PSYC1004 Biological Psychology ANU
1/194
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
195 Terms
What is biological psychology
Scientific study of behaviour and mental processes
Five perspectives to studying biological psychology
Describing the behaviour
Evolution of behaviour
Development of behaviour over the life span
Mechanisms of behaviour
Application of biological psychology
Three approaches to studying biological psychology
Somatic intervention
Behavioural intervention
Correlation
Somatic intervention
Manipulating body structure or function and looking for changes in behaviour
E.g., Administering a hormone, and measuring strength of mating behaviour
Behavioural intervention
Manipulating behaviour and looking for changed in body structure or function
E.g., Putting male in presence of female, measuring changes in hormone levels
Levels of analysis
Molecules
Synapses
Cells
Circuits
Brain regions
Systems
Organ
Social
Reductionism
The scientific strategy of breaking a system down into smaller parts to understand it
Biological explanations for behaviour
Physiological
Ontogenetic
Evolutionary
Functional
Peripheral nervous system
Lies outside the brain and spinal cord, and its responsibilities are the transmit information and carry out commands.
Divided into two systems;
1. Somatic nervous system
2. Autonomic nervous system
Somatic nervous system
Axons conveying information from sense systems to CNS, and back to muscles
What the autonomic nervous system controls
Controls heart, intestines, and other organs, aiming for homeostasis
What do neurons do
Send messages all over the body to allow everything we do.
Approximately 86 billion neurons in the human nervous system
