BIOCHEM 501 Exam 3 MASTERY : All Actual Exams with Expert-Verified Q&A on Metabolic Pathways, Enzyme Kinetics & Molecular Biology (Latest Updates)
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
Gibbs free energy does NOT provide information about
the rate of a reaction
Which molecule has a larger Gibbs than ATP?
PEP
Why is pyruvate converted to ethanol?
NAD+ must be replenished for glycolysis to continue
Which molecule provides the most energy if completely oxidized to CO2 and H2O?
ethanol
How many moles of acetyl-CoA are formed when one mole of glucose proceeds through glycolysis and then the PDC?
2
What is the path through which electrons travel in the PDH complex?
pyruvate -> Lipoic acid -> FADH2 -> NADH
How many steps of the CAC are oxidation reactions?
4
How many molecules of each (CO2, NADH, FADH2) are formed by one turn of the CAC?
2 CO2, 3 NADH, 1 FADH2
Oxidizing the acetate of acetyl-CoA in the CAC does NOT result in a net increase in
malate
If a person was not able to make normal levels of carnitine, which of the following metabolic processes would be most affected?
Fatty acid oxidation
Which compounds are involved in the production of urea via the CAC?
aspartate, ATP, and Carbamoyl Phosphate
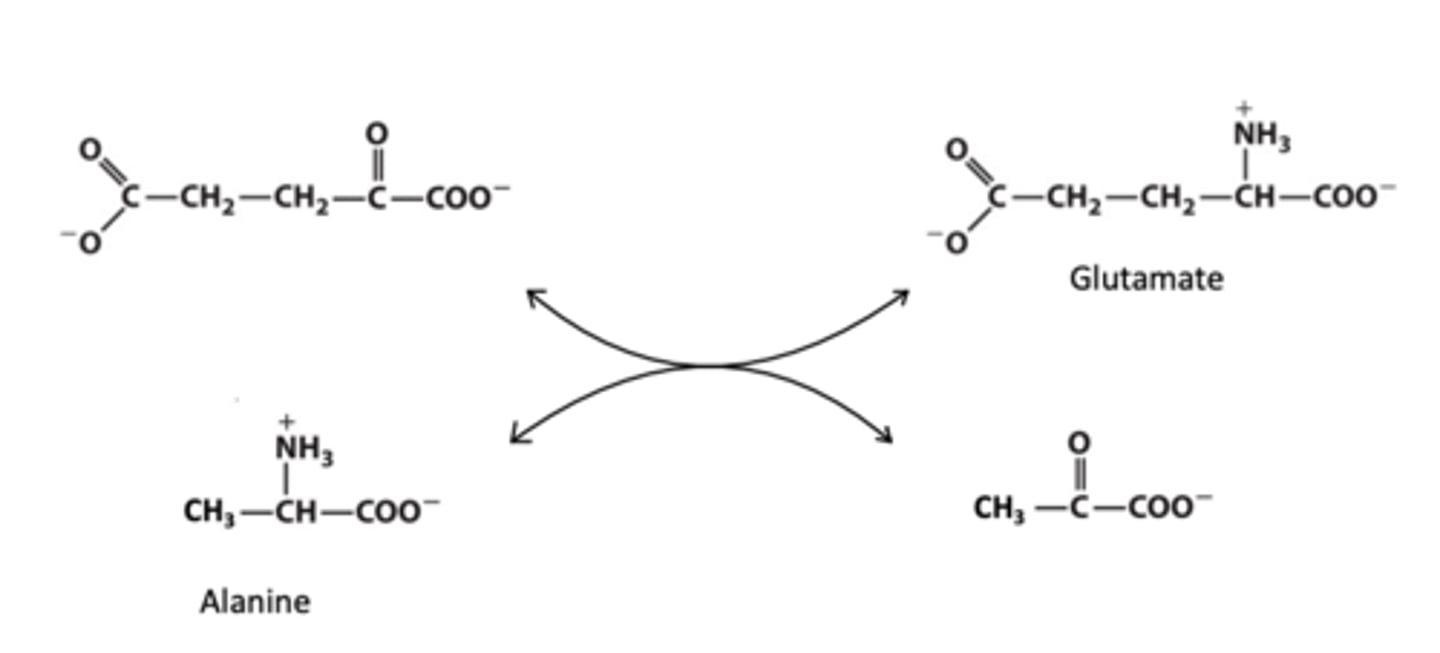
This reaction is a _____ reaction, where the amino acid ___ is ____ to form _____
transamination; alanine; deaminated; pyruvate
PDC regualtors
inhibited by ATP, promoted by AMP
The final acceptor of e- transport in your mitochondria is
O2
Complex 2 does not do what
pump protons
If DNP is added, what will continue to be consumed?
