Micro
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
133 Terms
Ceteris paribus

* Natural resources
* Labor
* all human effort
* Capital
* tangible facilities
* Entrepreneurship
* Risk taker, management
* Manages the FOP
Command economies

Pros, cons of command economies

pros, cons of market economies

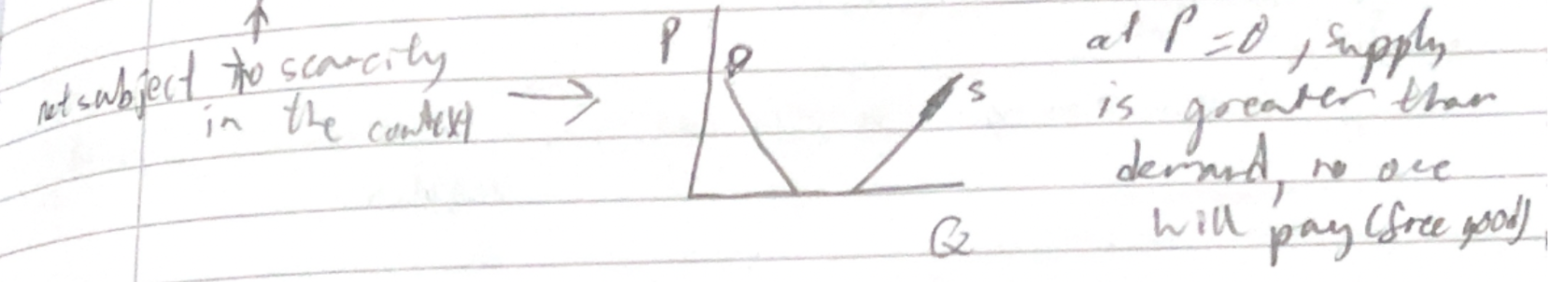
Economic vs free goods

Opportunity costs, and importance
the value of the next-best alternative when a decision is made

PPC looka at capacity to produce not price
PPC
points on curve is potential output

Increasing cost PPC
Opportunity cost increases

PPC curve increases
increases in Q or Quality of FOP
Potential output increase
Reallocation
Moving resources of one to another production
* High price
* signals to consumers to consumer less
* To producers to produce more-higher profits
* Rationing
* More scarce
* demand exceeds supply
* Higher price, conserved
* Incentive
* Prices incentive certain behaviors
* high wage = work
* High price = join market, produce
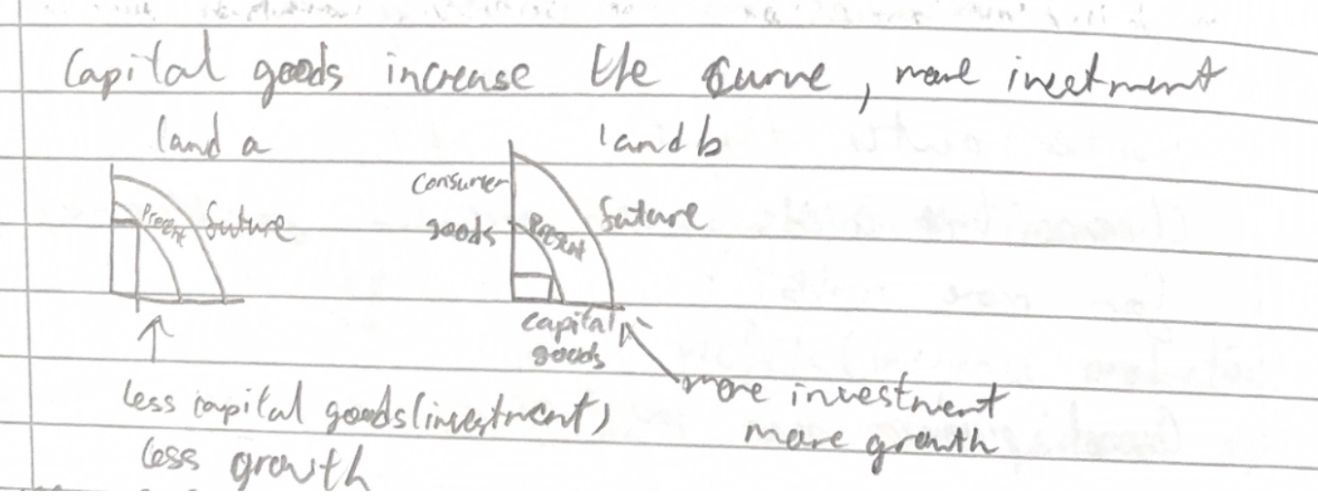
PPC - effect of Capital goods (investment)
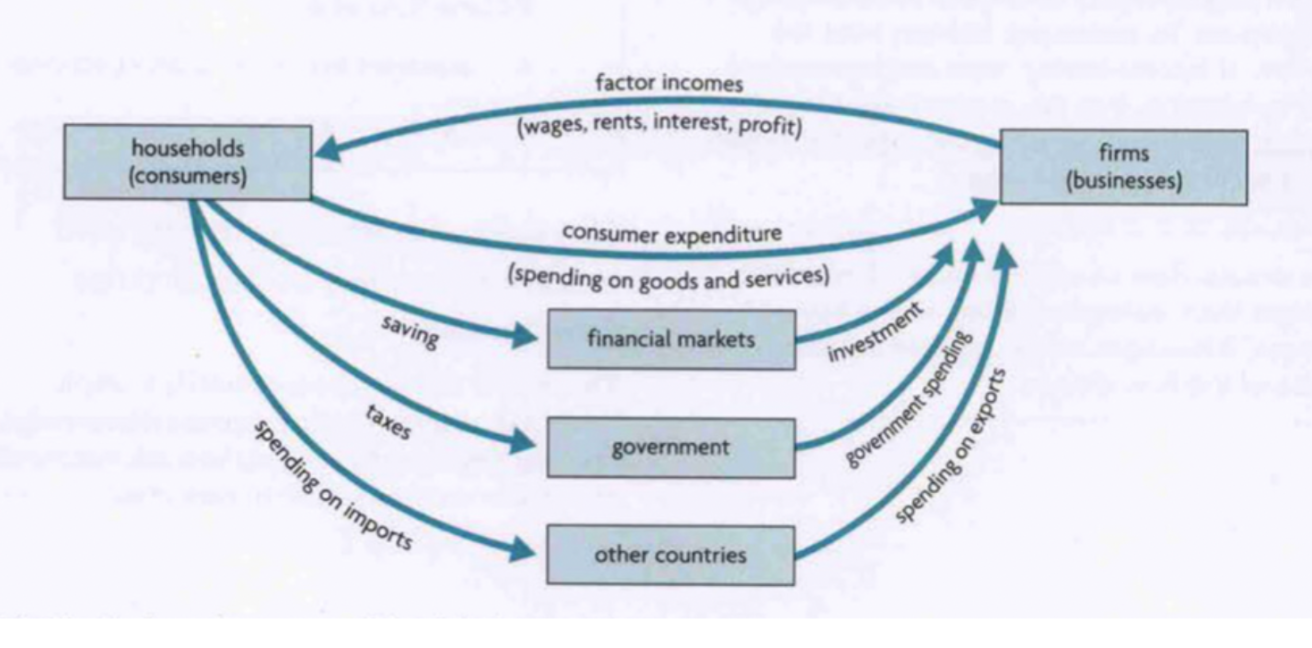
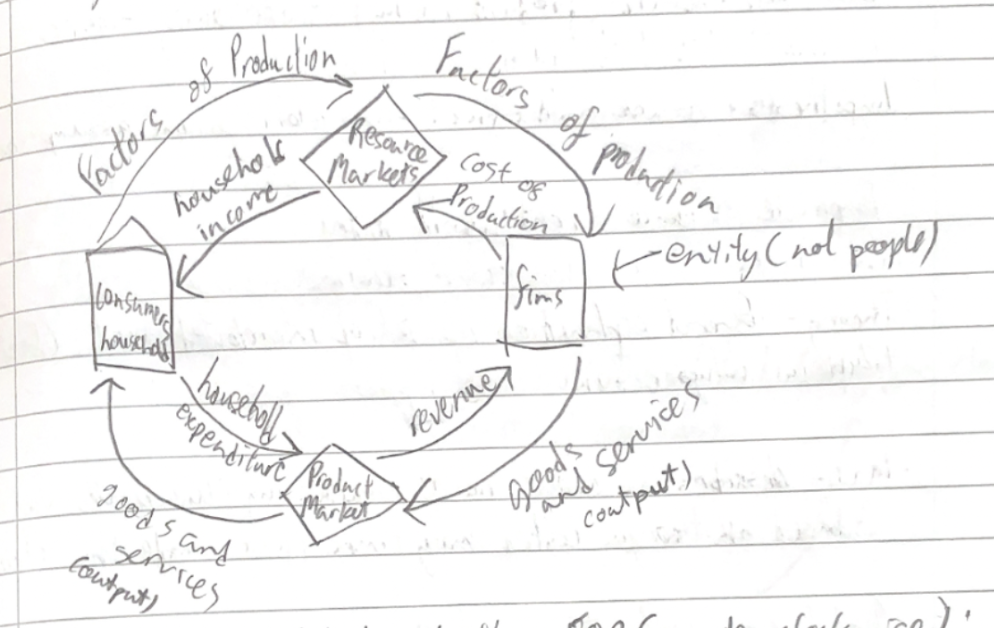
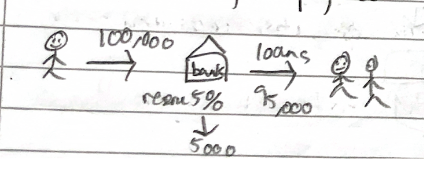
Circular flow of income model
mixed economy more gov intervention
Planned economy, no private sector -gov controls resource and product sector
Behavioral econ ctritizes this