Afferent axon/efferent axon/interneuron function
Afferent axons brings information into a structure
Efferent axons carries information away from a structure
Interneuron has its axon and dendrites within the same structure
Neuron structure
Dendrites, soma, axon, terminal buttons
Dendrites
Receives information from other neurons
Sends information to the soma
Soma
Contains nucleus, ribosomes, and mitochondria
Maintains cell health and metabolism
Receives information from the dendrites
Facilitates neurotransmission
Sends information to the axon
Axon
Receives information from the soma
Sends information to other neurons
Myelin sheath for efficient / rapid conduction
Protein / fatty substance that protects axons and helps with efficient / rapid conduction
Glion
Support cells
Types of glia
Astrocyte
Microglia
Oligendrocytes
Schwann cells
Radial
Resting potential of neuron
Neurons are covered by a membrane
H2O, O2, and CO2 can pass across the membrane
Membrane maintains an electrical polarisation between the inside and outside of the cell Inside is slightly more negative
Resting potential is the voltage difference between the inside and outside approximately 70 mV (millivolts)
Ionic concentration in neuron
The number of K+ is greater inside the neuron and Na+ is greater outside of the neuron
Action potential of neuron
Messages sent by axons are called action potentials.
Sub-threshold stimulation keeps the neurons at rest.
After 55mv threshold;
Rising: Rapid depolarisation, Na+ channels open
Peak: Na+ channels close
Felling: depolarisation, K+ channels open
Undershoot: hyper-polarisation, refractory period (1-4ms), and return to resting potential
Synapse