O2
ATP needs the proton gradient to
release bound ATP from the active site of the enzyme
In the light reactions of photosynthesis, light energy is converted into chemical energy, which of the following molecules contain chemical energy derived from light reactions?
ATP and NADPH
What becomes reduced in the reverse steps of glycolysis?
3-phospjhoglycerate
Although the standard free energy of the reaction which forms G3P is positive, why is the reaction product favored?
The subsequent steps of glycolysis keep the cellular concentration of the product G3P low relative to the levels of reactants
Which of the following statements about phosphofructokinase is NOT correct?
ADP inhibits phosphofructokinase activity
The path that is the most regulated
path with most negative Gibbs free energy value
the conversion of pyruvate to lactate, a type of fermentation, permits glycolysis to continue in anaerobic conditions because it regenerates
NAD+
Two molecules of ethanol have a higher energy density than one glucose because
glucose has a higher percentage of oxidized bonds (such as C-OH) than ethanol
In the CAC, some of the energy of the resulting from oxidation of the C-C and C-H bonds of acetyl-CoA is preserved in what two molecules
NADH and FADH2
PDC and alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex
both catalyze the oxidation of a substrate, some of the energy of a substrate oxidation is preserved in a thioester bond to coenzyme A
What occurs in the mitochondria?
CAC, reduction of O2 to H2O, fatty acid oxidation
Where does glycolysis occur?
cytosol
How many molecules of CO2 are produced in one turn of the CAC?
2
Which of the following enzymes of the CAC does not catalyze the oxidation of a CAC intermediate?
citrate synthase
Complete B-oxidation of a 14:0 fatty acid results in
7 Acetyl-CoA, 6 NADH, and 6 FADH2
In the series of reactions that result in formation of urea from ammonia and aspartate, the energy of ATP is used to
create a high energy intermediate from bicarbonate so that adding ammonia to bicarbonate is a favorable reaction
what is hydration
the addition of water across a double bond
Which two molecules inhibit the CAC
ATP and NADH
Complex ___ obtains e- from __ and reduces __ to __
NADH, ubiquinone, ubiquinol
Which is not correct regarding coenzyme Q?
used to move electrons from complex III to complex IV
DNP would NOT cause this to happen
oxygen consumption decrease
In the light reactions of photosynthesis, the energy of light is converted into chemical energy in the form of
NADH and ATP
In photosynthesis, the source of electrons that flow through the e- carriers in the chloroplast membrane is
H2O
In eukaryotic plant cells, some of the light energy that the chloroplast captures is transported out of chloroplast into the cytosol as chemical energy in the form of
dihydroxyacetone
If the standard free energy change of C-> C is large and positive, which of the following could result in the conversion of C to D in a cell?
Couple the reaction to ATP hydrolysis
One molecule of glucose goes through glycolysis to form two molecules of pyruvate
2 molecules of NADH are formed, and there is a net gain of 2 ATP
What is a characteristic of the three irreversible, regulated steps in glycolysis?
they have large and negative delta G naught values
Phosphofructokinase is an enzyme of glycolysis. What type of reaction does the phosphofructokinase catalyze?
phosphorylation
When bacteria ferment milk into yogurt under anaerobic condition, pyruvate is converted to lactate because
this enables the NAD+ to be replenished so that glycolysis can continue
What is the order of molecules that when completely oxidized in a cell would produce the least -> most energy?
lactate, pyruvate, glucose, ethanol
what type of reaction does E1 catalyze and what molecule is it associated with?
decarboxylation, thiamine
what type of reaction does E2 catalyze and what molecule is it associated with?
oxidation, lipoic acid
what type of reaction does E3 catalyze and what molecule is it associated with?
electron transfer, FAD
In the CAC, how many steps involve enzymes that catalyze dehydrogenase reactions?
4
What is not accomplished by the CAC?
