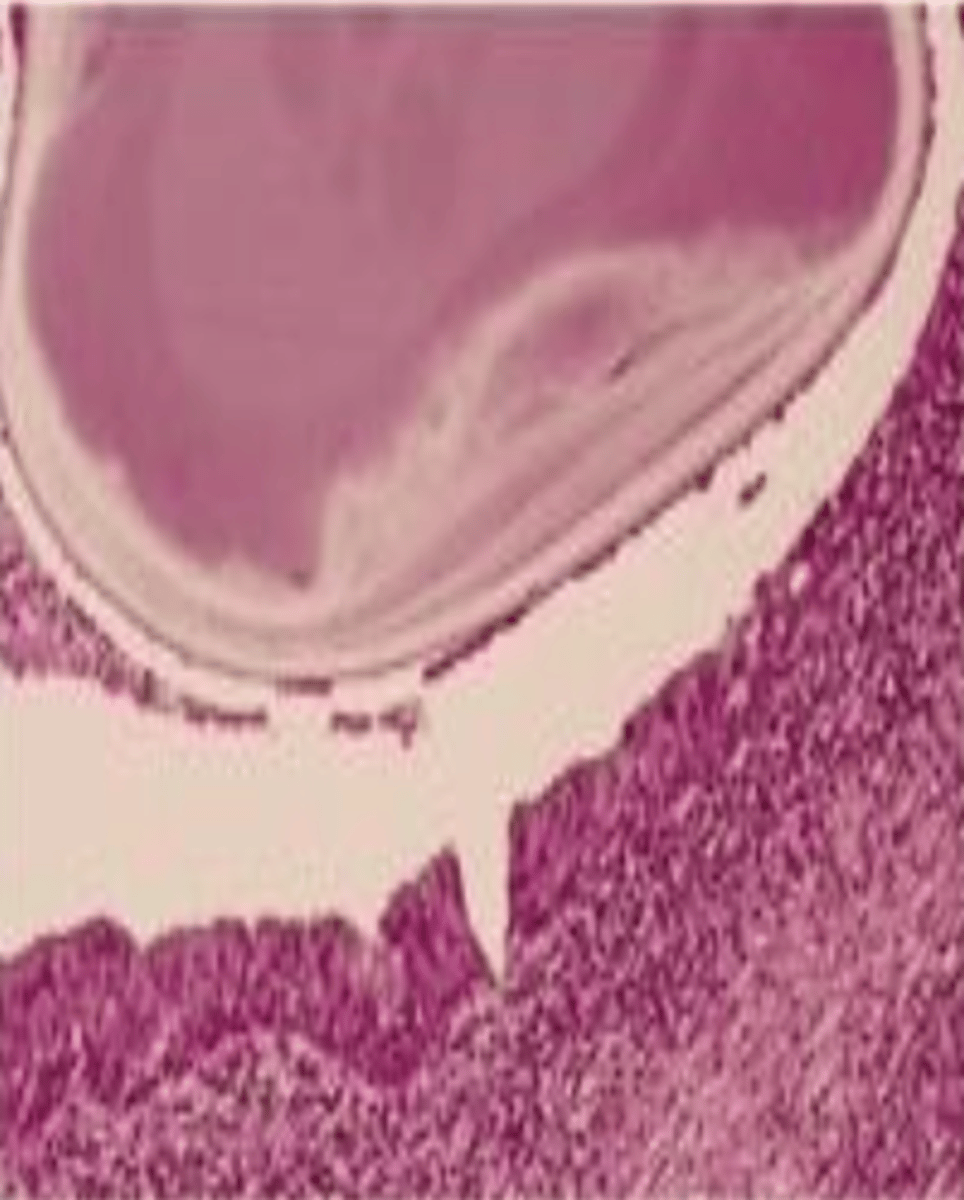
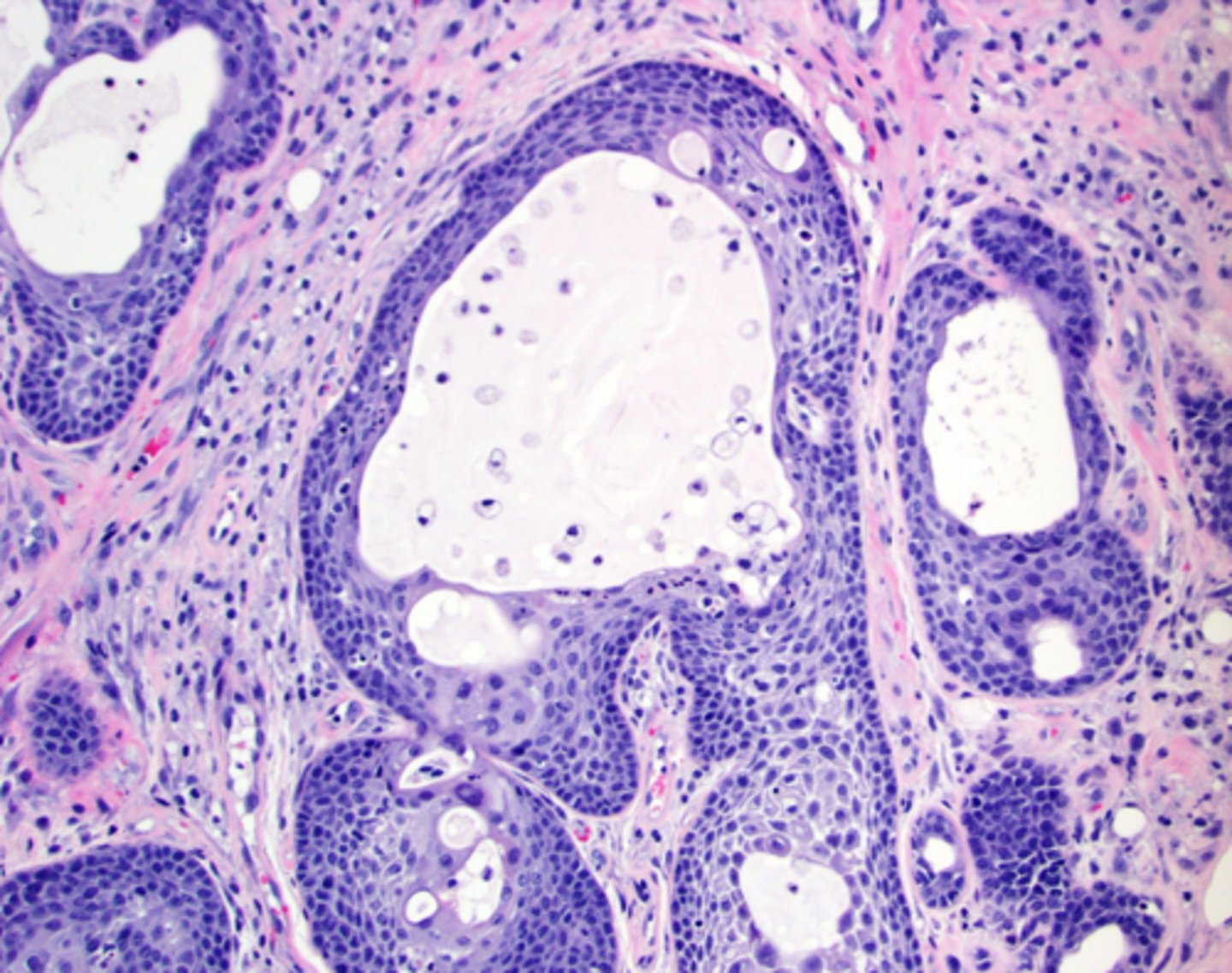
Necrotizing Sialometaplasia
Ischemia of the salivary glands of the hard palate, Often bilateral and symmetrical, starts out initially as a swelling
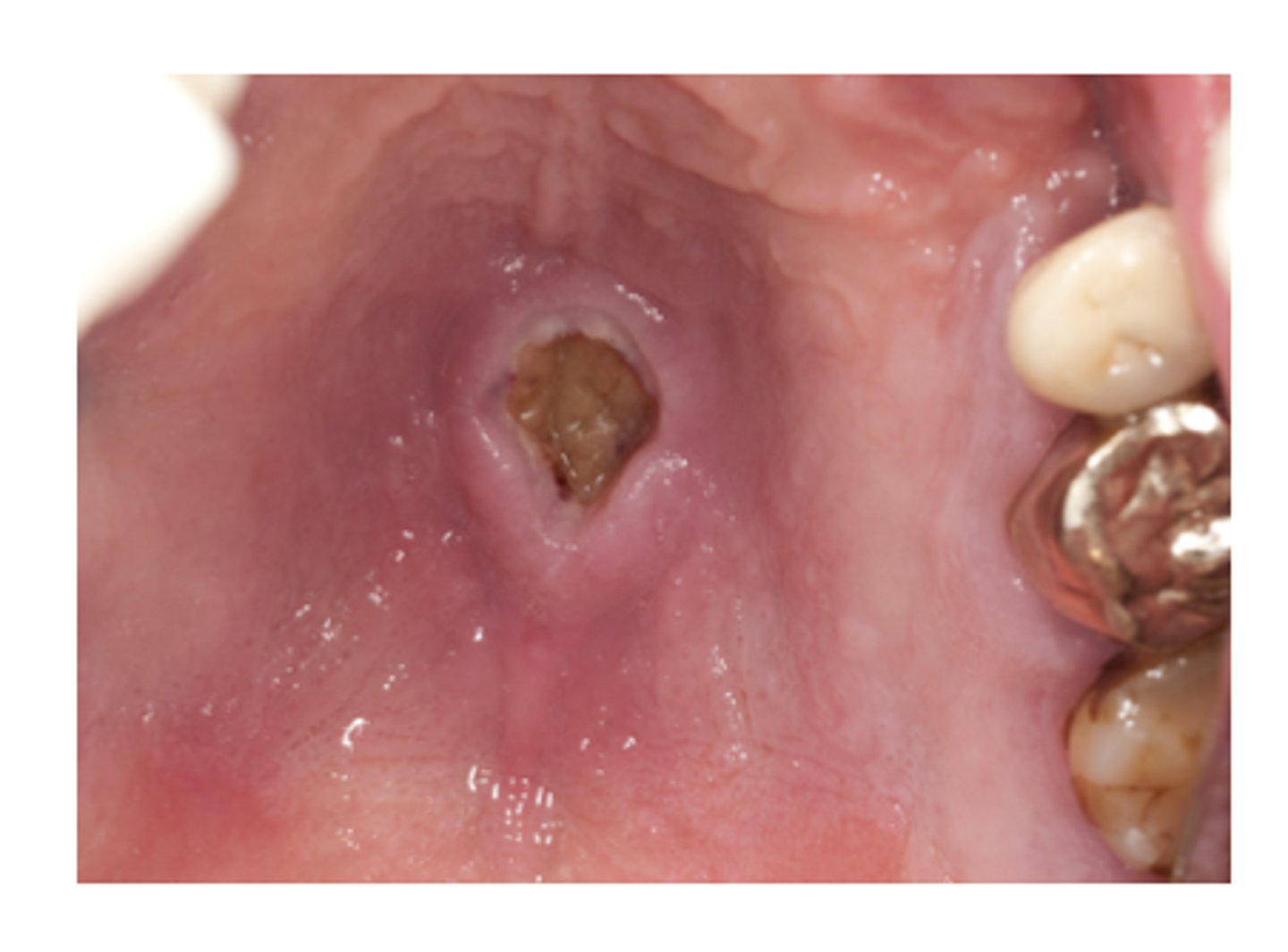
Necrotizing Sialometaplasia
What condition can mimic squamous cell carcinoma?