Synapse is a small gap between two neurons
Presynaptic neuron
Neuron that delivers synaptic transmission
Postsynaptic neuron
Neuron that is stimulated by events at the synapse
Neurotransmitters
Chemicals created in the axon or soma and diffused across the synapse
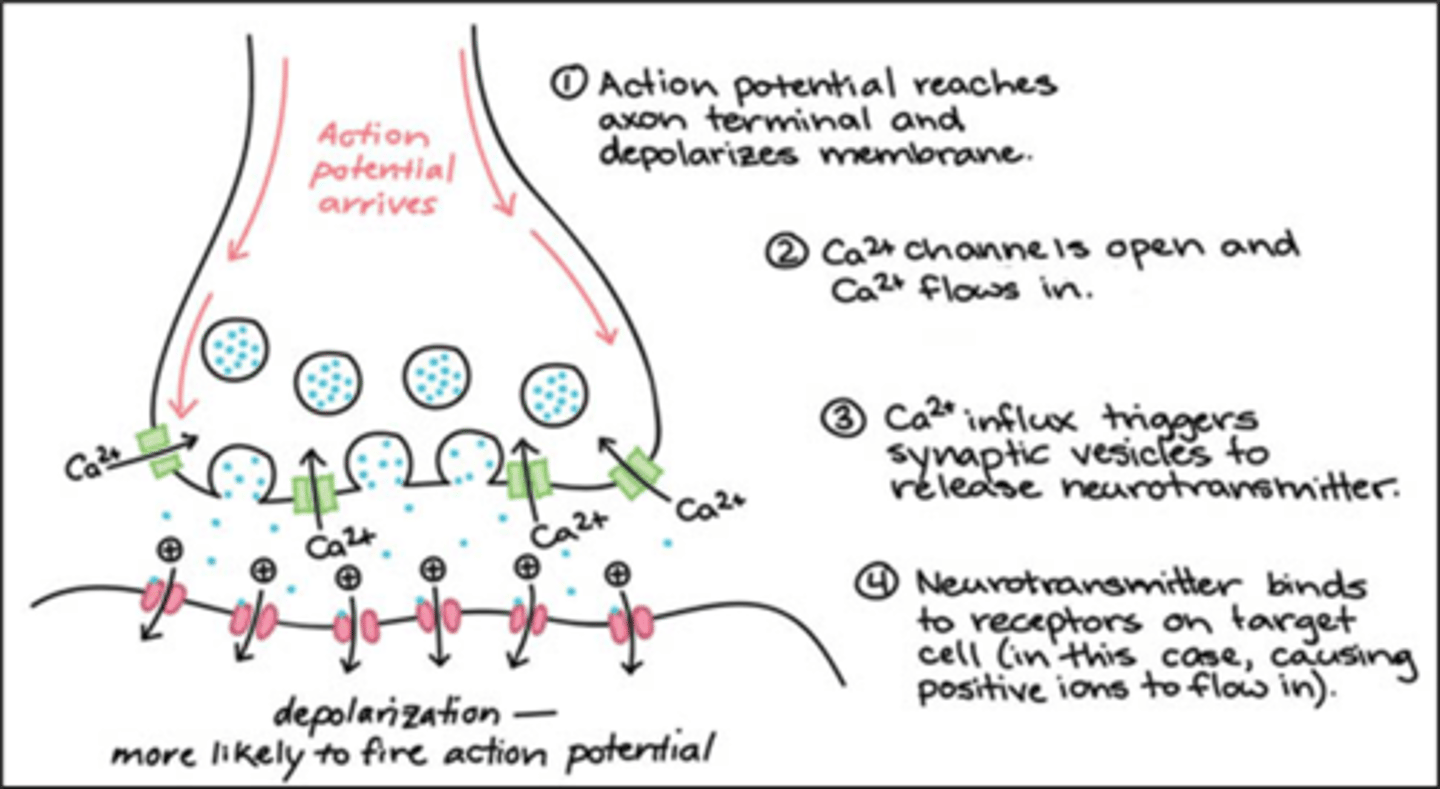
Synaptic transition process (~7 steps in detail)
1. Neurotransmitters are synthesised in the terminal buttons or soma, then stored there
2. Action potential arrives at the terminal buttons and opens the Ca+ channels and releases the neurotransmitters - called exocytosis
3. Neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the dendrites (or soma) of the post-synaptic neuron
- Neurons release many different types of neurotransmitters
- Neurotransmitters can bind to different receptor types, allowing for complex signalling
4. Neurotransmitters separate from the post-synaptic neuron
5. Neurotransmitters are reabsorbed by the presynaptic neuron
6. Postsynaptic neurons release retrograde neurotransmitters
7. Negative feedback sites respond to retrograde neurotransmitters
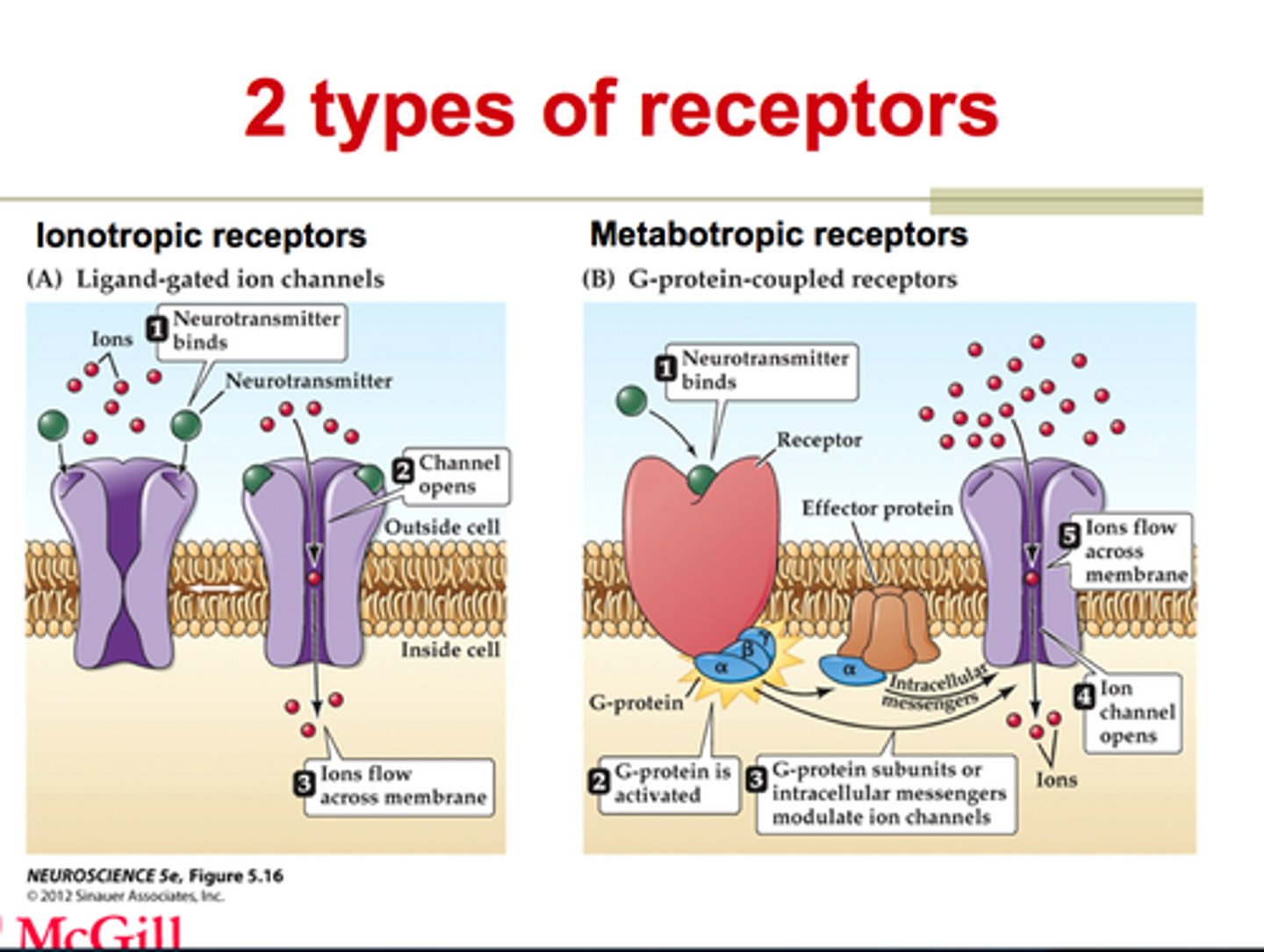
Types of neurotransmitter receptors
ionotropic receptors and metabotropic receptors
Ionotropic receptors
Receptor binding immediately opens ion channel
Directly affects the membrane
Very rapid signalling (1-20ms)
Short duration (100-500ms)
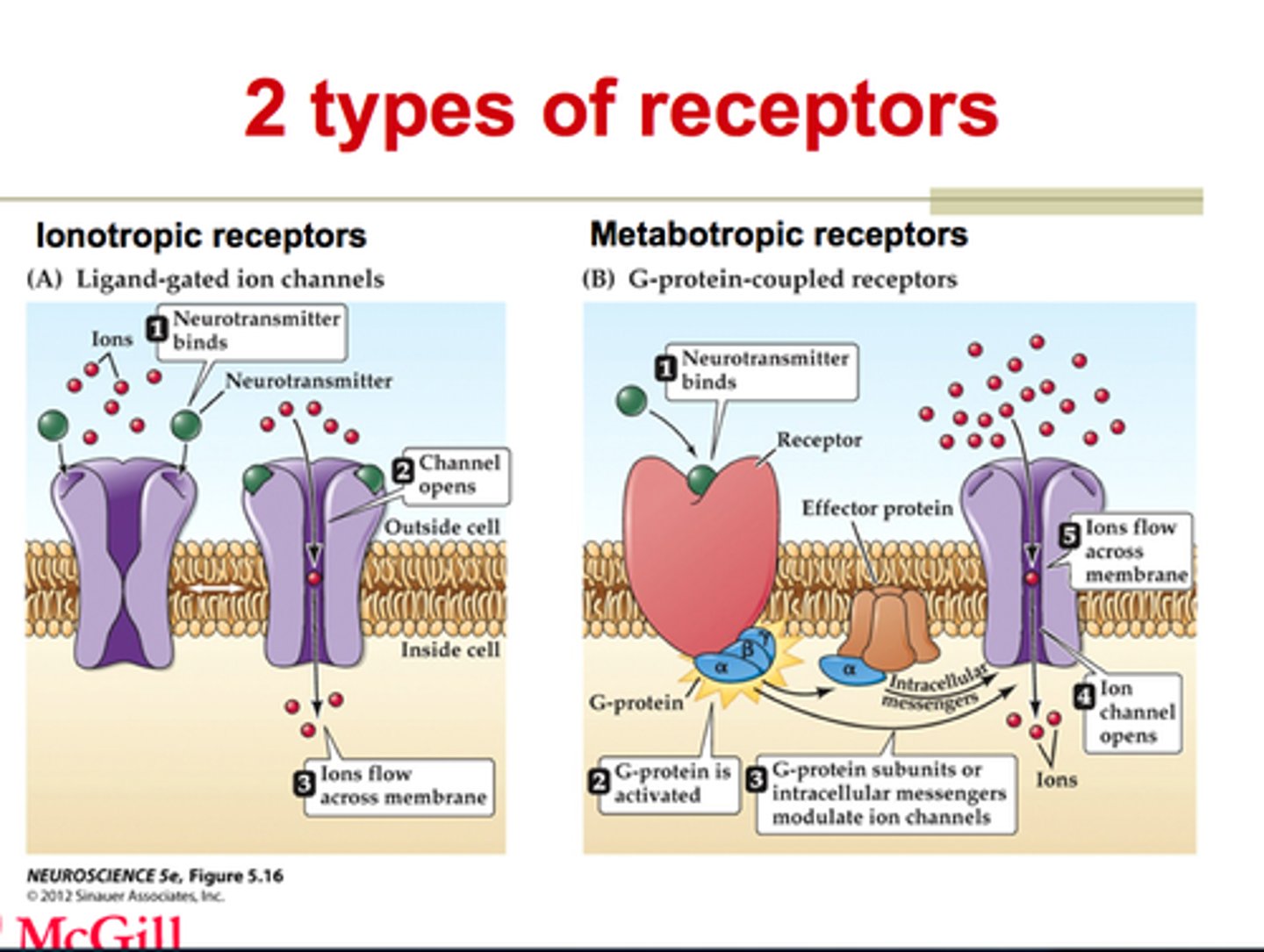
Metabotropic receptors
Receptor binding activates an intracellular messenger, without immediately opening
Intracellular messenger opens ion channel
Slower sequence of metabolic reactions (> 30ms)
Longer lasting (seconds, minutes, or longer)
Most common types of neurotransmitters
Glutamate and GABA
