Chemistry vocab quizz 14.04.2023
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/16
Last updated 8:41 AM on 4/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
1
New cards
Particle
One of the very small parts of matter.
2
New cards
Kinetic theory
The theory that all matter consists of tiny particles (atoms, ions, molecules) that are moving constantly- they never stop.
3
New cards
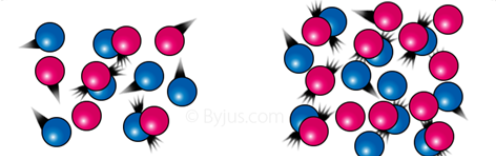
Collision
An instant of one moving object striking violently against another.
4
New cards
Elastic collision
When objects collide to each other and they are able to resume their normal shapes spontaneously, after contraction.
5
New cards
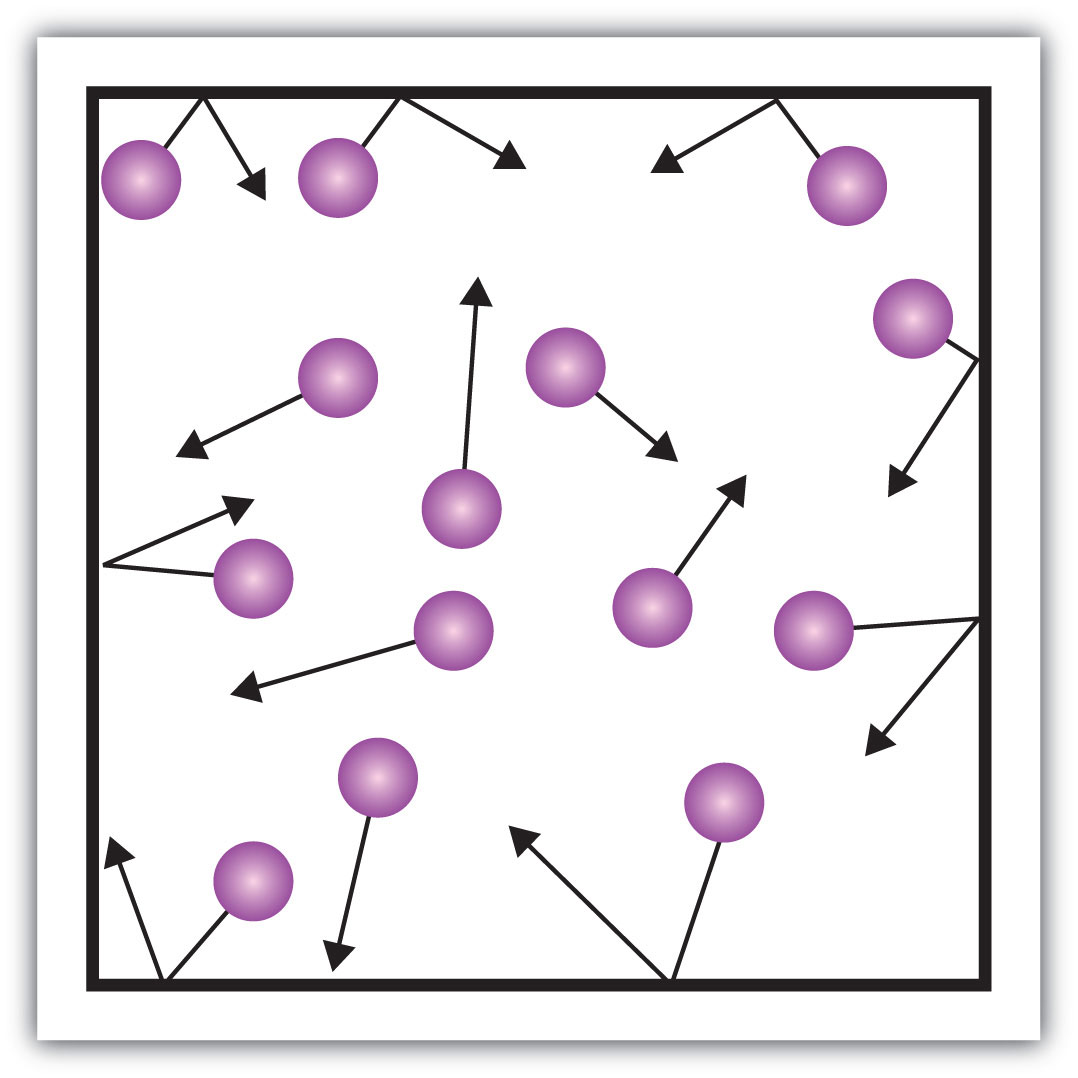
Gas pressure
The force exerted by a gas on a surface.