Substrate level phosphorylation of NADH to regenerate citric acid
Why is the conversion of malate to oxaloacetate favorable when operating in the citric acid cycle?
the concentration of oxaloacetate is extremely low relative to malate
What is decarboxylation
loss of a CO2 group
Carnitine
essential for transport of fatty acids across the mitochondrial membrane
Citrate synthase and isocitrate dehydrogenase are inhibited by
ATP and NADH
In the conversion of an 8-carbon saturated fatty acid to CO2 via the -oxidation pathway AND the citric cycle:
How many molecules of acetyl-CoA would be formed from the fatty acid?
4
In the conversion of an 8-carbon saturated fatty acid to CO2 via the -oxidation pathway AND the citric cycle:
How many molecules of NAD+ would be reduced to NADH?
15
What is the process of urea production?
glutamate combines with ammonia to form glutamine, and glutamine travels to the liver through the bloodstream
Urea synthesis takes place in the
liver
If DNP used, the rate of NADH oxidation will
increase
If DNP used, the rate at which the citric acid cycle is operating will
increase
Which complex is NOT required for electrons to flow from NADH to O2 in mitochondrial electron transport?
Complex II
If pyruvate, lactate, NAD+, and NADH were mixed under standard equilibrium conditions, what would be free energy change if the system were to reach equilibrium?
-20 kJ/mol (need to use the equations provided on the exam formula sheet)
Which process generates the most reactive oxygen species and may contribute to aging?
mitochondrial electron transport
Release of ATP from ATP synthase requires what?
a proton gradient
True or False: ATP synthase can catalyze the hydrolysis and synthesis of ATP
True
What occurs in the Calvin cycle?
Acetyl-CoA provides the reducing power to convert CO2 into triose sugars
The combustion of paper to form CO2 and H2o releases heat because
products have more stable chemical bonds than the reactants
Keq > 1
more products at equilibrium and negative Gibbs free energy
The reaction A -> B has a standard free energy change of +11 kJ/mol, the formation of B is coupled to the conversion of C -> D. What must the Gibbs standard free energy change be?
less than -11 kJ/mol
What is one characteristic of the preparatory steps of glycolysis?
ATP is consumed
Which compound has an unfavorable donation of a phosphate to ADP to form ATP under standard conditions? (substrate-level phosphorylation)
glucose-6-phosphate
When yeast are grown anaerobically the amount of glucose consumed per amount growth is much lighter then during aerobic growth because:
the yield of ATP per glucose is much higher in aerobic than in anaerobic conditions
During the fermentation of glucose to ethanol in yeast, pyruvate is converted to ethanol because:
NAD + must be replenished for glycolysis to continue
How many steps of the citric acid cycle produce CO2?
2
How many steps of the citric acid cycle are oxidation reactions?
4
Why is the reaction by which malate is converted to oxaloacetate in the CAC positive and unfavorable for standard free energy change?
The conversion of malate to oxaloacetate is coupled to the reduction of NAD+
What enzymatic activity would be decreased by thiamine deficiency?
pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
How many cycles of β-oxidation are required to completely convert an 18 carbon fatty acid into acetyl-CoA?
8
Which type of molecule (if they all have the same number of carbons) will make the most Acetyl-CoA?
the fatty acid
How is it possible that the E3 subunits are identical in pyruvate dehydrogenase and alpha-ketoglutarate?
The E3 subunits do not interact with pyruvate or α-ketoglutarate, and the reactions that the E3 subunits catalyze have identical substrates and products in both complexes.
Almost all of your energy is derived from
the conversion of C-H and C-C bonds into H2O and CO2
What does an aminotransferase do?
catalyzes the transfer of an amino group from an amino acid to a keto acid (glutamate + oxaloacetate → α-ketoglutarate + aspartate)
The conversion of arginine to ornithine is a step in the synthesis of
urea
What is true of ATP and NADH regarding the regulation of citrate synthase?
NADH and ATP inhibit enzyme activity
Why do electrons transferred to the electron transport chain from FADH2 make fewer ATPs than electrons that are transferred to complex I from NADH
FADH2 enters the electron transport chain at complex II, which does not pump protons
E naught values are proportional to
how likely the reactant is to be reduced (the more negative E naught values are harder to gain electrons)
What does DNP do?
increases the rate of NADH oxidation and can decrease ATP production
Ubiquinone
soluble electron transporter in the electron transport chain that connects the first or second complex to the third
In light reactions of photosynthesis, light energy is used to
dissociate water into O2, protons, and high energy electrons
RNA enzymes were present before protein enzymes
True