Glutamate
An excitatory neurotransmitter
Binds to NMDA and AMPA receptors
Causes an. Excitatory post-synaptic potential
GABA
An inhibitory neurotransmitter
Binds to GABA receptors
Causes an inhibitory post-synaptic potential
Excitatory postsynaptic potential
Makes the postsynaptic neuron more likely to produce an action potential
Inhibitory postsynaptic potential
Makes the postsynaptic neuron less likely to produce an action potential
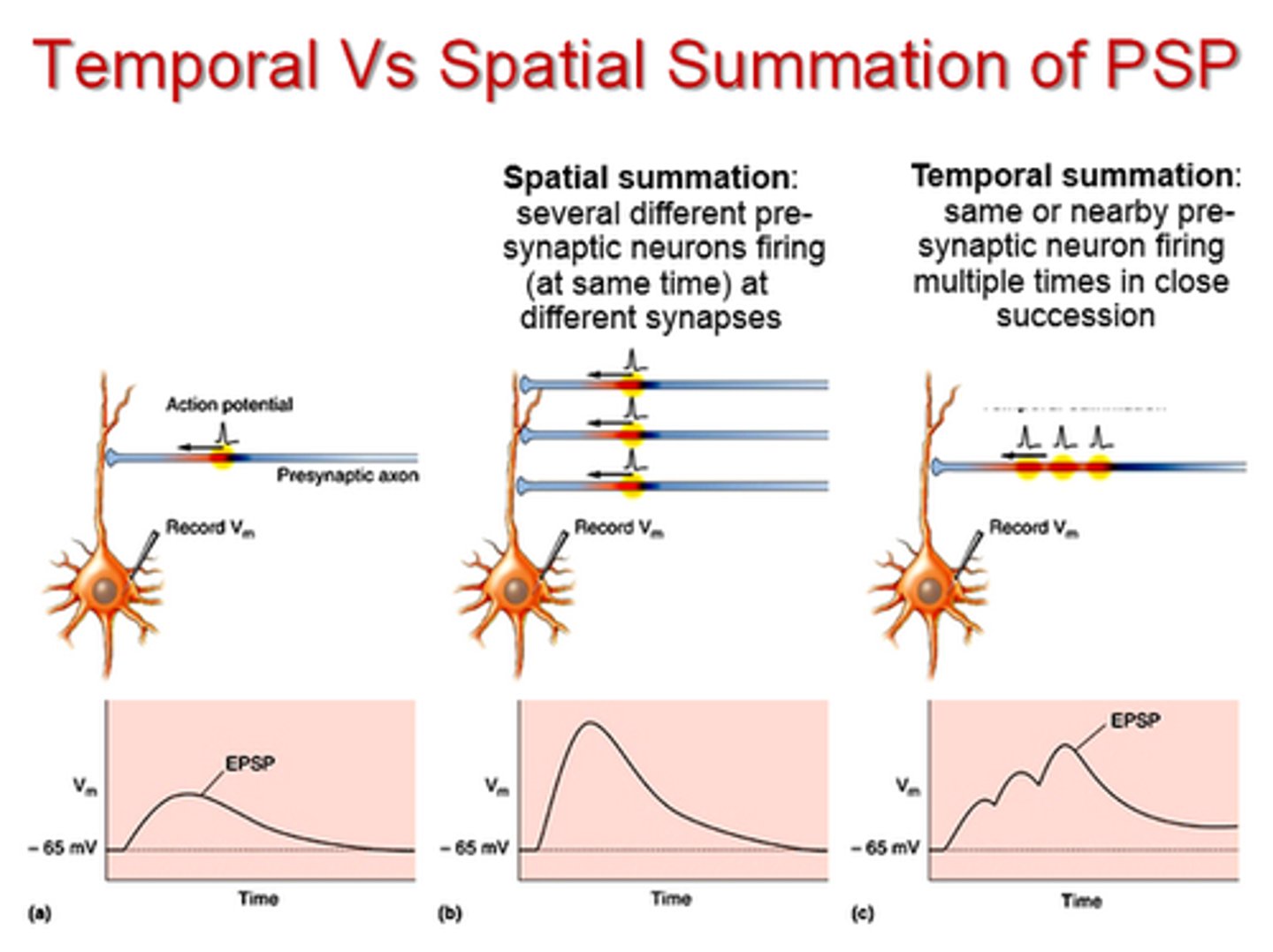
Types of summation
spatial summation and temporal summation
Spatial summation
summing potentials that arrive at different synapse
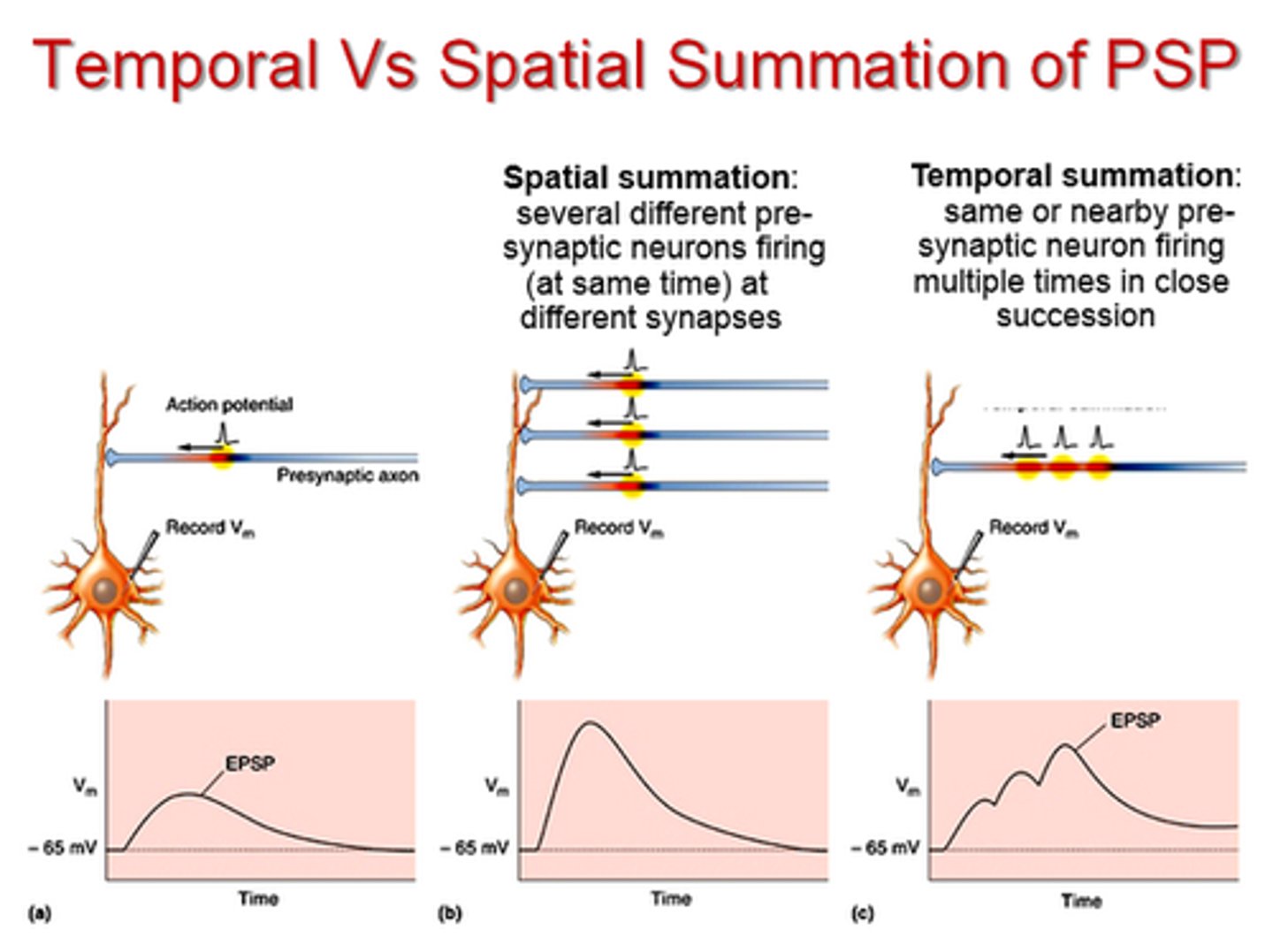
Temporal summation
summing potentials that arrive at different times at the same synapse
Neuromodulators (drugs)
Do not excite or inhibit the neuron directly
Can increase or decrease the release of neurotransmitters
Effects can be widespread because they are released into extracellular fluid, ventricles, or bloodstream
Agonist drug
drugs that mimic or increase the effect of neurotransmitters
Antagonist drug
drugs that block the effect of neurotransmitters
Inverse agonist drug
drugs that decrease the effect of neurotransmitters
Inverse antagonist
drugs that activate the effect of neurotransmitters
Direct drugs
drugs that bind to neurotransmitter receptor
Indirect drugs
drugs that do not bind to neurotransmitter receptor
Drugs affecting the glutamate system and its effects
Phencyclidine and ketamine
Indirect NMDA receptor antagonist
Causes general anaesthesia in high doses
Causes hallucinogenic symptoms at low doses
Drugs affecting the GABA system and its effects
Alcohol, barbiturates, and benzodiazepines
Indirect GABA receptor agonist