6
New cards
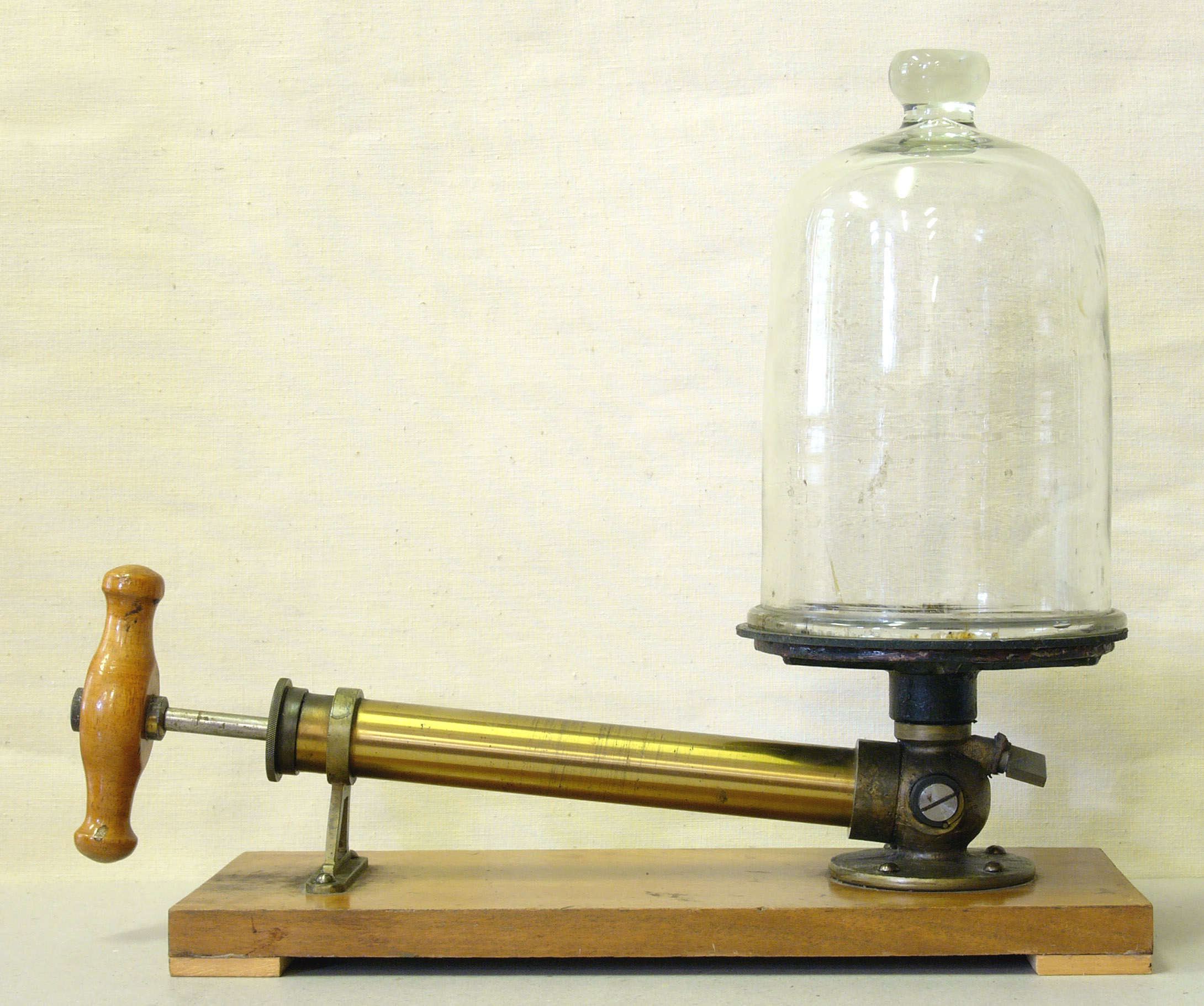
Vacuum
An empty space with no atoms or molecules in it, so it has no pressure.

