Physical Oceanography Exam 2
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Ocean Currents - Description
Objective
3D picture of the movement of ocean water
Ocean Currents - Description
Things to think about
Timer interval
What can we measure directly?
Ocean Currents - Description
Problems
Constantly change
Limited number of test instruments and personnel
Cannot get simultaneous image of entire ocean
Measuring Currents
Lagrangian
Move with current
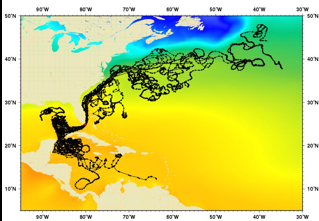
Measuring Currents
Eulerian
Stationary
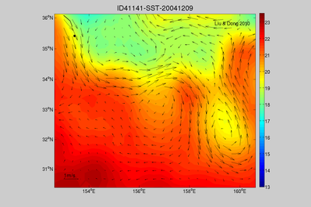
Examples of Lagrangian devices
Displacement of a ship
Drift bottles (some are tracked, some aren’t)
ARGO (measures temp and salinity, 4,162 floats)
Tracking spills (Oil spills, dye studies, cargo spills, natural disasters, garbage patch, wrecks)
Research submarine (1969 - Ben Franklin
Disadvantages of Lagrangian devices
Ship/satellite time may be required
Wind a factor
Long-term studies
Monitoring and recovery
If not monitored - don’t know what it did between deployment and recovery
Eulerian devices
Measurment at a single depth (current meter)
Measurment at multiple depths - ADCP (Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler)
Describing Currents
Direction
Wind direction - Call it the direction it comes from (North wind coming from North)
Current Direction - Call it the direction it is moving (North current going North)
Describing Currents
Discharge
Rate or volume of water per unit time
Sverdrup = 1,000,000 cubic meters per second