Causes reduced coordination, depressed feelings, reduced anxiety/stress
Central nervous system
Spinal cord
Connects brain to rest of body Sensory nerved carry information from the body to the brain via spinal cord Motor nerves carry information from the brain to the body via spinal cord
The grey matter is densely packed with cell bodies and dendrites
- Neurons send axons to the brain
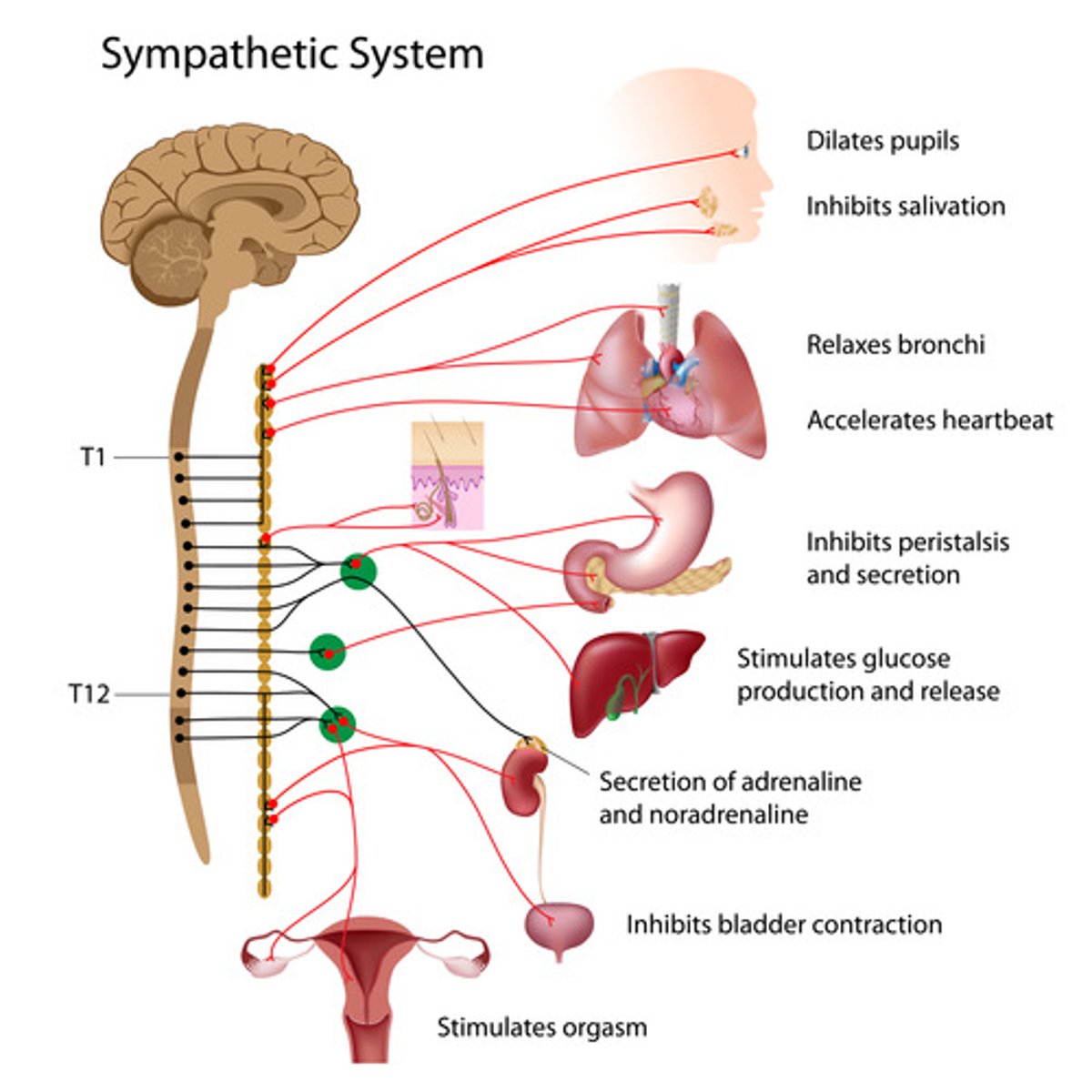
Autonomic nervous system is comprised of
sympathetic nervous system and parasympathetic nervous system
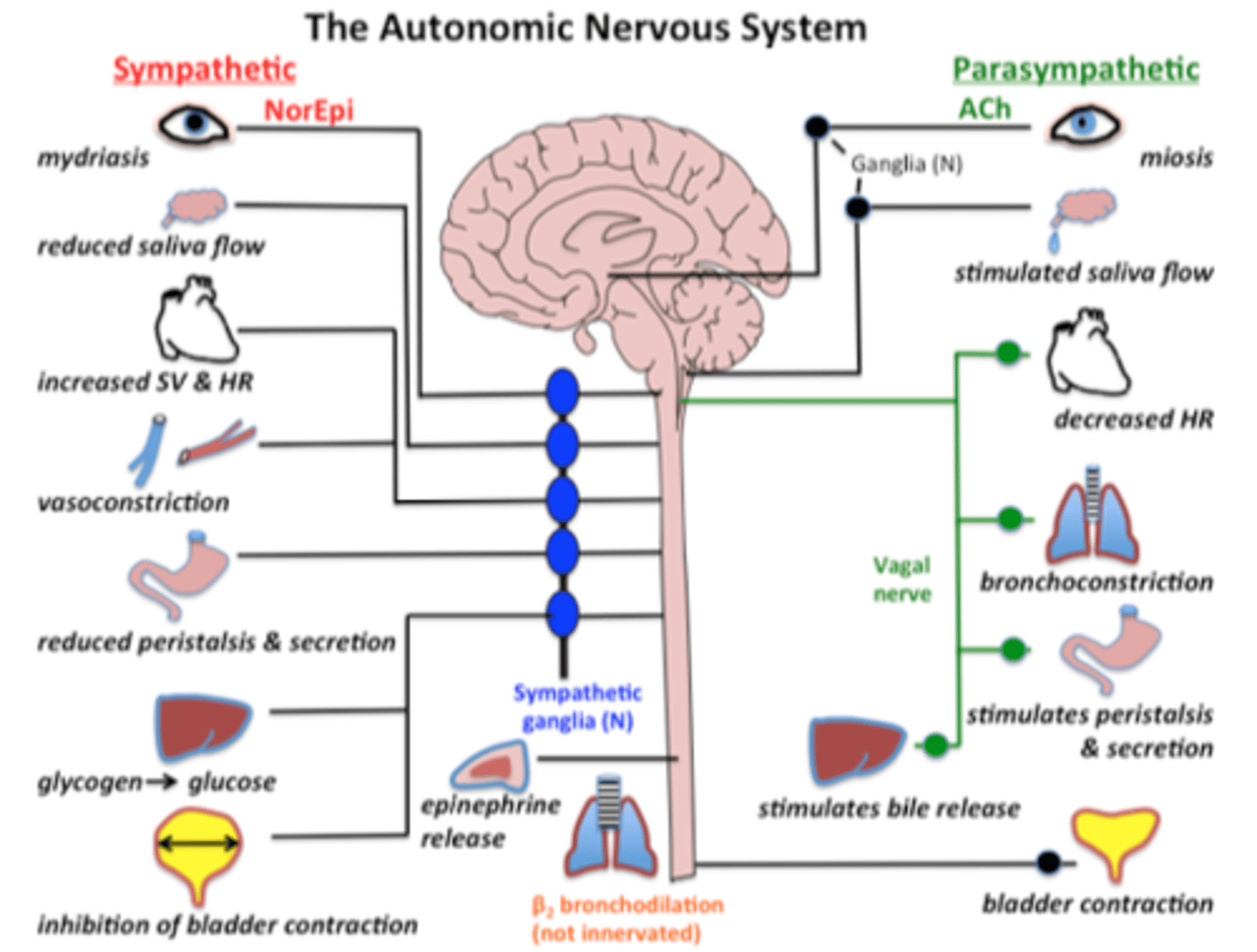
Sympathetic nervous system
Network of nerves that prepare the organs for rigorous activity Chains of ganglia
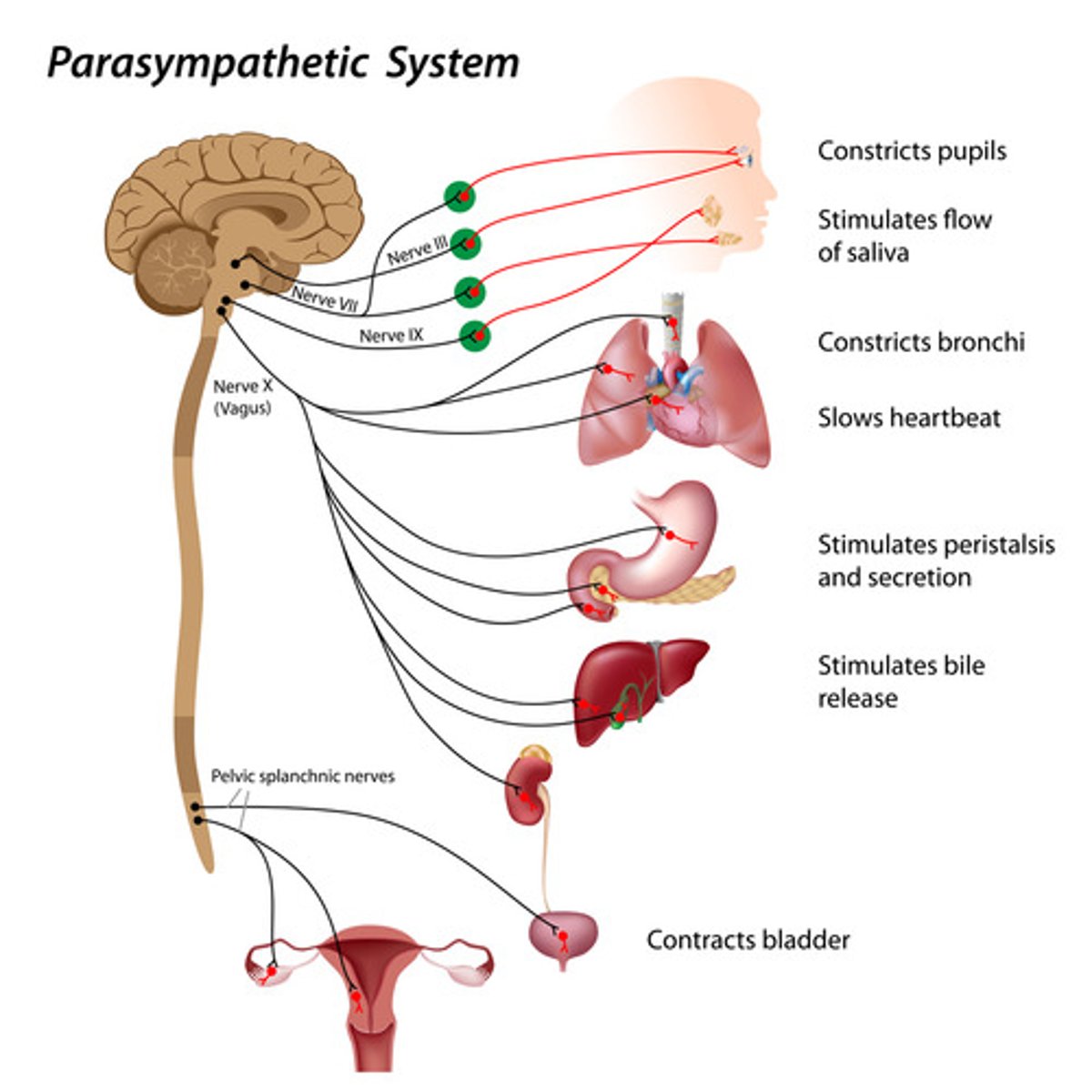
Parasympathetic nervous system
Facilitates vegetative, non-emergency response
Conserves energy
Anterior
In front
Posterior
Toward the back
Superior
Above another part
Inferior
Below another part
Lateral
Toward the side
Medial
Toward the middle
Coronal plane
Seen from front or back
Sagittal plane
Seen from side
Horizontal plane
Seen from above or below
Proximal
Close
Distal
Far
Ipsilateral
On same side
Contralateral
On opposite side
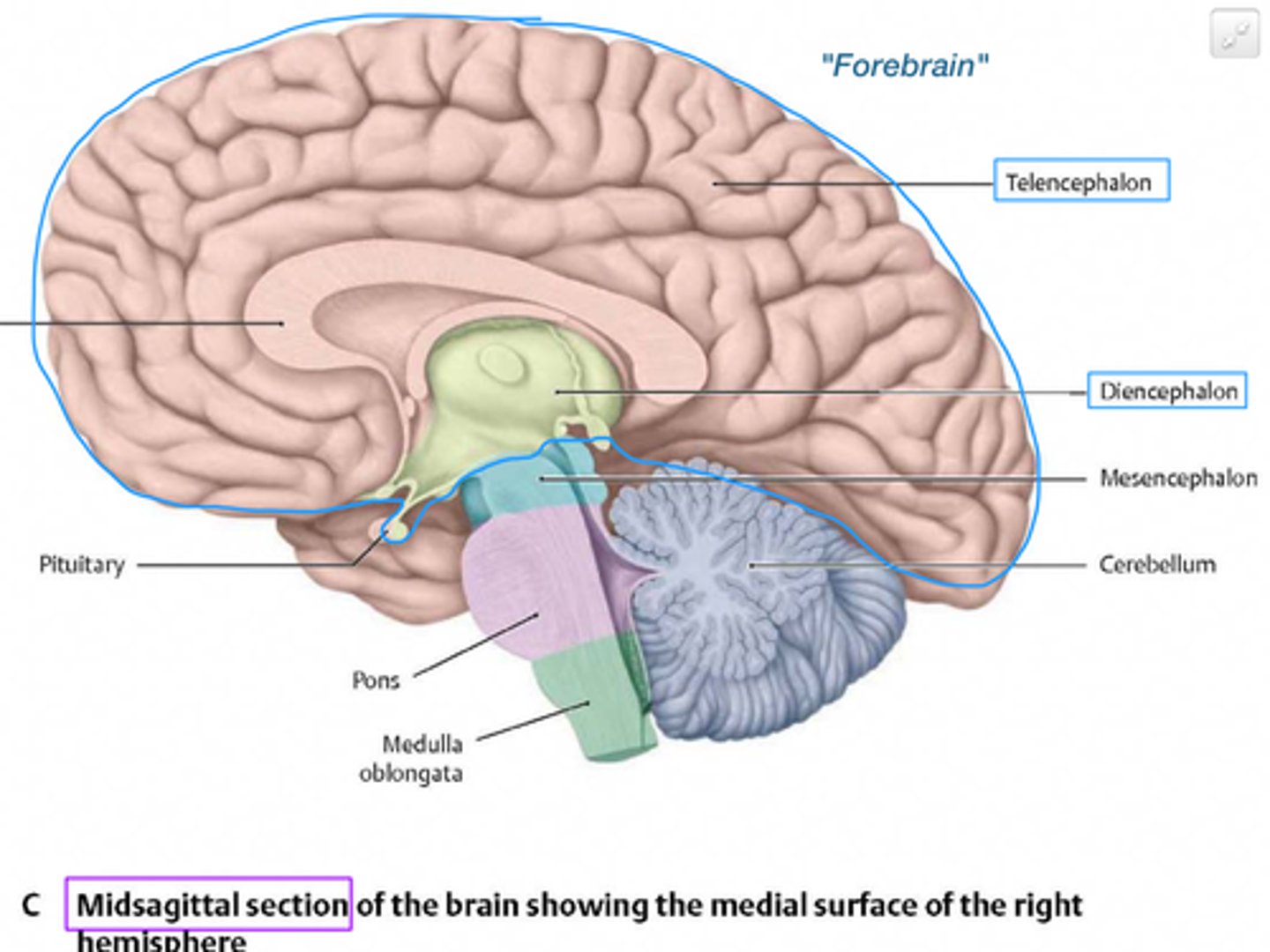
Forebrain comprised of
Cerebrum
Interbrain
Limbic system
Limbic system consists of
thalamus, hypothalamus, amygdala, hippocampus, basal ganglia, cingulate gyrus
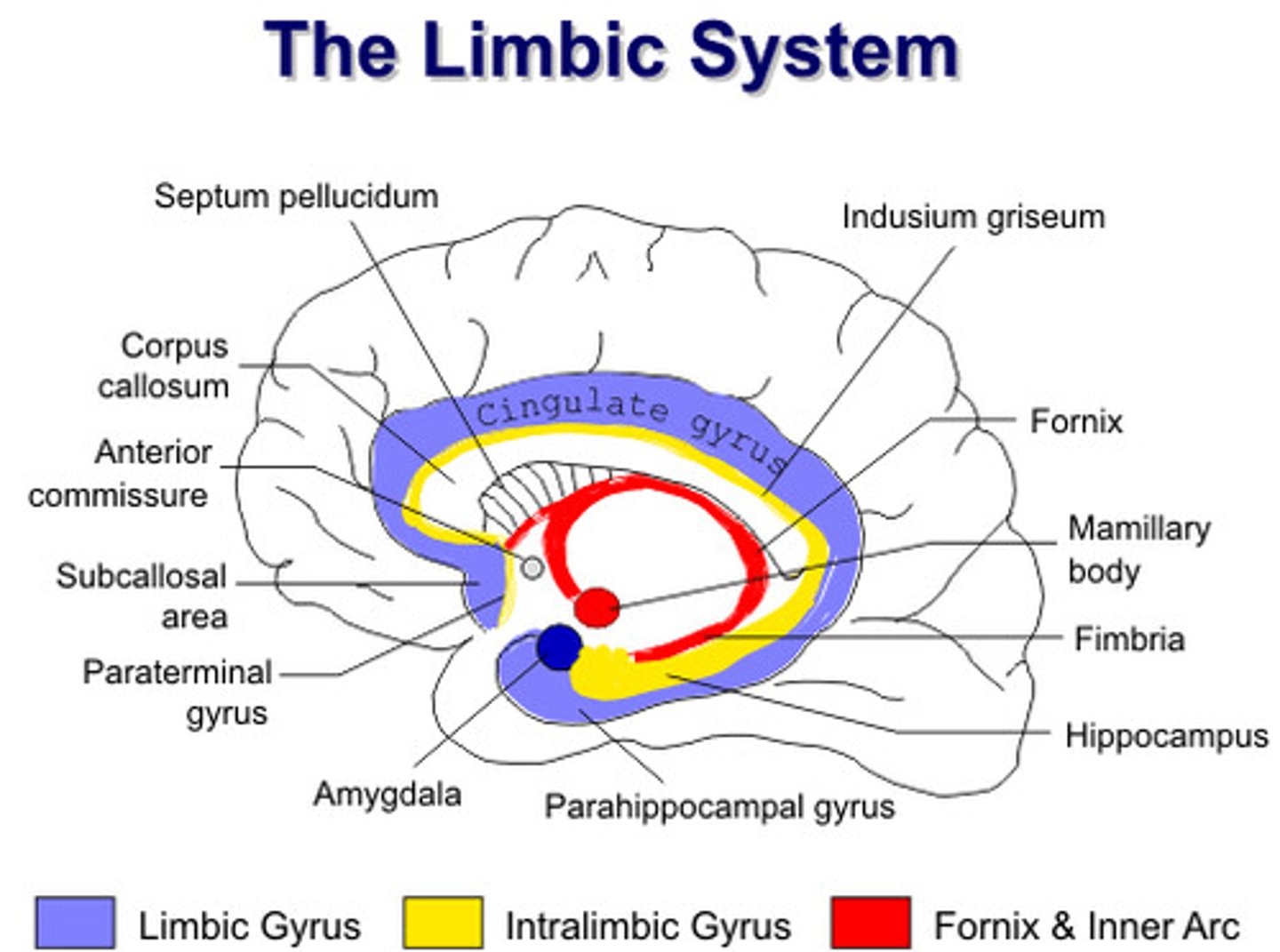
Thalamus
Located above midbrain
Sensory information through the thalamus (except olfactory)
Hypothalamus
Located in front of the thalamus
Communicated with the pituitary gland after the release of hormones
Damage leads to abnormal eating, drinking, temperature regulation etc.
