IMED1004 - Breastfeeding (L14, L15)
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
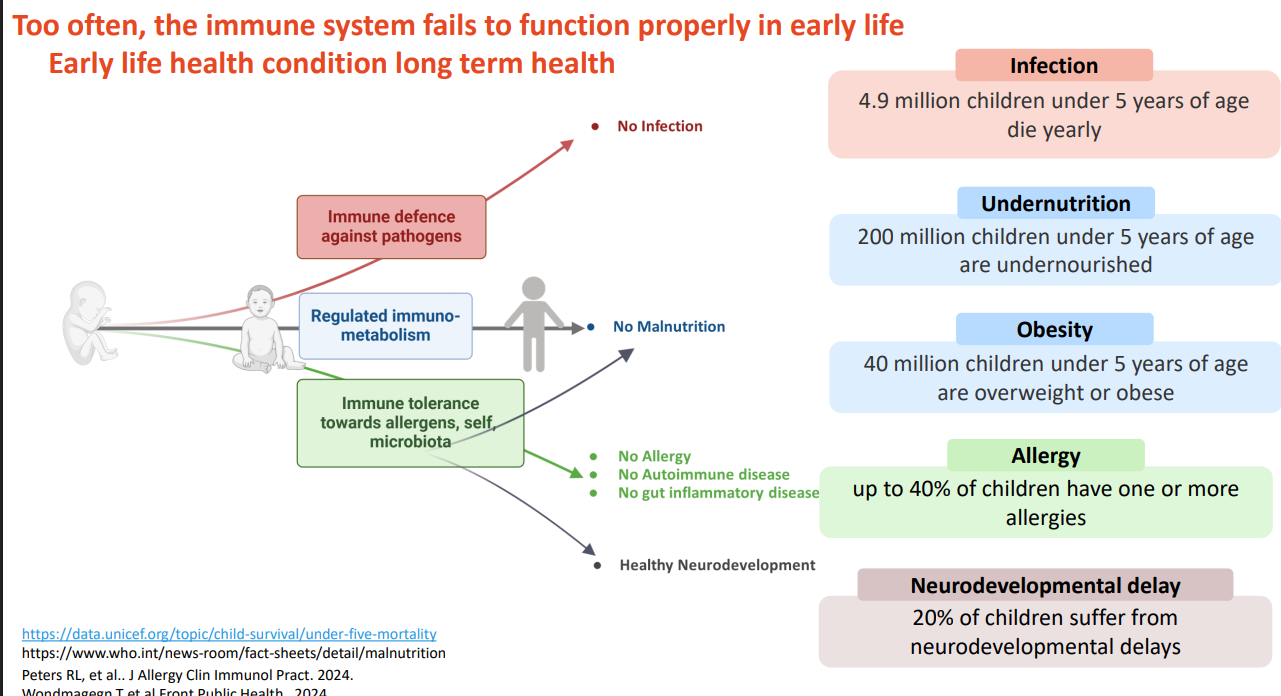
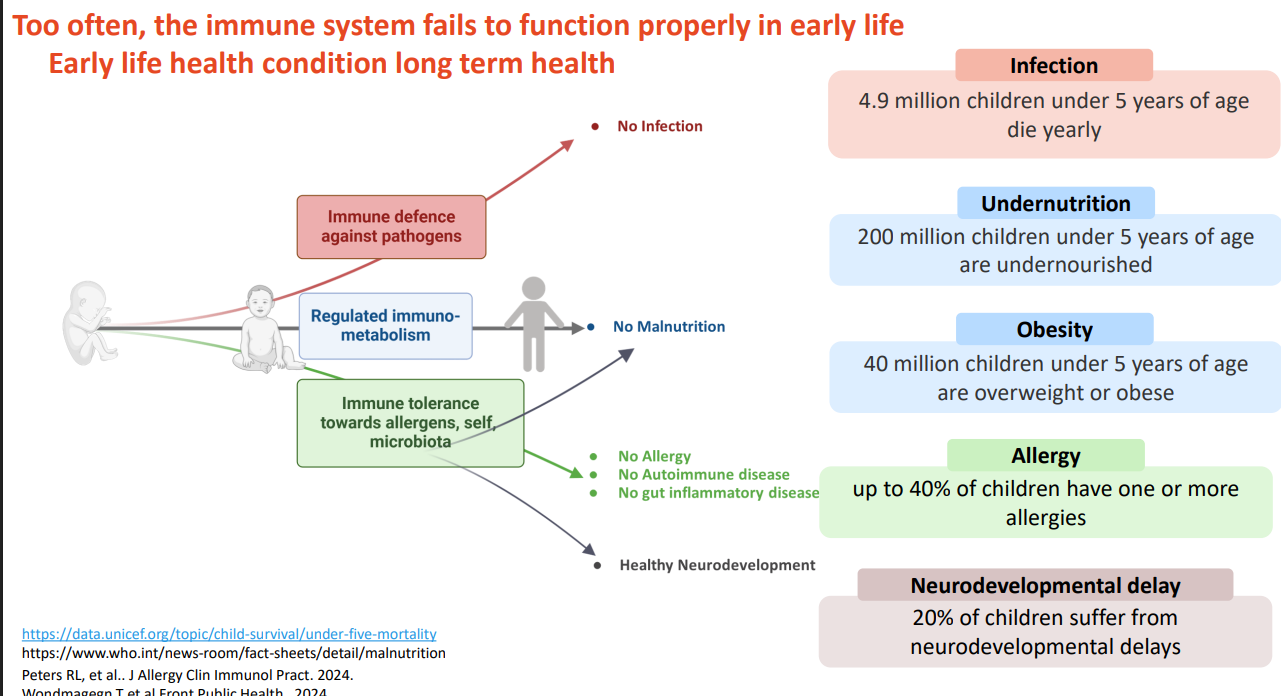
Too often, the immune system fails to function properly in early life. earth life health condition long term health
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 2
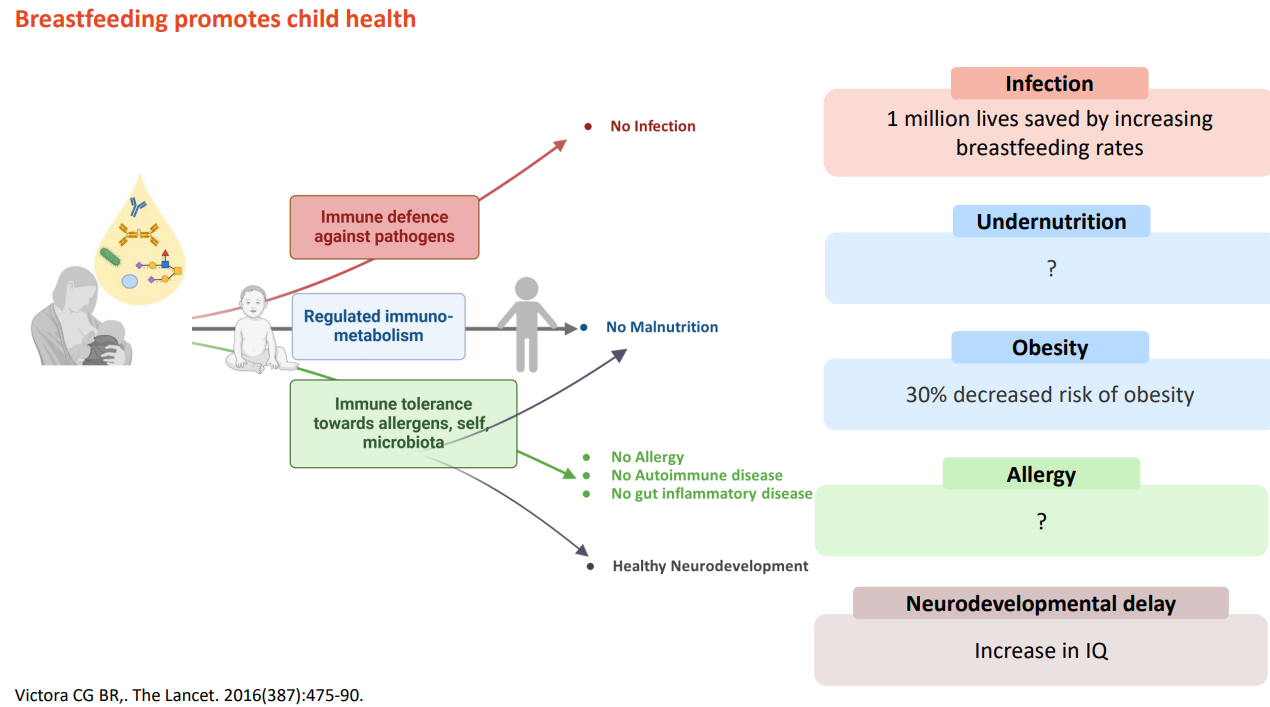
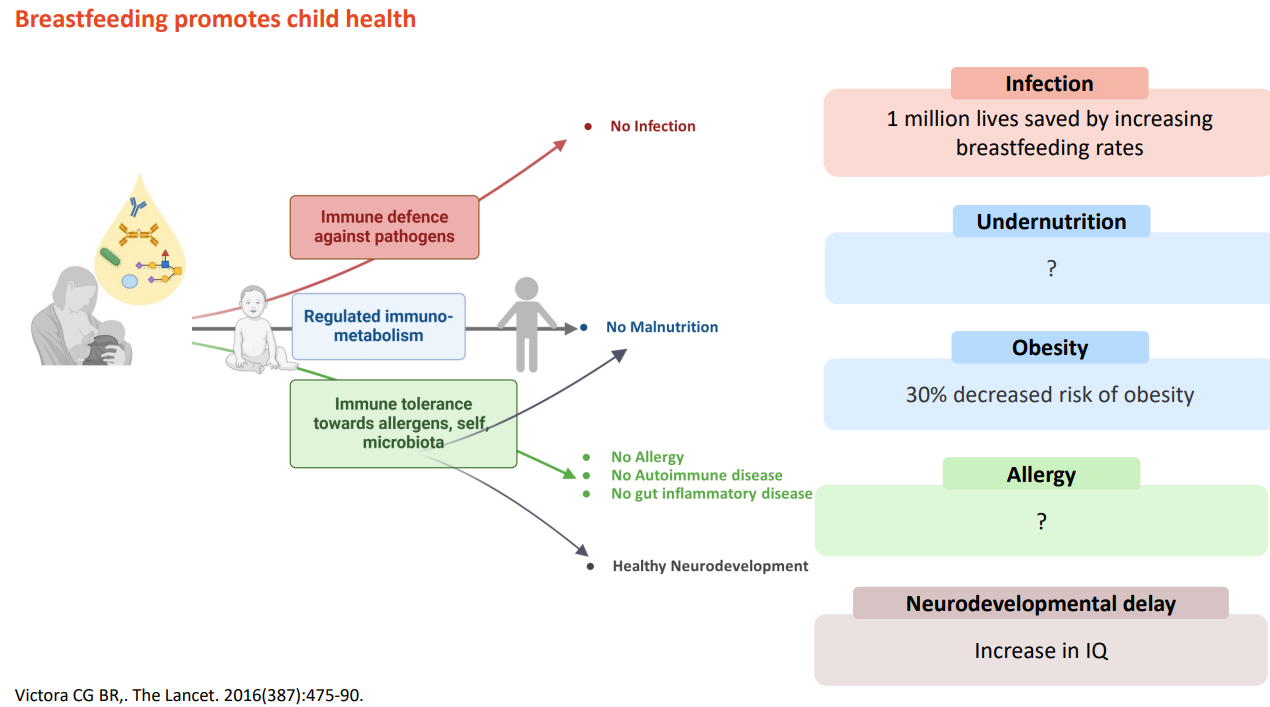
Breastfeeding promotes child health
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 4
Human milk complements the infant's immune system, lays the foundation for immune resilience and shapes its development in a personalised way
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 5
Breastfeeding protects from allergy
NOT TRUE, its a myth. no evidence supports that breastfeeding protects from allergy
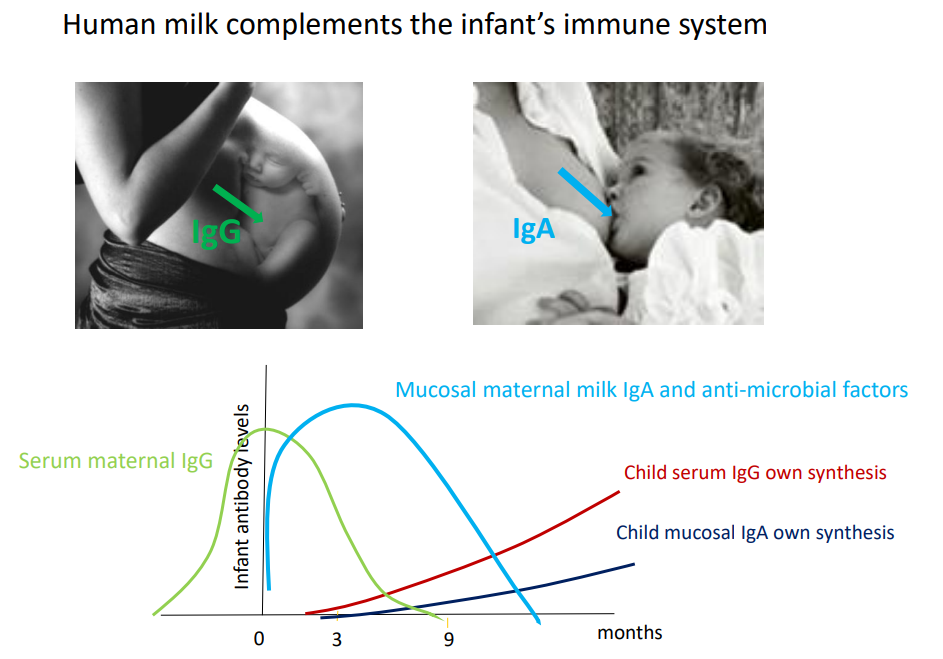
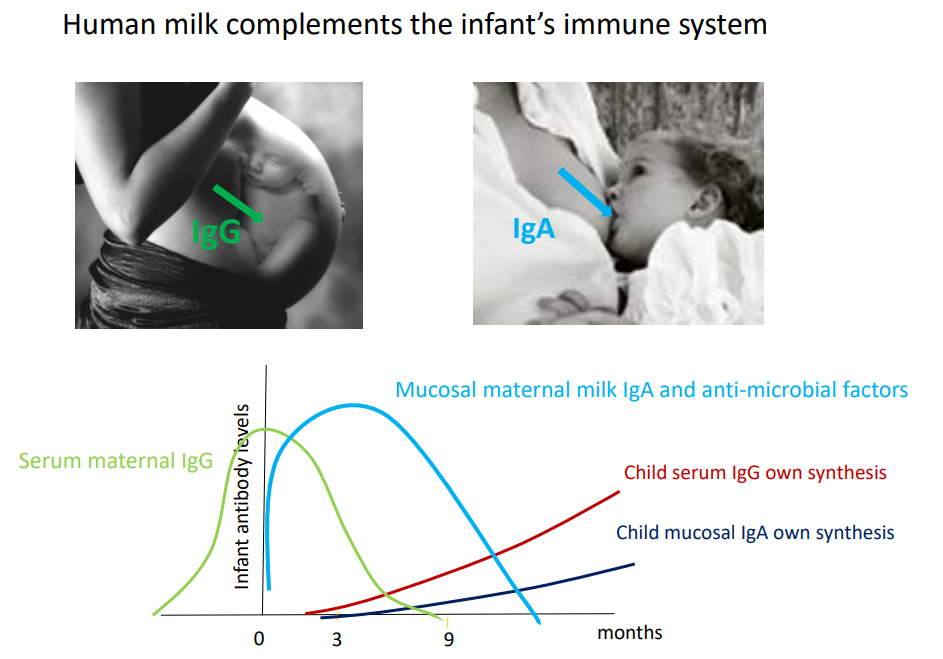
Human Milk complements the infant's immune system
- IgG given during pregnancy
- IgA given during breastfeeding
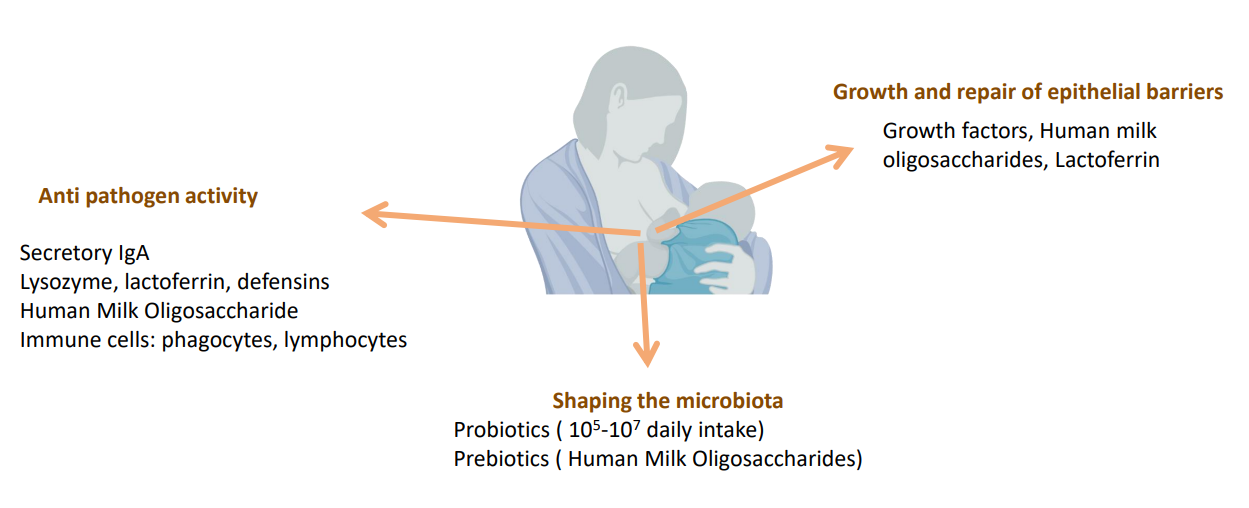
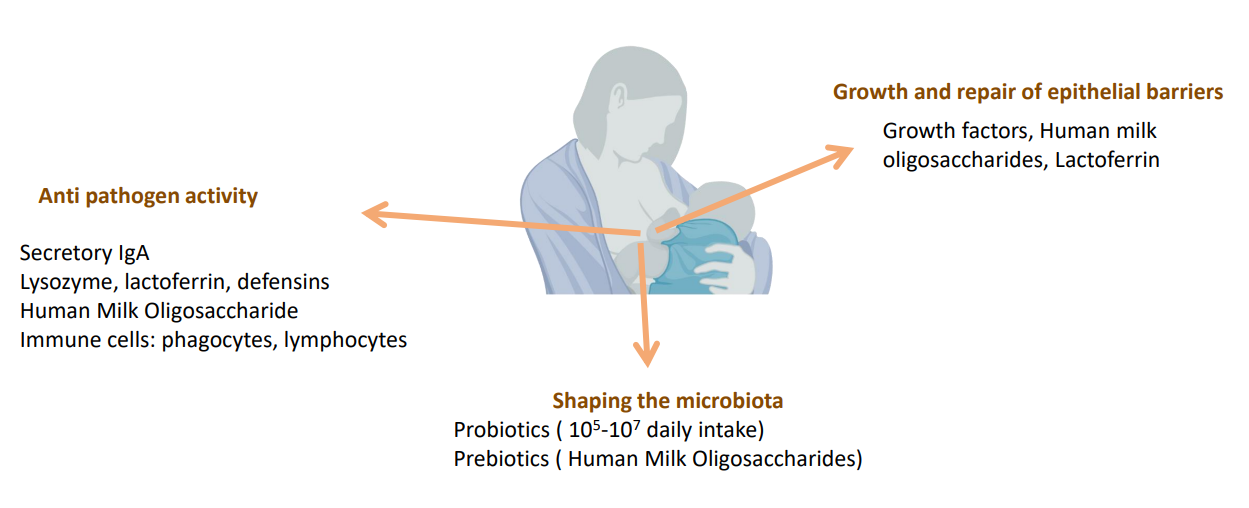
A multifaceted approach for infectious disease prevention
ANTI PATHOGEN ACTIVITY:
- Secretory IgA
- Lysozyme, Lactoferrin, defensins
- Human Milk Oligosaccharide