Cognitive biases
systematic influences in thinking

Limits to rationality
Bounded rationality - Limits in ability to process all information, thus consumers seek a satisfactory outcome instead of the best
Bounded self-control: People are self contorled only within limits
Bounded selfishness: selfish within limits
Imperfect information
Nudges
when have limited finances do
Choice architecture
framing to influence choice
Illusion of free choice

Pros of behavioral econ
Create more socially responsible outcomes


Cons of behavioral econ
Like a gov regulation but disguised as choice
Unexpected outcomes Electricity neighbours comparison People who spent lower, will spend more
Not in individuals benefit

Growth maximiztion for firms why?

satisficing
A decision-making strategy where one chooses the first option that meets the minimum requirements, rather than seeking the optimal solution.
For firm: Instead of maximizing one objective achieve satisfactory result from multiple
Critiques of rational behavior


Demand

Law of diminishing marginal utility
the principle that consumers experience diminishing additional satisfaction as they consume more of a good or service during a given period of time

Shifts of demand
Income
Preference
Substitute goods
Complementary goods
Number of consumers
Supply

* Quality/efficiency of FOP
* Tech advancements
* Price of goods
* competing for same resources
* Joint supply - products that result from use of other resources
* Producer price expectations
* Rising prices, may withhold supply from market
* Number of firms
* Government intervention
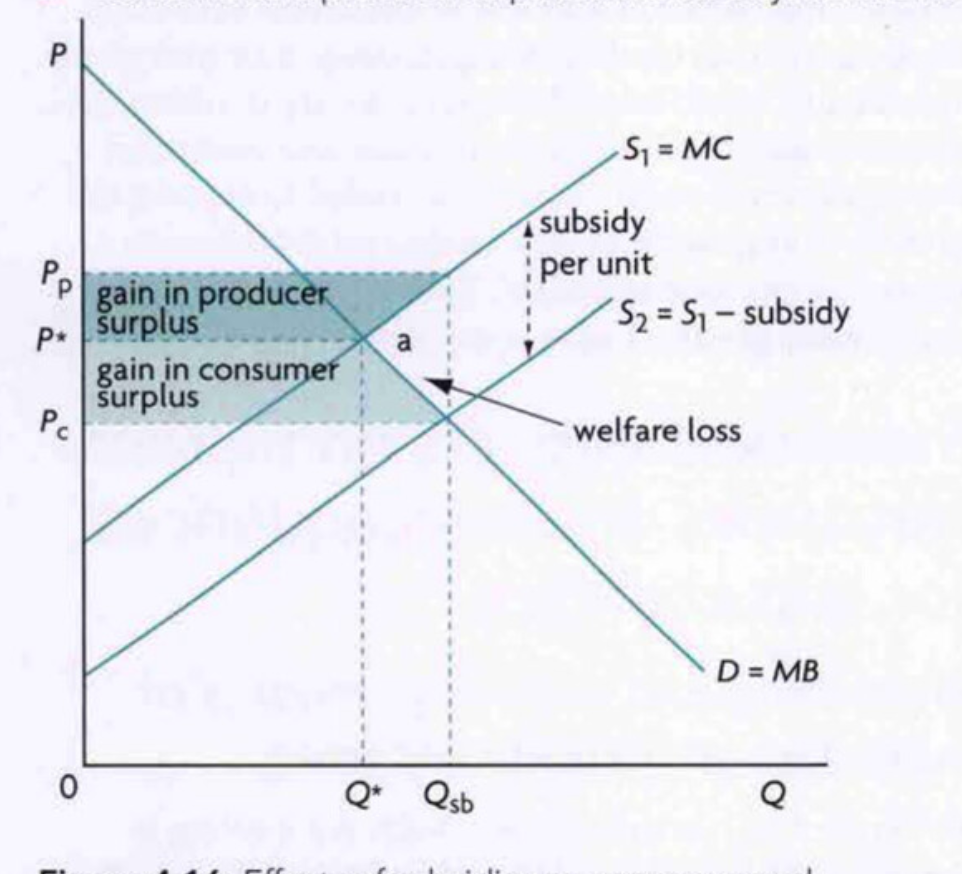
* Subsidies
* encourage production
* Indirect taxation
* decrease supply
* Taxes paid of G&S
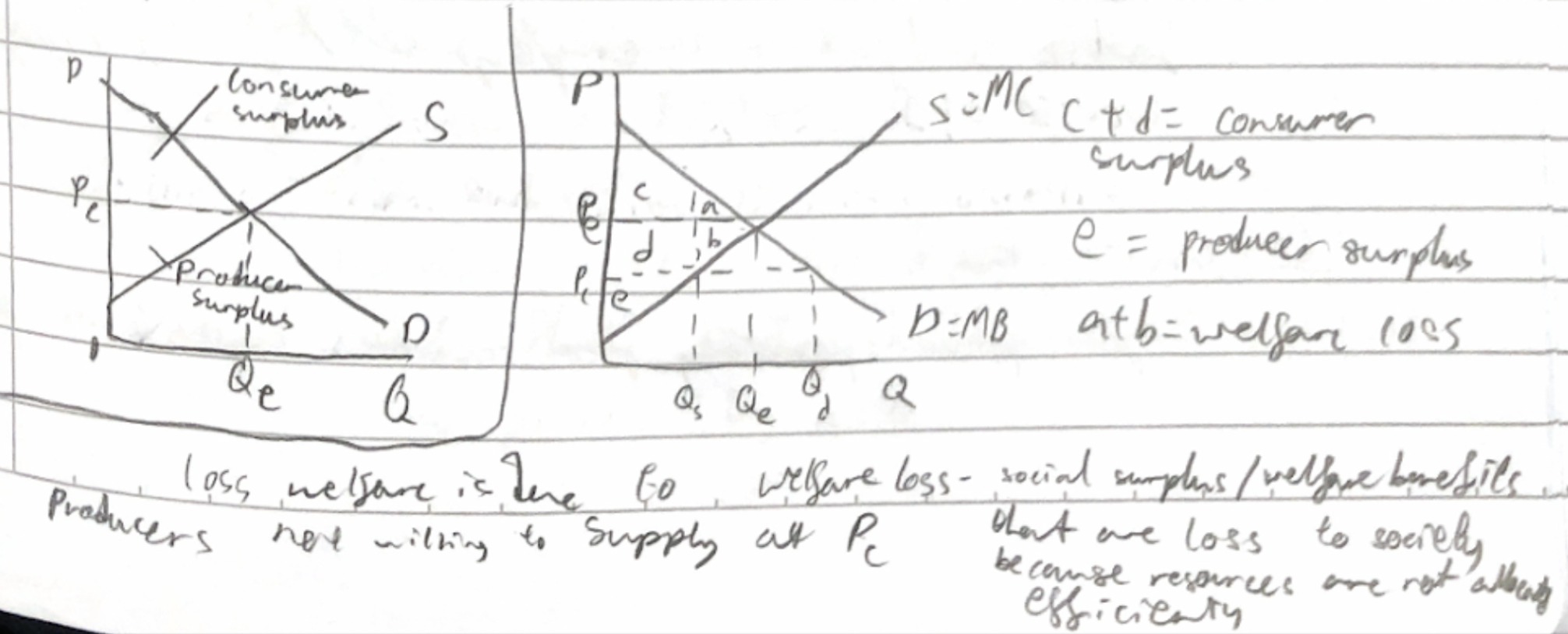
Allocative Efficiency
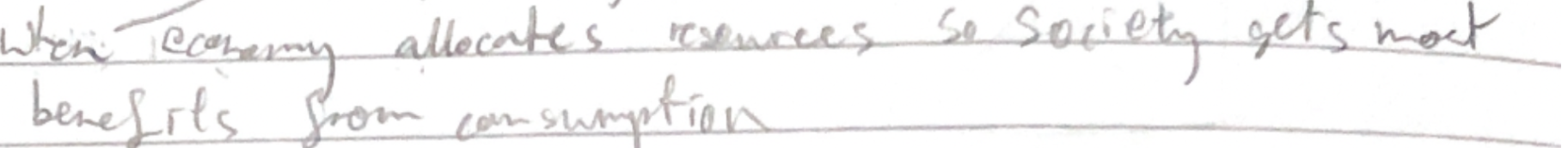
Consumer and producer surplus
When consumers pay price below willing and able to pay
When producers sell at price above willing and able
* Demand is MB because as each extra unit consumed, benefit decreases. So the curve shows how customers only willing to pay if price falls.
* Supply is MC because extra unit produced, cost increases. So price must increase to cover the costs (curve shows price willing to accept to produce additional unit)
\