Basal ganglia
Located in front of the thalamus
Integrates motivation and emotional behaviour
Critical for learning and remembering skills
Damage leads to difficulty in starting, stopping, or sustaining movement
Hippocampus
Located below the thalamus and behind the amygdala
Associated with memory
Cingulate gyrus
Located above the corpus callosum
Involved in emotional behaviour
Amygdala
Located below the basal ganglia
Major processing centre for regulating emotions, especially fear and aggression
Involved in tying emotional meaning to memories, and decision making
Midbrain is comprised of
Tectum
Superior colliculus
Inferior colliculus
Tegmentum
Substantia nigra
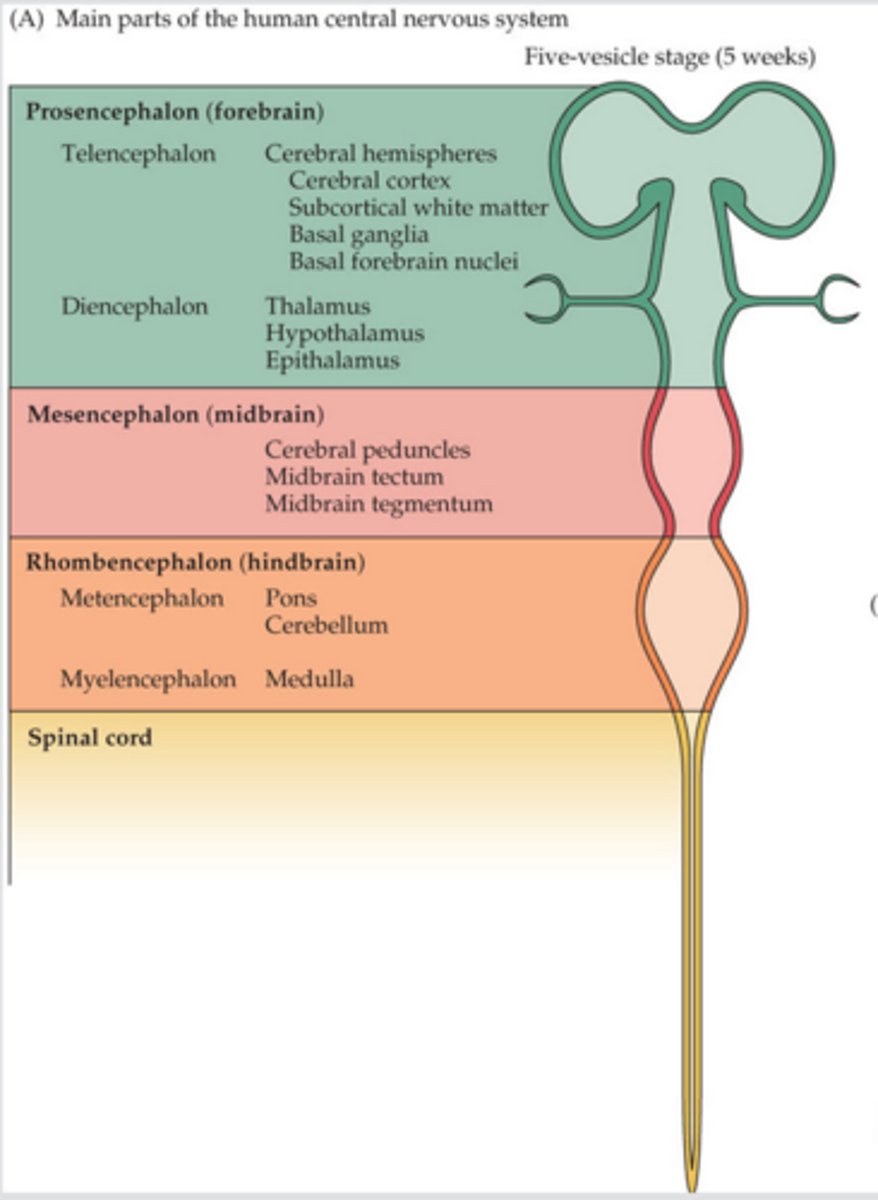
Hindbrain is comprised of
Medulla, pons, cerebellum
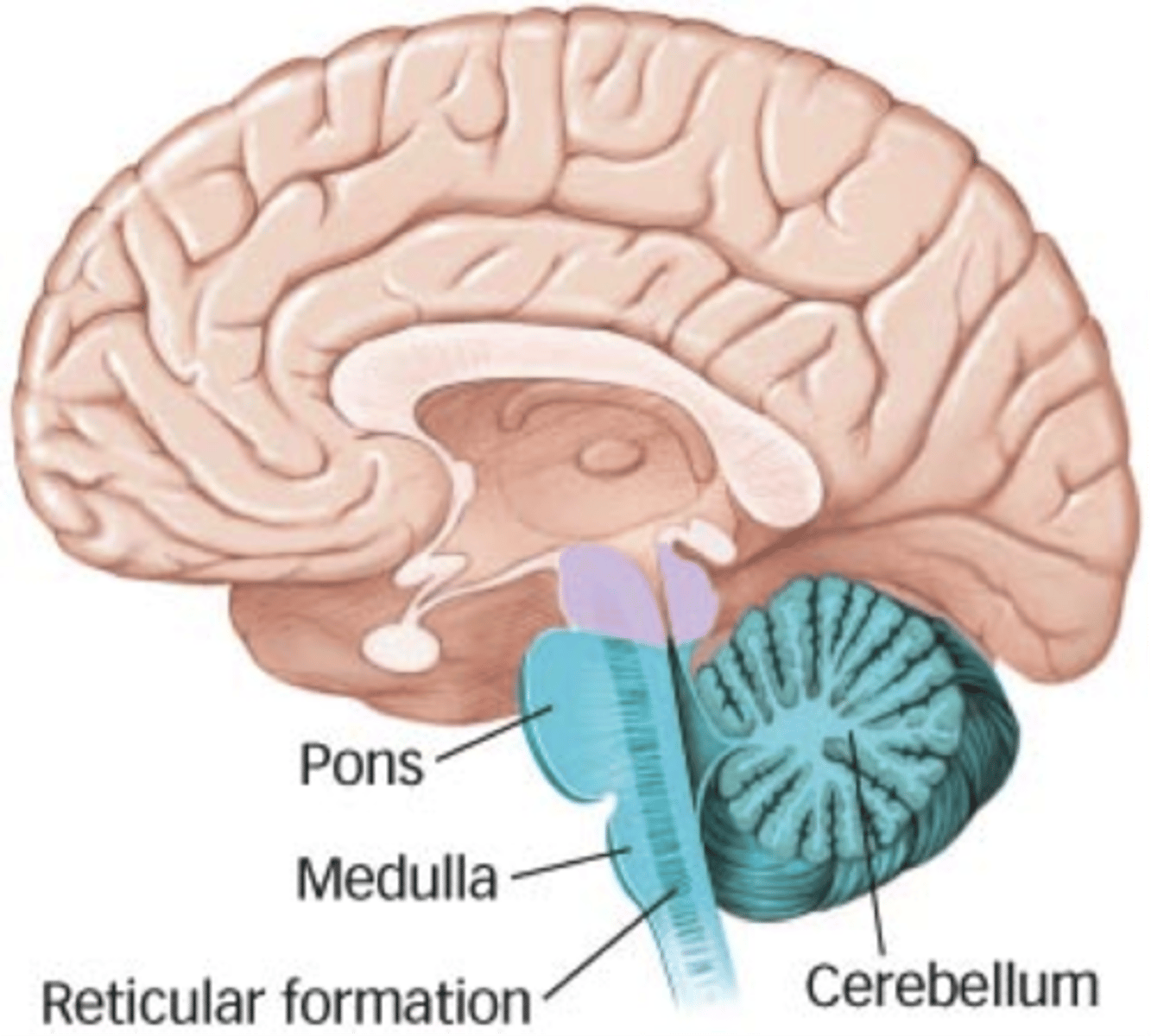
Medulla
Located at the base of the brain, above the spinal cord Connects brain to spinal cord
Controls vital reflexes through the cranial nerves
Pons
Located above the medulla
Axons from the brain cross over to the other side of the body
Cerebellum
Located above the medulla, behind the pons
Contains approximately 70 billion neurons
Responsible for a wide range of functions
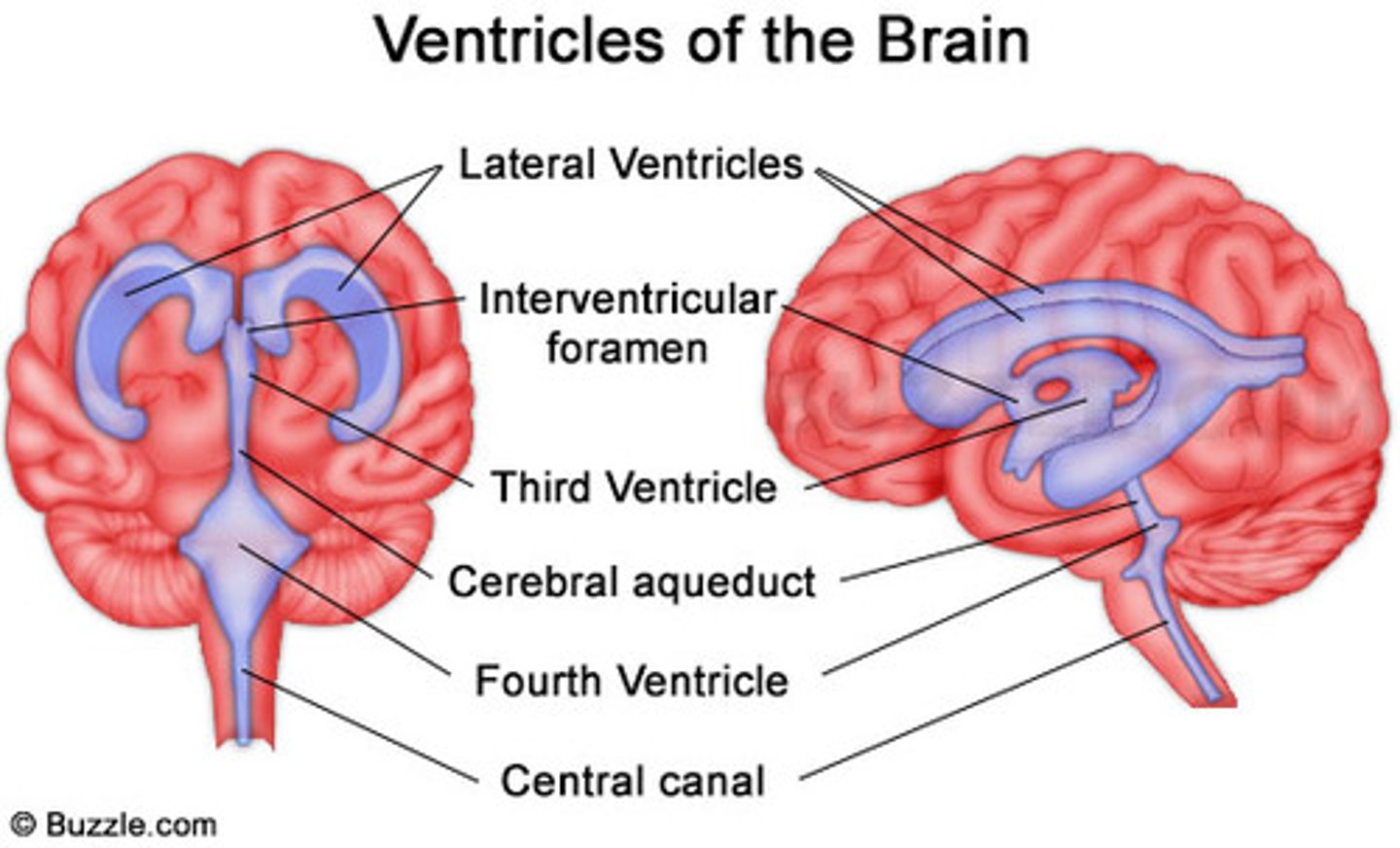
Brain ventricles
Fluid filled cavities
Four in the brain
Fluid also goes into the narrow space between the brain and the meninges
Swollen blood vessels in the meninges are responsible for the pain of a migraine headache