- Immune cells: phagocytes, lymphocytes
.
GROWTH AND REPAIR OF EPITHELIAL BARRIERS:
- Growh factors, human milk oligosaccharides, lactoferrin
.
SHAPING THE MICROBIOTA:
- Probiotics (10^5-10^7 daily intake)
- Prebiotics (Human milk oligosaccharides)
4 phases you need to know about
- Prebiotic, Probiotic, Symbiotic, Postbiotic
- pre is before the bacteria (food for good bacteria)
- probiotic is the good bacteria
- postbiotic bacteria is what a good bacteria produce (e.g short chain fatty acids)
- symbiotic is the pre and post biotic together
Human Milk (colostrum) lays the foundation for a strong and resilient immune system
- Globally, at least 1/3 newborns are not optimally colostrum, fed in WA, 1/2 newborns are not optimally colostrum fed
- colostrum is yellow because of high levels of Vitamin A
- Vitamin A is important for immune function but also epithalia development
- all this vitamin A + growth factor closes the open epithellia in an infant (since we know its epithelia is open)
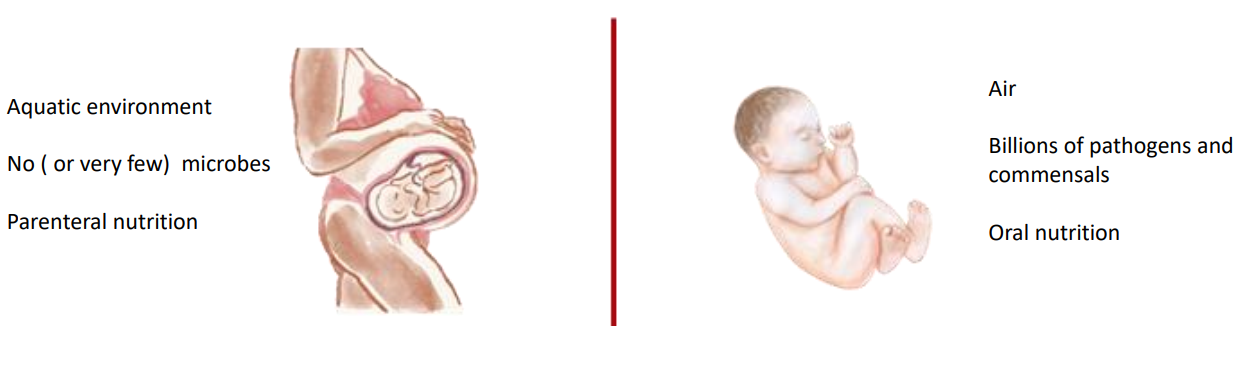
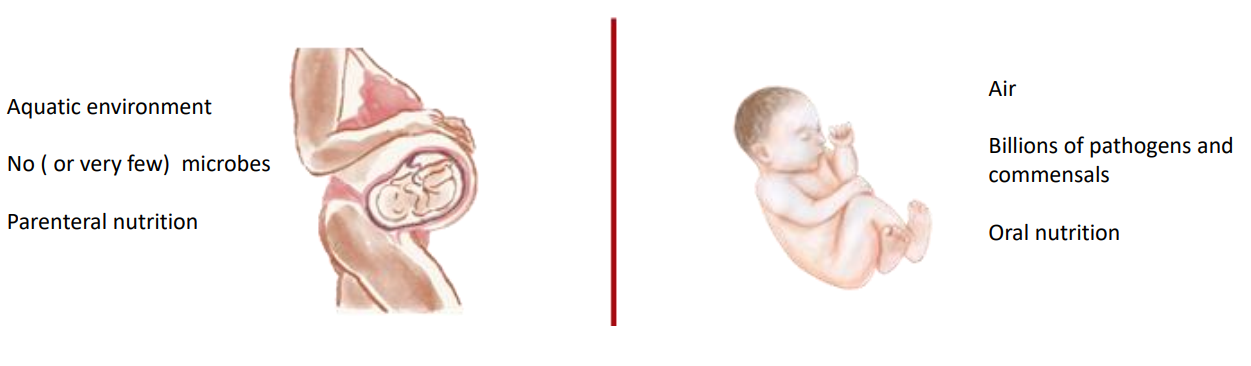
"The transition from a foetus to a newborn is the most complex adaptation that occurs in human experience"
- Aquatic environment
- No (or very few) microbes
- Parenteral nutrition
.