7
New cards
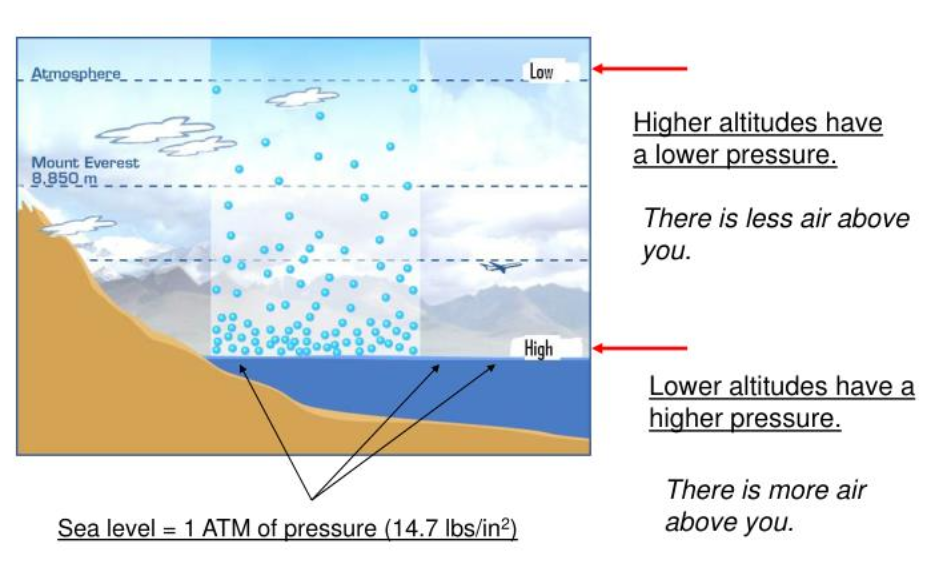
Atmospheric pressure
All the air that surrounds the Earth to a height about 12km.
8
New cards
Kinetic energy
The (movement) energy an object has due to its motion.

