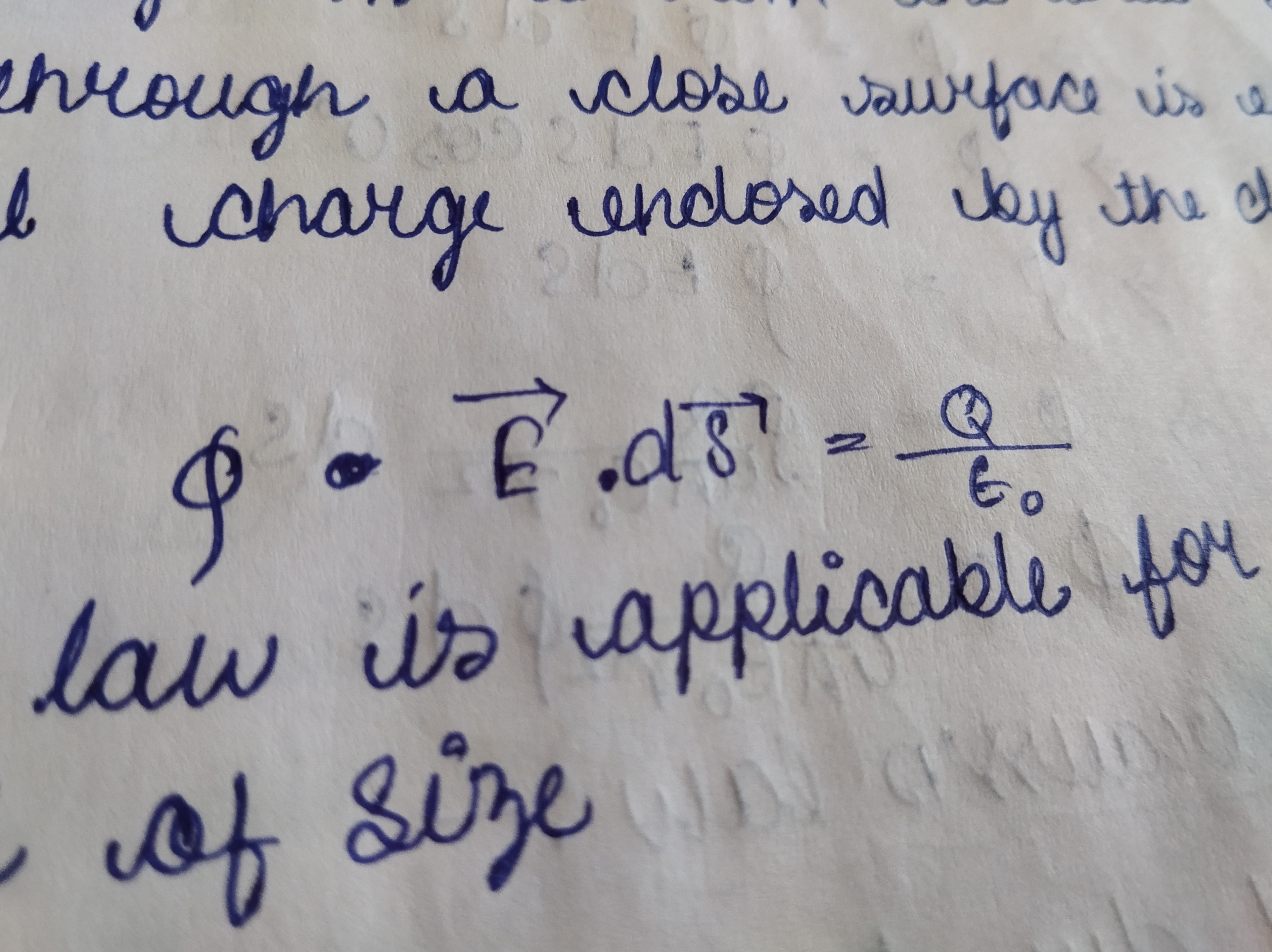electric charges and field
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Properties of electric charges
Quantization of charge
Conservation of charge
Additivity or additive nature of charge
What is Additive nature of charge
The total charge in a distribution is found by the algebraic sum of all the charges in the distribution.
What is conservation of charge
The total charge in an isolated system remains conserve this is known as conservation of charge
Quantization of charge
The total charge of a body is integral multiple of charge of electron
Charge of an electron
1.6 × 10–¹⁹ coulombs

State coulomb's law
The electrostatic force between the two points charges is directly proportional to the product of magnitude of the two point charges and inversely proportional to the square of distance of separation between the two points charges
If q1 and q2 be the two point charges separated by a distance ‘r’ then according to coulomb's law , the electrostatic between the point charges, ?
F ∝ q1 q2
∝1/r²
F= c q1 q2
r²
Where c is the constant of proportionality,
C = ?
1/4π€o = 1/4π€o€r = 1/4π€ok
Si unit of permittivity
C²N–¹m–² or C/Nm²
Definition of coulomb
Coulomb is the unit of electric charge .
Value of €o
8.854×10–¹²C²N–²m–²
If q1q2 =1C and r=1
F=?