- Air
- Billions of pathogens and commensals
- Oral nutrition
Is colostrum necessary for the newborn to adapt to extra-uterine life and lay the foundation for healthy life?
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 10
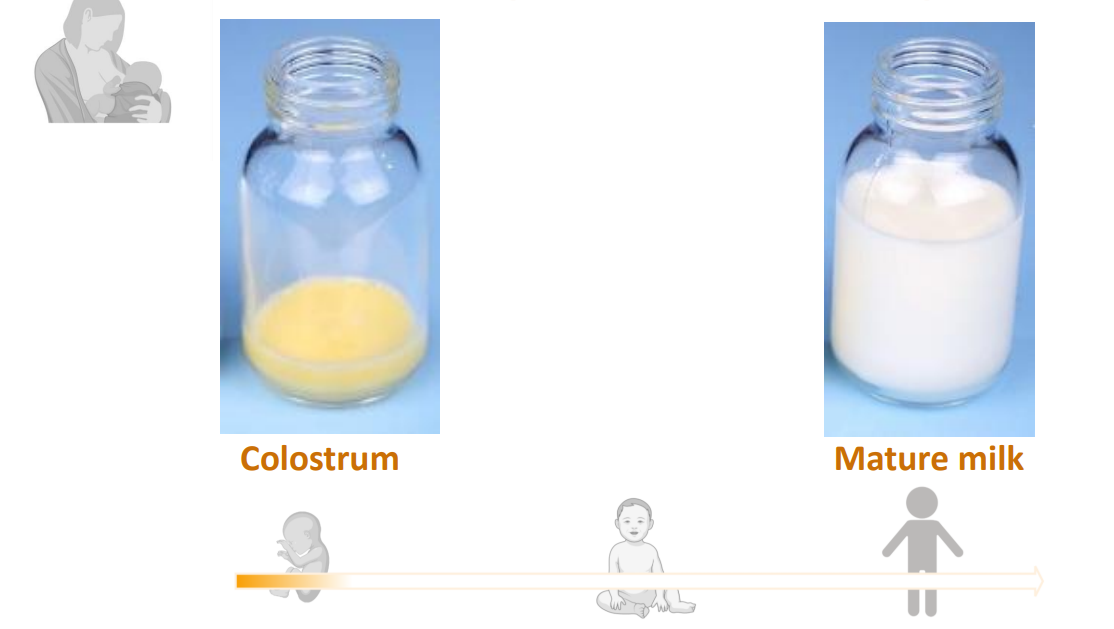
A cocktail of bioactives personalised to developmental stage
- Colostrum
- Mature Milk
.
- during pregnancy the intestine grows by 50% as an adult and you generate new tissue
- breast is creating ductic alveoli, a lot you create new tissue
Colostrum is yellow because of its high beta-carotene content, while mature milk is white due to its balanced composition of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates that are essential for the growing baby's nutritional needs. This color change signifies the milk's transition from colostrum to transitional milk and then to mature milk, adapting to the baby's increasing demands for calories and other nutrients
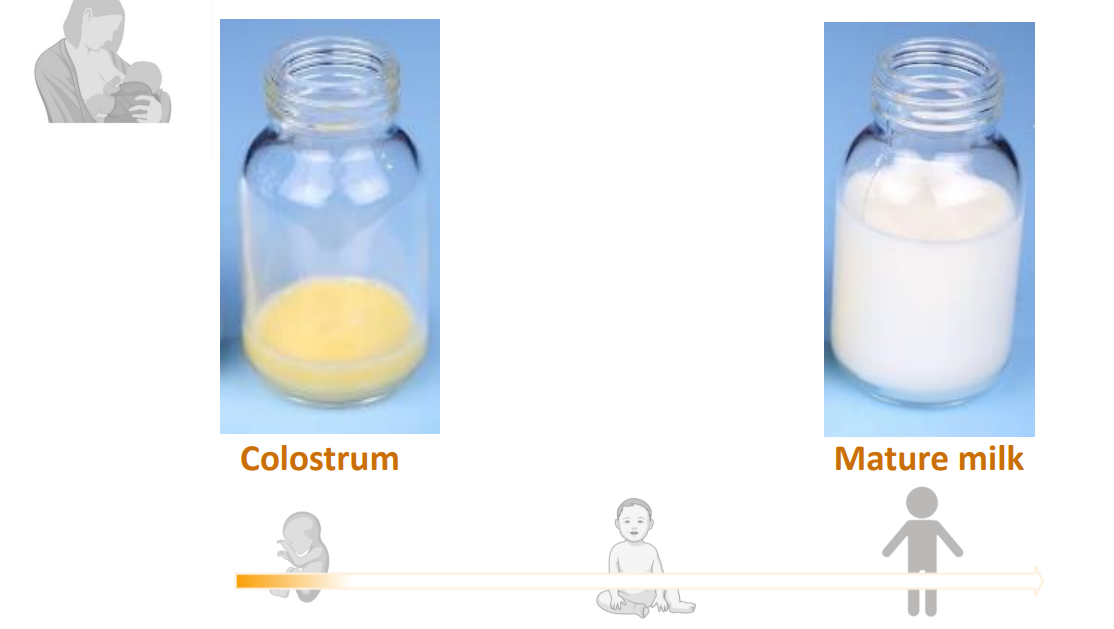
What is so special about colostrum
high protein/low fat/low sugar/high growth factors/high antimicrobials/microbiota shaping
- preterm colostrum content is even higher in protein, growth factors and antimicrobials
What do we know about beneficial effects of colostrum feeding?
- not much
Non-optimal breastfeeding practice leads to 2 outcomes:
- Exposes the newborn to potentially harmful agents (pathogen, allergen)
- deprives the newborn from colostrum bioactives

What do we know about the impact of the diet during the first 3 days of life on health outcomes
- delayed initiation of breastfeeding
- Neonatal mortality - infection
.
- FORMULA SUPPLEMENT DURING HOSPITAL STAY
- Cow's milk allergy
- Early cessation of breastfeeding
.
FORMULA SUPPLEMENT VS DHM/MOM -> NEC

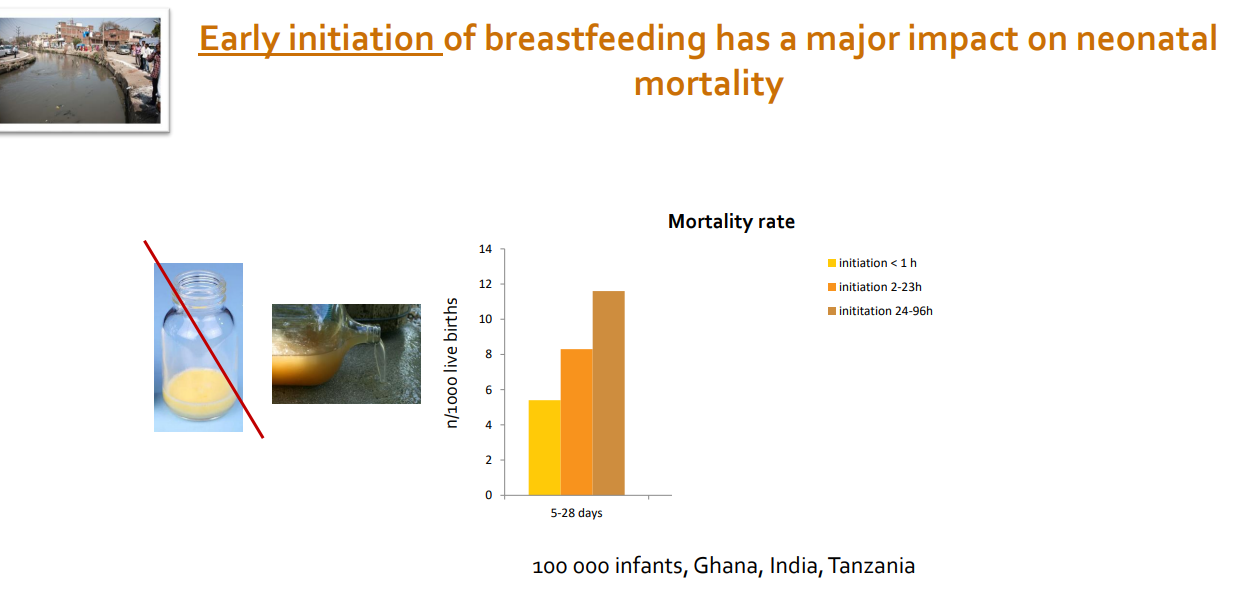
Early initiation of breastfeeding has a major impact on neonatal (newborn) mortality
- shows that mortality rate is very high if infant is not breastfed
- also need good hygiene, vaccination etc.