9
New cards
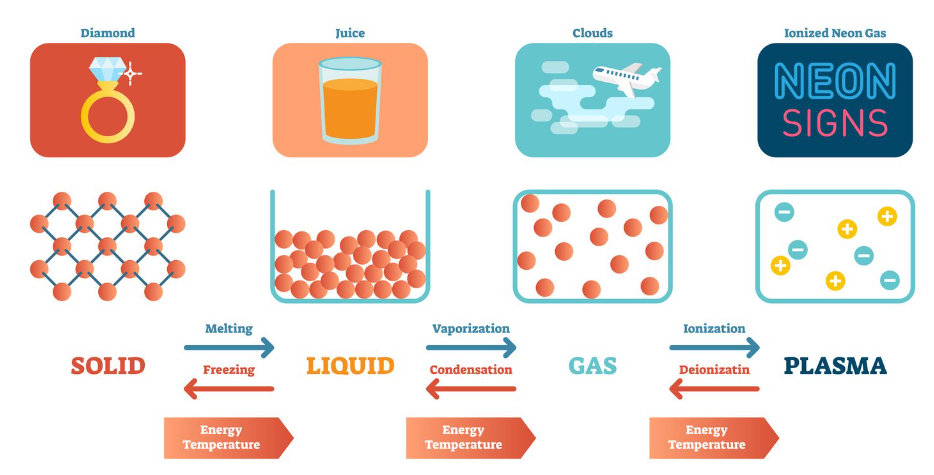
State of matter
____ is also called as phases, which includes: solid, liquid, gas and plasma (rare).
10
New cards
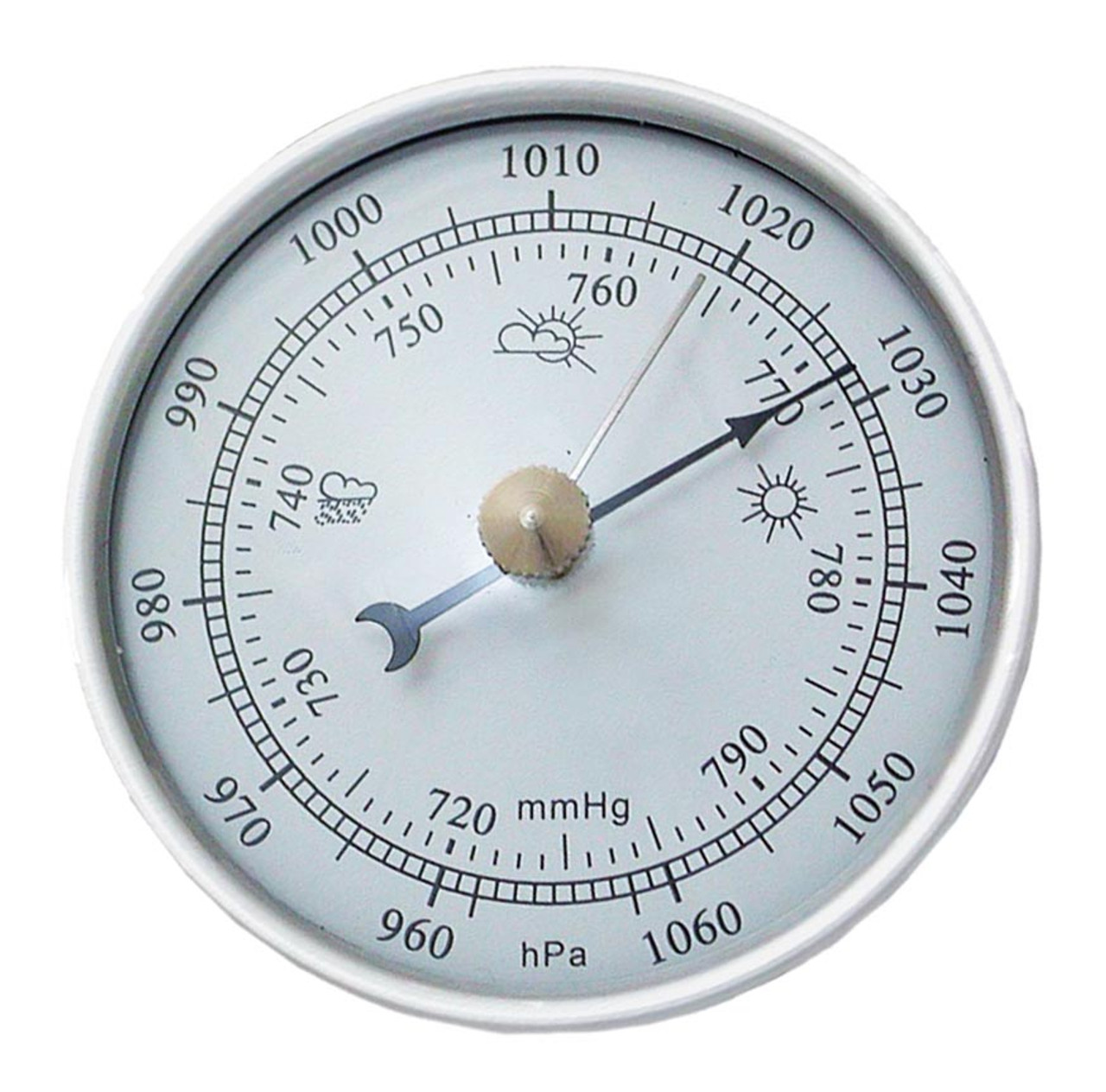
Barometer
A device that measures air pressure and shows when the weather is likely to change

11
New cards
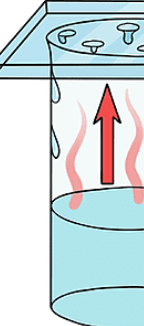
Vapor
A gas that forms above a liquid surface due to the evaporation of liquid particles.
