Quiz Topic 3, Constitution, & Spirit of 87'
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Flexibility
constitution has to be able to change over time
Convention
special legislature with a more narrow purpose (alt. to legislatures)
checks & balances
interdepending of the branches
What was the delegates of Spirit of 87 main goal
Fix problems of AOC, determine what makes a gov legitimate, political reality =create compromises
Characteristics of AOC
Too democratic, League of friendship among states, 2 delegates per state or max of 7, sovereignty in states, transitioned from a parliamentary, unicameral
Formal change
constitution change in words =amendments
8 amendments known as
hanging horse thiefs
Informal change
changing interpretation of constitution by Supreme Court ex: 8 amendment- not executing people for crimes anymore but nothing in the constitution changed physically
Amendment procedure- Article V
1)Proposal of legislation: - 2/3 both houses of congress, 2/3 of states call for national constitutional convention
2) Ratification: -3/4 state legislatures, ¾ state conventions (example of federalism)
-final approval of constitution, treaty, or amendment
What is the beauty of our amendment process
we can ratify any policymaking institution that is fundamentally out of whack
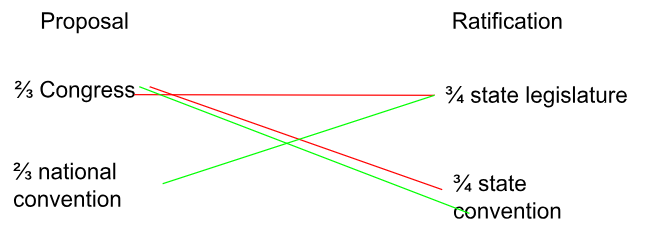
How many ways are there to amend?
4
2 things that are unamendable
congress cannot end international slave trade until 1808 (1.9.1), equal representation of senate (article v)
Shays Rebellion
people fought in revolutionary war and didn’t get paid back, taxes were I and farmers were going into debt because they weren’t paid back, farmers had guns from war and tried to stop judges chanting “no taxation w/out representation”, Habes Corpus was created
Constitution
nations fundamental law or “the supreme law of the land”, sets rules and basic principles, contains 27 amendments
Outline of U.S. Constitution
Preamble- purpose of the Constitution
Article I- creates the legislative branch
Article II- creates the executive branch
Article III- creates the judicial branch
Article IV- relations among the states
Article V- amending the Constitution
Article VI- national debts, supremacy of national law, and oaths of office
Article VII- ratifying the constitution
Types of Federal Courts
1) Constitutional- formed under Article 3 to exercise judicial power of U.S
2) Special- Article 1 courts, court of appeals, etc
6 basic principles of constitution
1)popular sovereignty- consent of governed, power to people
2)Limited gov-gov is restricted in what it can do
3)separation of powers- 3 equal branches
4)checks & balances-permits branches to check each other
5) judicial review-court determines constitutionality of gov action
6) federalism-written constitution separates power between central, national, regional gov
Framers ideas of limited gov
gov poses a threat to individual liberty, exercise of gov power must be restrained, to divide power is to curb it and prevent its abuse
bicameral
legislative body w/ 2 chambers
Executive article
article 2 of constitution that establishes presidency + gives executive power of federal gov to president
inferior courts
lower federal courts, under supreme court
constitutionalism
gov and governed must obey the law
rule of law
everyone is above law
veto
rejecting a bill
Spirit of 87
what is driving us, what do we value, electoral college is more complicated
power of federal gov
maintain army/ navy, declare war, coin money, regulate trade, make treaties
power of state
conduct elections, establish schools, reguluate business within a state, establish local gov, regulate marriage/divorce, assume powers
shared power between federal and state
enforce laws, establish courts, collect taxes, borrow money, secure pop., make laws, build infrastructure
Bill of rights
first 10 amendments
Implied power doctorate
congress has power that is “necessary and proper” to carry out powers because its something they can actually control ex: national bank isn’t mentioned in the constitution but its implied
Writ of Habeas Corpus
cannot be put in jail w/out explanation from the judge and there has to be an ok from them before anything
amendment
change/addition to constitution/law
executive agreement
binding agreement w/ law that does not require senate consent
syntax
pick a product and make less affordable ex: cigs
Northern vs. Southern States
-slave war-
N- didn’t want S to have > power because they wanted slavery
-3/5 clause: count a slave as 3/5 of a person (FEDERAL RATION IN AOC)
-fugitive slave clause: if a slave runs away, its the other states responsibility to return that slave to their original state
-1808 clause: we cannot end the international slave trade until 1808
Necessary and proper clause = implied power
treaty
formal agreement w/ 2 or more sovereign states
electoral college
select pres. and vice pres.
cabinet
advisory body to pres
senatorial courtesy
unwritten rule that is closely followed in the senate
advantages of federalism
-division of powers-
allows for local action in matters of local concern and national actions in wider concern, allows for differing circumstances among states, location enacts policies, allows for innovation in solving public policy issues, provides strength from union
disadvantages of federalism
lack of coordination via overlapping jurisidictions ex. natural disasters, controversial topics= unorganized efforts
Types of delegated powers
1) Expressed-(enumerated powers) spelled out directly in C
2)Implied- explicitly states in C but implied by expressed power
3) Inherent- any gov of any sovereign union would have
division of powers
geographic basis
reserved powers
powers not granted by constitution to national gov or deny states
-police power, power of state to protect public health, public morals, public safety, general welfare
concurrent powers
both national and state possess and exercise
-collect taxes, make laws, set punishments for crimes, take private property for public, build roads
Supremacy Clause *Linchpin of Constitution*
provision of U.S. C taht states federal treaties are the “supreme law of the land” (used to resolve problems of federalism and make it a working reality)
Admitting new states procedure
1) area residents ask congress to formally approve
2)area holds a convention to write a constitution (enabling act)
3)area voters and congress need to approve
4)congress passes an act of admission
5)president signs off
only congress has the power to admit
shared powers in federal system
federal grants in aid- federal $ or other resources to states, cities, counties,etc.
Types of federal grants to states
1) Block- used for broad purposes where states have freedom to decide how to spend the money ex: social services, transportation, education
2)Categorical- used for closely defined purposes w/ conditions set by federal gov ex: construction of airports, wastewater plants, support for senior citizens, distribution of school lunches
3)Project-used for individual projects that states, localities, and private agencies compete for ex:research into diabetes, implementation of an innovative educational program
enabling act
directs people to frame constitution as a step toward admission to the union
act of admission
admitting a state to the union
interstate compacts
formal agreement w/ consent of congress among states and foreign states
Full faith and credit clause (only civil not criminal matters)
requirement that each state accept public acts (laws of a state), records (documents like birth certificates), and judicial proceedings (outcome of court decisions)
extradition
legal process which a fugitive from justice in one state is returned to that state
Priveleges and immunities clause
all citizens are entitled to certain “priveleges and immunities regardless of their state of residence
bigamous cohabitation
marrying and living together while a previous marriage is still legally in effect
bonafide (lowkey irrelevant but just incase)
good faith (relates to nevada in reading)