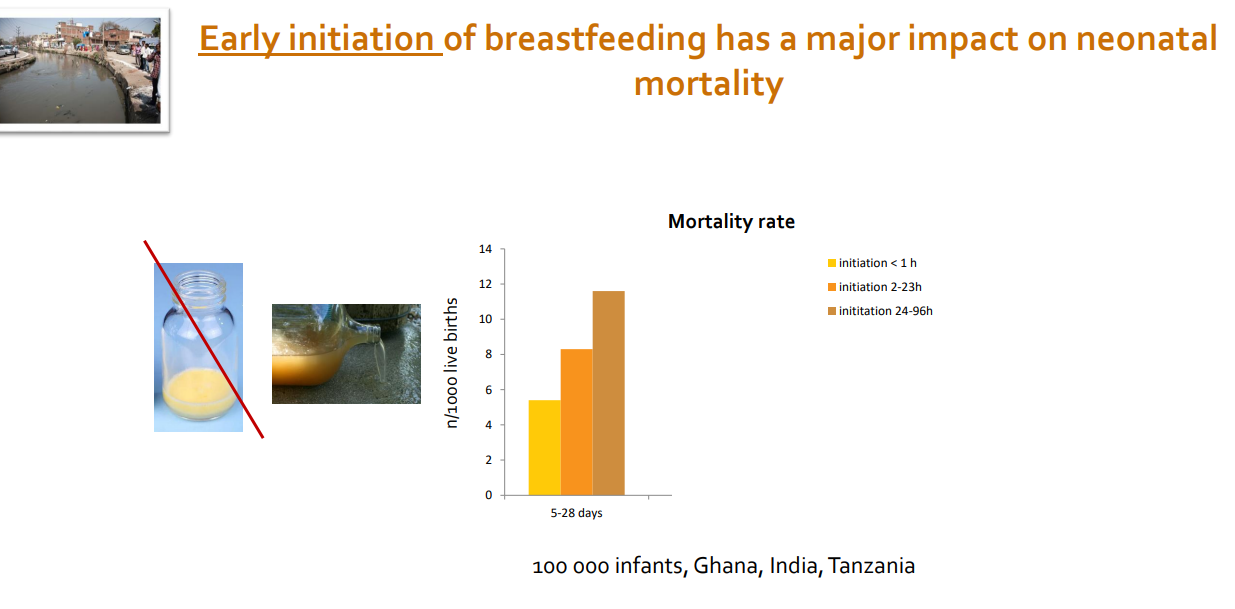
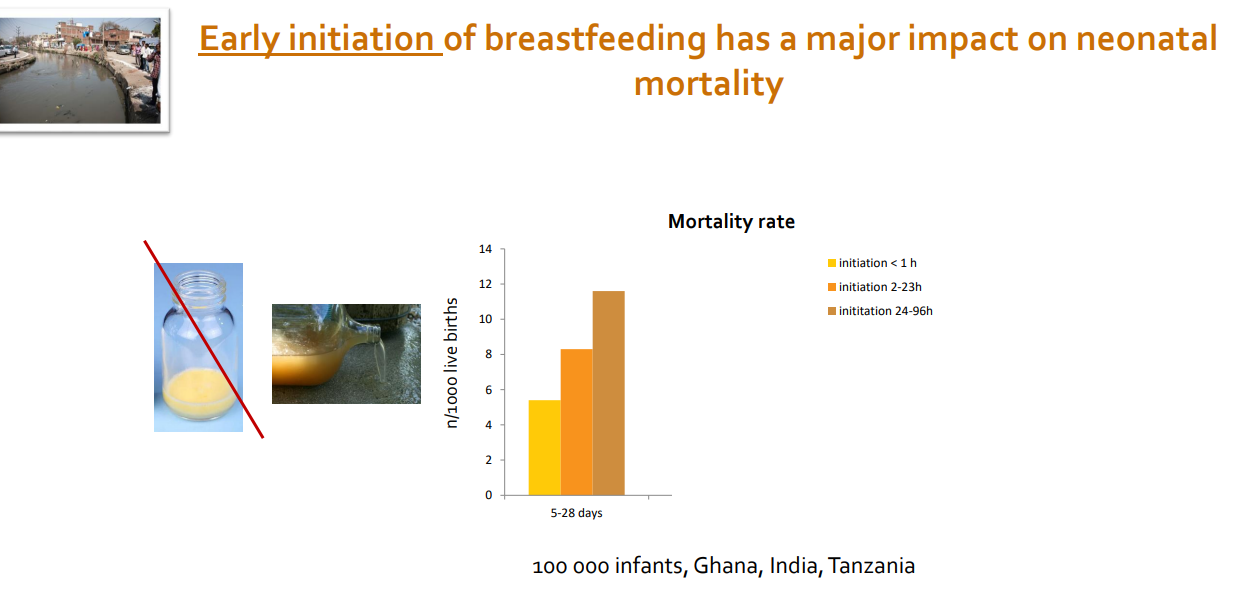
Long term effect of no breastfeeding
- still some protection but need to breastfeed early in life
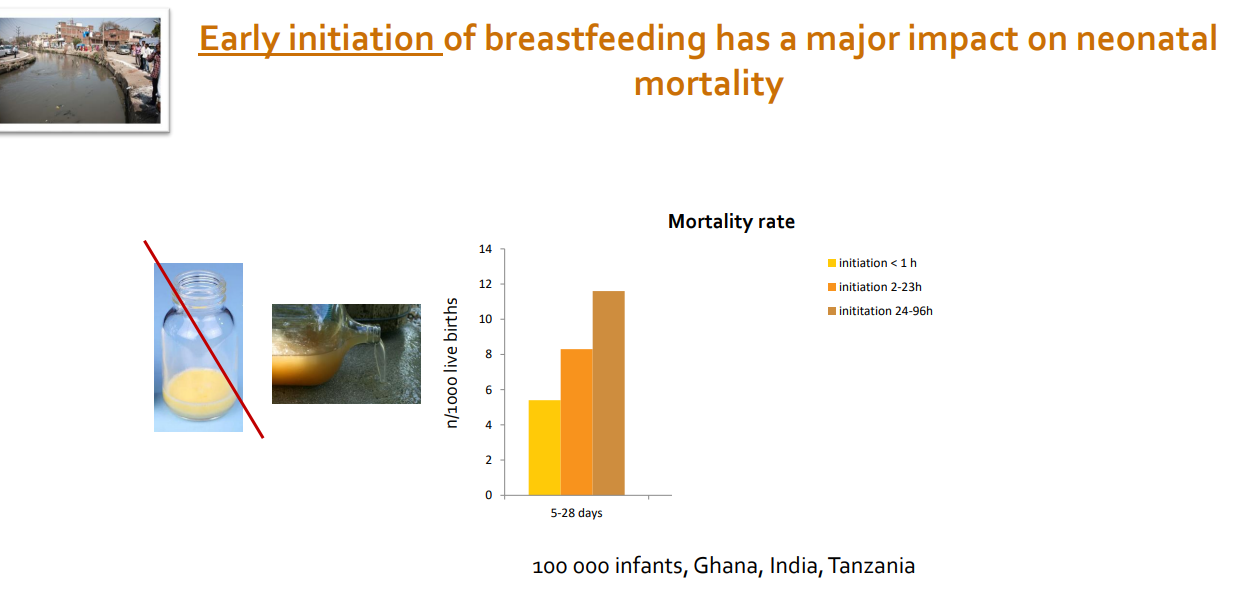
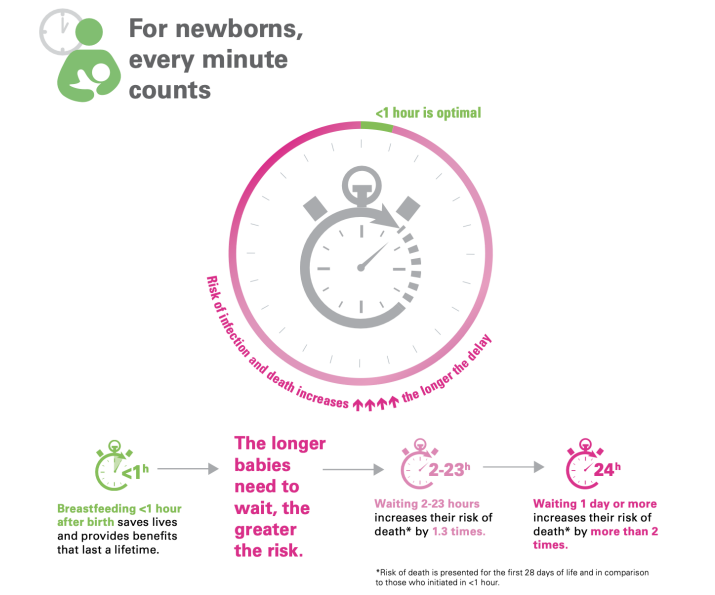
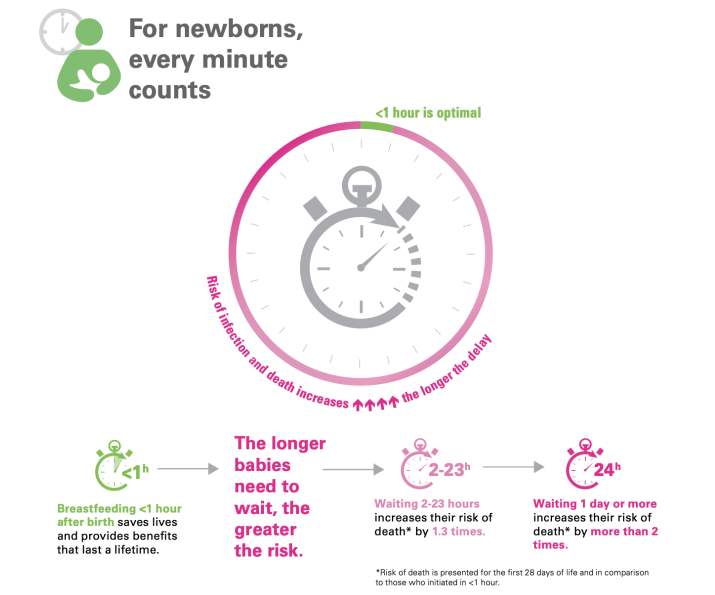
breastfeeding under an hour after birth saves lives and provides benefits that last a lifetime
- the longer babies need to wait, the greater the risk
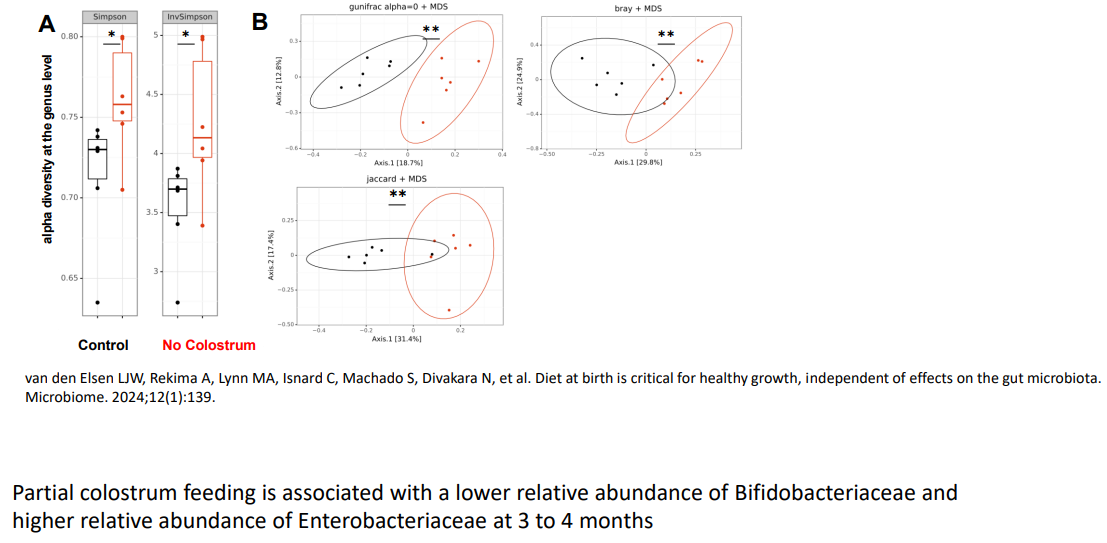
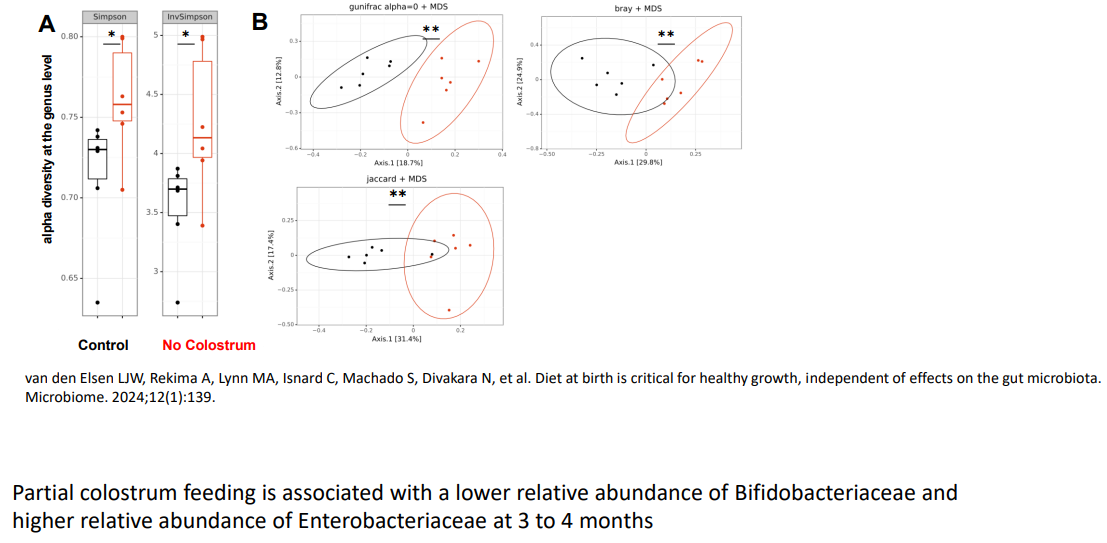
Colostrum at birth shapes the gut microbiota in infants
- partial colostrum feeding is associated with a lower relative abundance of Bifidobacteriaceae and higher relative abundance of Enterobacteriaceae at 3 to 4 months
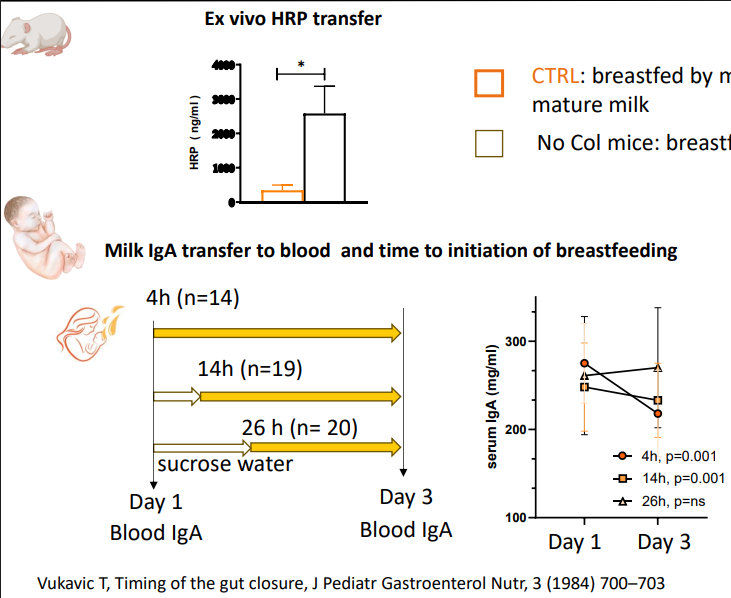
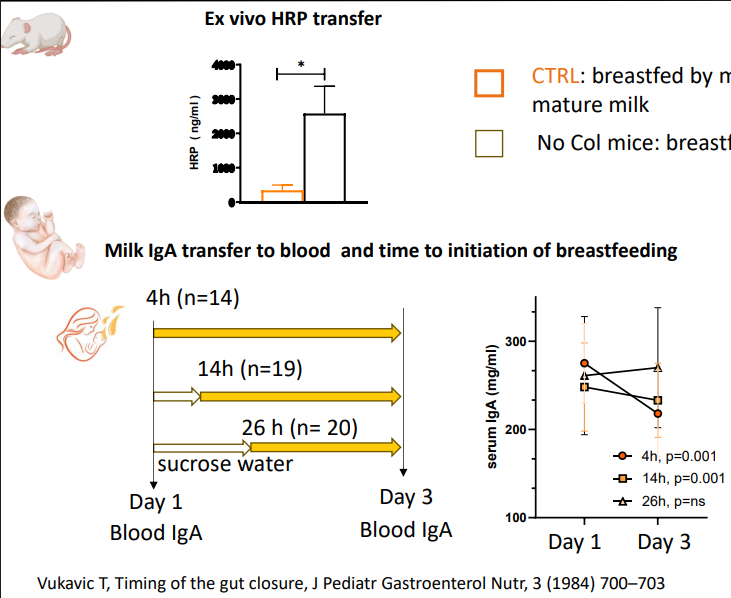
Colostrum promotes epithelia development
- Gut permeability
- CTRL: breastfed by mothers providing colostrum at birth, followed by mature milk