Describing Currents
Speed
Can use many different measurements
Knots (old measurement to measure ship _____)
Features of all surface currents
Horizontal
Driven by wind
Slow - current is 3% of the wind speed
Shallow
Role of currents in heat budget
Warm water goes from equator to the poles
Cold water from the poles goes to the equator
Winds 2/3, currents 1/3 of head distribution
Noth Atlantic surface currents
N. Equator current
N. Atlantic current
Gulf stream (western boundary)
Canary current (easter boundary)
Equatorial counter current
Norway current
Labrador current
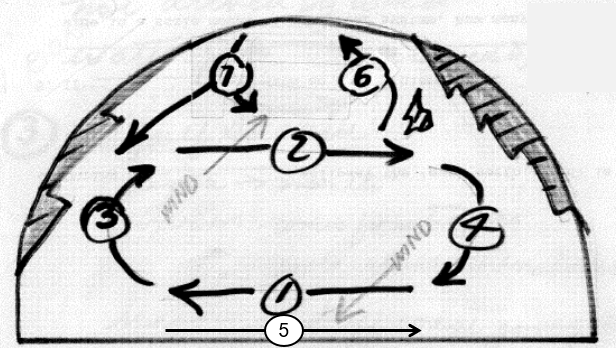
South Atlantic surface currents
S. Equatorial current
Westwind drift
Brazil current (western boundary)
Benguela current (eastern current)
Equatorial counter current
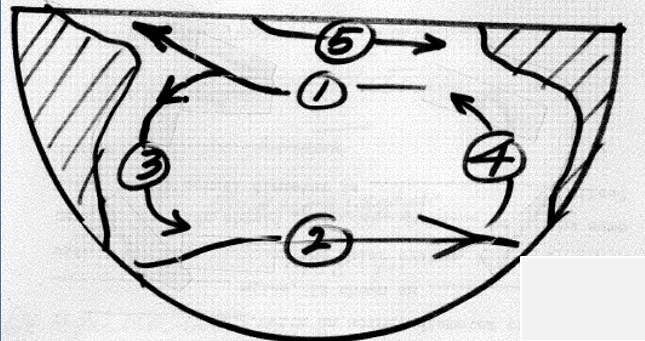
Western
Warm
Narrow
Fast
Deep
Easter
Cold
Wide
Slow
Shallow
Conditions in center of North Atlantic Gyre
Climate
Salinity
Water temperature
Nutrient content
Dissolved oxygen
Sargasso Sea
No shoreline
Biological “desert”
Sargassum
Water color
North Atlantic Garbage Patch
Importance of Gulf Stream
Earth’s heat budget
Climate on land
Weather - hurricanes
Sailors
Power generation
Dead Zones
Natural dead zones'
Made dead zones
Dead zones getting bigger
Dead Zone: A place with little to no oxygen
Seasonal issue
Gulf of Mexico hypoxic zone
Huge portion of the US drains into the Gulf of Mexico
Drains from the Mississippi river
Happens in the spring
Buffer zones decrease nutrient drainage and yield better crops