Cerebral cortex
Basic organisation of the brain is similar across species
Differences between species occur in the size of the cerebral cortex and the degree of folding
Contains up to six laminae (layers of cell bodies that are parallel to the surface of the cortex)
Neutrons are also organised into columns of cells
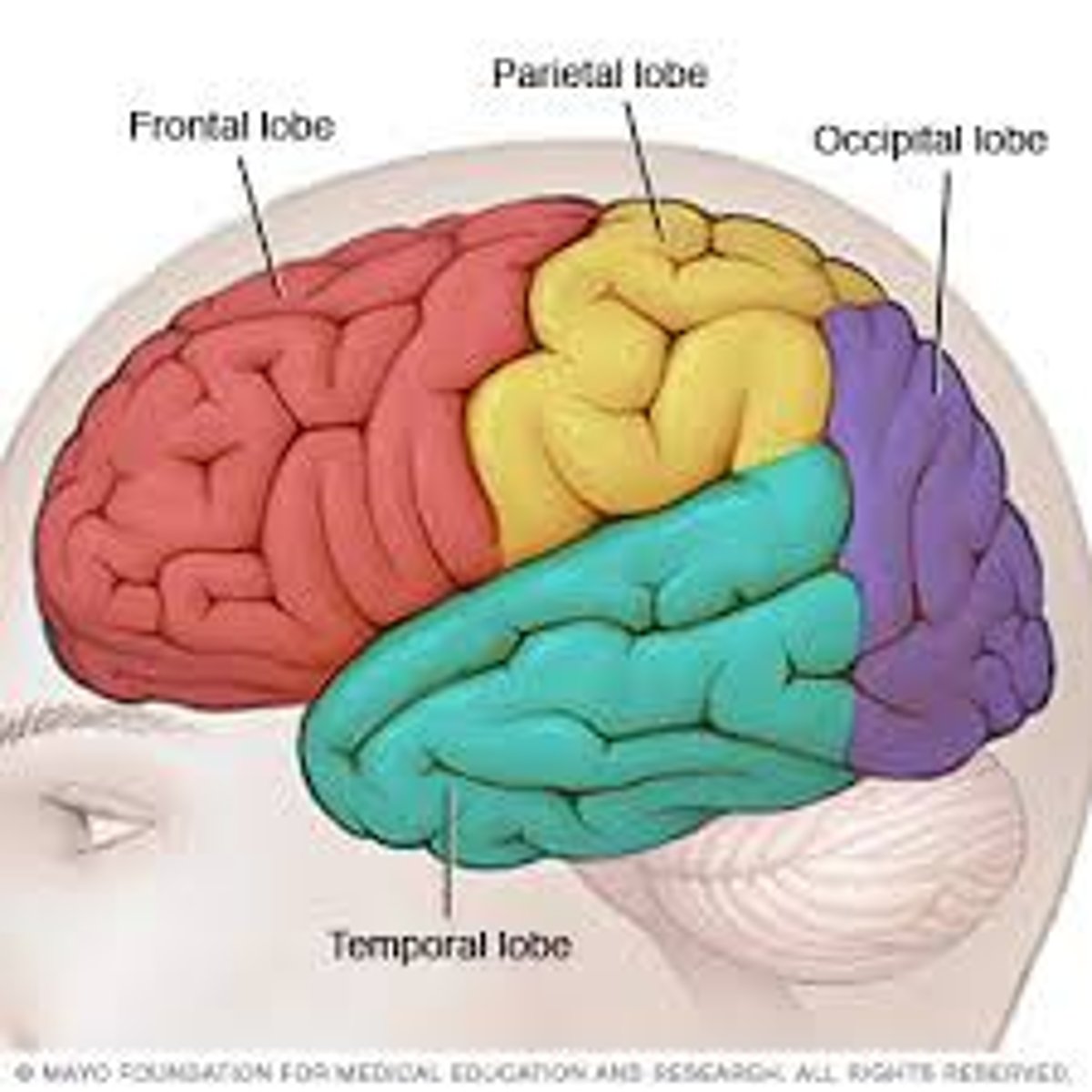
Frontal lobe
Motor control
Speech production
Attention
Working memory
Making decisions
Problem solving
Parietal lobe
Touch perception
Body orientation
Sensory discrimination
Temporal lobe
Process auditory information
Occipital lobe
Vision
Visual experience
Maturation of the brain
Human central nervous system begins to form wen the embryo is approximately 2 weeks
Muscle movements at about 7 weeks
Brain weights;
- 350g at birth
- 1000g by the end of the first year
- 1200-1400 in adulthood
Six stages of development
Neurogenesis, migration, differentiation, myelination, synaptogenesis, pruning
Vulnerability of the brain during development
Vulnerable to malnutrition, toxic chemicals, and infection
E.g., alcohol interferes with proliferation, migration, differentiation, and synaptic transmission
Neuroplasticity
The ability of the nervous system to change its activity in response to stimuli by reorganising its structure, functions, or connection
- E.g., blind people training their brains to improve their other senses
Can occur after brain damage