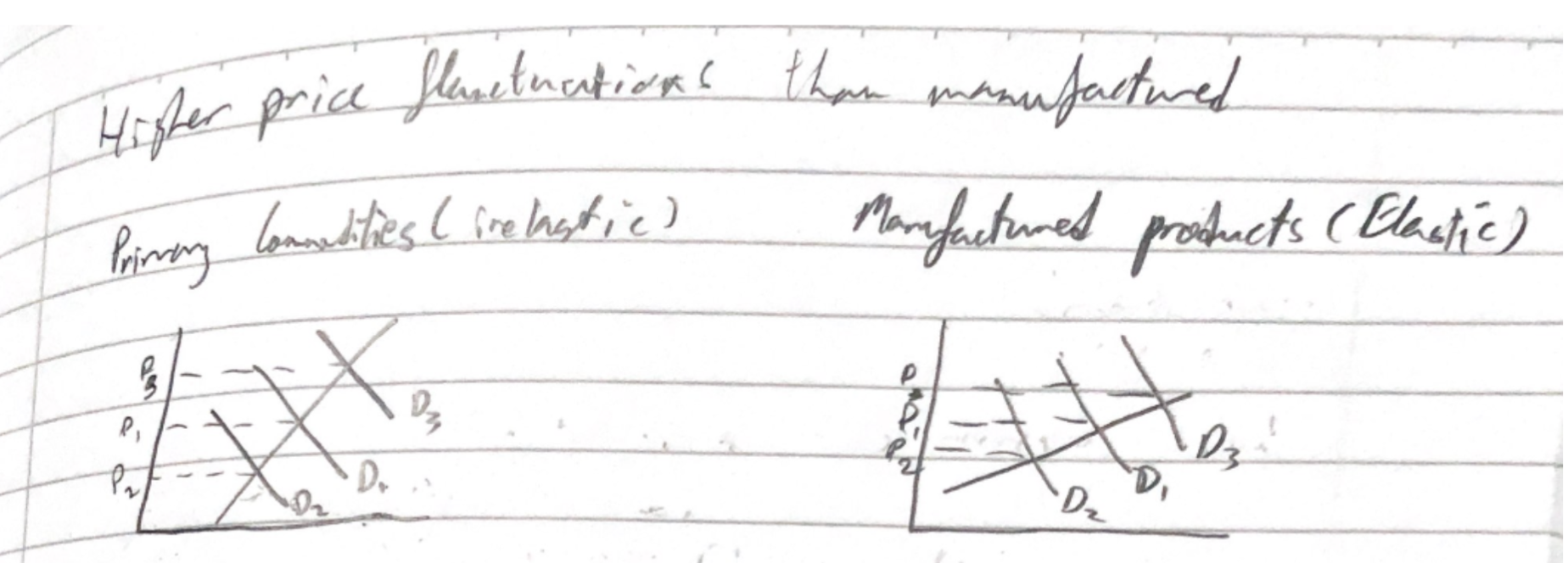
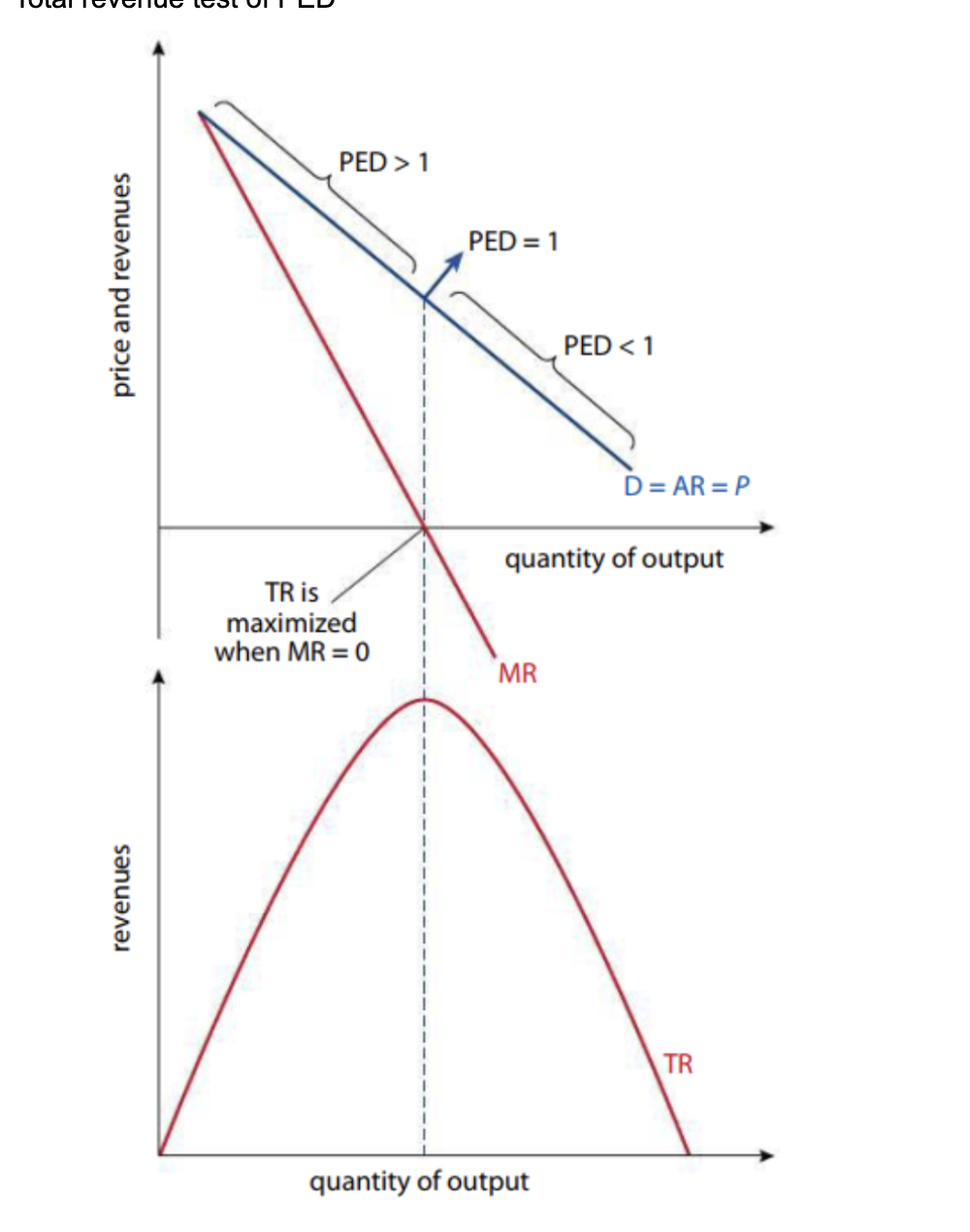
PED

