Primate Intestinal Cestode Parasitology
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
4 Terms
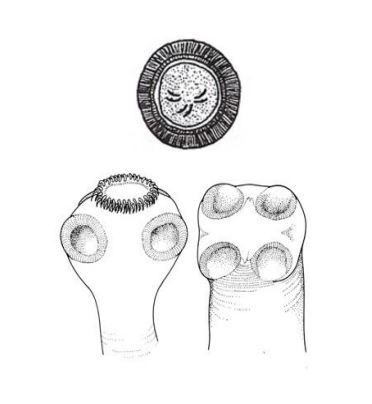
Taenia spp.
• Many species can potentially infect primates (2 major species in humans)
T. solium (pork)-larval stage (cysticercus) in pigs
T. saginata (beef)-larval stage (cysticercus) in cattle
• Cannot be distinguished by morphology of ova
• Number of uterine branches of gravid segments may be helpful in speciation
• Infection by larval Taenia causes Cysticercosis which can infect muscle, brain, eye and other tissues
• T. solium adult can be fatal due to autoinfection

Hymenolepis spp.
•Hymenolepis (Rodentolepis) nana
•Size: 40-65µm
•Hymenolepis diminuta
•Size: 60-90µm
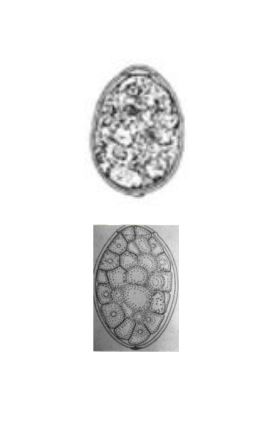
Diphyllobothrium spp. / Spirometra spp.
• Normal tapeworm of fish eating carnivores
• Similar morphology
• Life cycle differs in second intermediate host
• Size: 60x40µm
• Relatively harmless adult worm but may cause Vitamin B12 anemia
• Ingestion of infected 1st intermediate host can cause more serious disease
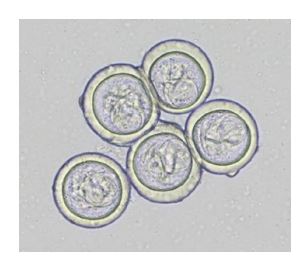
Bertiella spp.
• Related to Moniezia and Anoplocephala
• Parasite of Old World Primates • Proglottids resemble a piece of elastic band
• Size: 45-50µm
• Clear, colorless capsule containing oily droplets
• Pyriform apparatus with 2 “horns”
• Oribatid mites (soil mites) are the intermediate hosts