9×10⁹N
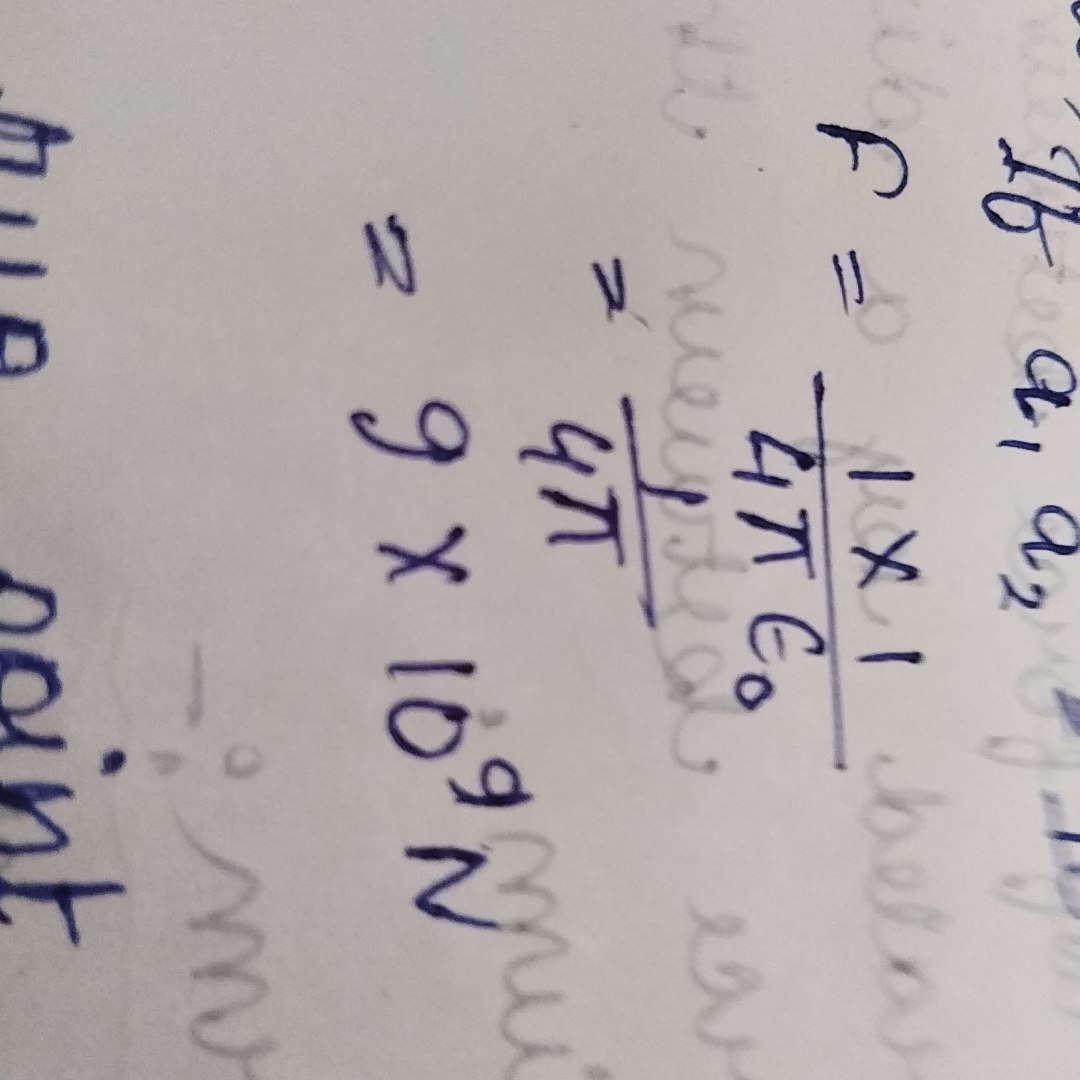
What is principal of super position ?
In an assembly of charge the net force on a point charge is the vector sum of all the individual force given by the other charges
Electric field
Electric field at a point is defined as force acting on unit positive charge placed at that point
Electric lines of force or electric field lines
Electric field lines of force are imaginary lines. It is defined as the path followed by unit positive charge placed at that point
Properties of electric lines of force
Electric lines of force originates from the positive charge and terminates at the negative charge
Electric lines of force is the path followed by unit positive charge placed at a point.
Tengent drown at any point on the electric lines of force gives the direction of electric field at that point
Two electric lines of force never intercept at a point
Electric field at point is equal to total electric linesof force passing normally (electric flux ) through unit area, surrounding that point.
Electric dipole
Two equal and opposite charge separated by a very small distance are together known as electric dipole.
What is dipole moment
The product of magnitude of one charge of the dipole and distance of separation of the two charges are known as dipole moment of the electric dipole
If the charges+q and -q and separated by a distance 2d then dipole moment of the dipole ?
P= 2dq
Electric dipole moment is a vector quantity and it's direction will be from the negative charge towards the positive charge
Si unit of dipole moment ? Dimensional formula of dipole moment
SI unit is Cm
Dimensional formula- [ L A T ]
Electric flux
Electric flux through a surface is total electric lines of force passing normally through the surface.
Gauss’s theorem
According to Gauss's theorem the total electric flux passing through a close surface is equal to 1/Eo
Mathematical,
∮ E ⋅ dA = Q / ε₀
Φ = Q / ε₀