elastic vs inelastic
More responsive to price changes
Less responsive
Lower price, less elastic - price so low no one cares
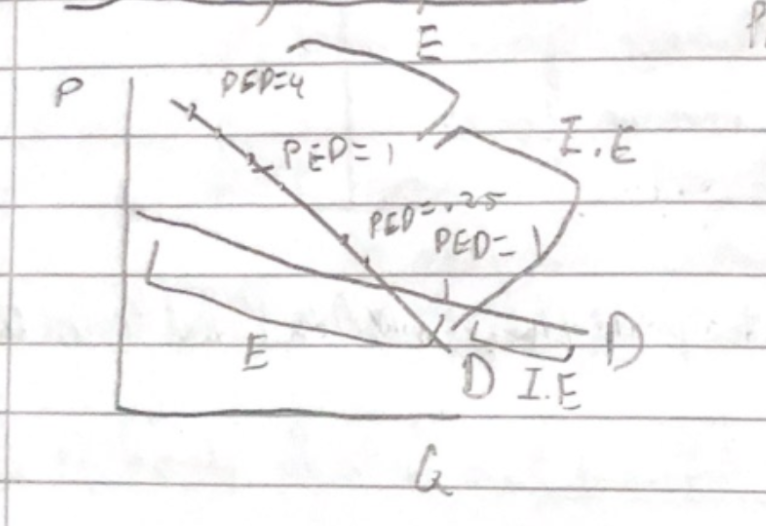
* More time = more elastic
* Have more time to respond
* SPLAT
* sub
* proportion
* Luxury
* Addiction
* Time

