Age of Exploration
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Diffusion
The process by which elements of culture such as beliefs practices, technologies, ideas, languages, and customs, spread from one group or society to another
Indigenous
Original native inhabitants of a country region
Colonization
The action or process of settling among an establishing control over the indigenous people of an area
Circumnavigate
To travel completely around the Earth by water
Missionary
Someone sent to do religious work in a territory or foreign country
Persecute
Cruel and unfair, mistreatment of individuals and groups, most often for the religious beliefs, ethnic background or political opinions
Sultan
Muslim leader/monarch
Sphere of influence
Area in which an outside power claims exclusive investment or trading privileges
Mercantilism
Policy by which a nation sought to export, more than it imported in order to build a supply of gold and silver
Isolationism
The policy of a nation, deliberately avoids involvement in foreign affairs, particularly alliances and conflicts to focus on its own domestic interest and self-sufficiency
Christopher Columbus
Sailed the ocean blue technically he’s Italian but sailed for Spain because they funded his trips. Was trying to find a route to India, but got blown off course and ended up finding the New World lands in the Bahamas then further explore to find the mainland with America. Open the floodgate up to European explorers coming to America and lead to colonization of the Americas
Francis Drake
An English man from England closely associated with the queen Elizabeth the first and served as her second and command during the battle with the Spanish armada. Was second person to circumnavigate the world from 1577 to 1580
Vasco Da Gama
Portuguese explore first to make trip on Africa all the way to India landed there in 1498. Found an important trade route from Europe to India and east India too. Begin annual voyages from Portugal to India ocean region. One voyage was blown off course and ended up claiming Brazil for the Portuguese
Francisco Pizarro
Spanish conquer between 1509 and 1541. Explored many regions of what today central and South America. Eventually fought and defeated the Ican empire, which is modern Day Peru
Ottomans
emerged as a political and economic power after the conquest of Constantinople. Developed an Asia minor. Expanded by conquering territories in Southwest Asia, Balkan Peninsula, and North Africa. Became one of the largest empires in history. It became too big to control and there was corruption and a strained economy. After it fell now it is modern day turkey
Ferdinand Magellan
From Spain. His crew made first around the world (circumnavigated the globe) from 1519 to 1522 proved for certain that the world was round and was killed in the Philippines. Didn’t make it home but still gets credit for getting all the way around the world since his crew finished the expedition. Named the strait of Magellan after him.
Hernando Cortez
Spanish explorer from 1519 to 1541. Most famously known for leading a Spanish expedition in the Americas that led to the downfall of the Aztec empire. Aztecs had developed what is today Mexico. Conquered and ended this empire in 1525.
Jacques Cartier
From France. Explored the northern regions of the Americas looking for the Northwest passage. Northern route from the Atlantic to Pacific. eventually claimed Canada for the French. Also would later map much of the St. Lawrence River region
Prince Henry the Navigator
Portuguese Royal Prince, who sponsored many trips along West Coast of Africa, which led to the age of discovery and start of the transatlantic slave trade. He established Portugal early colonial holdings in the Atlantic of the Madeira and Azores islands
Mughals
Developed in northern India descendants of the Mongols. Established a big empire based on spreading Islam throughout India. Mughals and Ottomans were very competitive with each other. Treated with Europeans a lot on silk Road. Well known for southern India trading they traded silk spices gems, and remained independent, even when the British came. Mughals calls big influences on our architecture of this time and built Taj Mahal. Hindu and Muslim conflict in British conquered which tore their empire apart.
When and where did the age of exploration begin?
Begin in Europe, led by the Portugal and the early 15th century
Why did the age of exploration begin? Give multiple reasons
Economic motives, such as the desire for new trades and wealth from Asia and competition for resources and power
What were the ultimate outcomes/ effects of this time? Give multiple effects.
Established global trade networks, rise of European colonial empires, the collapse for indigenous people due to disease,Transatlantic slave, trays, and the Columbian exchange (exchange for crops and ideas)
What country was most dominant in the age of exploration
Spain
What role did religion play in the exploration? give two things
spreading Christianity and escaping persecution)
Describe the Colombian exchange. Give example examples of goods orienting for both the new and old worlds.
Transfer of goods and ideas between the old world (Europe, Asia, Africa) and the new world (the Americas) following Columbus’s voyage.
New World: Coco, tobacco, potatoes, tomatoes, etc.
Old World: horses, wheat, sugar, coffee, and disease
What were the effects of the Colombian exchange? Give multiple effects.
Collapse of native American population, rise of the transatlantic slave trade to meet demands, and devastation of indigenous people
describe the triangular trade. What kinds of goods oriented in the America, Europe, and Africa
Goods, raw materials, and enslaved people traded in a circular route. Europe sent manufactured goods like cloth, guns and rum to Africa and exchange for slaves, who then were shipped to America. The Americas then provided raw material like tobacco, cotton, sugar to Europe
What effect did the concept of mercantilism have an exploration and the colonies
Creating economic advantages for countries to find and claim new lands, acquire raw materials, and establish new markets, which increased national wealth and power
Where did the Ottoman Empire originate? Where did it expand? (what regions did it take over?)
Originated in northwestern Anatolia (Turkey). It expanded across three continents, including the Balkans, North Africa, in the Middle East. Key takeovers include Constantinople, which became the capital of the Byzantine empire and large areas of Greece, Hungary, Middle East, and Europe
What religion does the Ottomans practice? Were they tolerant of others?
The Ottomans were a Muslim empire govern by the Islamic law. They allowed Christians and Jews to practice their faith under a system of religious communities called millets
What were the most popular products traded from the Ottoman Empire?