- No Col mice: breastfed by mothers providing mature milk from birth
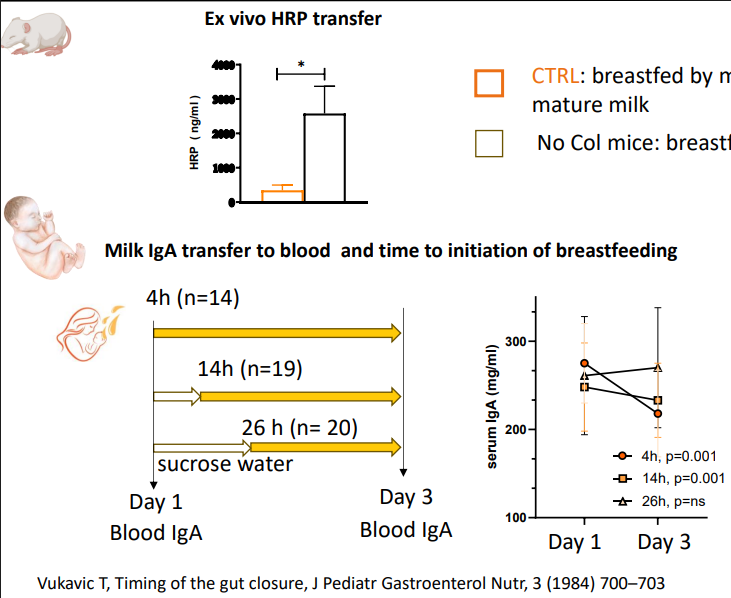
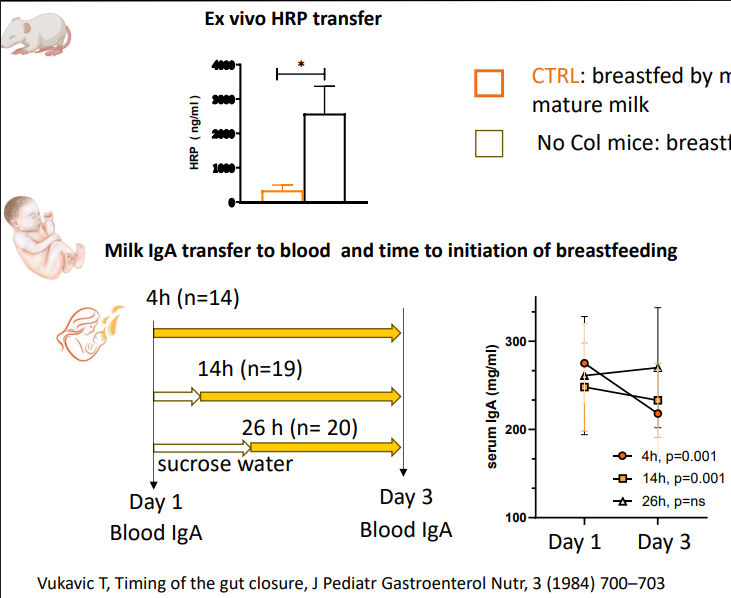
Lactulose/mannitol
- significantly lower intestinal permeability in Preterm infants who receieved the majority of feeding as human milk when compared to infants receieving minimal or no human milk at postnatal day 7
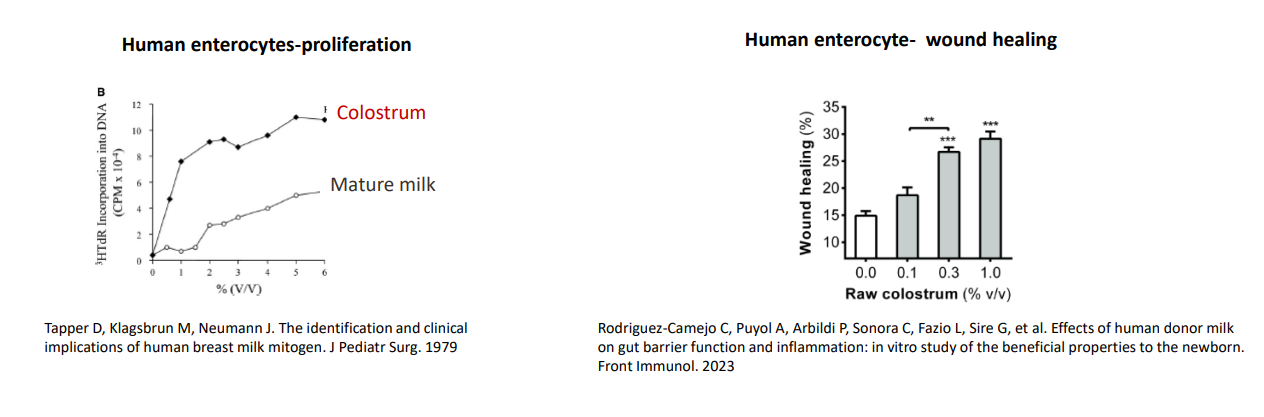
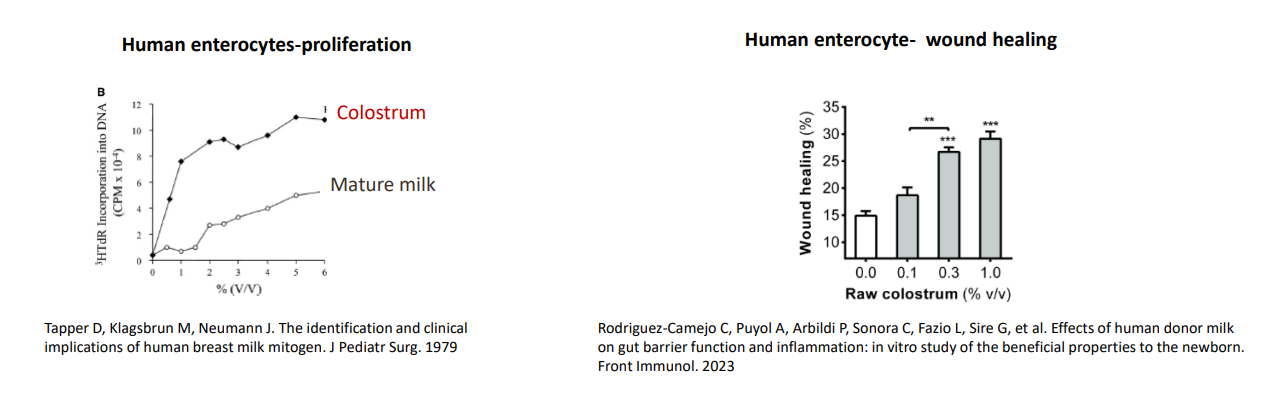
Colostrum promotes epithelia development - Gut epithelium
- colostrum is full of vitamin A and growth factors
- if you put epithelial cells with mature milk or colostrum you see how it makes the cell grow
- gave rise to epithelial growh factor
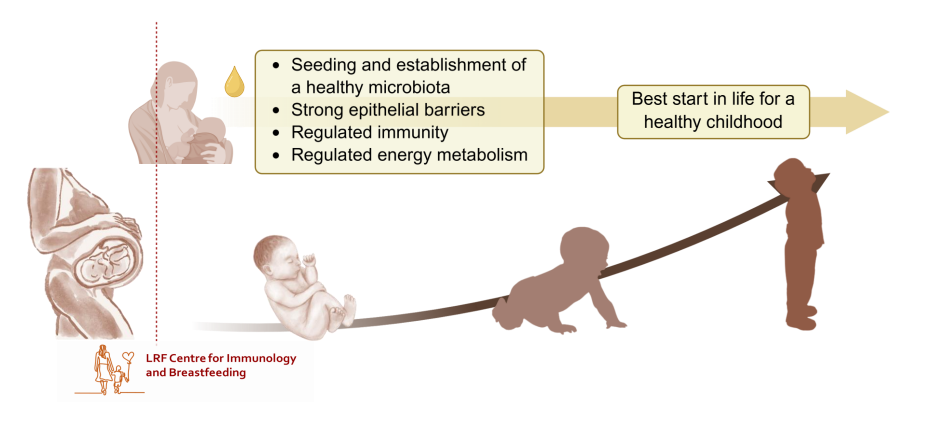
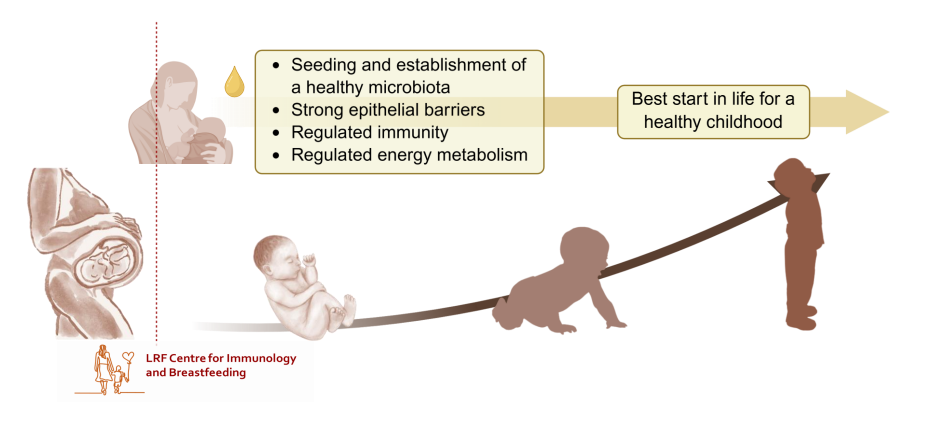
Colostrum, designed to lay strong foundations for a healthy immune system
- Seeding and establishment of a healthy microbiota
- Strong epithelial barriers
- Regulated immunity
- Regulated energy metabolism
.