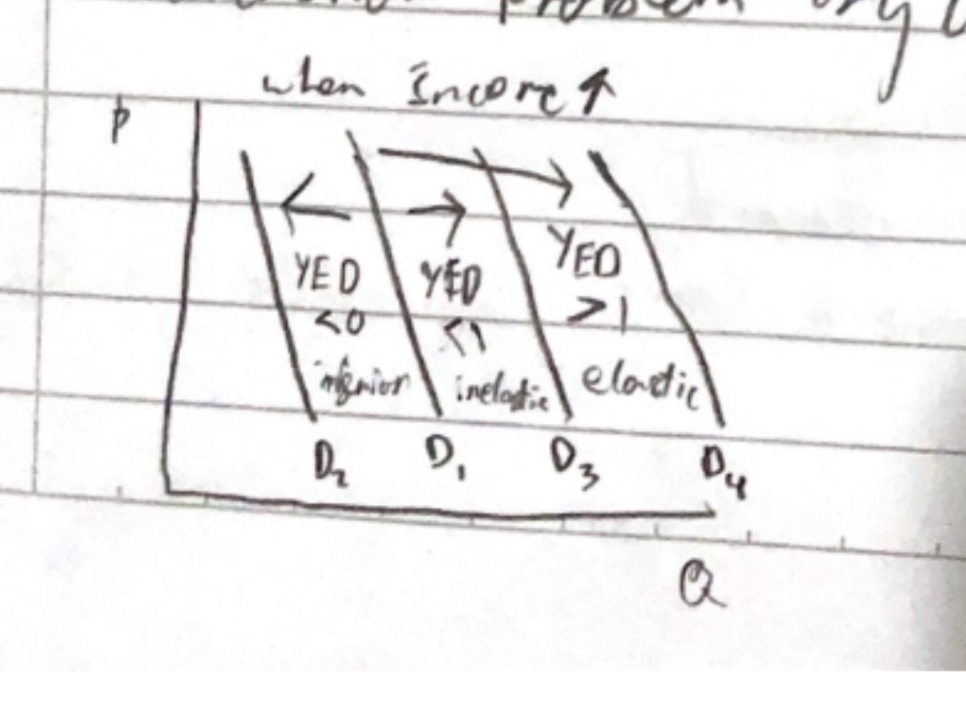
YED

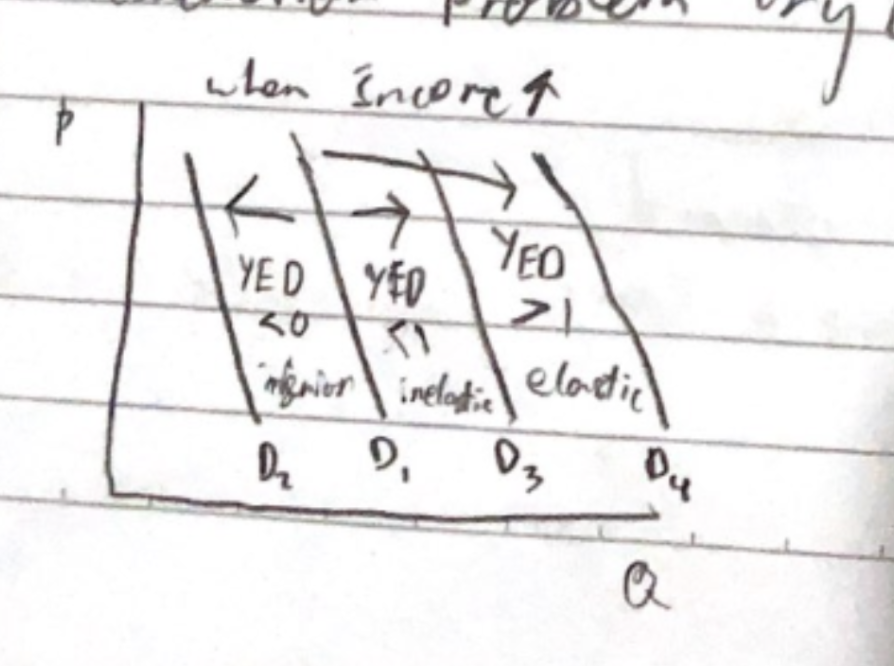

YED on the economy/industries

YED on recessions

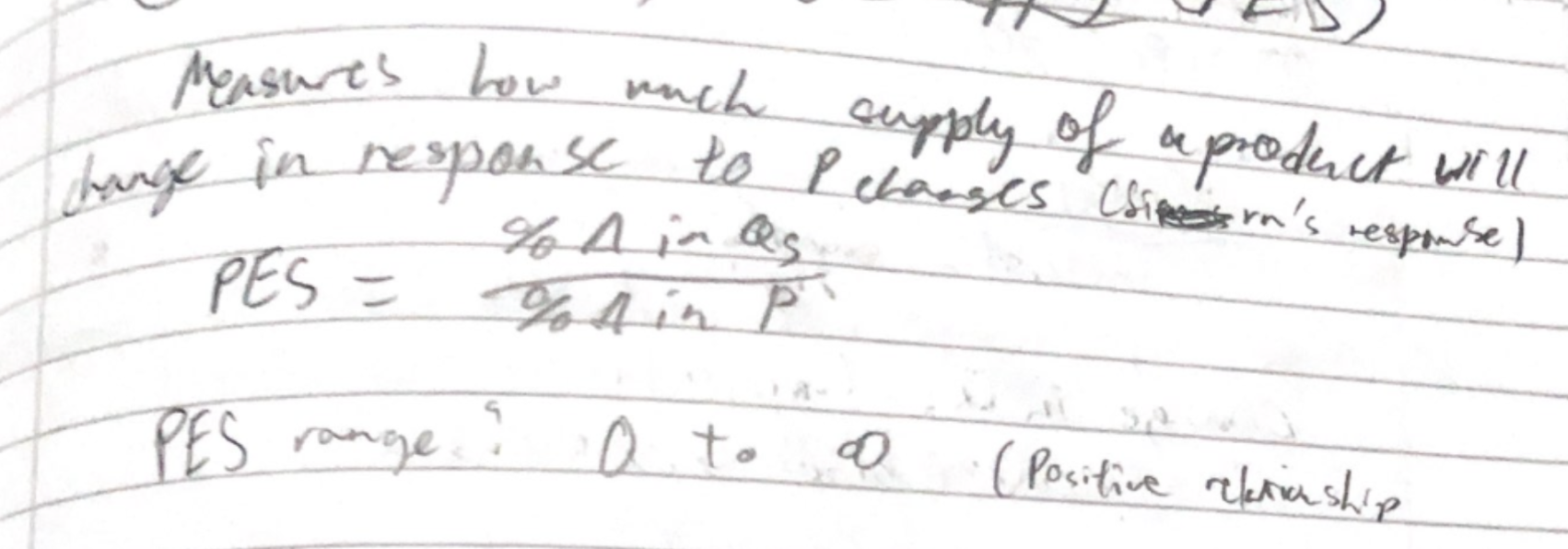

PES and graph intersecitons

* more time higher PES
* Mobility of FOP
* Ease of shifting FOP
* Spare/unused capacity of firms
* More capacity higher PES
* Ability to store stocks
* Quicker to react
* Rate of input cost increases
* Higher rate - lower PES
* Don’t want the costs, harder to get FOP
* \
* so gov will support

Why govs intervene + Methods
Tax revenue
low ped good
Support for firms
Smaller firms to be able to compete with larger
Encourage the production of certain good
Protect domestic firms
tariffs, import quotas
Trade protection measures
Support low-income households
Meet basic needs
Decourage production of certain good
tax
Influence consumption levels
Demerit merit goods
With subsidies, direct provision of goods, nudges, taxes
Command and control methods
compulsary education
Correct market failure
Not allocative efficient
Promote equity
Fairness
Helps redistribute income

Price ceilings - consequences, how it looks
Lower P
Lower Qs
