biology test 1
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
what is the endosymbiotic theory and what are the proofs of it?
the theory that states how eukaryotic cells were formed. It is proven because mitochondria and chloroplast have their own DNA
what organelles are unique to animal cells?
centrosomes and lysosomes
what organelles are unique to plant cells?
chloroplast, cell wall, vacoule
why do functional groups affect the properties of macromolecules?
Functional groups affect the bonds that hold a macromolecule together and determines the shapes of the macromolecules
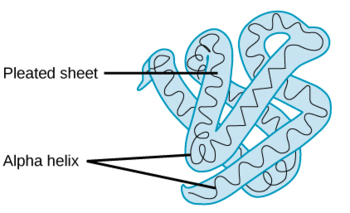
what level of organization is this?
tertiary protein structure- when the certain attractions are present between alpha helices and pleated sheets
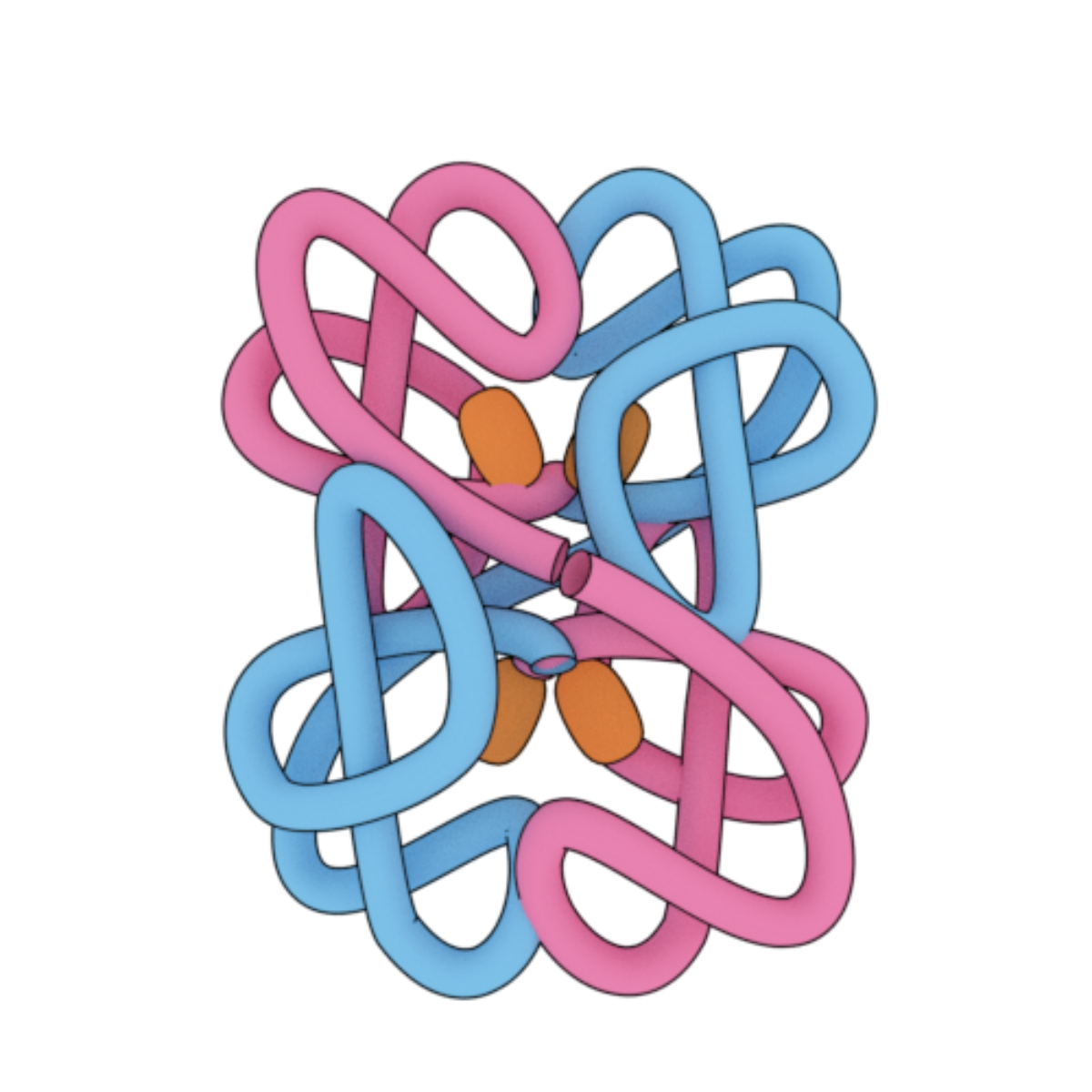
what level of organization is this?
quaternary protein structure- a protein consisting of more than 1 animo acid chain

what level of organization is this?
secondary protein structure- when the sequence of amino acids are linked by hydrogen bonds
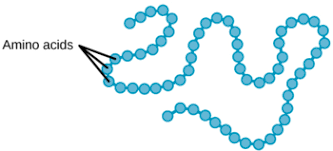
what level of organization is this?
primary protein structure- a sequence of chained amino acids
what is the organization of biology?
atom ➡ molecule ➡ organelle ➡ cell ➡ tissue ➡ organ ➡ organ system ➡ organism ➡ population ➡ community ➡ ecosystem ➡ biosphere
what is the type of microorganism are not considered living and why?