ALL OF THESE give the best start in life for a healthy childhood
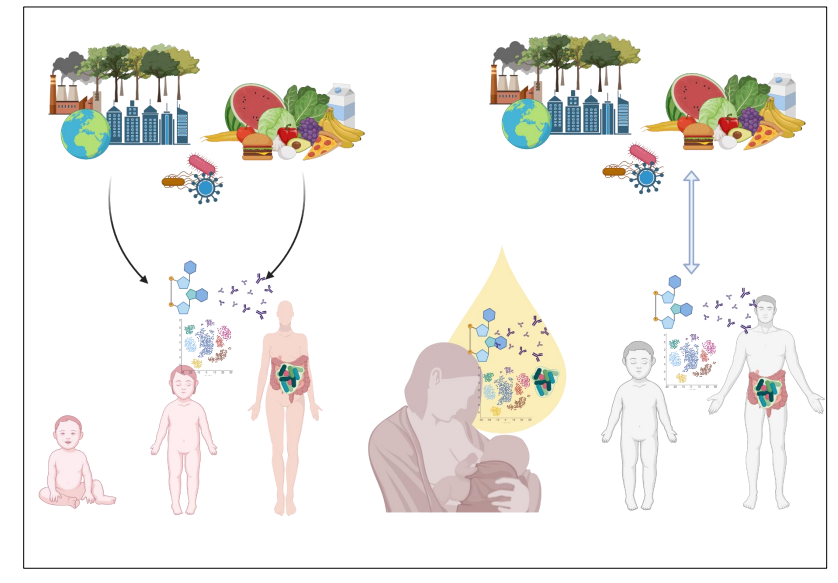
Human milk complements the infant's immune system and shapes its development in a personalised way
LEFT IMAGE:
- we have an individual, which is the mother
- exposed to certain city, certain pathogens and that will change the physiology of the future mother
- She has antibodies against the microbes
- she has certain metabolites circulating from her microbiota
- all her physiology and metabolism is affected by the environment
.
RIGHT IMAGE:
- now the individual becomes a mother
- the milk encapsulates the whole environment from the whole history of the mother
- if the mother that eats something that will change her milk composition, if a mother is exposed to a microbe, we will see a change in antibodies
- the milk is a reflection of the whole environment
.
- and then the baby is receieving this environment (digested by mother) and that is then given as a source of information and hopefully then the infant is able to to become adult as well and respond to the environment
Example of the way breastfeeding is similar to migration
- when migrants come to a new country and they have a high risk of allergy
- Asian population coming to Australia have a burden of allergy that is huge
- meanwhile in their country they dont have allergy and they arrive here, suddenly they have huge allergy immediately
-
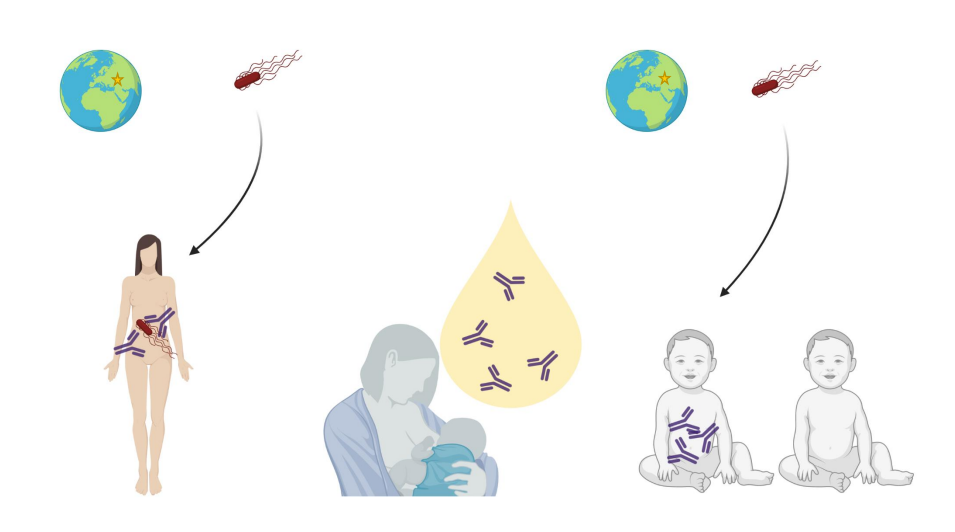
Maternal antibodies tailed to the child environment (the entero-respiratory mammary axis)
LEFT:
- imagine a mother living in a certain country exposed to Microbe A
- this mother has a good immune system, she makes antibody in her gut, will eliminate the pathogen
- but also these antibody migrate to the B cells, the cell producing antibody the plasma cell migrate to the mammary gland and they produce the same antibody
.
OTHER IMAGES:
- so of course if the mother is exposed to the pathogen, there is a big chance the baby is also exposed
- so the baby needs to receive the exact same antibody
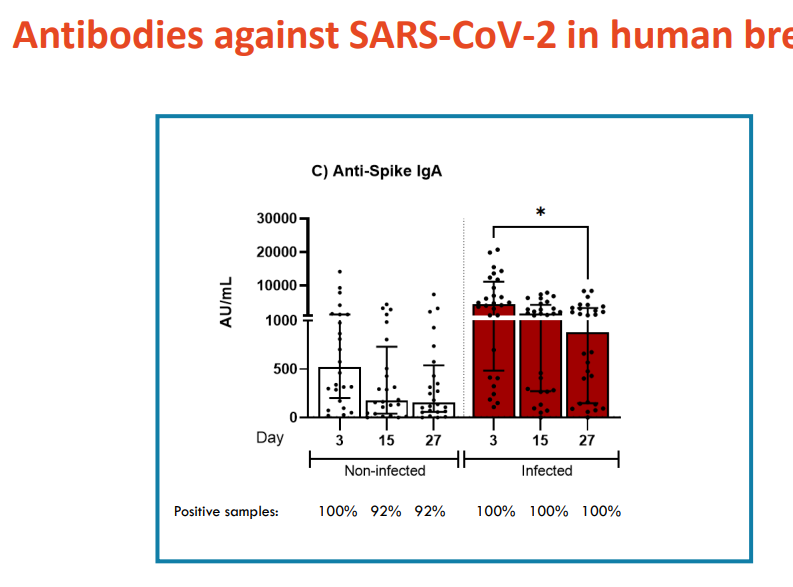
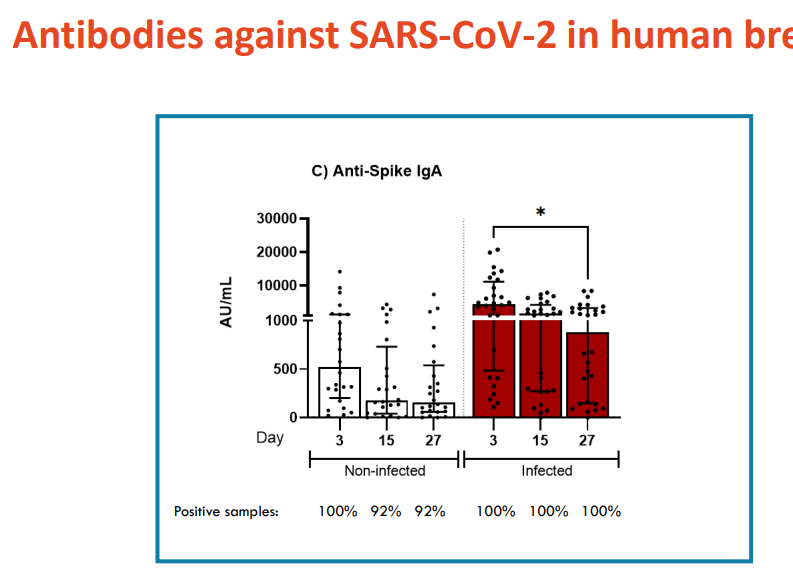
Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 in Human Breast milk
- graph shows the level of antibodies in the breastmilk
- study shows that analysis of colostrum with mother pre-pandemic. We look at antibodies against Sars-CoV-2
- once exposed, the antibody level in the breast milkk greatly increases
.
SUMMARY:
- shows that when mother produces antibodies against a certain illness, the breastmilk quickly has antibodies too (real time, in 3 days)
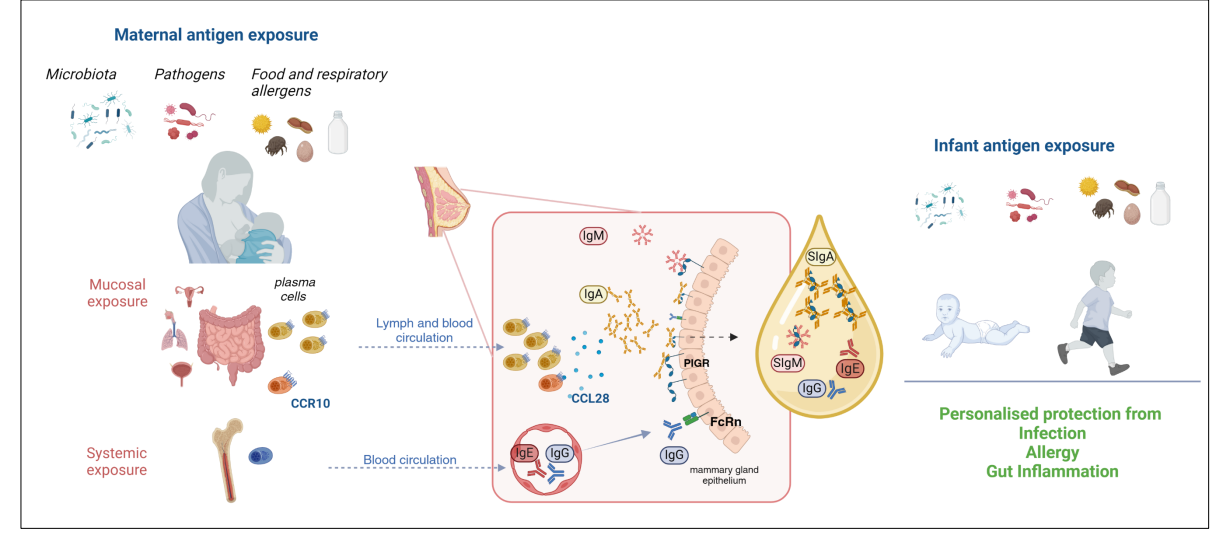
Breat milk real time adaptation to the environment the infant is exposed to
- The maternal immune system - mammary gland axis
.