Lower Rev
Higher Qd
Disequilibrium
Shortage
Not enough resources allocated

* Divide up resources
* no longer use price
* Underground markets
* Buying/selling that isn’t recorded
* illegal
* Those willing to pay more
Consumers gaining more benefit than cost of society to produce
* Consumers partially gain and lose
* Those buying lower price win
* Cannot then lose
* Producers are worse off
* Reduce price for substitute goods, using subsidies
* Or rationing good
* Shift s curve right
* Subsidies, less tax
* Direct provision
* Buffer stock


* Protect product markets
* Minimum wages
* Dispose surplus through
* Exports
* Storing
* Or just pay them the money but don’t produce good

* No incentive to reduce costs
* Overallocation
* Welfare impacts
* Consumers: a
* Producers gain from S above to Qs, below Pf
* F is not welfare loss bcs it’s gained through this
* Gov must buy the excess supply from Qs to Qd rectangle
* Welfare loss = rectangle-f
* Other countries
* Worse off for them bcs selling at lower price so may lower market price in world



* Tax burden
* shared by consumers and producers
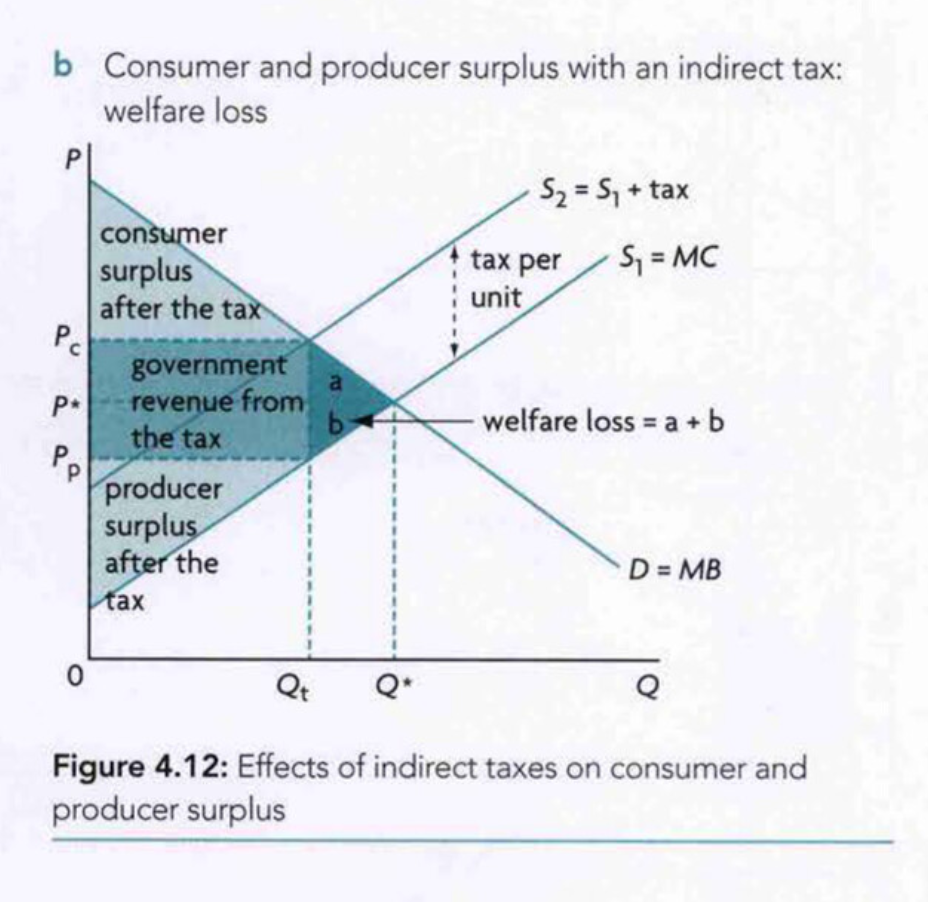