- E.g., after stroke
Weber-Fechner law
Perception doesn't change as much as the stimulus changes
Transduction
conversion of a stimulus into an action potential by a sensory receptor
Transmission
transfer of information between neurons
Modulation
process in which neural activity is regulated by the central nervous system
Field of view
The centre of visual field is seen by both eyes, known as the binocular field
The periphery of vision field is seen by only one eye, known as the monocular field
Optical nerve
Transmits information from the retina to the brain
Composed of axons from the retinal ganglion cells, forming a thick, cable-like bundle
Optic chaism
Allows for the partial crossing of visual information from each eye, contributing to binocular vision
Optic tract
Transmits information from the optic chaism to the lateral geniculate nucleus of the thalamus
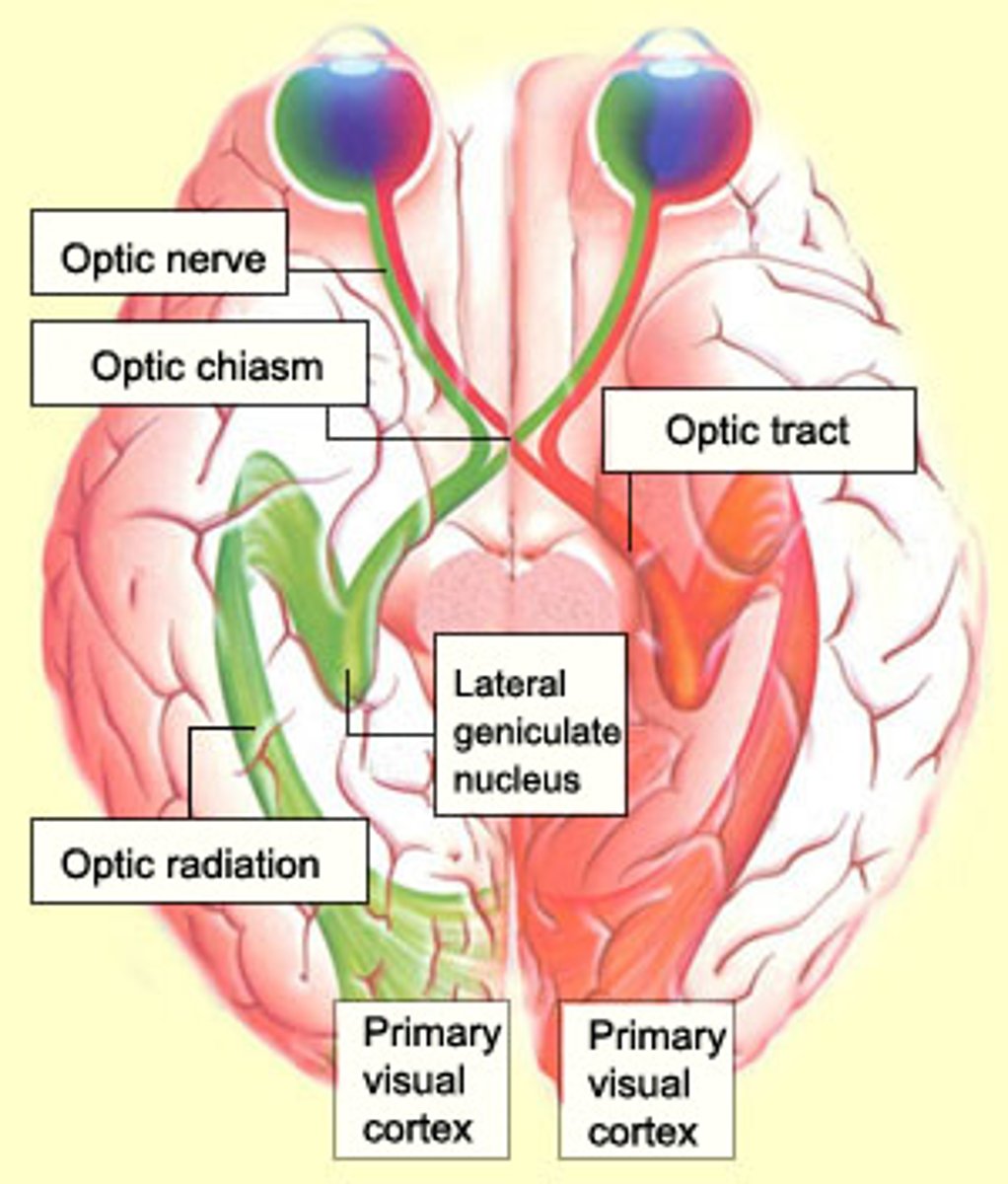
Lateral geniculate nucleus
Sorts visual information based on various attributes
Optic radiations
Transmits information from the lateral geniculate nucleus o the primary visual cortex
Composed of nerve fibres that fan out from the lateral geniculate nucleus
Primary visual cortex
Initial cortical area responsible for processing basic visual information
Located in occipital lobe
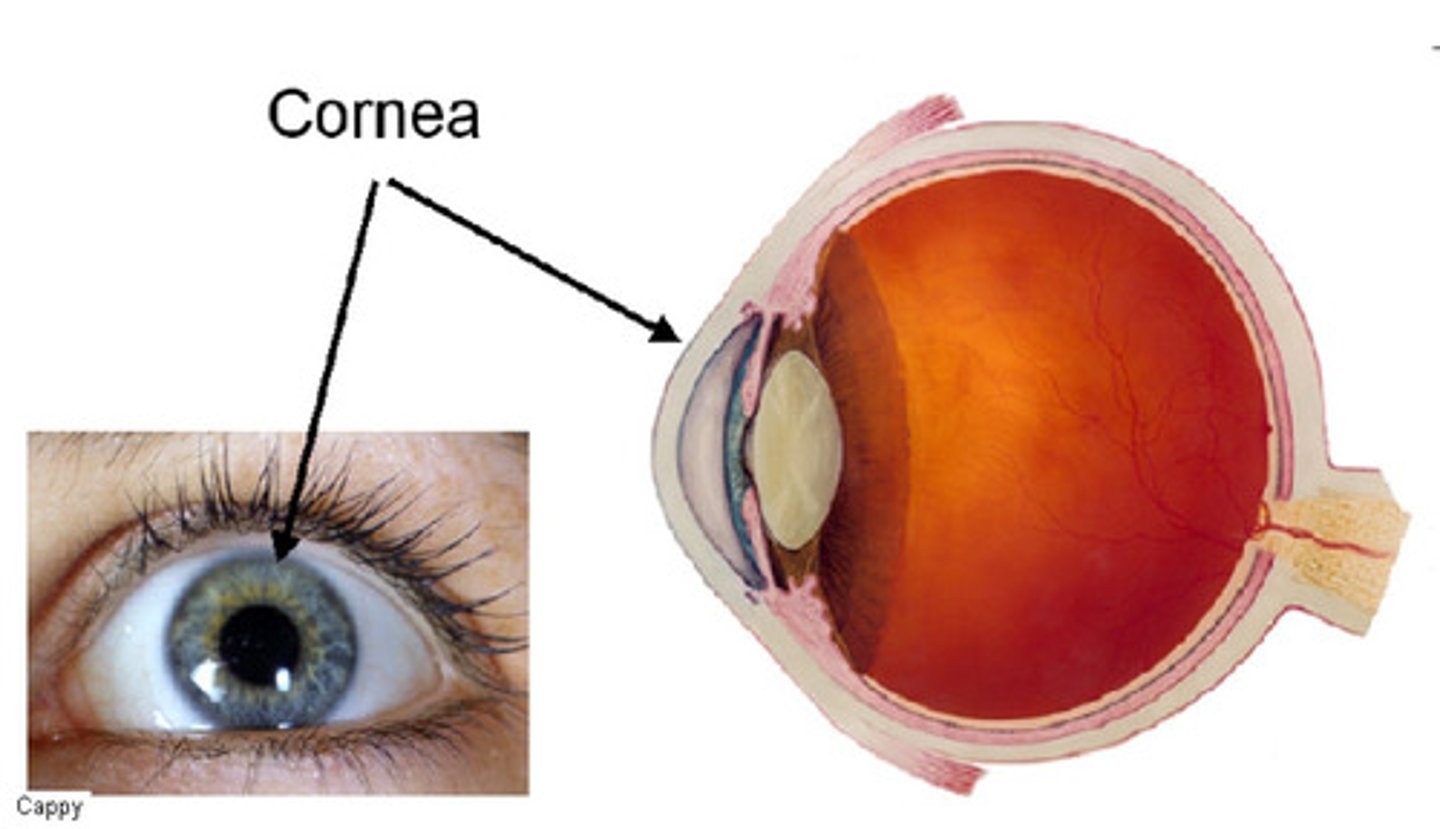
Cornea
Focuses light entering eye
Pupil
adjustable opening in iris controlling light entering