Necrotizing Sialometaplasia
Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia, Coagulative necrosis of
the adjacent glands
Necrotizing Sialometaplasia
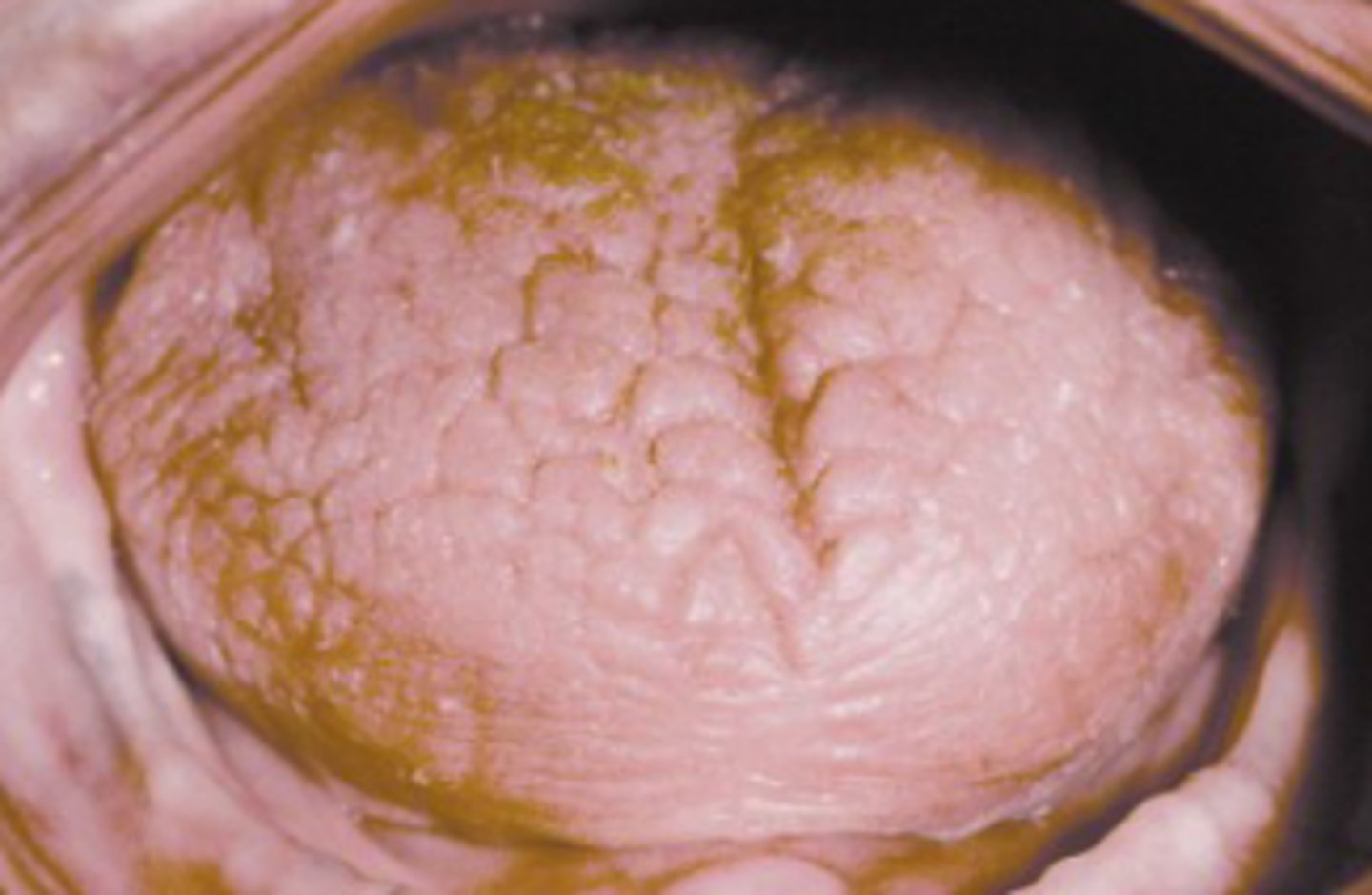
Sjogren Syndrome
Autoimmune disease, Enlargement of the salivary
glands
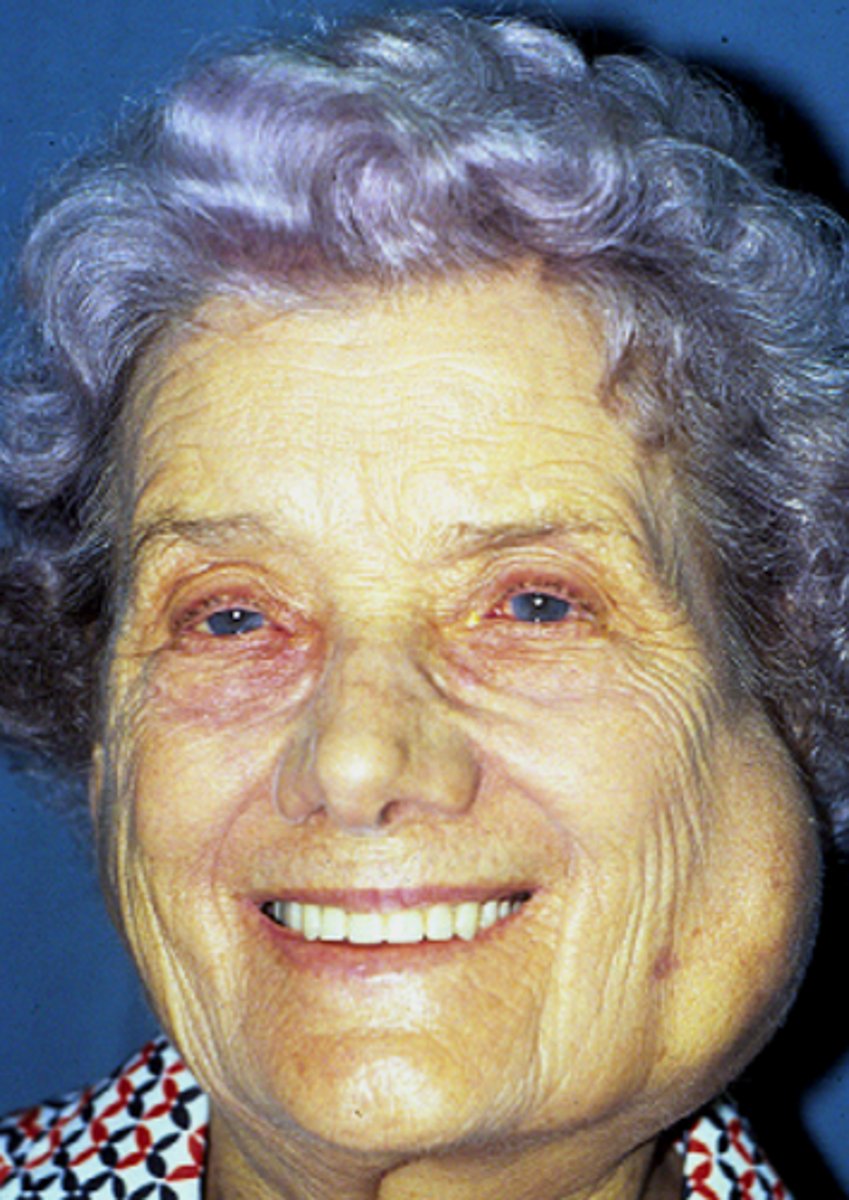

Primary Sjogren Syndrome
Dry mouth + eyes
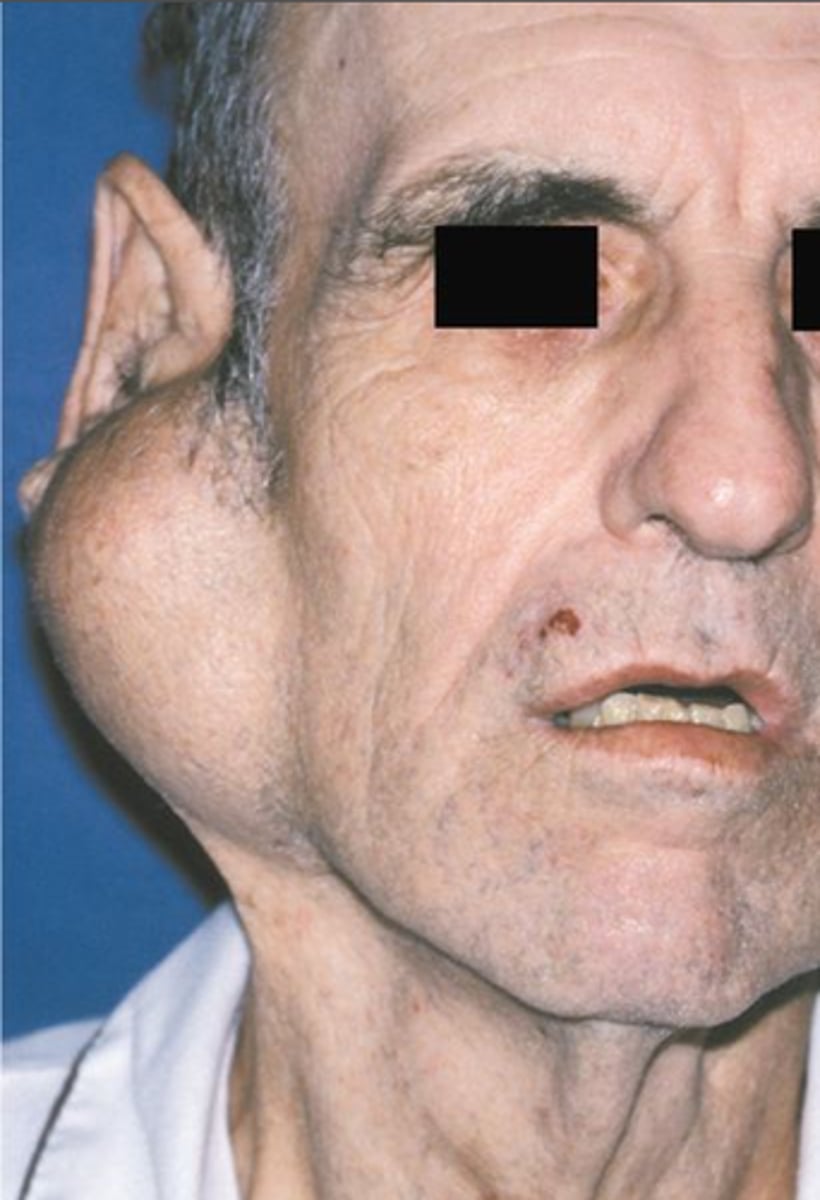
Secondary Sjogren Syndrome
Dry mouth + dry eyes + CT disease (RA or SLE)
Minor salivary gland biopsy, Sialogram, Rheumatoid Factor (RF), Anti-SSA (anti-Ro), Anti-SSB (anti-La)
Sjogren Syndrome diagnostic tests
artificial tears, saliva, topical fluoride, OHI, Recalls
Sjogren Syndrome treatments
lymphoma (MALT)
In patients with Sjogren Syndrome, there is an increased risk of...
parotid
Salivary Gland Tumors most occur in the...
RM, FOM, tongue
which salivary gland tumors are considered aggressive
benign
In the parotid, 3/4 of the time, is it benign or malignant
benign
In the submandibular, 55% of the time, the tumor is
malignant
In the sublingual, 70-95% of the time the tumor is
benign/malignant
Minor salivary gland tumors in the palate (most common) 50% of the time are
benign/malignant
Minor salivary gland tumors in the buccal mucosa 50% of the time are
benign
Minor salivary gland tumors in the upper lip 80% of the time are
malignant
Minor salivary gland tumors in the lower lip 85% of the time are
malignant
Minor salivary gland tumors in the tongue 90% of the time are
malignant
Minor salivary gland tumors in the floor of the mouth 90% of the time are
malignant
Minor salivary gland tumors in the retromolar pads 95% of the time are
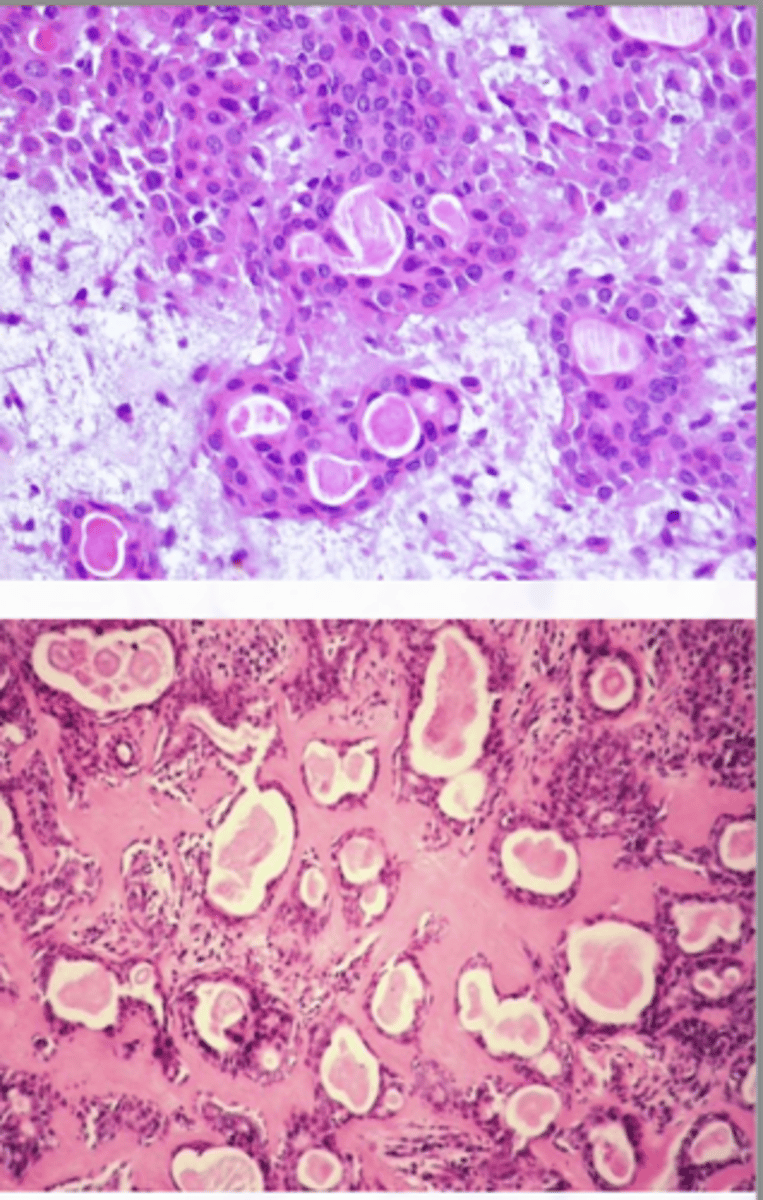
Pleomorphic Adenoma
Benign Salivary Gland Tumors:
Most common salivary gland neoplasm, Mix of epithelial and mesenchymal elements
Pleomorphic Adenoma
Various patterns within the tumor, Encapsulated
Double layered ductal structures and myoepithelial cells, Stroma appears myxoid, cartilaginous, and hylanized
surgical removal (Small percentage of tumors undergo malignant transformation)
Treatment for Pleomorphic Adenoma
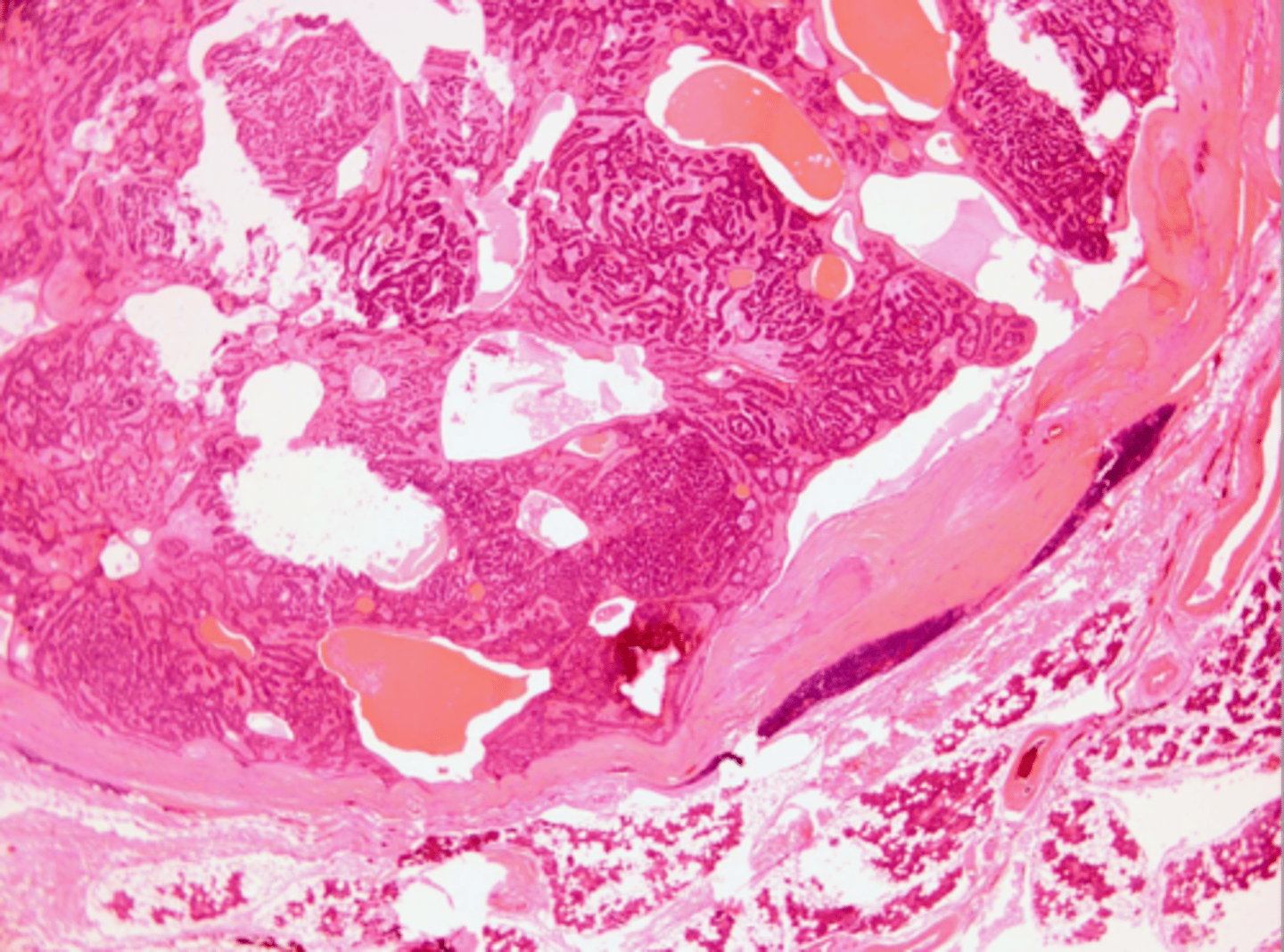
Canalicular Adenoma
Benign Salivary Gland Tumors:
Most common site is the upper lip, bluish, happens most in middle aged females >50yrs
Canalicular Adenoma
Well encapsulated, Cell are similar in appearance, Look like canals
Basal Cell Adenoma
Benign Salivary Gland Tumors:
Uncommon, Primarily tumor of Parotid
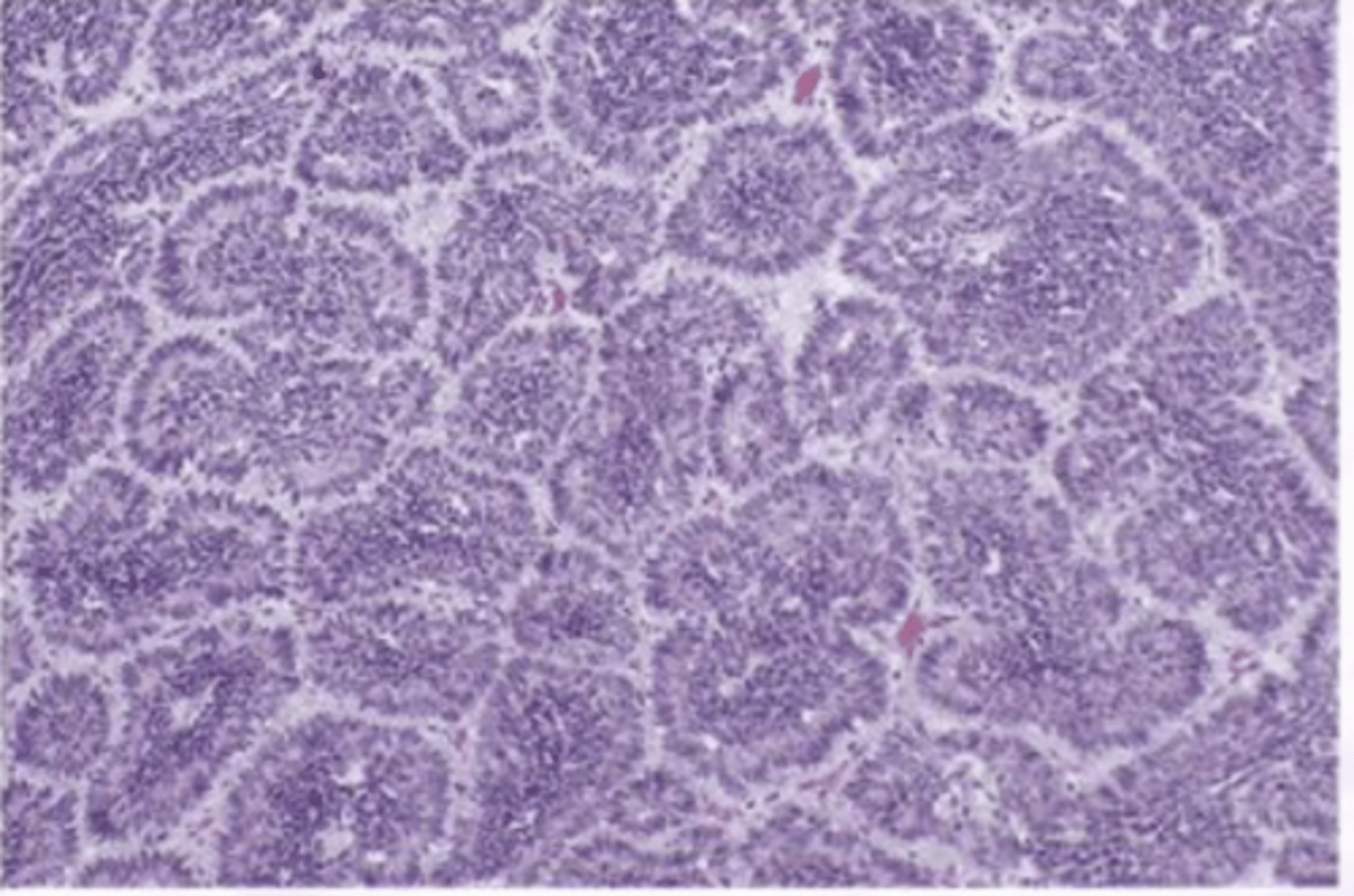
Basal Cell Adenoma
Which condition presents a slow growing moveable tumor that is part of the superficial lobe of the parotid?