- key idea is that the antibodies in the breast milk is personal for waht the child needs
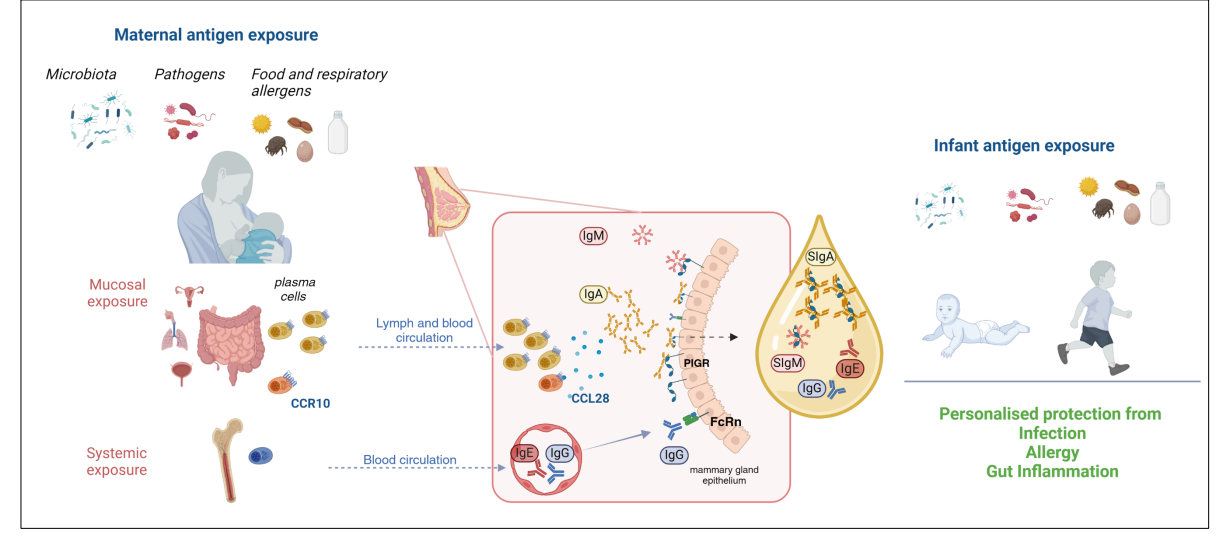
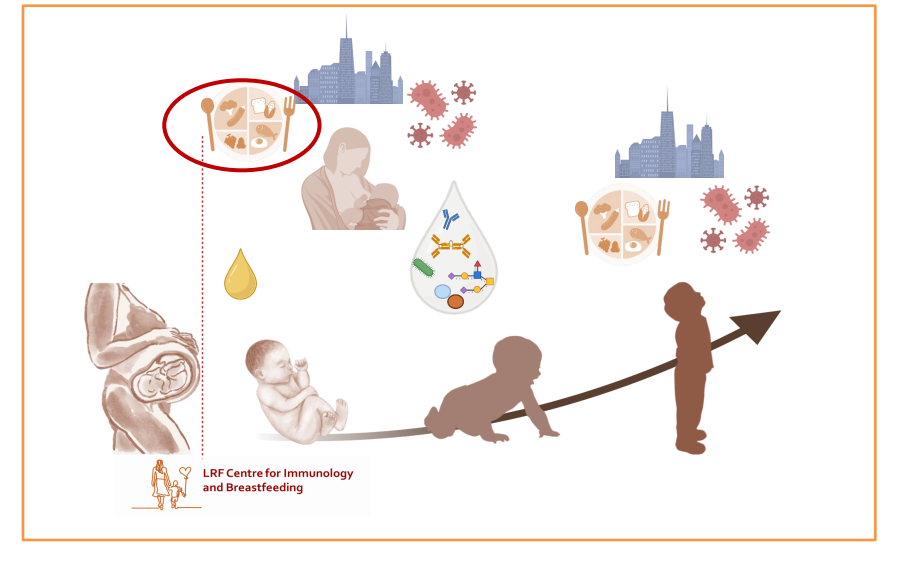
Human milk shapes immune development in a personalised way
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 30
Breatmilk real-time adaptation to the environment the infant is exposed to: The maternal environment - mammary gland axis: allergens
- it used to be the thing where people used to say avoid allergens because they thought the baby was responding to it negatively (crying etc)
- but its actually the opposite. if you want your immune system to accept something, you need to educate
- you need to expose
- two parts of the immune system defines tolerance
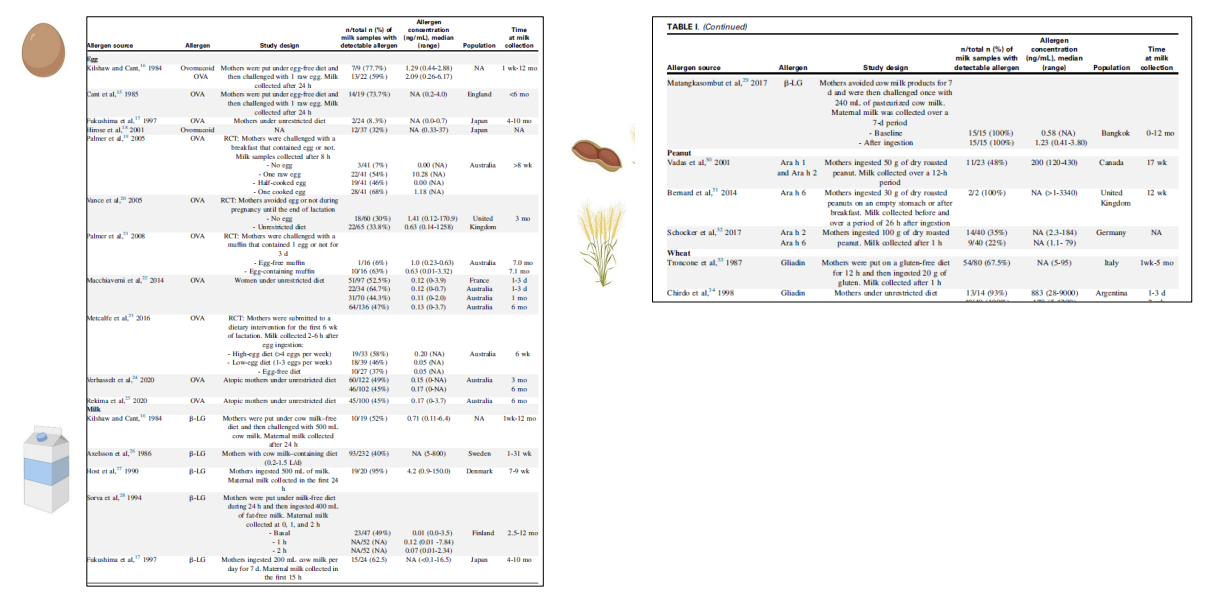
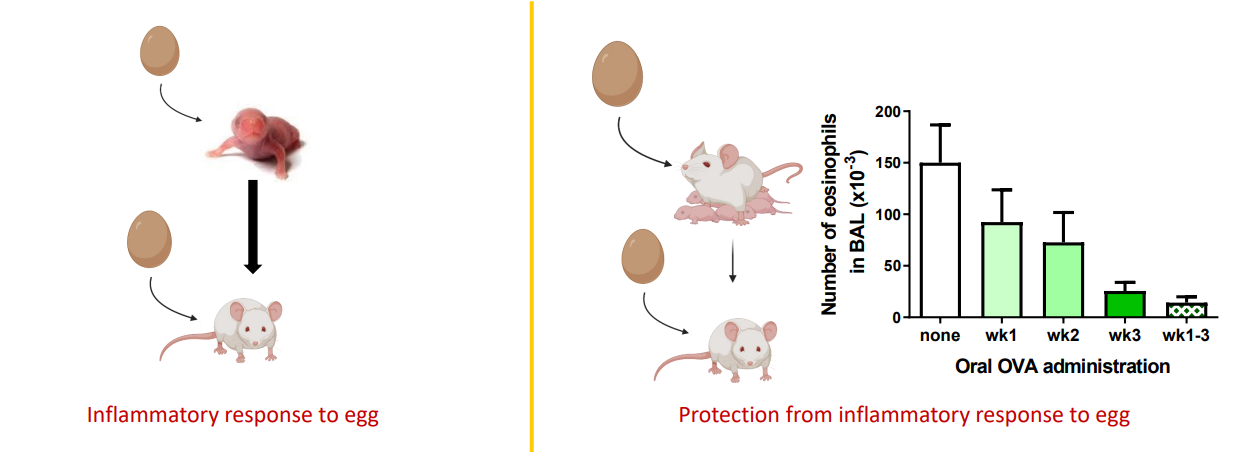
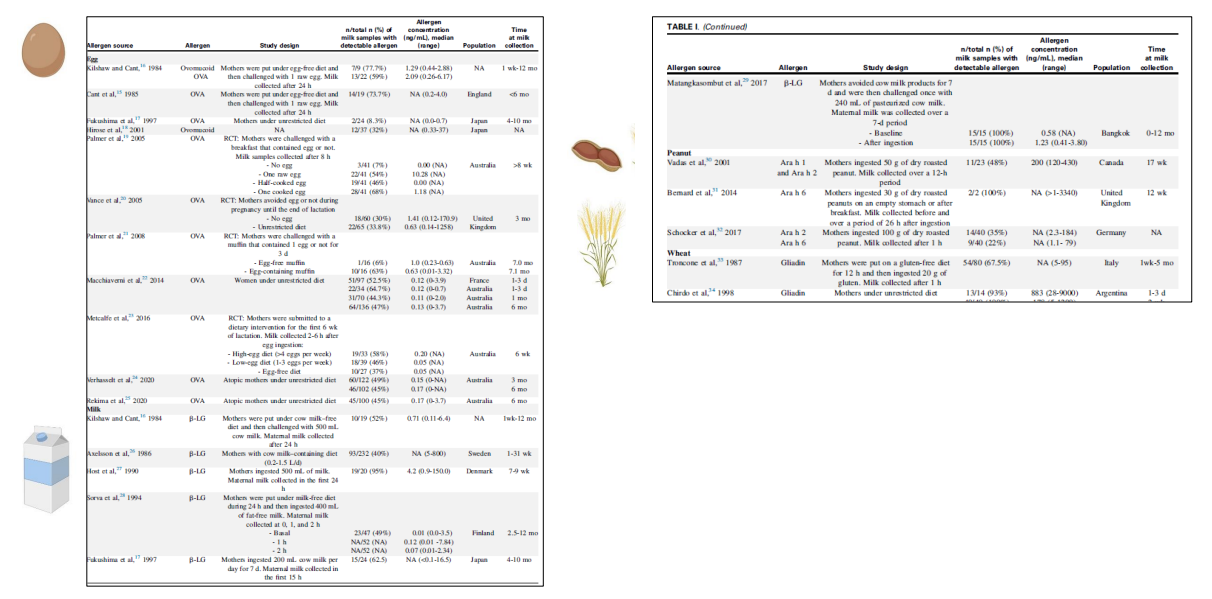
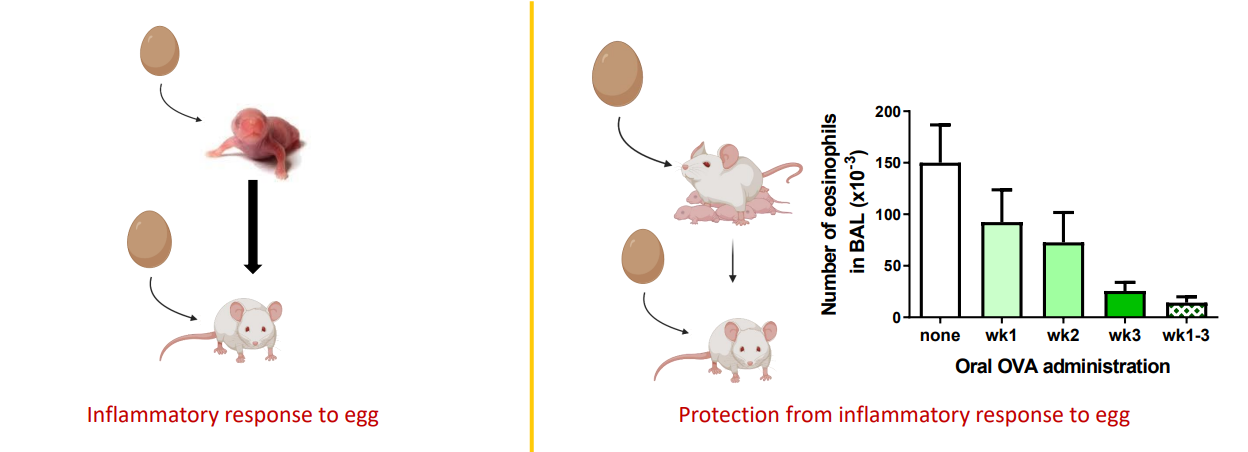
Egg allergen exposure through breast milk enhances the efficacy of oral tolerance induction during the first weeks of life
- inflammatory response to egg
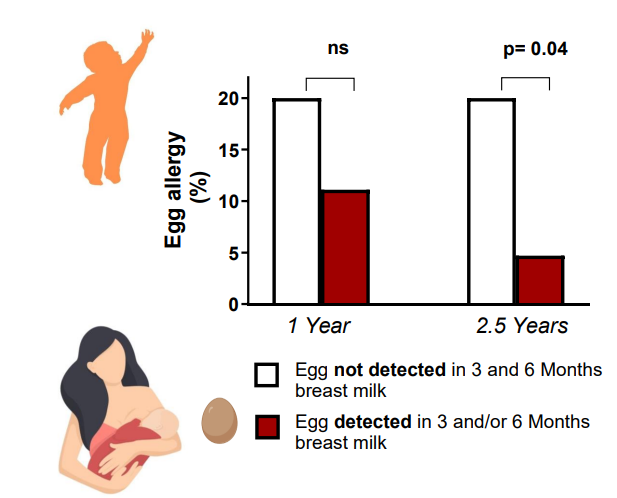
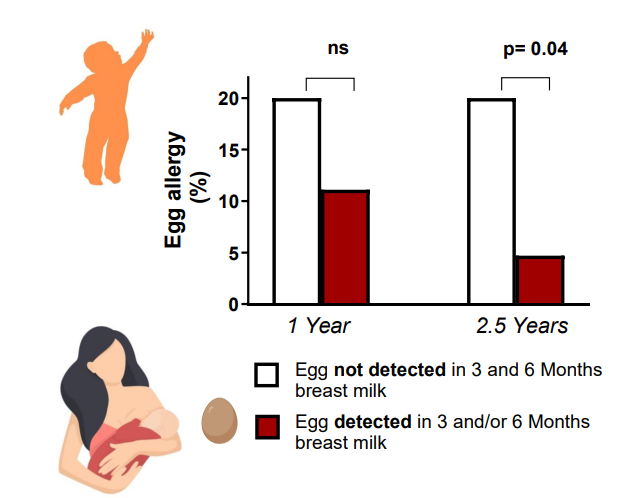
Egg allergen exposure through breastmilk is associated with egg allergy prevention
- look at how the fact that egg was detceted in breast milk, and how that had a lower percentrage of egg allergy
Recommendation for mother to eat egg during breastfeeding?
