Chemistry- Unit 1
Unit 1.1
Household Product Safety(HHPS)
Types of frames used around the symbols are
- Inverted Triangle- It means that the container is dangerous
- Octagon- It means the product inside the container is dangerous
Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System (WHMIS)
| Pictograms | Name | The danger |
|---|---|---|
 | Exploding Bomb | Explosives, Self- reactives, Organic Peroxides |
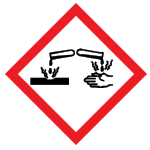 | Corrosion | Skin corrosion/burns, Eye damage, Corrosive to metals |
 | Flame Over Circle | Oxidizing gases, liquids and solids |
 | Gas Cylinder | Gases under pressure |
 | Enviroment | Aquantic toxicity |
 | Skull & Crossbones | Acute toxicity(fatal or toxic) |
 | Exclamation Mark | Irritant(eye & skin), Skin sensitizer, Acute toxicity,Narcotic effects, Respiratory tract irritant, Hazardous to ozone layer(non-mandatory). |
 | Health Hazard | Carcinogen, Mutagenicity, Reproductive toxicity, Respiratory sensitizer, Target organ toxicity, Aspiration toxicity. |
 | Flame | Flamemables,Pyrophorics,Self-heating, Emits-flammable gas, Self reactives, Organic peroxides. |
Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) identifies the ==specific== chemical and physical hazards associated with the product.
Properties and Classification of Matter
Properties: describe the physical appearance and composition of a substance
==Physical== Properties include:
- Boiling or condensation point
- Melting or freezing point
- Malleability(capable of being altered or controlled by outside forces or influences.)
- Ductility(the ability of a material to be drawn or plastically deformed without fracture)
- Color, state, and solubility
- Crystal formation
- Electrical conductivity and magnetism
==Chemical== Properties describe how reactive a substance is
Chemical properties include:
- Ability to burn and flash point
- Behavior in air
- Reactions with water, acids, heat and litmus
Pure Substances and Mixtures
- Pure substances- All substances that make up the substance are identical, so its chemical and physical are constant. (element of compound)
- Element- Pure substance that @@cannot@@ be broken down into an other substances
- Compound- chemical combination of two or more elements in a specific ratio.
- Mixtures- Combination of two or more pure substances
- Hetereogenous Mixtures (different):
- Mechanical Mixtures- different substances are visible
- Suspentions- Where componets are in different states
- Colloids- Suspended substances cannot be easily seperated
- Homogenous mixture(same throughout):
- Solutions- seperate compounds are not visible;one substance is dissolved in another.
Chemical Reactions
Two important features of a chemical reaction are:
- New substances with new physical and chemical properties are formed
- Energy flows into or out of the system during a reaction.
To indicate a chemical change 2 or more of the following should occur:
- Heat or light is produced or absorbed
- the starting material is used up, or a new substance is produced
- There is a change in color
- A percipitate( solid) or bubbles(gas) formed in the liquid
- The change is difficult to reverse
- New odour forms
Atomic Models
Greek Theory- Proposed that matter could be composed of small, indivisble particles
John Dalton (Billiard Ball Theory)-
- He rediscovered the atomic concept of matter
- States the law of multiple proportions
- When 2 or more elements form a series of Compounds form a fixed mass that have interger ratios of each other
- Ex. Methane:CH4, has a 1:4 ratio of carbon:hydrogen
- To behave in this manner atoms need to be formed
JJ Thompson (Plum Pudding or Raising Bun Model)-
- Most famous for discovering the electron
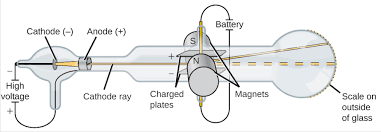
- Thompson worked with a Cathode Ray Tubes(CRTs) .
- Cathode ray tubes showed that all atoms contain tiny negatively charged subatomic particles or electrons.
- Thomson proposed the plum pudding model of the atom, which had negatively-charged electrons embedded within a positively-charged "soup."
Rutherford (Planetary model)-
- Rutherford fixed the problem in Thompson’s model
- Rutherford designed an eperiment that helped fix the problem called the scattering experiment.
- Alpha particles were expected to pass through the thin gold foil with little scattering.
- Rutherford assumed that the alphas were interacting electrositcally with solid centers of the atom.
- He discovered the nucleus with protons and neutrons.
Niels Bohr (Bohr Model)-
- Bohr modified Rutherfors’s theory
- He observed that electrons don’t orbit the nucleus but they exist with diffrent energy levels.
Schroedinger ( Electron Cloud or Quantum Mechanical Model)-
- An elvolving model but currently thought of as a cloud of negative charges.