Viruses because they need a host to live
what are the 3 tenents of cell theory?
cell is the basic unit of life
all cells come from other cells
all living things are made of cells
what is the main difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
prokaryotes lack organelles while eukaryotes have membrane bound organelles
deductive reasoning is ___
general to specific
inductive reasoning is ___
specific to general
isotopes are atoms of the same element but differ in the number of?
Neutrons
Covalent bonds ___
SHARE electrons
ionic bonds ____
transfer of electrons
Organic compounds MUST contain ____
carbon
what are the chemical components / elements of the 4 macromolecules
CHO (carbs and lipids) ,CHON with a little bit of S (proteins), CHONP (nucleic acid)
what type of bonds are used in secondary protein structures
Hydrogen bonds
what type of bonds are used in primary protein structures
peptide bonds
Domain is ____
the structural and functional unit of the protein
what are the different functions of proteins?
enzyme catalysis, defence, transport, support, motion, regulation, storage
what is a triglyceride composed of?
what is the phospholipid layer composed of?
2 fatty acids + 1 glycerol + 1 phosphate
(hydrophobic tails, hydrophillic head)
What type of bond do unsaturated fatty acids have?
double bond
what type of bond do saturated fatty acids have?
single bond
where is cellulose located?
cell walls of plants, along with chitin
how many types of amino acids are there?
20 types
the movement of water from an area of high concentration to low concentration through a membrane is?
osmosis
animal cell walls are composed of:
cellulose
chitin
peptidoglycan
glucomannin
none of the above
none of the above! animals dont have a cell wall
blocking ribosomes prevents ____
protein assembly
what biomolecules contain peptide bonds?
proteins
the removal of water to form a chemical bond is called ____
dehydration synthesis
what type of amino acids would you expect to find in the transmembrane protein of a membrane protein
non polar amino acids
phospholipids are synthesized in the ____
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
how would you determine if cells are prokaryotic?
presence of a nucleus
true or false:
DNA bonds together through hydrogen bonds
true
how is the sodium potassium pump able to move ions against their concentration gradients?
expending ATP since its active transport
a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, which way will the water move? (water moves from high concentrations to low)
out of the cell
what is the process of the scientific method
observation, hypthesis, experiment, conclusion, theory
what are the characteristics and definitions of living organisms?
organization- cellular and ordered complexity
sensitivity- responds to stimuli
growth, development, reproduction- mitosis, sexual and asexual reproduction
energy utilization- producers, consumers, decomposers
homeostasis- maintain constant internal conditions
evolutionary adaptation- adapting to enviornment
what are taxonomy domains?
how animals are classified
what are the 3 main domains?
Archea, bacteria, and eukarya
what are ions?
charged particles with an unequal number of electrons to protons
What are cations?
atoms with MORE protons than electrons (net positive charge)
What are anions?
atoms with FEWER protons than electrons (net negative charge)
what are covalent bonds?
The sharing of electrons between elements
what are the two types of covalent bonds?
Nonpolar covalent bonds & polar covalent bonds
Nonpolar covalent bonds have
EQUAL sharing of electrons
Nonpolar covalent bonds have
UNEQUAL sharing of electrons
Ionic bonds ___
transfer of electrons
Electronegativity
an atoms affinity for electrons , difference in this dictates how electrons are distributed in covalent bonds
what are the properties of water?
high specific heat
high heat of vaporization
polar solvent properties
reactivity
organization (think hydrophilic and hydrophobic)
water can form ions
acids are
proton DONORS, they produce H+ in the solution
Bases are
proton ACCEPTORS, they produce OH-
motifs are ___
common elements of secondary structured proteins that are used to determine the function of the unknown protein
what is the function of the nucleus?
controlls the overall activity of the cell
what is the function of the plasma membrane
its a semi permeable phospholipid bilayer
what is the cytoplasm composed of
cytosol, salts, and organic material
what is the function of the cytoskeleton
holds the cell together
what is the function of the nuclear envelope
allows mRNA and proteins to move in the nucleus
what is the function of the nucleolus
produces and assembles the cells ribosomes
what is the function of the ribosomes
protein synthesis
what is the function of the rough ER
protein synthesis
what is the function of the smooth ER
lipid synthesis
what is the function of the mitochondria
powerhouse of the cell
what is the function of the chloroplast
energy producing organelle in plants and eukaryotic cells that carry out photosynthesis
what is the function of the golgi body
packages proteins and lipids
an acid with a pH of 3 is how many times more acidic than an acid with a pH of 6?
1000 times
the building blocks or monomers of nucleic acid molecules are called
nucleotides
the main characteristic that all lipids have in common is that?
they do not dissolve in water
What is the name of the process during which a bond between two monomers is broken?
hydrolosis
A dehydration synthesis reaction is the process in which ?
Water molecules are produced as a polymer is formed from monomers
The flow of genetic information in a cell, proceeds in what direction?
DNA -> RNA -> Amino acids
What is the main reason for cells being relatively small sized?
Surface area advantage to exchange material across plasma membrane
Plasmodesmata in plants and gap junctions in animals are functionally similar in that?
They form channels between cells that allow diffusion of small molecules