Basal Cell Adenoma
Encapsulated, Islands with
palisaded cells, Jigsaw pattern, May form ducts
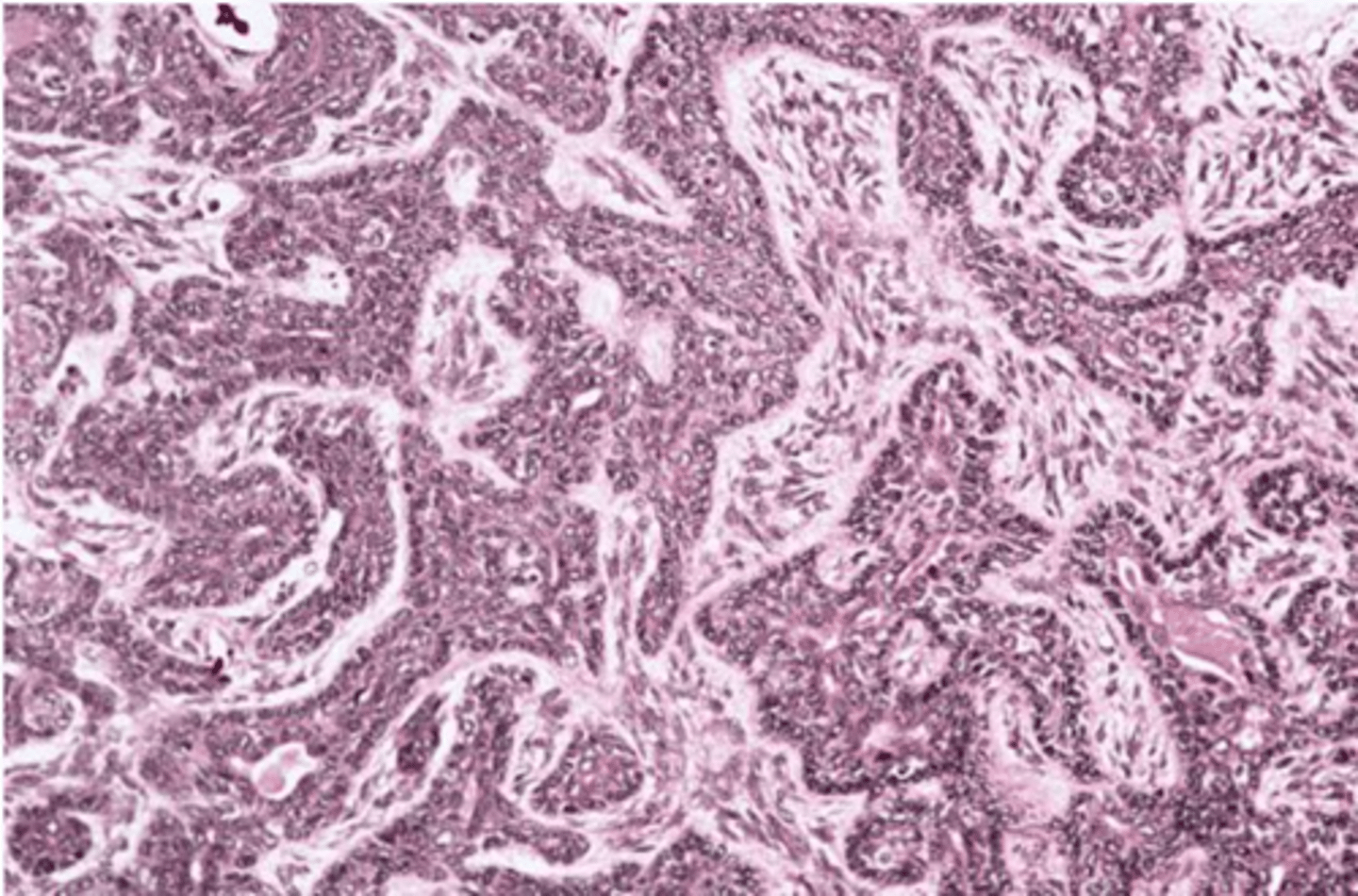
False, common
T or F: Recurrence after surgical removal of basal cell adenoma is uncommon
Ductal Papilloma
Benign Salivary Gland Tumors:
Exophytic and Papillary, Minor salivary glands
Inverted type
▫ lower lip and MD vestibule
▫ indentation
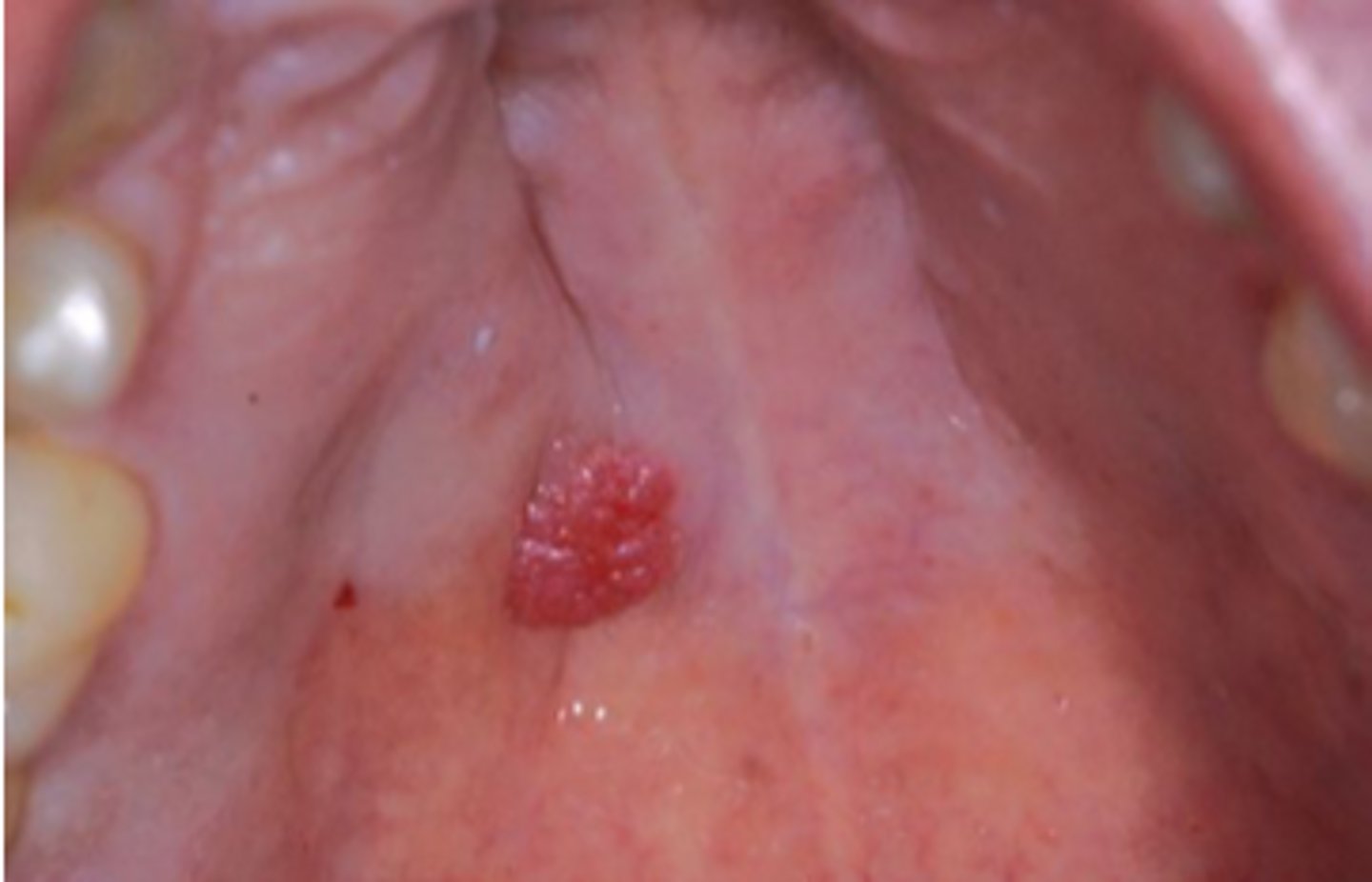
squamous papilloma
Ductal Papilloma mimics which papilloma?