Textiles, ceramics, carpets (manufactured goods). Grains, cotton, olive oil (agricultural products)
what were the causes of the decline of the Ottoman empire
Military overuse and defeats against European powers, failure to modernize economically and technologically, corruption, rise of national movement from external pressure from expanding European empires
Where did the Mughal empire develop? What religion did they practice?
Developed in the Indian subcontinent specifically in northern India, and they practiced Islam
What issue did the Mughals face when they conquered India? How did they resolve it?
How to govern in maintains stability over a vast diverse, prominently non-Muslim population. Emperor Akbar resolved this issue by implementing a policy of religious tolerance and cultural inclusion
What trade roots did the Mughals use? What items did they trade?
Silk Road and Sea roots via the Indian Ocean and bay of Begal. Traded textiles, silk, cotton, spices, gold, silver, tobacco, rice, diamonds, emeralds.
What caused the fall of the Mughal Empire? When did it end?
Weak later, rulers, dynastic warfare, external invasions, escalating, influence, and eventual control by British East India company. British Raj exiled the last emperor, Bahadur Shan II after the Indian rebellion
why did the Europeans have an interest in trade with China?
For its valuable luxury goods like silk, porcelain and tea, which commanded high prices in Europe and promised significant economic wealth
What is the name of the Mongol Dynasty in China? How long did it last?
Yuan Dynasty and it lasted for 97 years
Put dynasty restored Chinese control to the region? What were their accomplishments?
Ming Dynasty and they overthrew the Mongol led Yuan Dynasty
What government system was used in Japan prior to the age of exploration? What type of government was used in the 1600-1800s
Japan was ruled by military dictatorship known as a Shogunate which is a form of feudalism. During the 1600-1800 dominant government was the Tokugawa Shogunate
Other than slaves what else did Africa export? What did they import?
Exports: gold ivory, salt, and animal hides
Imports: textiles, metal goods, guns, and other goods
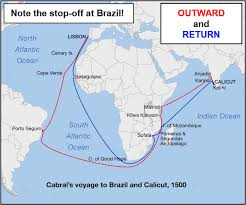
Who’s route is this?
Route of Bartholomeus Dias around Africa
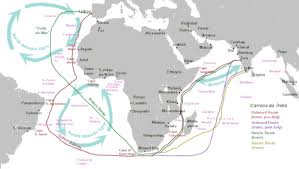
Who’s route is this?
Route of Vasco de Gama’s voyage to India
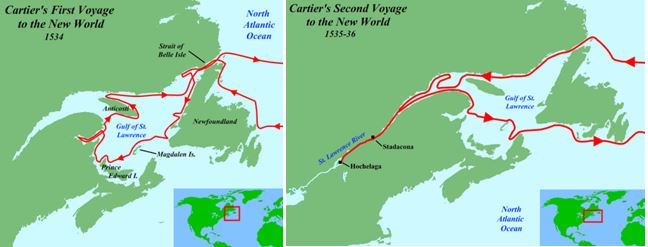
Who’s route is this
Route of Jacques Cartier to find a northwest passage
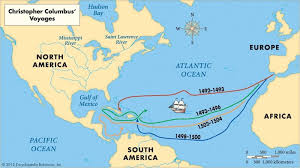
Who’s route is this
Route of Christopher Columbus to find the “New World” (America)
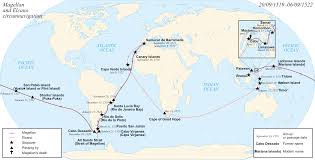
Who’s route is this
Route of Ferdinand Magellan’s voyage to circumnavigate the globe
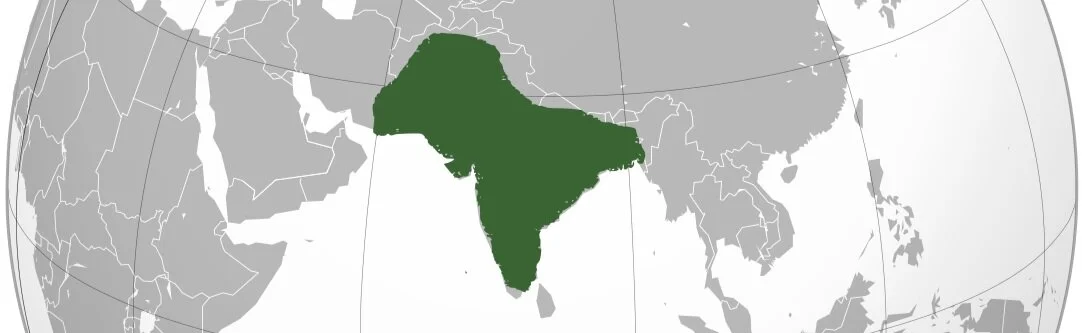
What empire is located here
Mughals
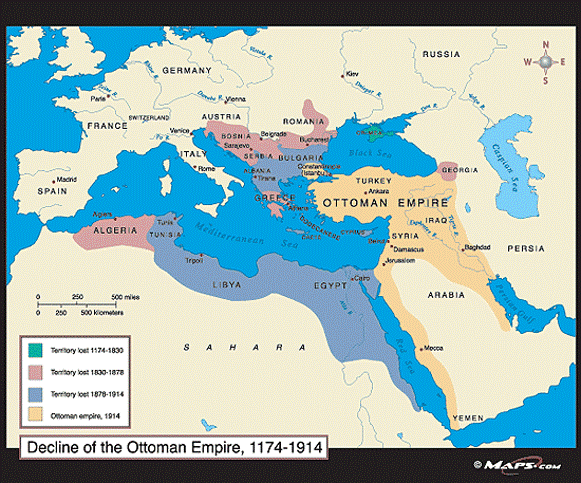
Which empire is located here
Ottoman