Pacific Ocean
N. equatorial current
N. Pacific current
Kuroshio current “black tide”
California current
Alaska current
Oyashio current
Equatorial counter current
S. equatorial current
West wind drift
East Australian current
Humbold current / Peru current (collapses when El Nino occurs)
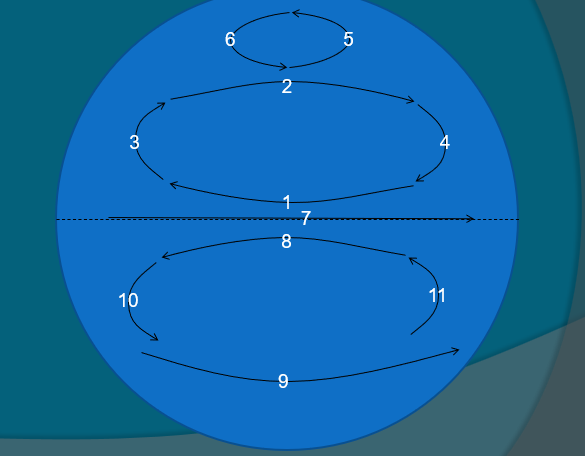
Indian Ocean
N Equatorial current
Equatorial counter current
S. Equatorial current
West wind drift
Agulahs current
W. Australian current
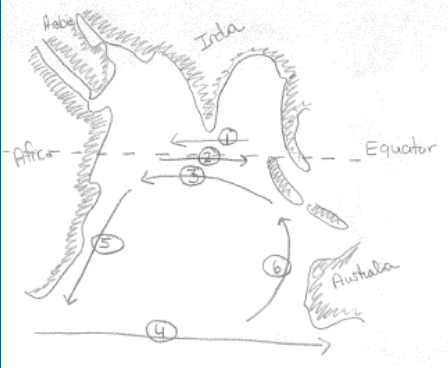
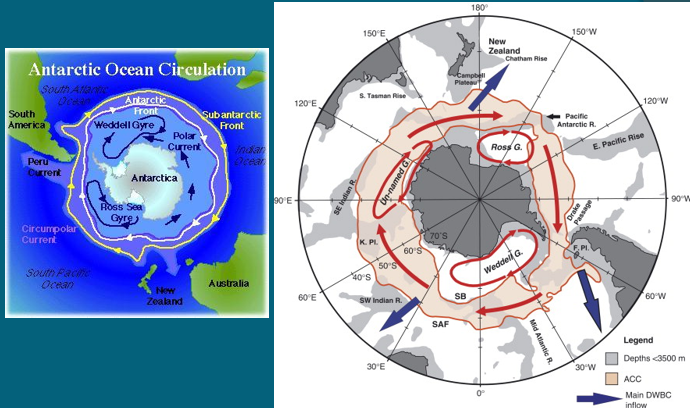
Around the South Pole
Ross G
Weddell G
Un-named G
Polar current
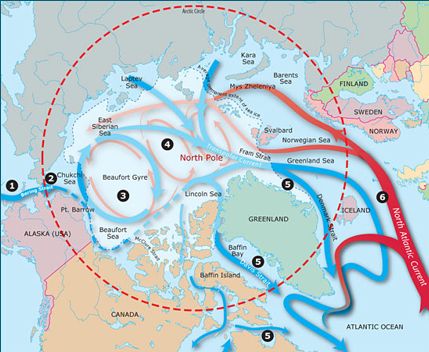
Currents around the Arttic Ocean
3 Beufort Gyre
6 North Atlantic Current
(cooked)
Currents in Seas
Type 1
Going in and out of marginal sea
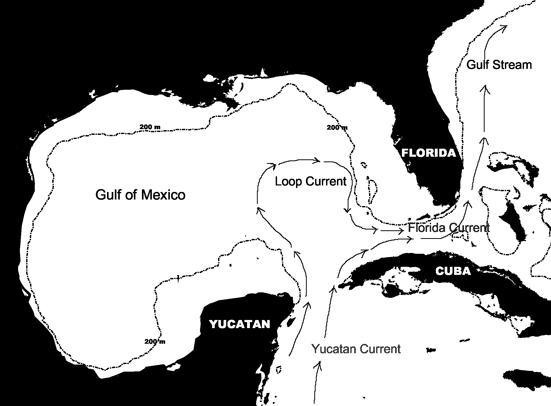
Currents in Seas
Type 2
Surface flow in, deep water coming out
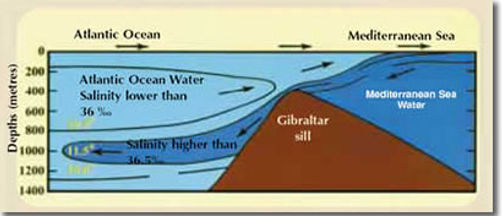
Currents in Seas
Type 3
Surface flow out only, well circulated
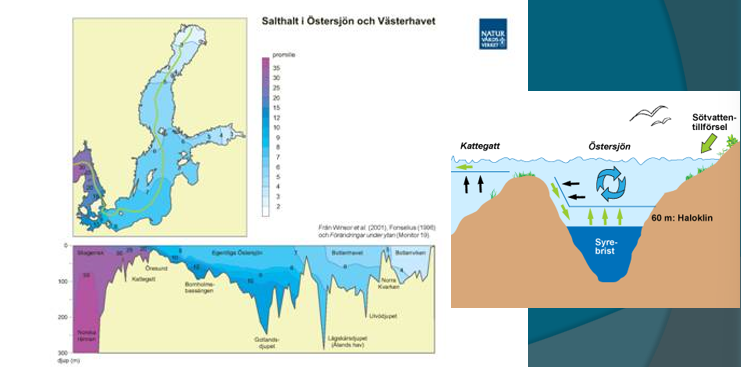
Currents in Seas
Type 4
Surface flow out only, stagnant
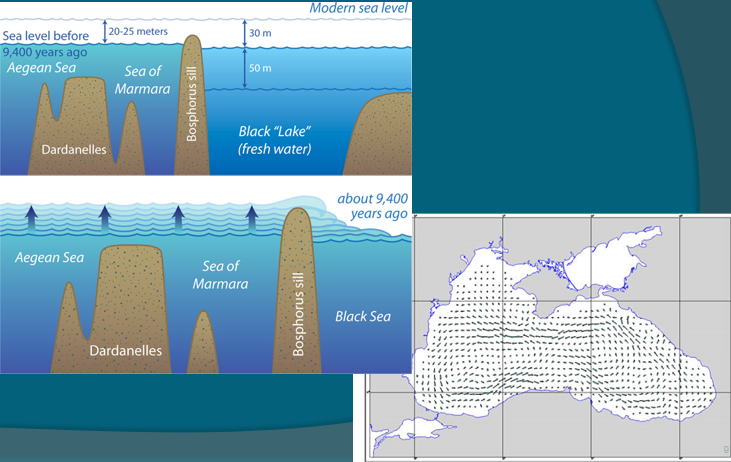
Features of all deep-water currents
Formed by vertical movement of water downwards
General pattern of flow
Slow speed
Coriolis effect
Earth’s heat budget (5,100 yrs to get from pole to pole)
Measurment devices for deep-sea currents
Drogues (flow with weight)
Ben Franklin (submarine)
Man made material (-H³ - Tritium)
Transient Tracers in the Ocean (TTO)
Swallow Floats - ARGO
ADCP
Thermohaline circulation