Ductal Papilloma
• Papillary projections
• Inflammation
• Intraductal
▫ inside a duct
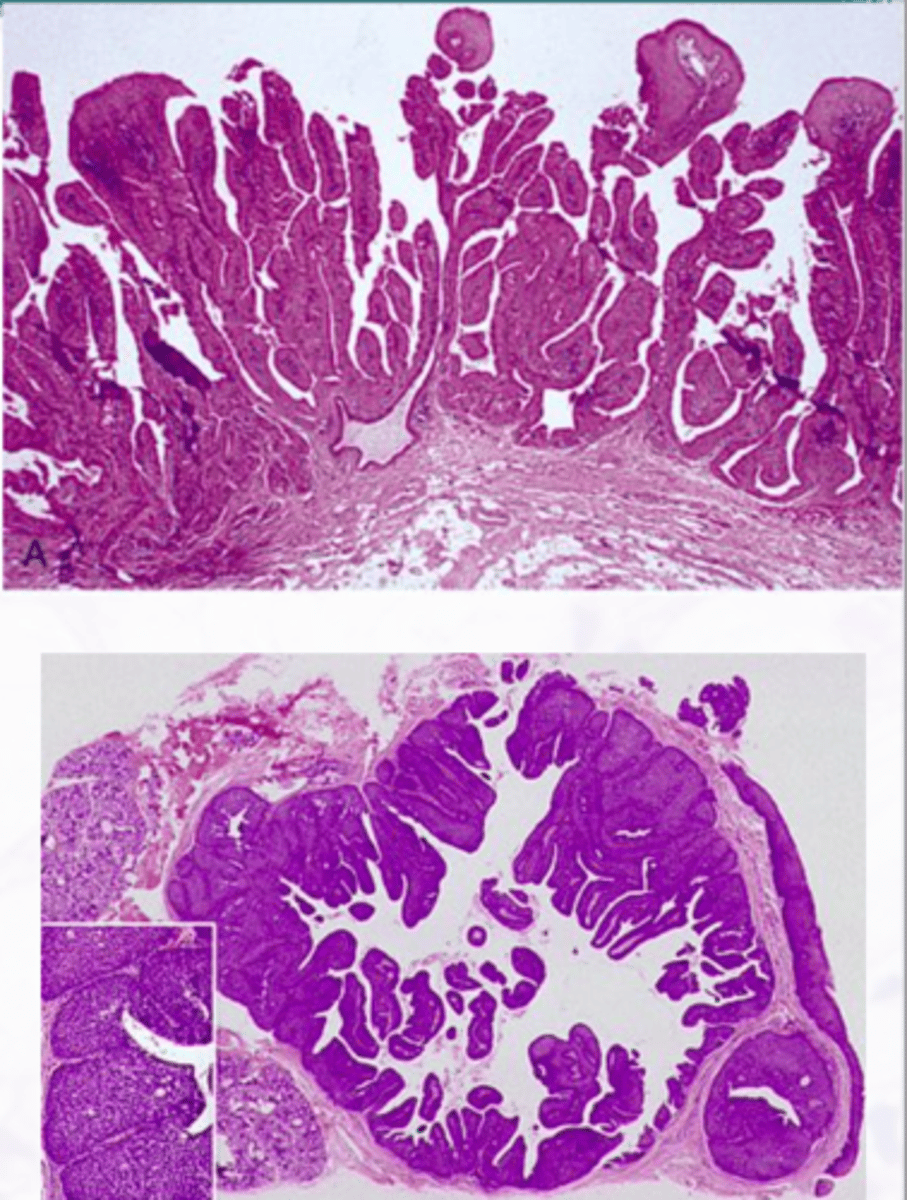
Warthin Tumor
Benign Salivary Gland Tumors:
-More common in males
-6th to 7th decades of life
-Association with smoking (8x)
-Slow growing painless mass of the parotid gland
-Proliferation of oncocytic cells and lymphoid cells
Warthin Tumor
-Cyst lined by uniform rows of oncocytic cells
-The lining is papillary in appearance
-The cyst wall is composed of abundant lymphocytes
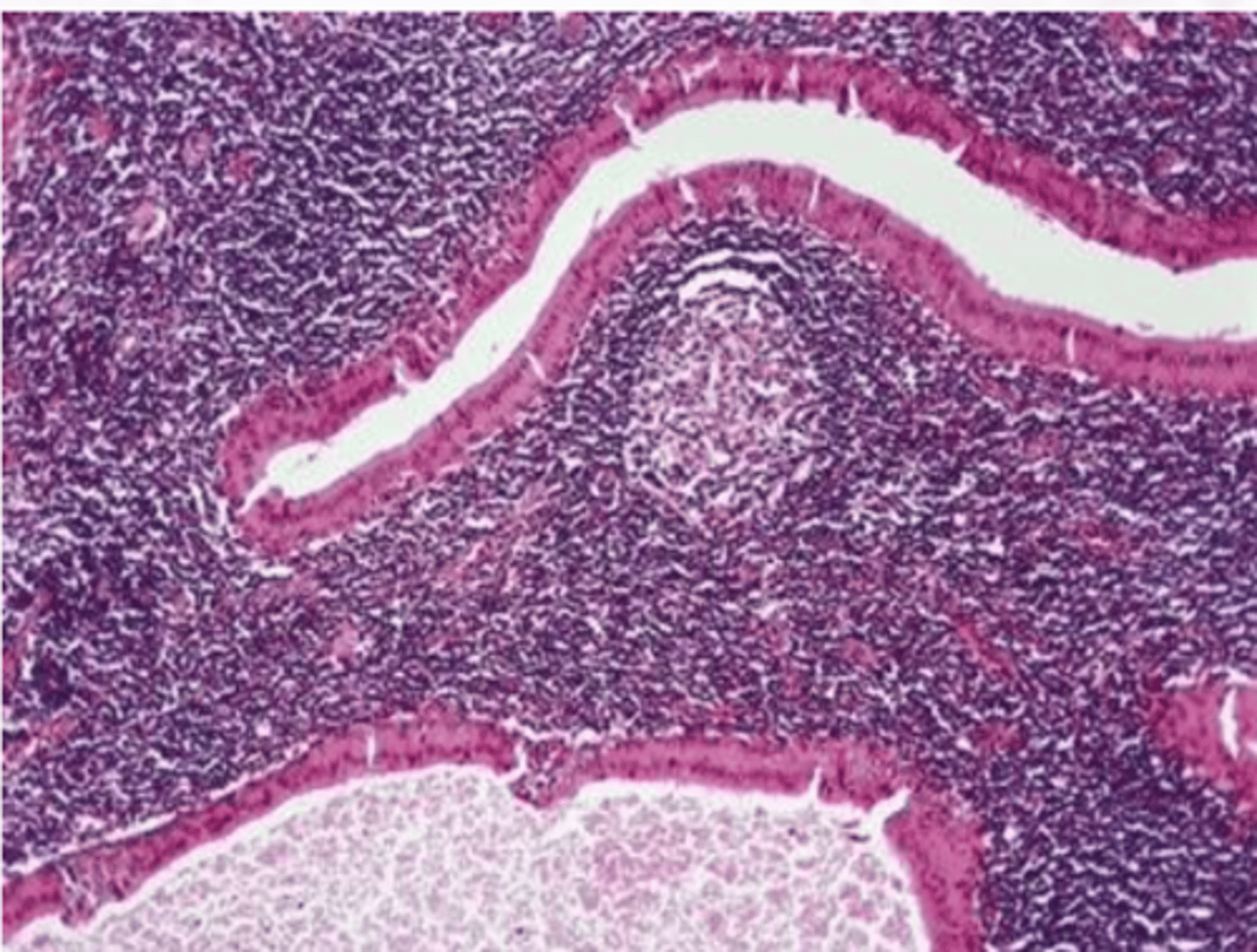
Warthin Tumor
6-12%
Warthin tumor has what percent recurrence after surgical removal?
Oncocytoma
Benign Salivary Gland Tumors:
• Rare salivary gland tumor
▫ Common in older
females
▫ Occurs in the parotid gland (85-90%)
▫ Presents as slow growing painless mass
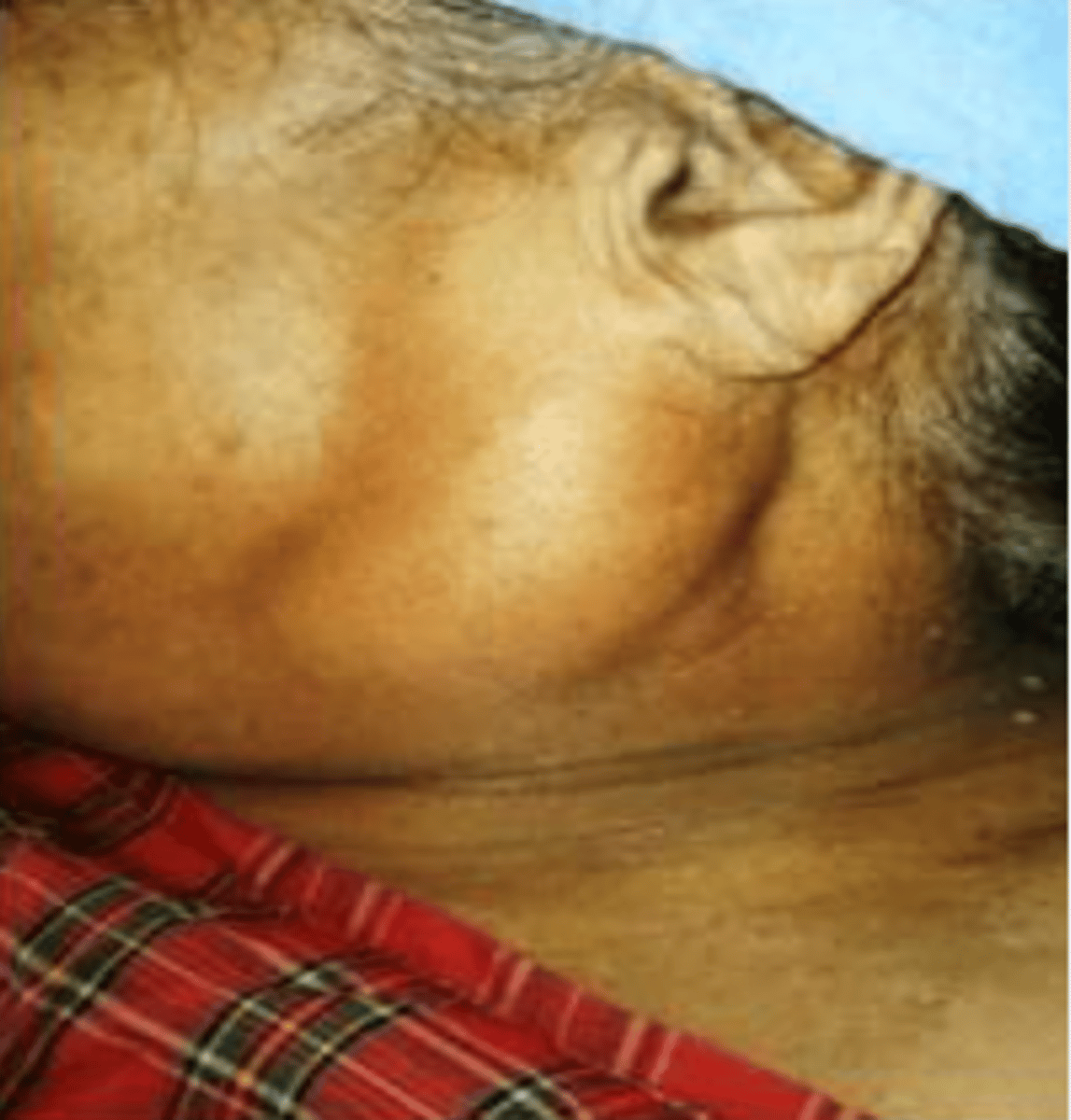
Oncocytoma
Large polyhedral cells with abundant granular cytoplasm
▫ Mitochondria
Cells are separated by thin fibrous septal
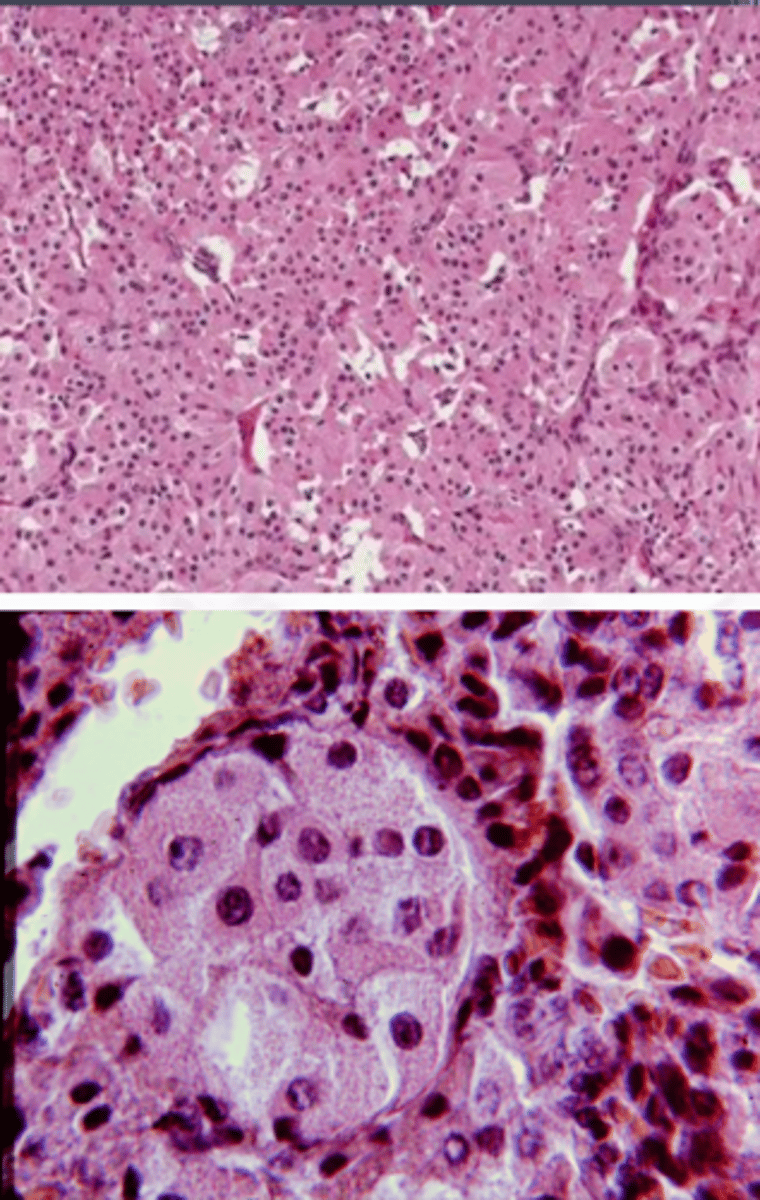
Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma
what is the Most common malignant salivary gland tumor?
Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma
Malignant Salivary Gland Tumors:
-Most common malignant salivary gland tumor
-Most common malignant salivary gland tumor in children
Parotid gland (major salivary
gland) (45%), Hard palate (minor) (21%)
Most common sites for Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma
mucocele
What can Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma mimic?
Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma
-Epidermoid cells
-Mucous cells
-Ductal structures
-Cystic spaces
-CRCT1-MAMl2 translocation ⇒ t(11;19)
Mucicarmine Stain
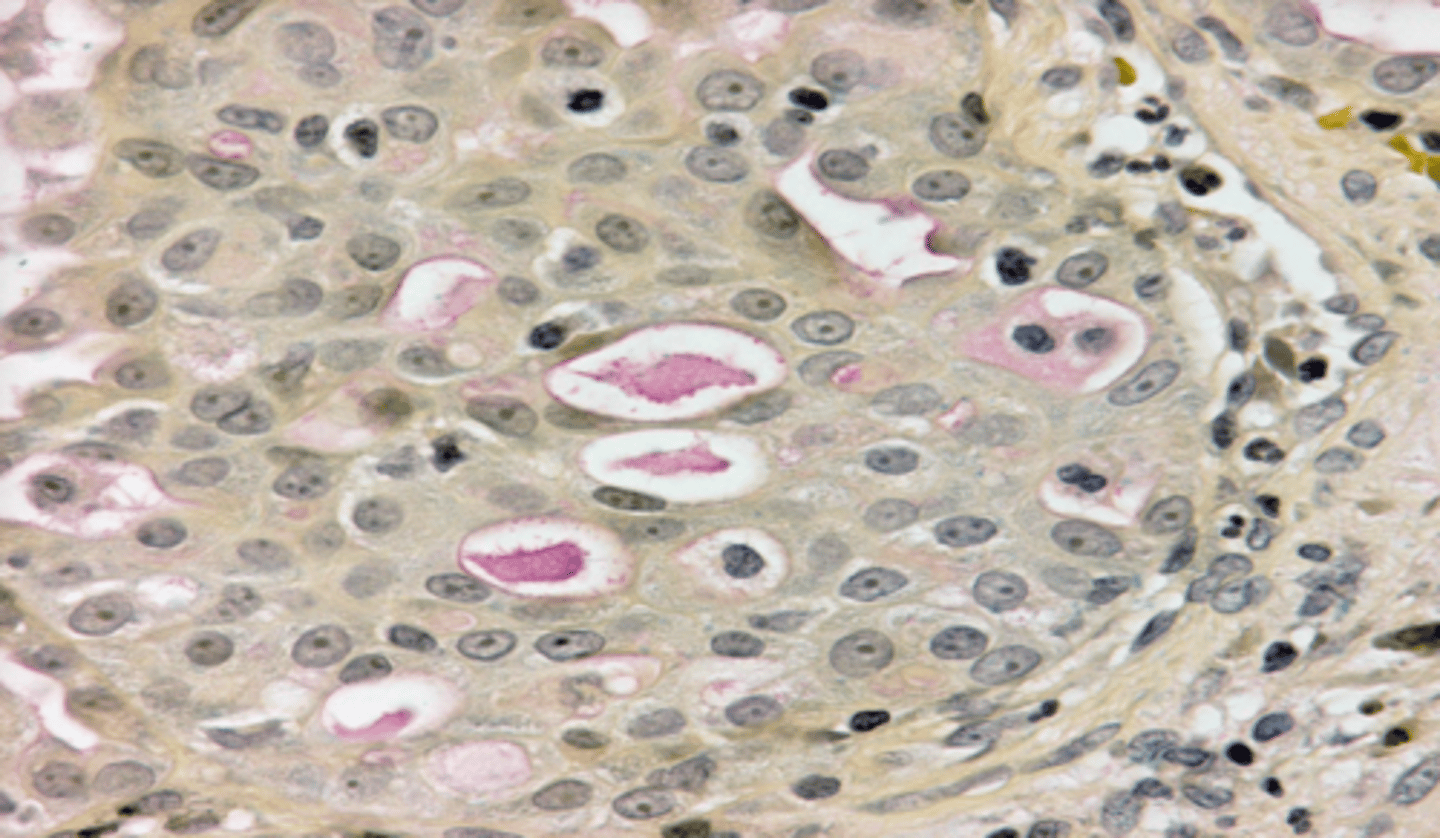
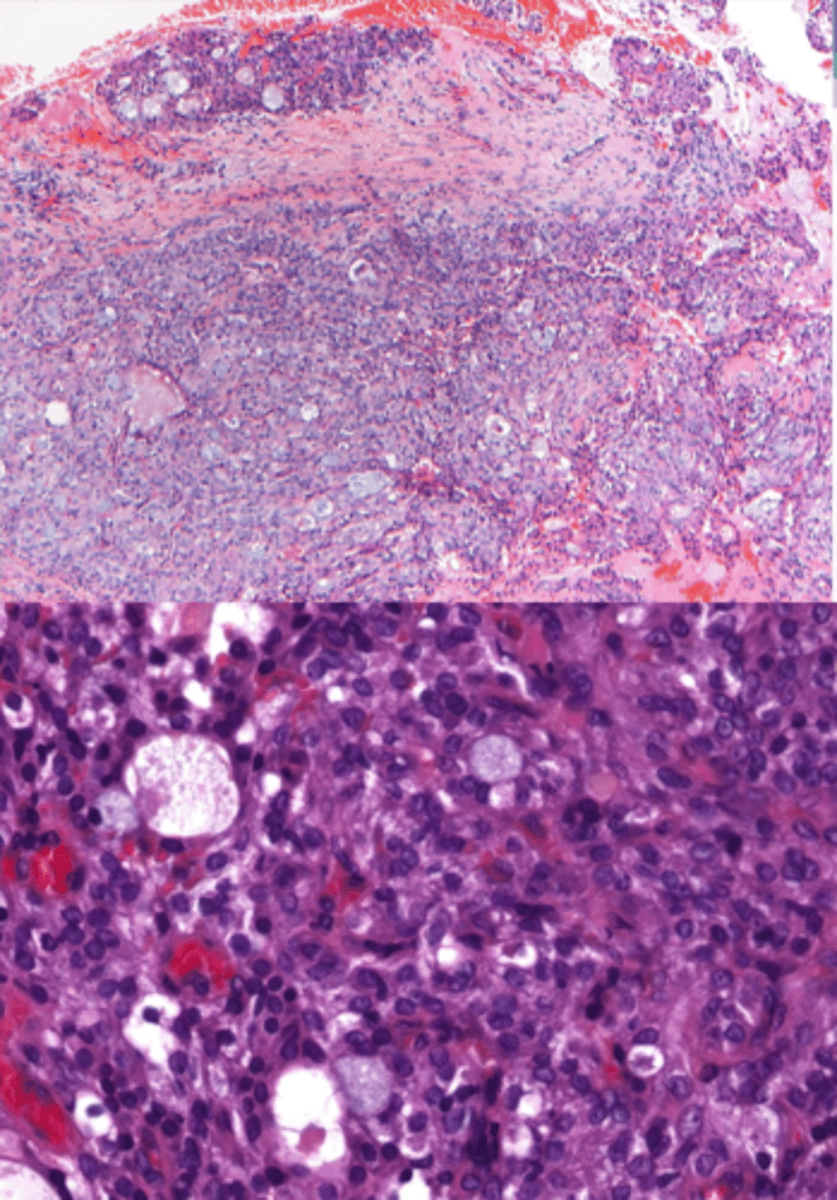
Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma
Malignant Salivary Gland Tumors:
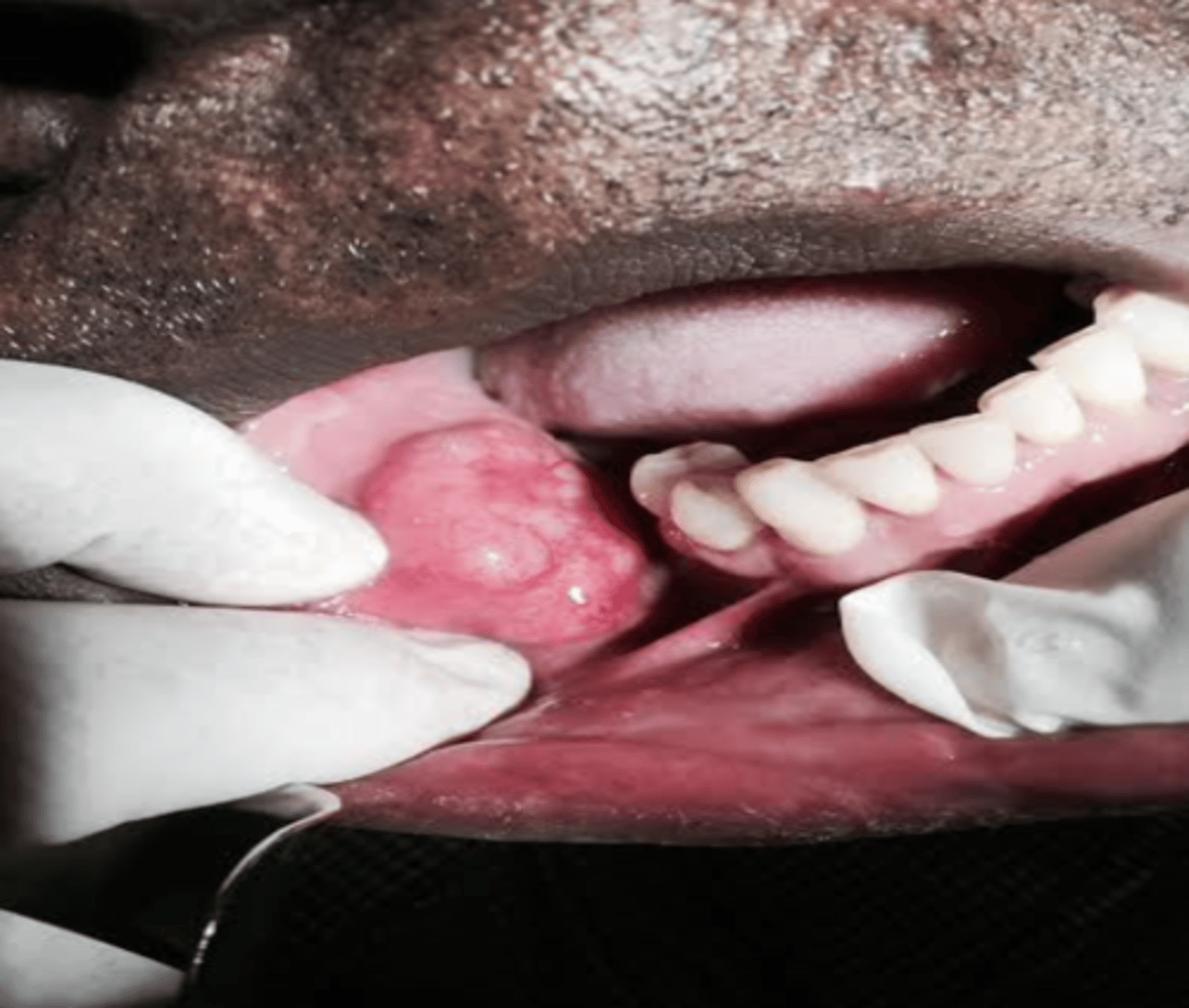
-Slowly growing mass
-Middle-aged females
-Painful or present with facial paralysis
-50% occur in minor glands (palate= most common)
Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma
• Swiss Cheese pattern
▫ Islands with a
cribriform pattern
▫ Myoepithelial and ductal cells are present
▫ Perineural and perivascular invasion
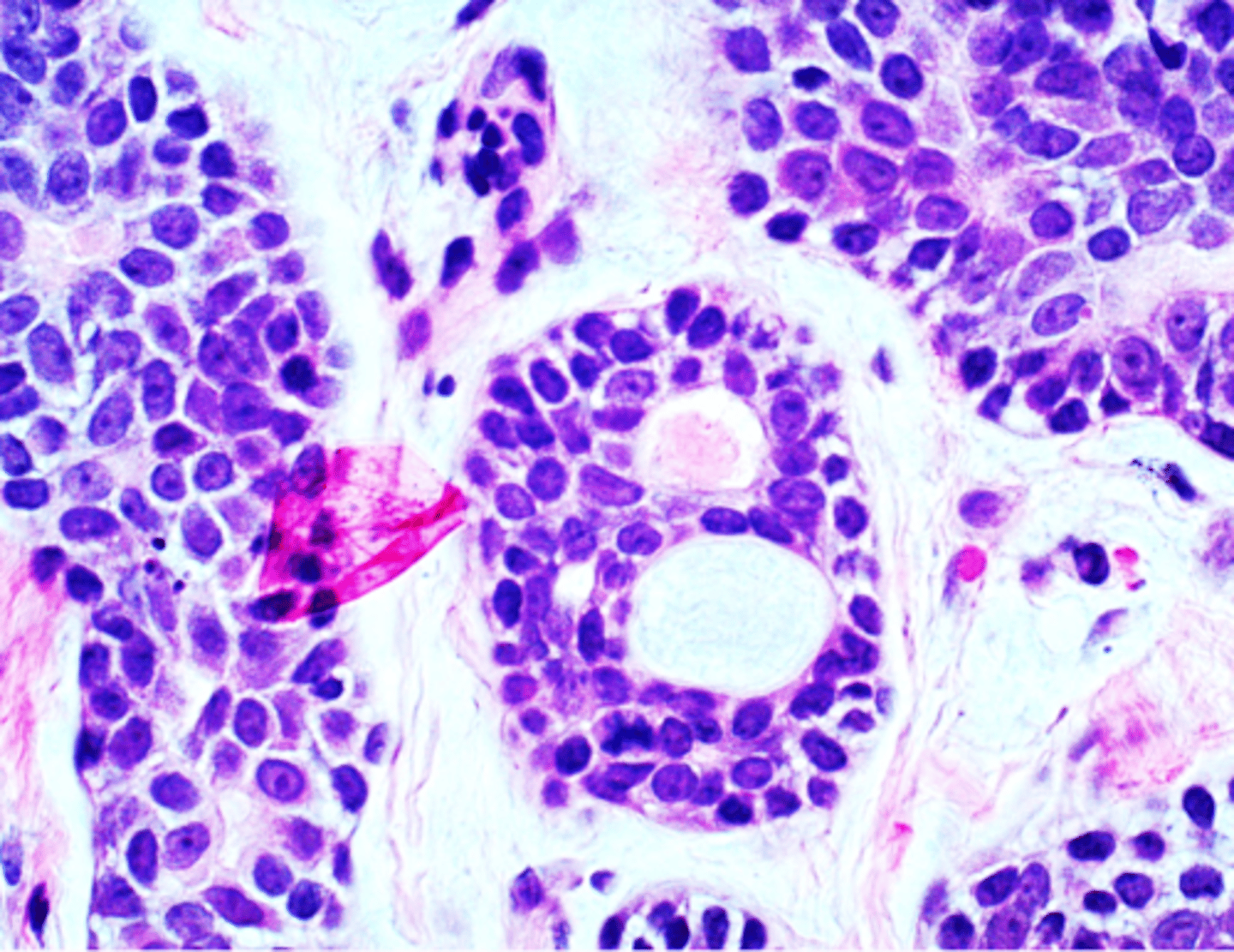
Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma
Surgical excision, Adjunct radiation (Relentless tumor)
Treatment for Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma
Polymorphous Adenocarcinoma
Malignant Salivary Gland Tumors:
-Tumor of the minor salivary glands
-6th -8th decades of life
-Female predilection
-Painless slow growing lesion
-Almost exclusively in minor salivary glands
-May infiltrate bone
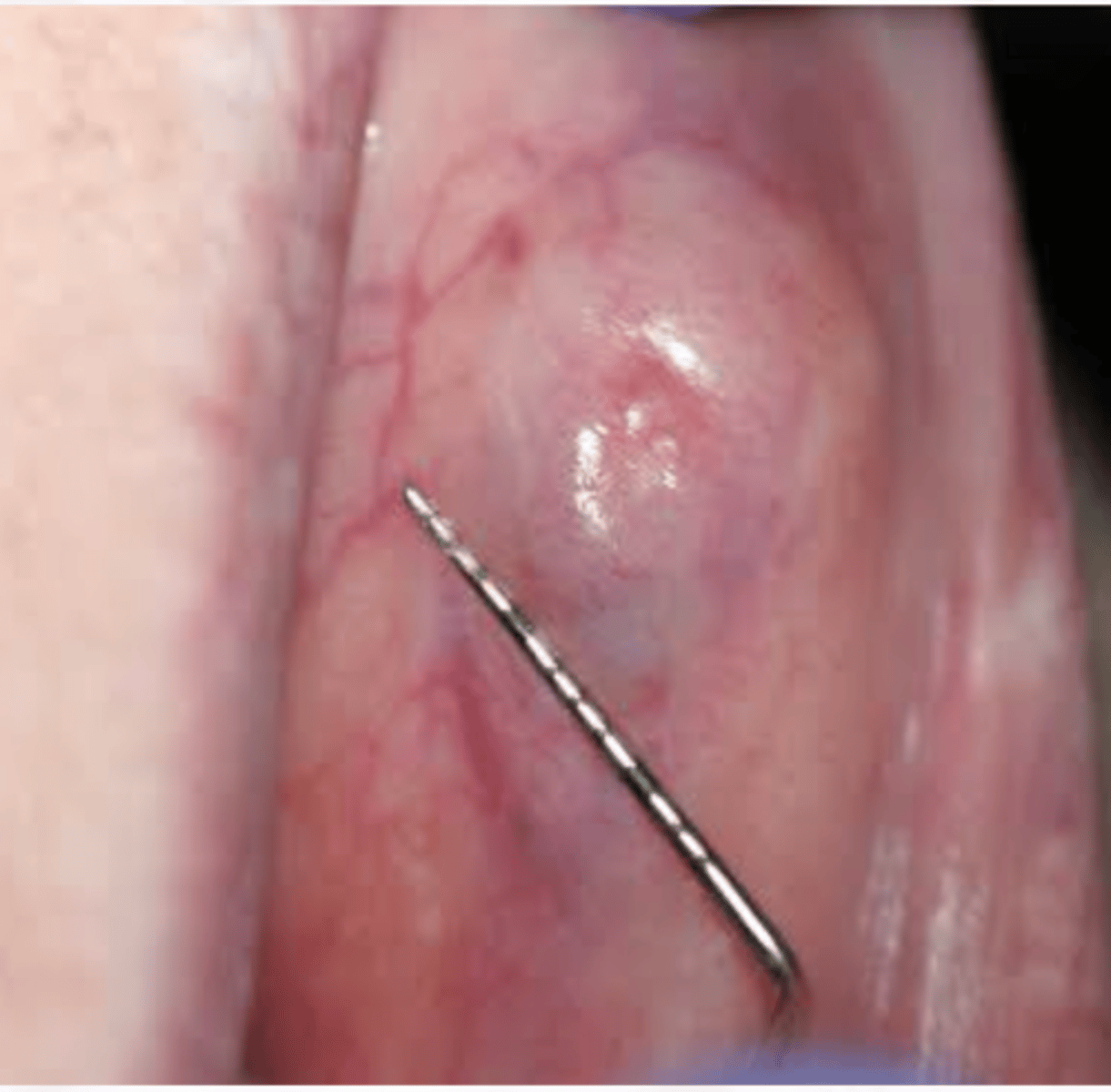
Polymorphous Adenocarcinoma
-Various histologic patterns
-Cells line up in single file line "Kindergarten filing"
-Perineural and Perivascular invasion
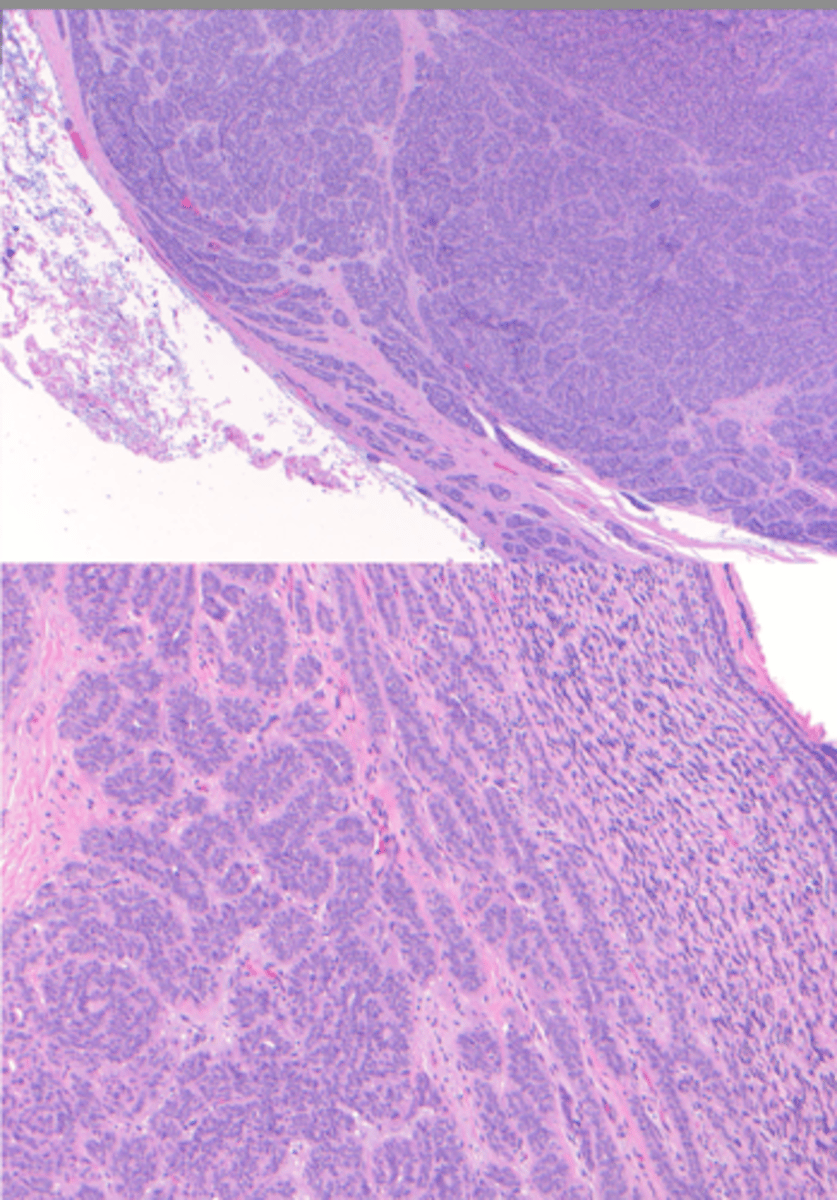
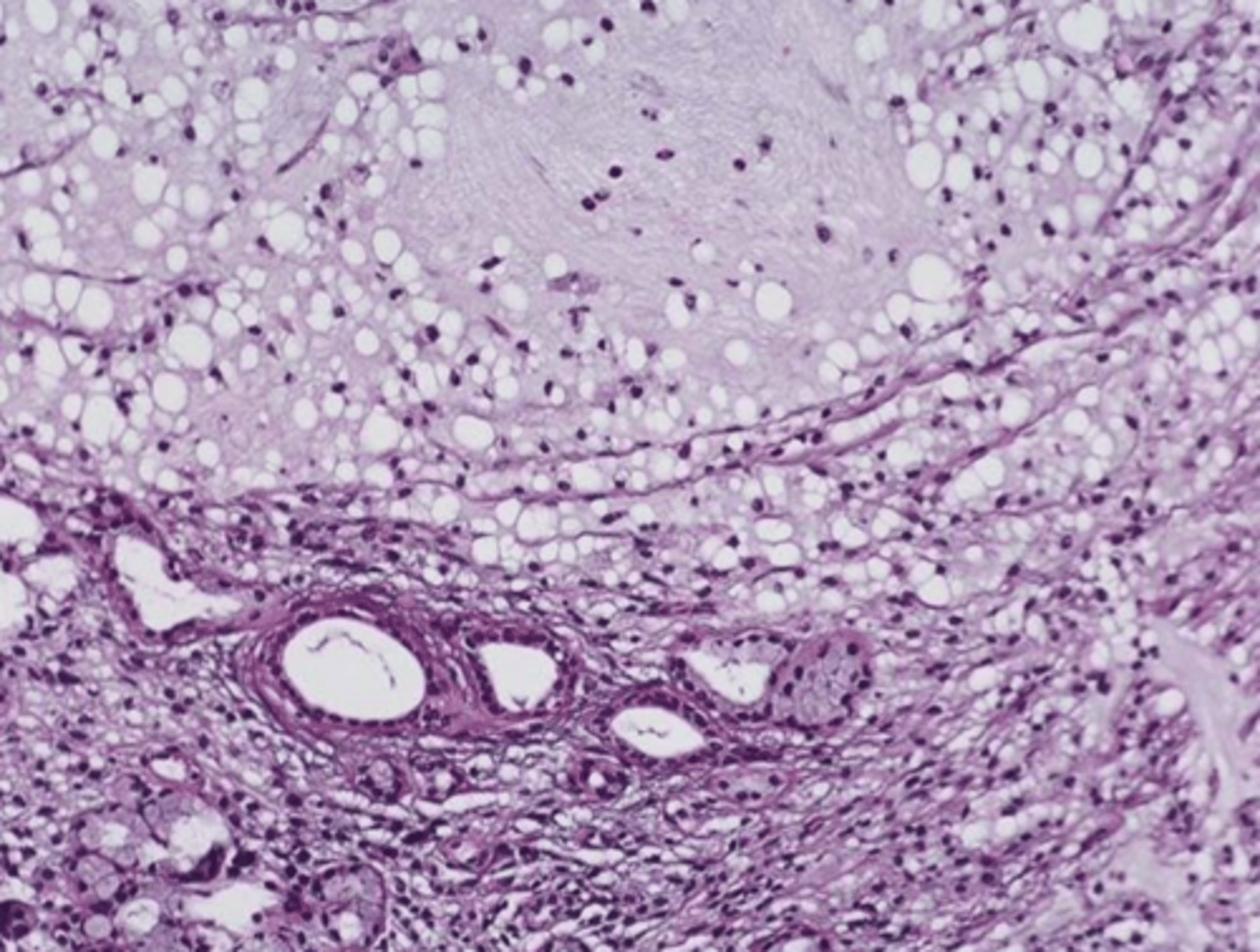
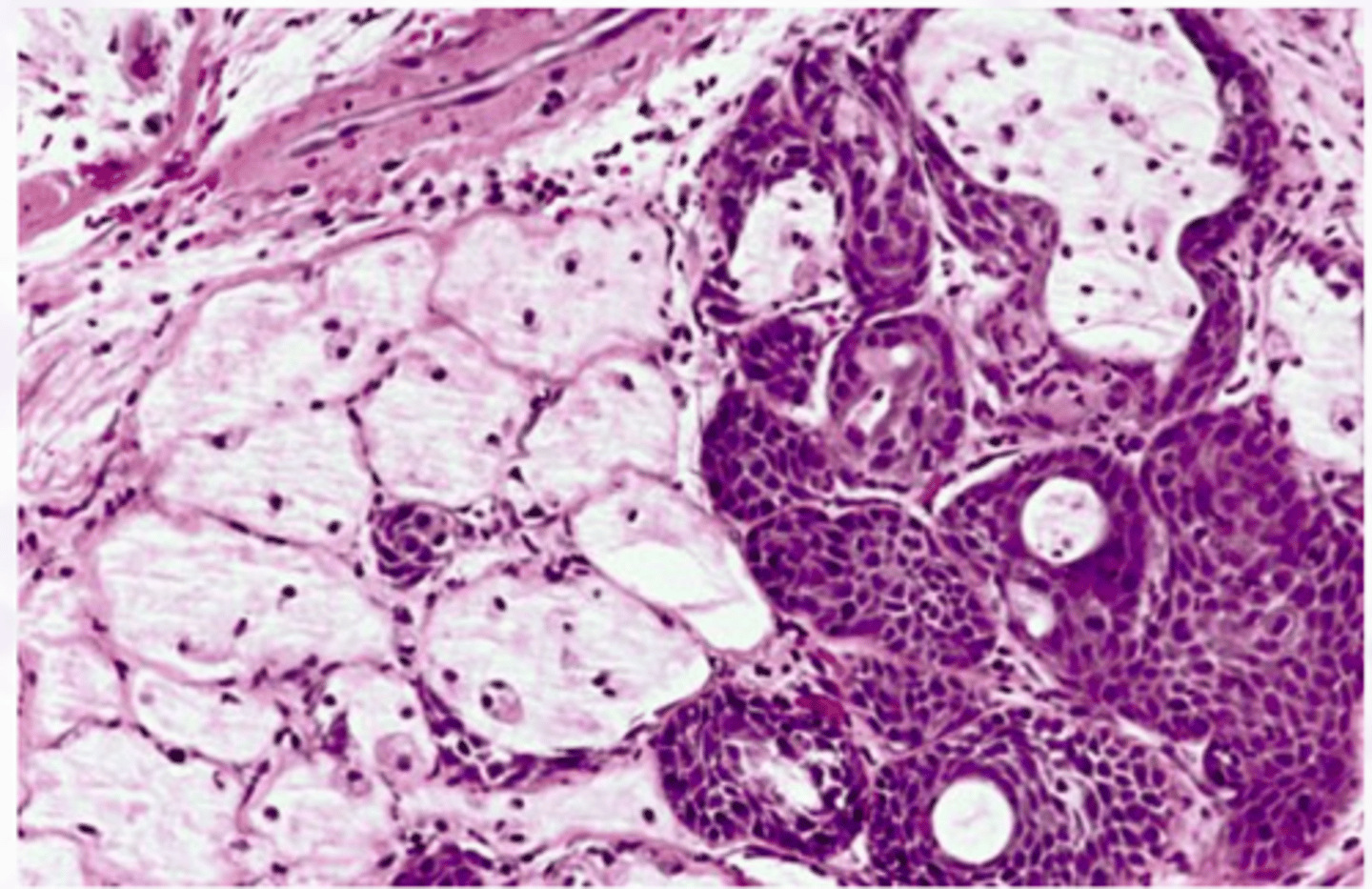