- eating eggs, eating peanuts will protect the child
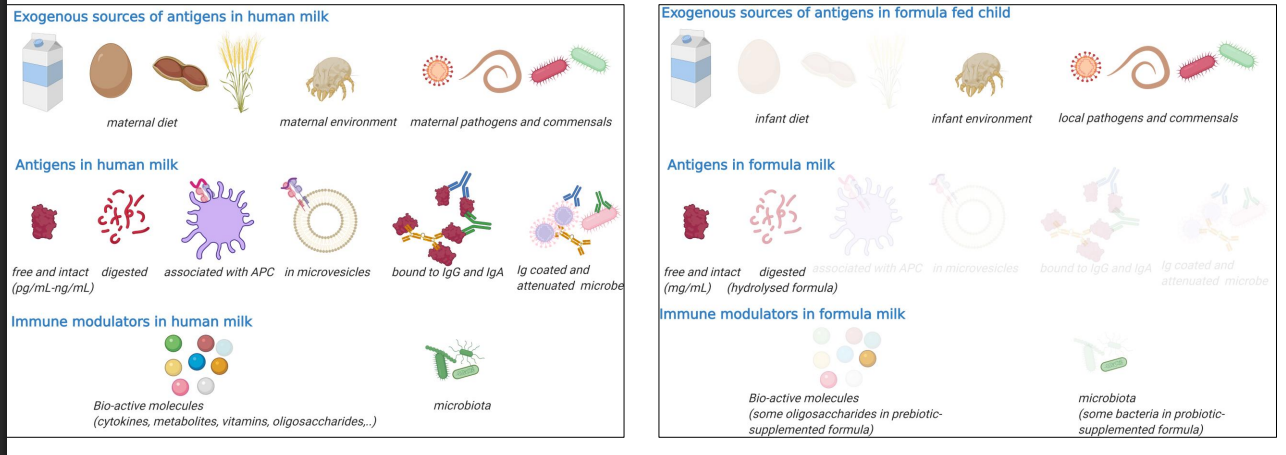
Antigen shedding in human milk has the potential to educate an infant's immune system
- translating into the biological language of the developing immune system
.
- HIV is transmitted through breastmilk (only 10% of infants who are breastfed by a mother that has HIV got HIV)
- nature has selected that you have a pathogen in the breast milk then the baby will usually not get it
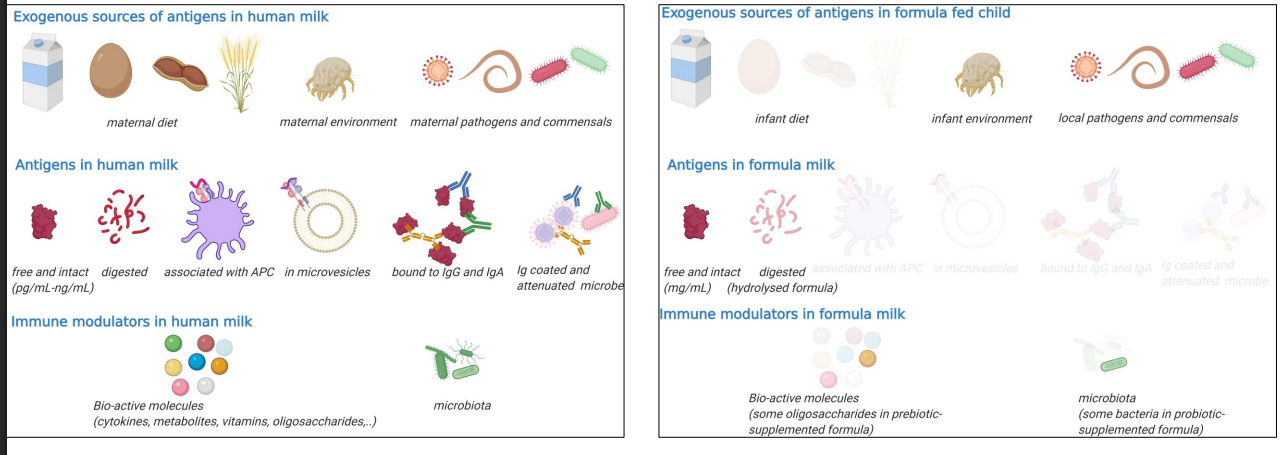
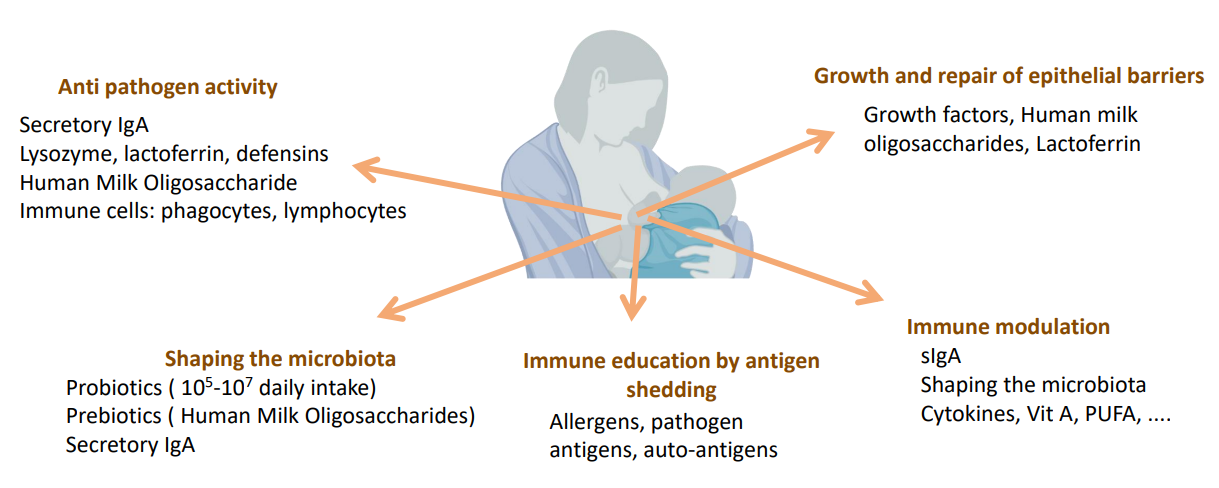
A cocktail of bioactives with a wide range of action and high adaptability
ANTI-PATHOGEN ACTIVITY:
- Secretory IgA
- Lysozyme, lactoferrin, defensins
- Human Milk Oligosaccharide
- Immune cells: phagocytes, lymphocytes
SHAPING THE MICROBIOTA:
- Probiotics (10^5-10^7 daily intake)
- Prebiotics (human milk oligosaccharide)
- Secretory IgA
IMMUNE EDUCATION BY ANTIGEN SHEDDING:
- Allergens, pathogen, antigens, auto-antigens
IMMUNE MODULATION:
- sIgA
- Shaping the microbiota
- Cytokines, Vit A, PUFA...
GROWTH AND REPAIR OF EPITHELIAL BARRIERS:
- Growth factors, human milk oligosaccharides, lactoferrin
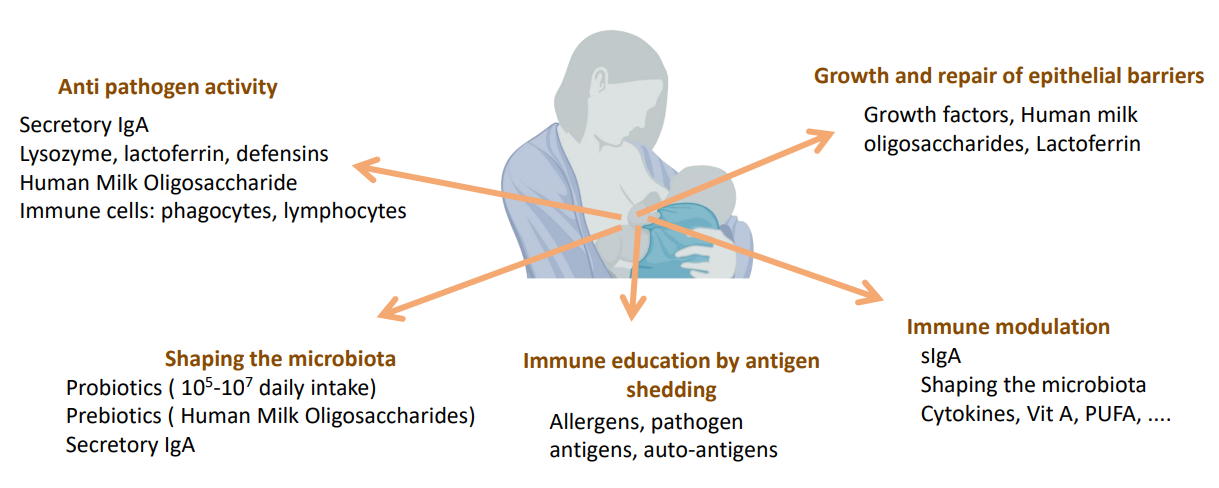

Cocktail of bioactives:
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 37


Summary
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 39

Human milk is the best way to prevent infectious diseases
Human milk acts as a personalised medicine (exmaples are IgA transfer/change in composition with age) and acts by multiple mechanisms including providing the breastfed child with antimicrobials/pre and probiotics/and repair molecules
Human milk has the potential to protect the infant in the long term from immune mediated disease such as allergies
Mechanisms include microbiota-shaping properties of breast milk, allergen shedding, factors promoting tissue integiry, and immune modulators that influecne the infants imnun response. Interveions such as the ones targetting a matternal diet have hte potetnail to make maternal milk more adapted to tghe western world and prevent allergies in offspring