Broecker (coined the term global warming)
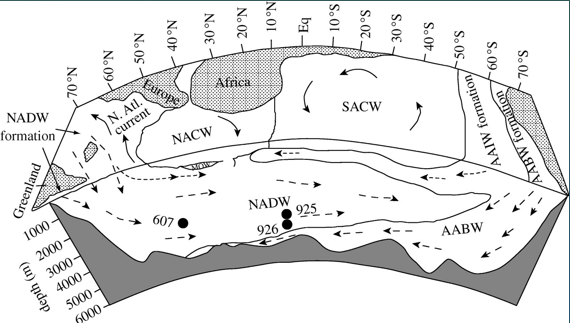
North Atlantic Deep-water (NADW)
Circumpolar Deep-water (CDW)
Antarctic Bottom water (AVBW)
Temp. constant - no sunlight
Salinity constant - no precipitation, evaporation, or land runoff
Movement driven by bottom topography
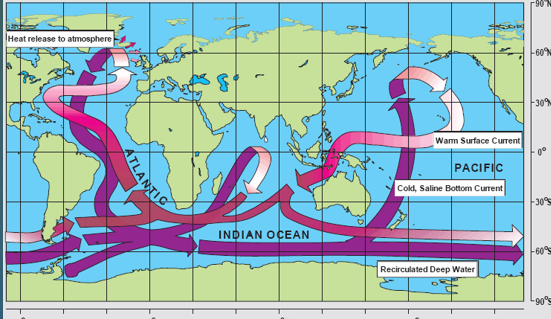
Atlantic Ocean (DEEP)
Surface waters - North Atlantic Central Water, South Atlantic Central Water.
Intermediate waters - Antarctic Intermediate Water, Mediterranean Intermediate Water
Deep waters - North Atlantic Deep Water, Antarctic Bottom Water
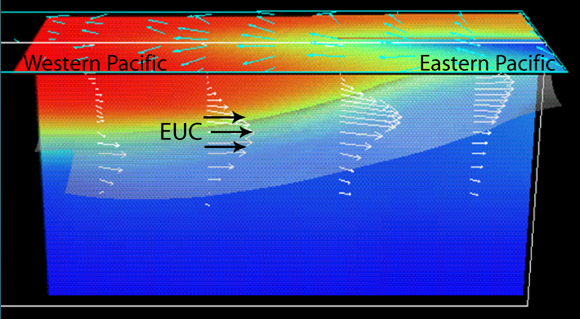
Cromwell Current
Pacific at equator
30,000,000 cm³ per second - 1.5 m per second
13,000 km long, 300 km wide
View photo
Nonrenewable
Energy from material that takes a long period of time to replace
Renewable
Energy from material that can be replaced in a short period of time
General principles (energy)
Need it to be dependable and of enough energy to get net energy
Fan-like turbine
Need to anchor to the bottom
Need to be well below the surface
Advantages
Continuous source of energy
Inexpensive to run
Doesn’t use valuable coastal land
Not an eye sore
Should be pollution free
Portable
Disadvantages
Navigational hazard for submarines
Interaction with marine life
Storm damage
Corrosion of metal parts '
Mooring
Cost
Environmental degradation
Steps in considering
High energy current
Energy input vs output
Consistency of energy
Impacts on organisms
Impacts on water quality
Cost of Maintenace