* Producer rev = Pp x Qsb
* Consumer surplus gained bcs of lower price
* Calculating
* just add on the surplus
* Producer: ((Pp - S1 int) x Qsb)/2
* Consumer: ((D int-Pc) x qsb)/2
* Foreign producers cannot compete with lower price
\
* No incentive to improve quality beyond standard
* Not applicable for all firms
* smaller firms cannot handle
* Large firms can lobby
* Sacrifice quality/effectiveness
* Not the most efficient in reducing environemental impacts
* Taxes better
* solutions to problems are well-known
Perfect comp Characteristics (HL)

Monopoly (HL)

Monopolistic competition (HL)

Oligopoly (HL)
homo or hetero

Competition and market power (HL)

Theory of firm (HL)
Firms acts in interest of maximizing profits
Calculating costs of firms (HL)

Perfect competition price and revenue graph (HL)
No influence on price
So must accept the market
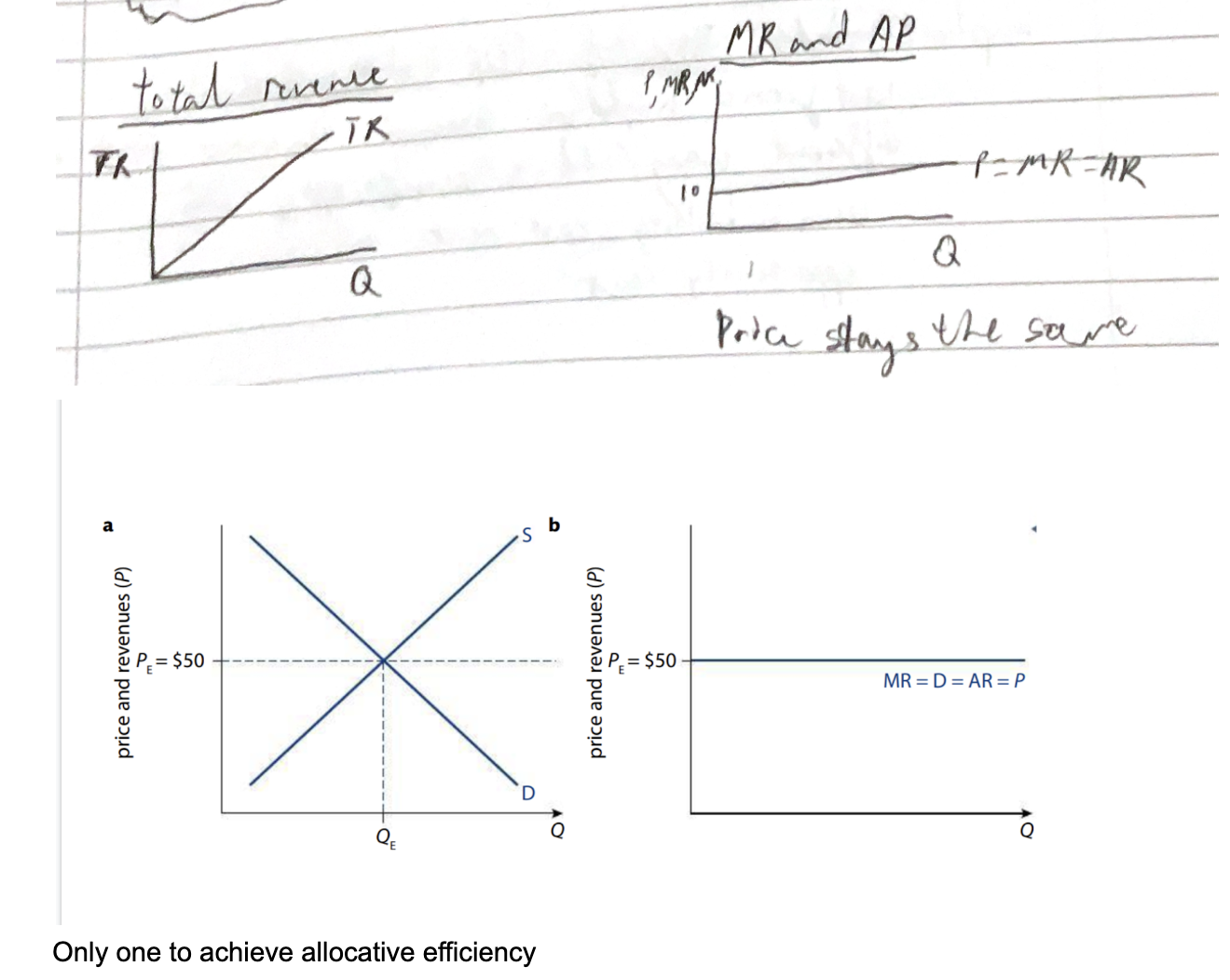
Non-Perfect competitiion revenue graph (HL)
MR. DARP
explicit vs implicit costs (HL)

MC vs AC (HL)


Long run AC curve - short vs long (HL)
Long run = normal profit in PC and MPC

Economies of scale (HL)
the property whereby long-run average total cost falls as the quantity of output increases / FOP increases
Profit (HL)
Short run only can have abnormal profit in Mon Comp and Perfect comp