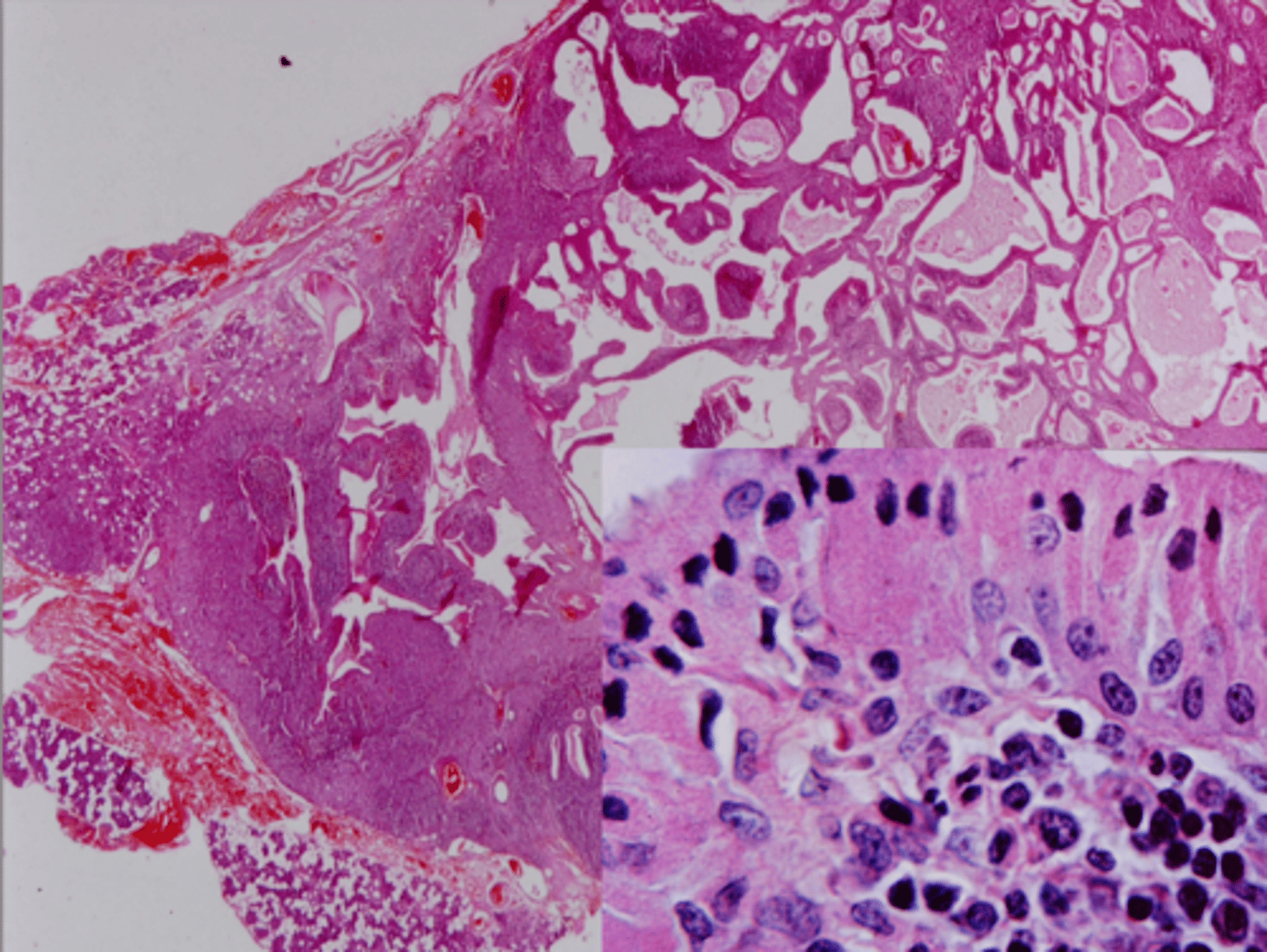
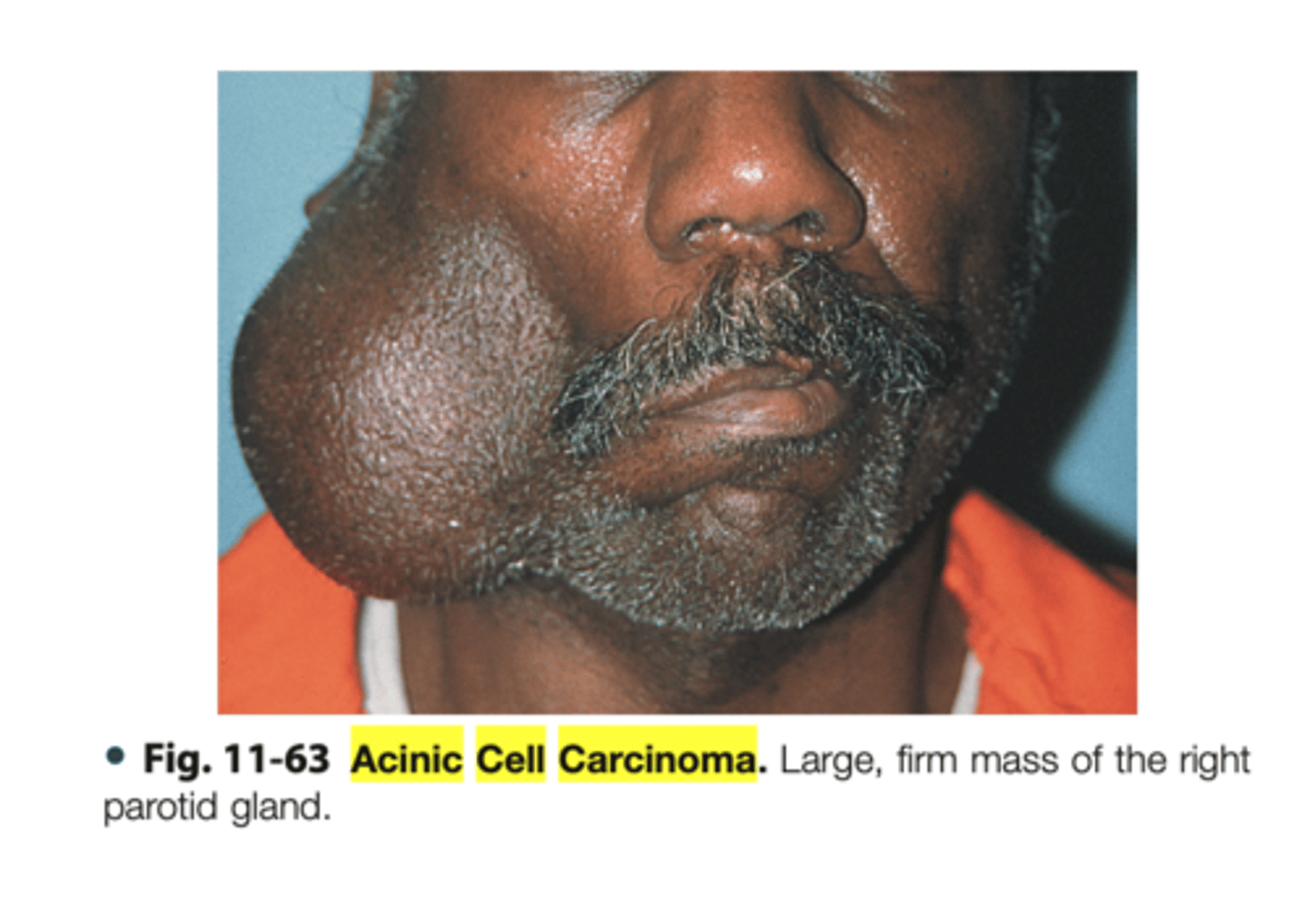
Acinic Cell Carcinoma
Malignant Salivary Gland Tumors:
-Low grade malignant tumor
▫ serous acinar cells
-Wide age range 2nd-7th decade of life
-Most common site: parotid gland (85%)
▫ 9% minor salivary glands
-Female predilection
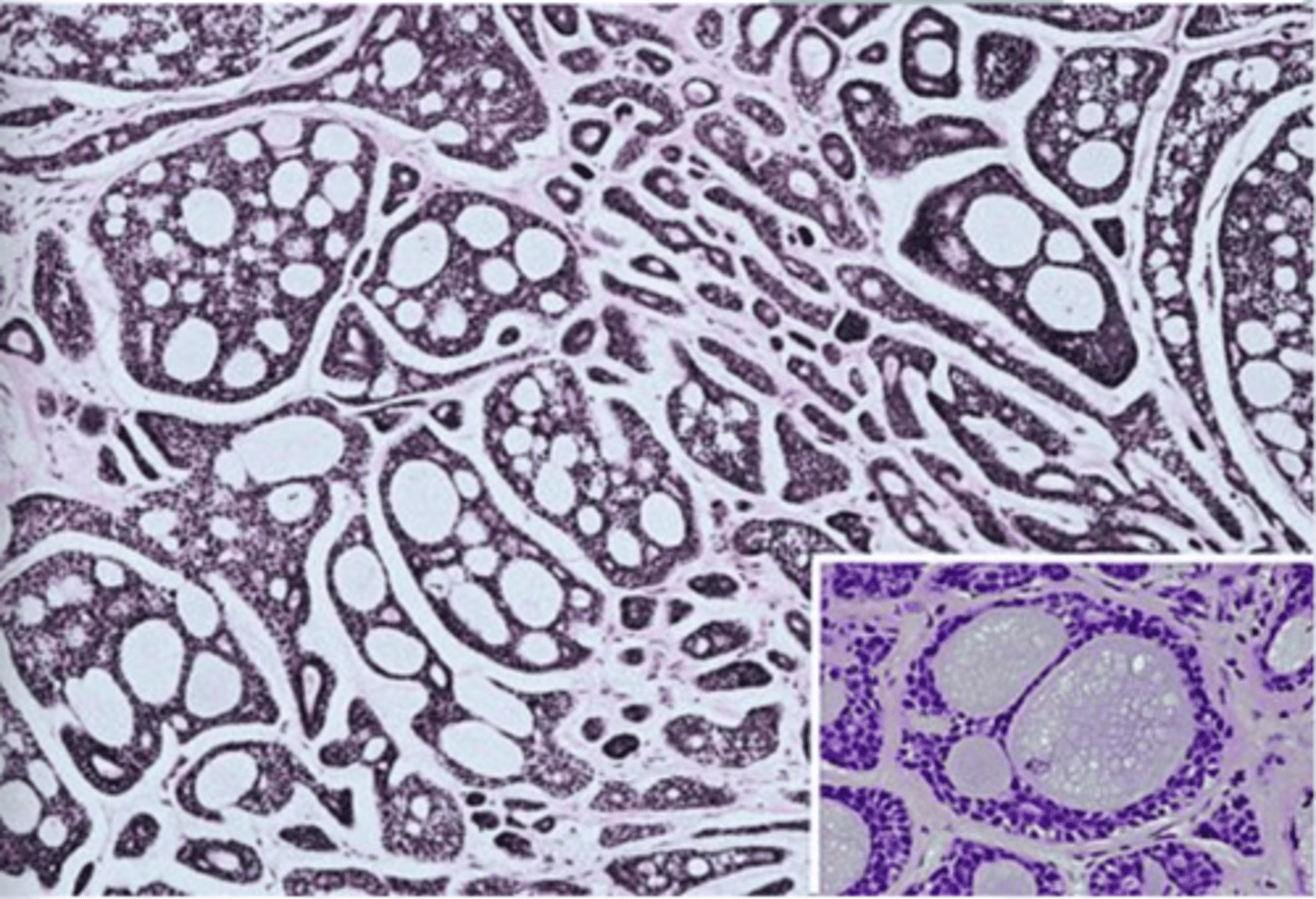
Acinic Cell Carcinoma
• Well circumscribed
• May show infiltration
• Serous acinar cell
▫ Cells containing abundant granular cytoplasm
▫ Zymogen granules
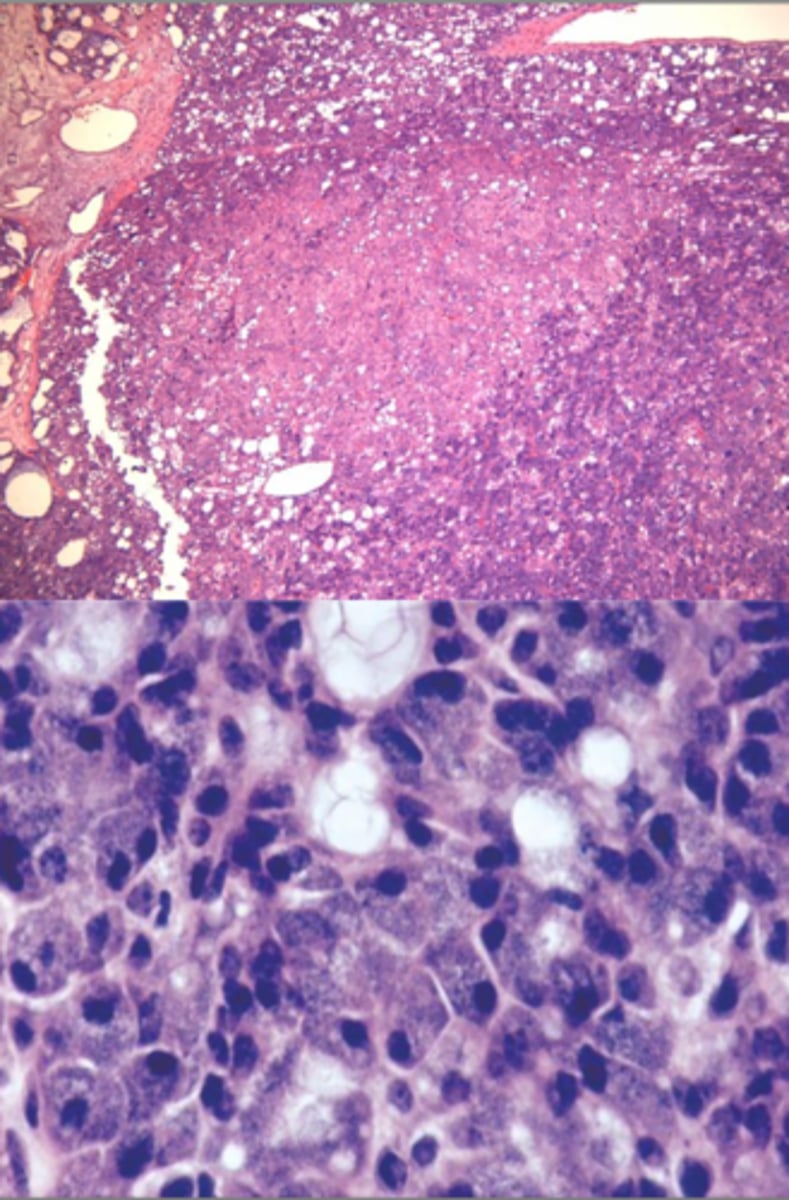
Normal Parotid Parenchyma
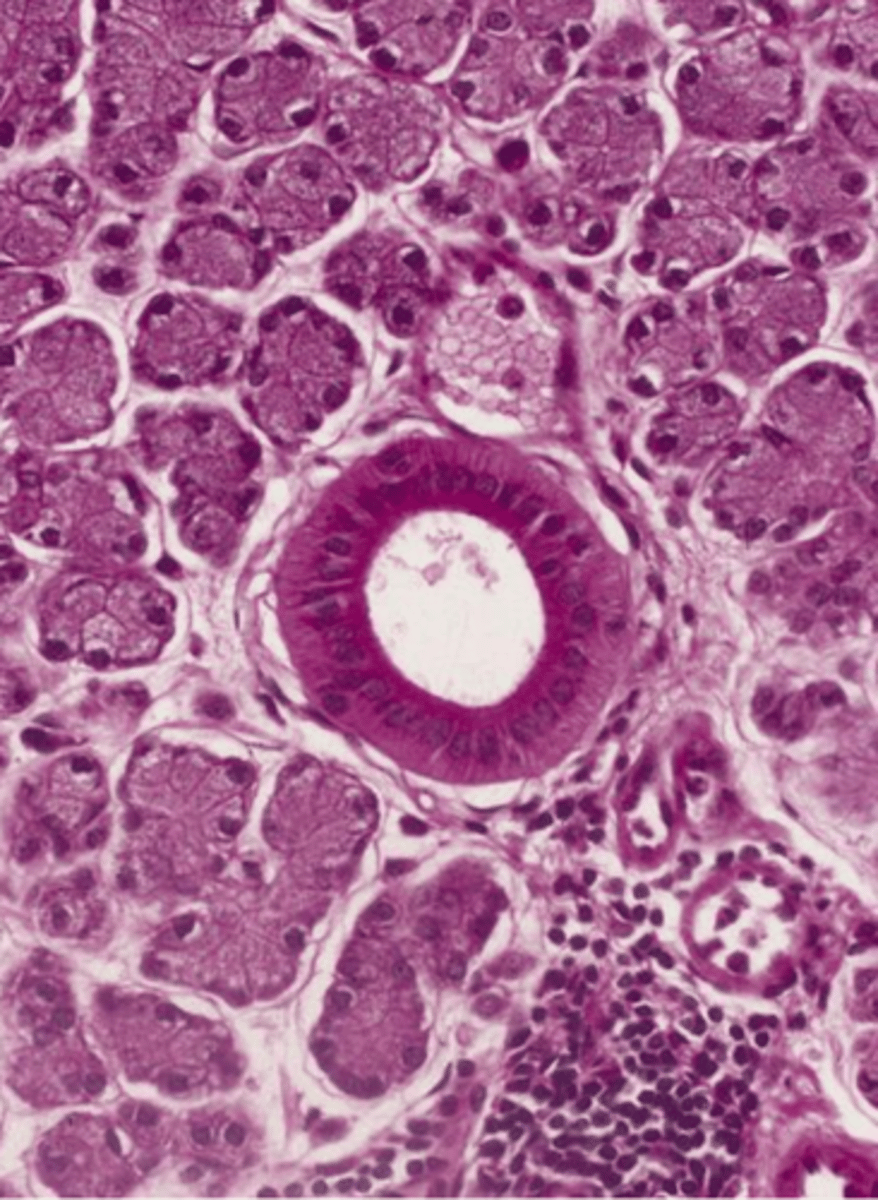
Acinic Cell Carcinoma
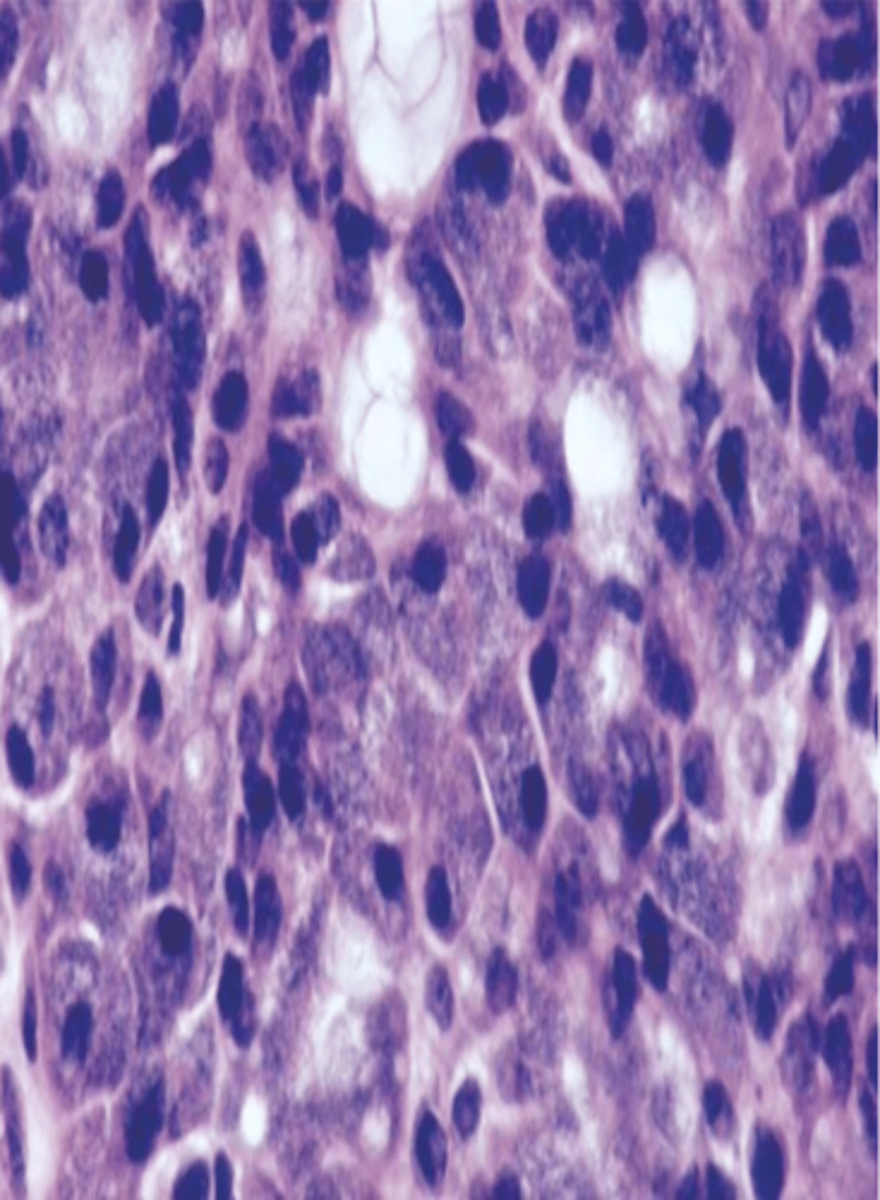
Secretory Carcinoma
Malignant Salivary Gland Tumors:
Used to be part of acinic cell carcinoma