12
New cards
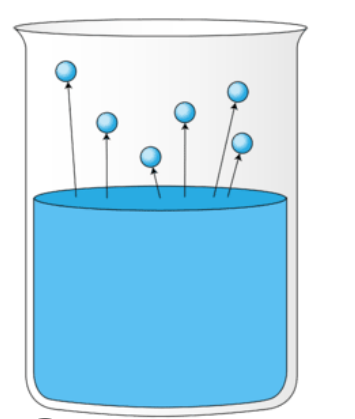
Evaporate
A form of vaporization occurs at lower temperature, where only a small proportion of particles near the surface have enough energy to enter the gas phase.
13
New cards
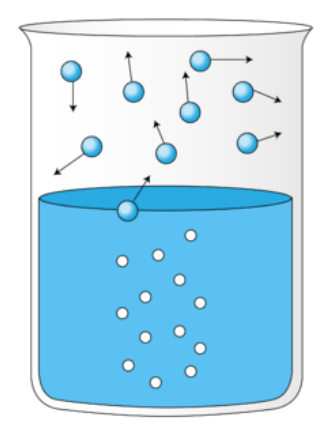
Vaporize
The conversion of a liquid into a gas.
14
New cards
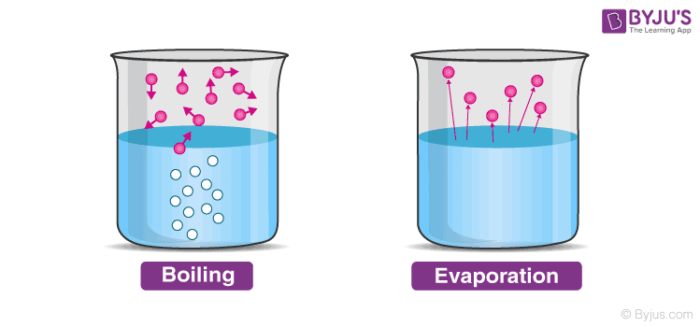
Boil
A form of vaporization occurs when the temperature is high enough that particles throughout the liquid have enough kinetic energy to enter the gas phase.
15
New cards
Condense
The conversion of a gas into a liquid.
16
New cards
Vapor pressure
The force exerted by a gas (vapor) above a liquid surface due to particle collision.
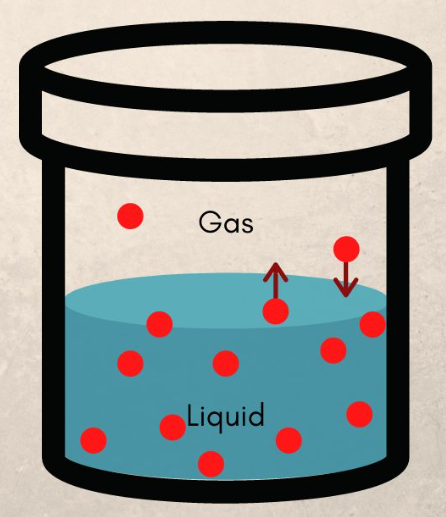
17
New cards
Dynamic equilibrium
A situation in which two opposite chemical reactions happen at the same speed (rate of evaporation = rate of condensation).