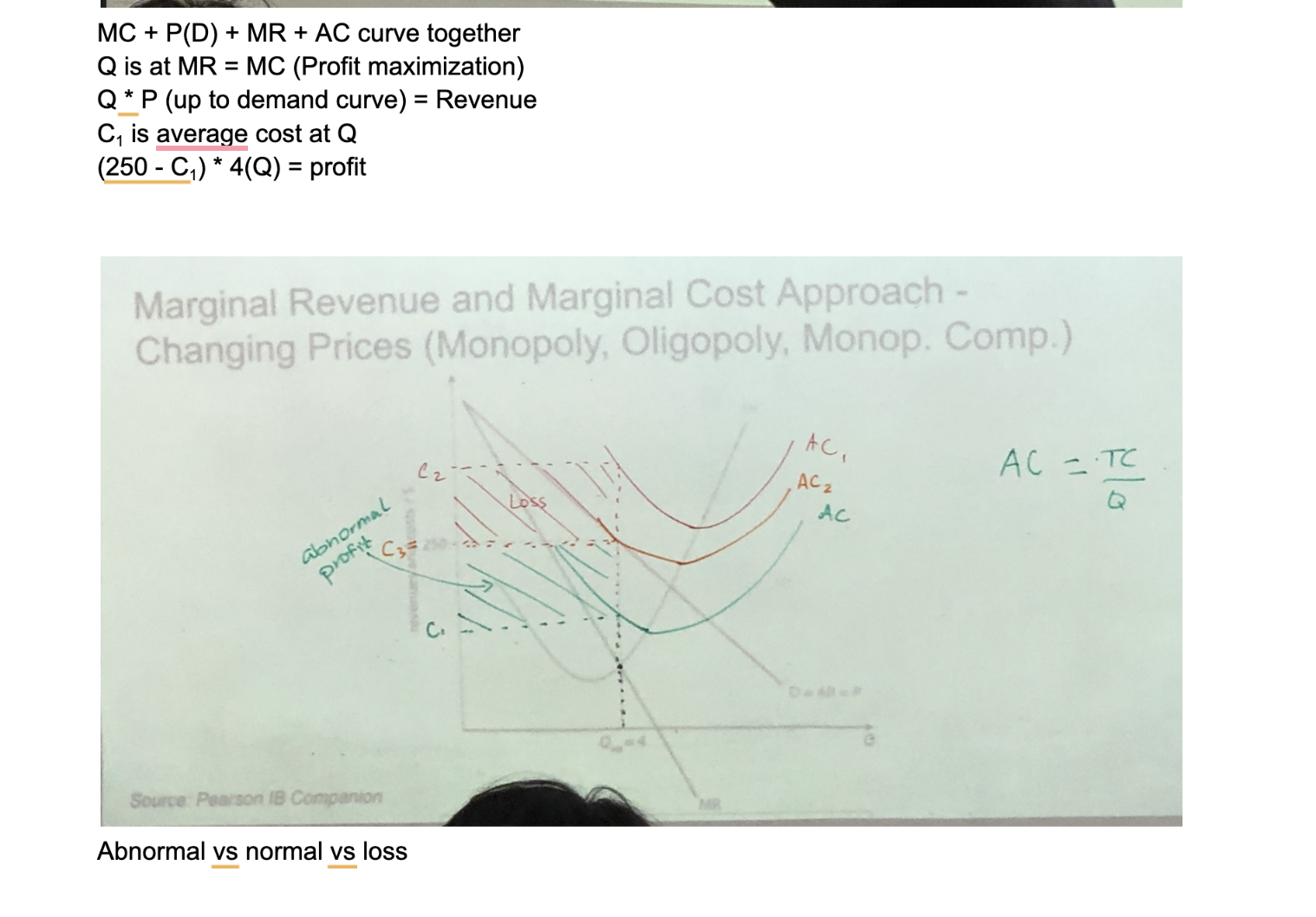
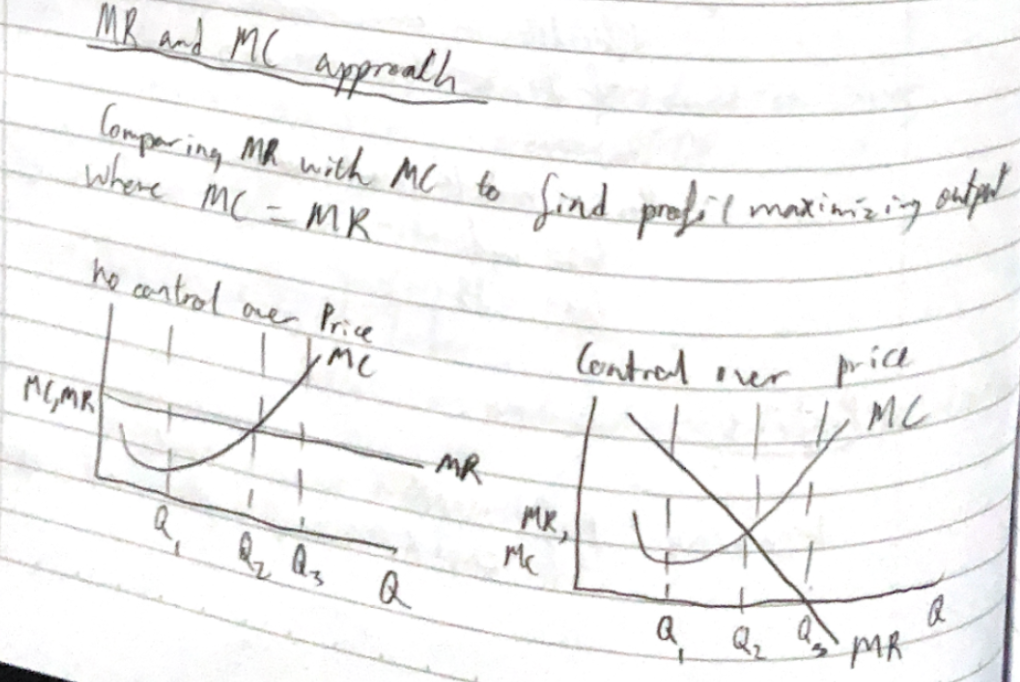
Profit max output (HL)
For non-perfect, need to go up to D
Normal profit meaning (HL)





* It is a loss of social benefits due to overproduction of the good caused by the externality.


* Carbon taxes
* Taxes on emissions
* Firms are incentivized to switch to greener sources
* Tradable permits
* Permits to pollute issued to firms
* over particular time period
* Traded in market
* Firms can sell the permits unused
* Incentivizes to switch
* MSC decrease


* need to determine cap
* cap too high, no effect
* too low, hardships for firms
* How to distribute fairly
* Big firms won’t feel cost of permits
* requires strong gov to uphold
* Taxes
* politically difficult
* How will it affect consumers
* low income cannot pay a higher price
* Large firms can just pay tax
* Identifying which pollutant is harmful and how to value the harm
* Countries
* Disadvantaging themselves against other countries
* Output will decrease
* If other country doesn’t use
* Malaysian haze, indo