▫ “zymogen poor”
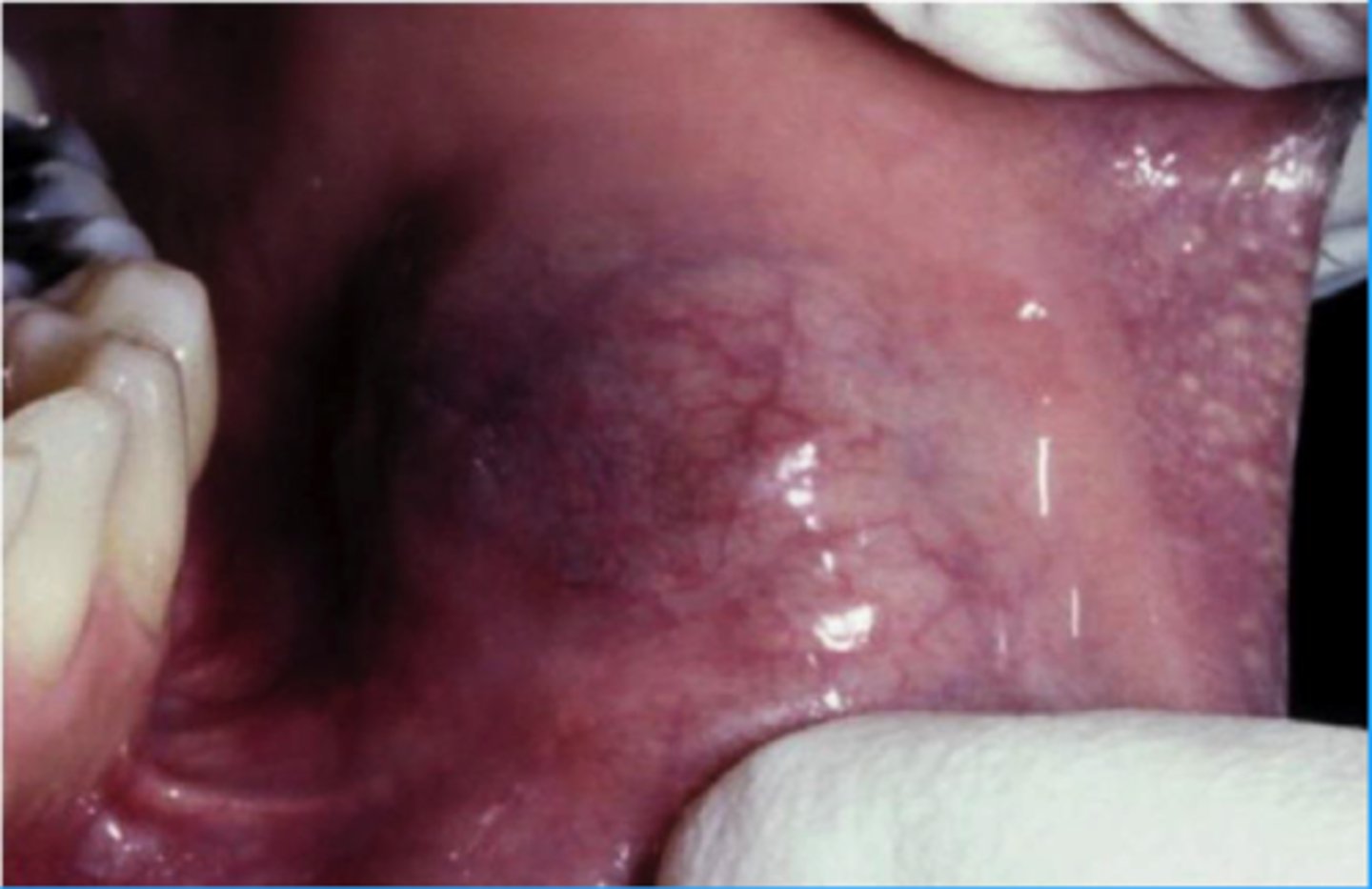
parotid
What is the most common location for secretory carcinoma?
Secretory Carcinoma
-Bland cytology
-Varying appearances
▫ "hobnail" cells
• Translocation!▫ ETV6-NTRK3 ⇒t(12;15)(p13;q25)
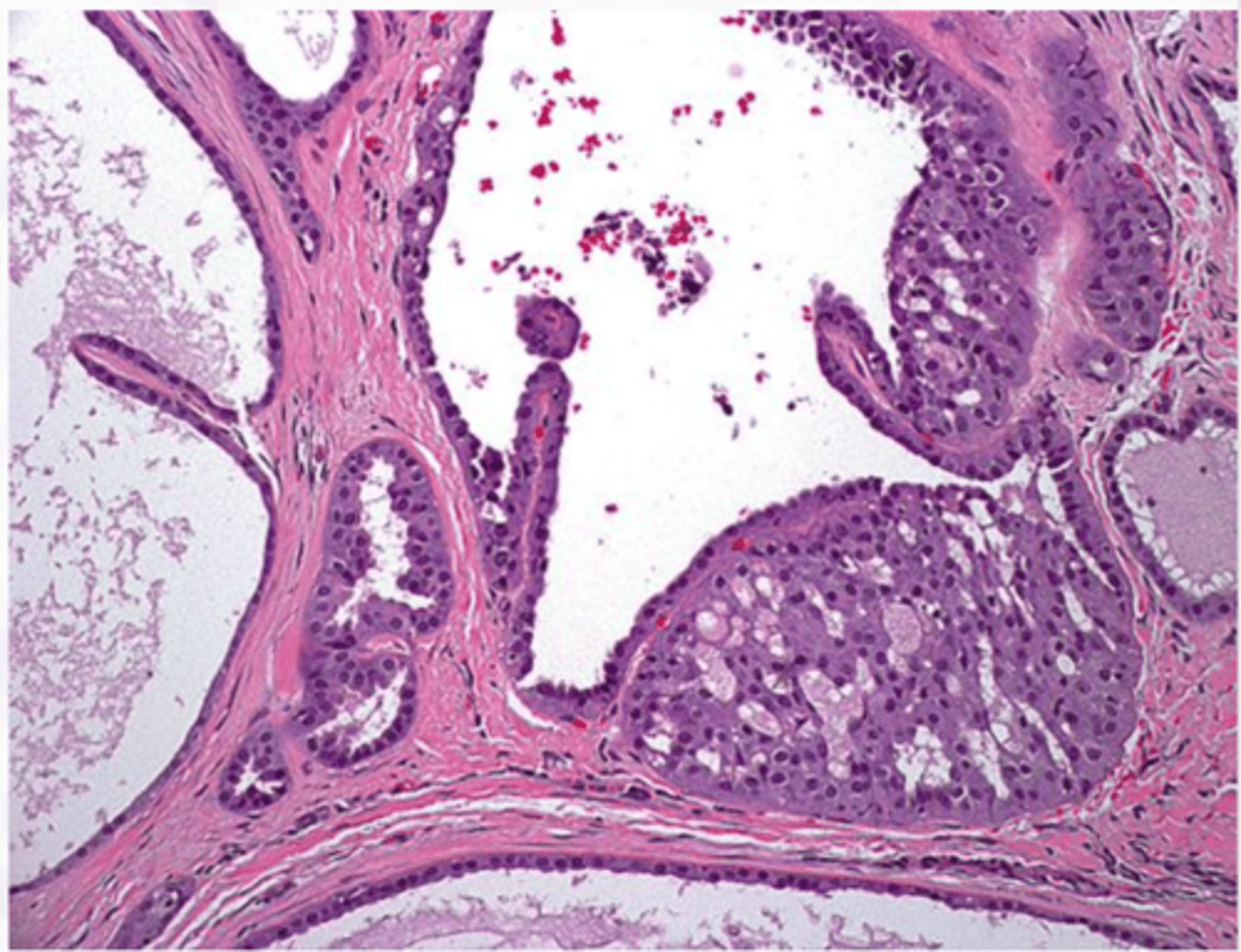
Carcinoma Ex PA
Malignant Salivary Gland Tumors:
-Malignant transformation of a PA(pleomorphic adenoma)!
-Middle aged and older
-History of a lesion present
for many years
-Rapid growth
▫ pain, ulceration
▫ facial nerve palsy
-Most in parotid
-Minor SG→ most on
palate
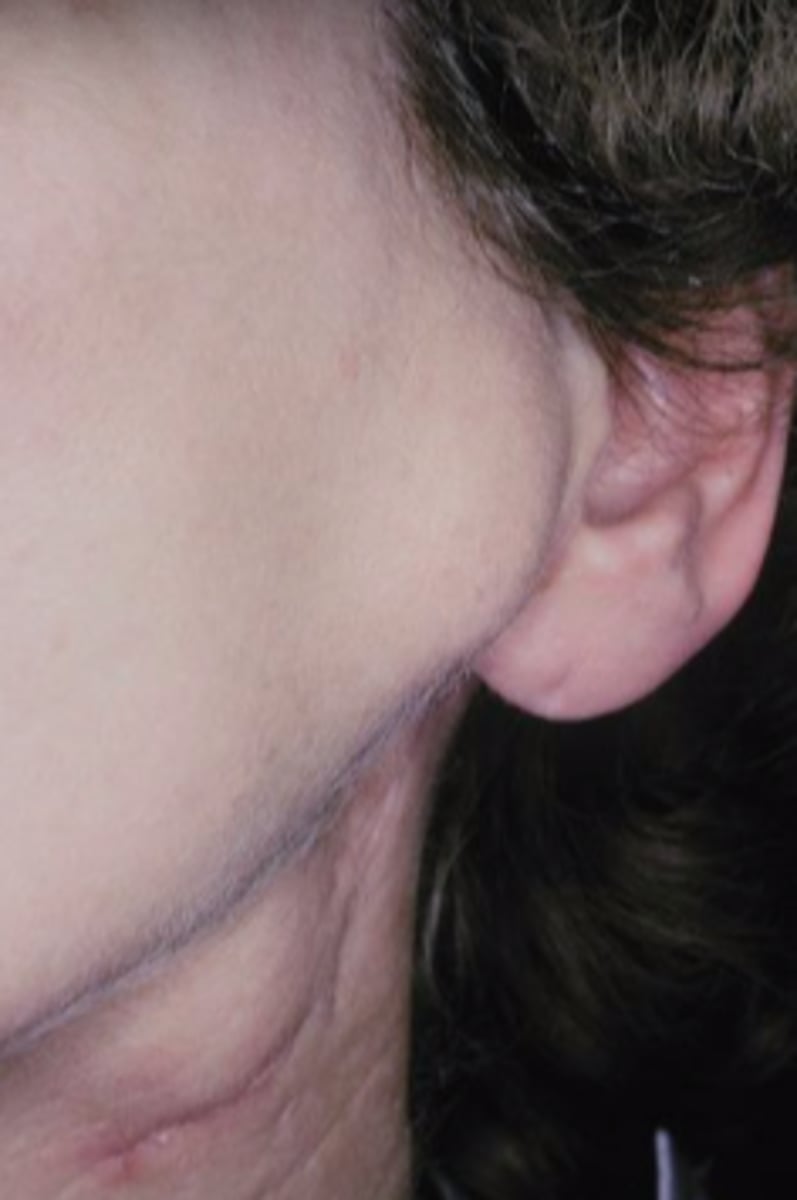
Carcinoma Ex PA
A: benign
B: Malignant
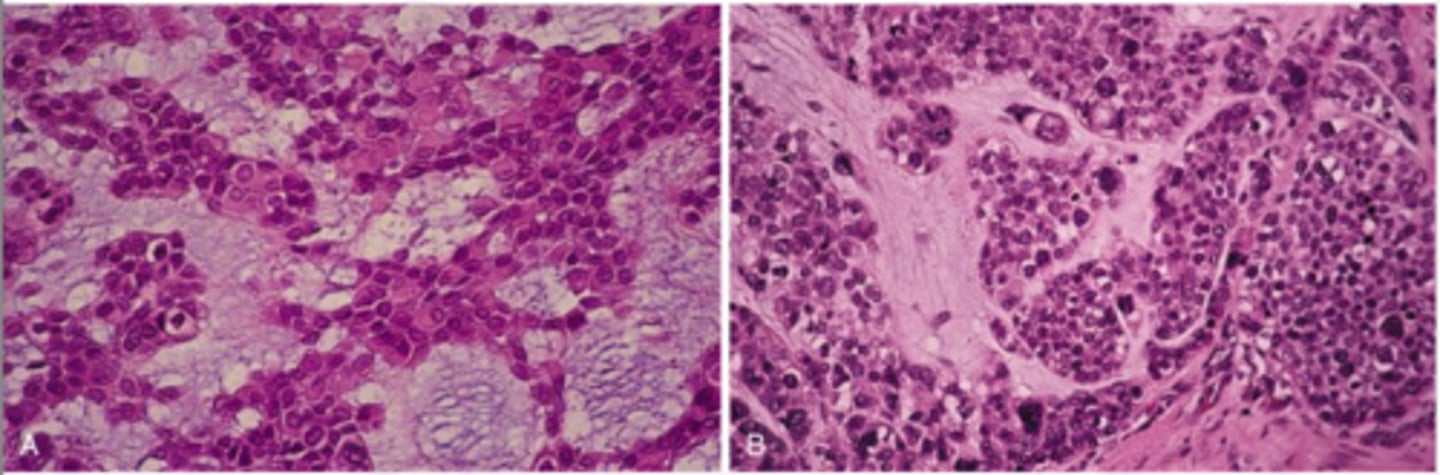
pleomorphic adenoma
The most common salivary gland tumor is...