Kingdom Protista
All ^^single-celled eukaryotes^^ come under this kingdom.
Currently, we include Chrysophytes, Dinoflagellates, Euglenoids, Slime molds, and Protozoans under Protista.
Characteristics of members of Kingdom Protista:-
- They are %%primarily aquatic%%.
- Being eukaryotes, the protistan cell body contains a ^^well-defined nucleus^^ ^^and other^^ ^^membrane-bound organelles.^^
- Some have motile organelles like %%cilia and flagella%%.
- Protists reproduce asexually and sexually by a process involving @@cell fusion and zygote formation.@@
- This kingdom forms a link with the others dealing with plants, animals, and fungi.
Chrysophytes:
Characteristics:
- They are found in freshwater as well as in marine environments.
- They are microscopic and %%float passively%% in water currents ^^(^^^^plankton^^^^)^^
- Most of them are @@photosynthetic@@@@.@@
- Examples: ==Diatoms and Golden Algae== ==(====Desmids====).==
Diatoms:
- The cell walls form two thin overlapping shells, which fit together as in a soap box.
- The ^^walls^^ are embedded with silica and thus the walls are %%indestructible%%%%.%%
- They leave behind large amounts of cell wall deposits in their habitat and this accumulation over billions of years is referred to as diatomaceous earth.
- This soil is used in ^^polishing, and filtration of oils and syrups^^ since it is gritty.
- They are the %%chief producers of the ocean.%%
Dinoflagellates:
- These organisms are mostly marine and photosynthetic and ^^appear yellow, green, brown, blue, or red^^ depending on the main pigments present in their cells.
- The cell wall has %%stiff cellulose plates%% on the outer surface.
- Most of them ^^have two flagella^^ - one lies longitudinally and the other transversely in a furrow between the wall plates.
- Very often, red dinoflagellates undergo such @@rapid multiplication@@ @@that@@ they make the sea appear red (red tides).
- ^^Toxins released^^ in such large numbers may even kill other marine animals such as @@fishes.@@
- Example: ^^Gonyaulax^^ (red dinoflagellate).
Euglenoids:
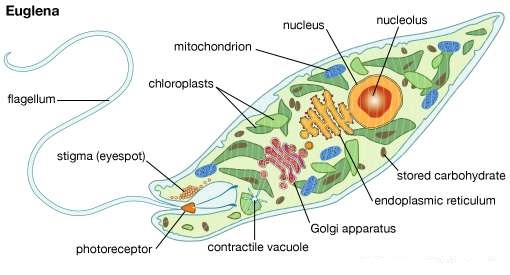
- The majority of them are freshwater organisms found in stagnant water.
- Instead of a cell wall, they have a @@protein-rich layer called a pellicle@@ which makes their body flexible.
- They have ==two flagella==, a short and a long one.
- Though they are %%photosynthetic in the presence of sunlight,%% when deprived of sunlight they behave like heterotrophs by predating on other smaller organisms.
- The pigments of euglenoids are identical to those present in higher plants.
- Example: ^^Euglena.^^
Slime Moulds:
- They are %%saprophytic%% protists.
- The body moves along decaying twigs and leaves %%engulfing organic material.%%
- Under suitable conditions, they ^^form an aggregation^^ ^^called^^ ^^plasmodium^^ which may grow and spread over several feet.
- During unfavorable conditions, the ^^plasmodium differentiates and forms fruiting bodies bearing spores^^ at their tips.
- These spores possess %%true walls and are dispersed by air currents.%%
- They are extremely ^^resistant^^ ^^and^^ ^^survive for many years^^^^,^^ even under adverse conditions.
Protozoans:
- All protozoans are heterotrophs and live as predators or parasites.
- They are believed to be @@primitive relatives of animals.@@
There are ^^four major groups^^ of protozoans:
Amoeboid Protozoans:
- These organisms live in %%freshwater, seawater, or moist soil.%%
- They move and capture their prey by putting out pseudopodia(false feet).
- Marine forms have ==silica shells== on their surface.
- Some of them are %%parasites.%%
- Examples: ^^Amoeba, Entamoeba.^^
Flagellated protozoans:
- The members of this group are either @@free-living or parasitic.@@
- They have flagella.
- The parasitic forms cause diseases such as ==sleeping sickness.==
- Examples: ^^Trypanosoma.^^
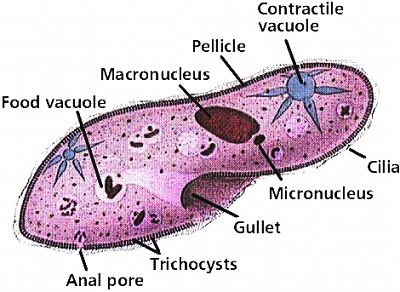
Ciliated protozoans:
- These are aquatic, actively moving organisms because of the presence of %%thousands of cilia%%%%.%%
- They have a cavity (gullet) that opens to the outside of the cell surface.
- The coordinated ==movement of rows of cilia== causes the water laden with food to be steered into the gullet.
- Examples: ==Paramecium.==
Sporozoans:
- It includes diverse organisms that have an %%infectious spore-like stage%% in their life cycle.
- The most notorious is ^^Plasmodium^^ ^^(malarial parasite) which causes^^ ^^malaria^^^^, a disease that has a^^ ^^staggering effect on the human population.^^