Biological Science Freeman Chapter 4
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
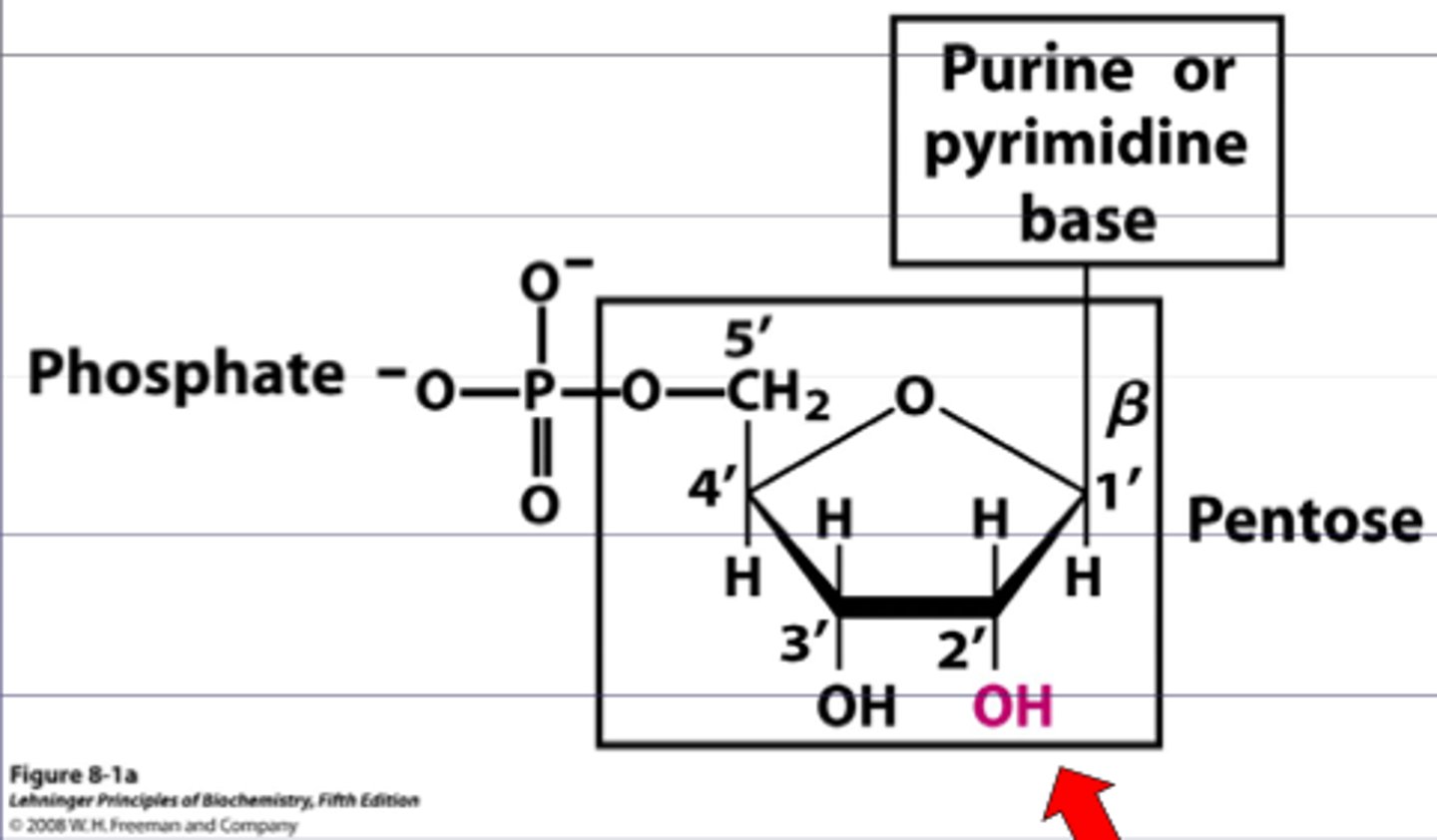
Nucleic Acids
-The polymer subunits that make up nucleotide monomers
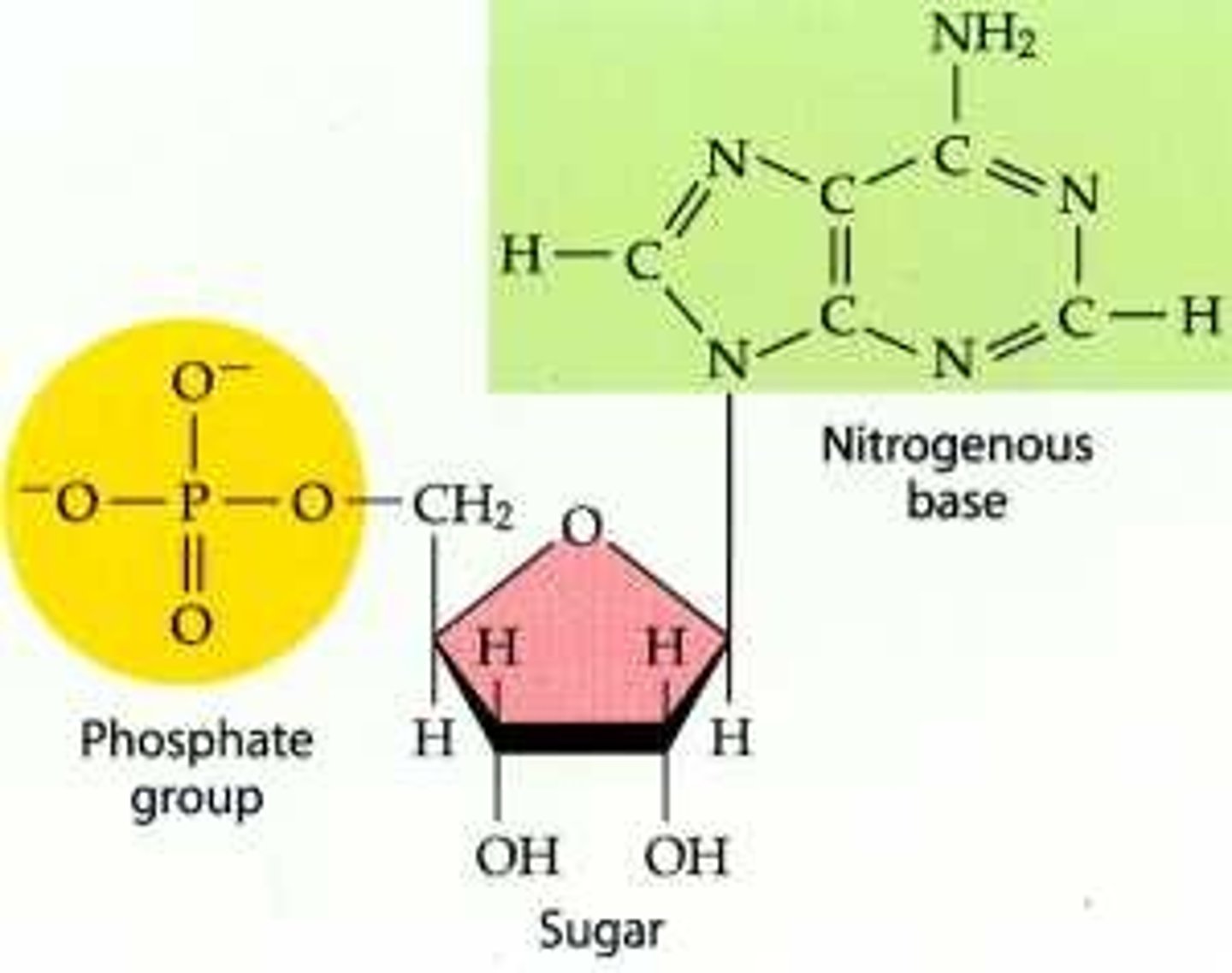
1. phosphate group
2. five carbon sugar
3. nitrogenous (nitrogen containing) base
-both the the phosphate group and nitrogenous base are bonded to the sugar molecule
1. phosphate group
2. five carbon sugar
3. nitrogenous (nitrogen containing) base
-both the the phosphate group and nitrogenous vase are bonded to the sugar molecule
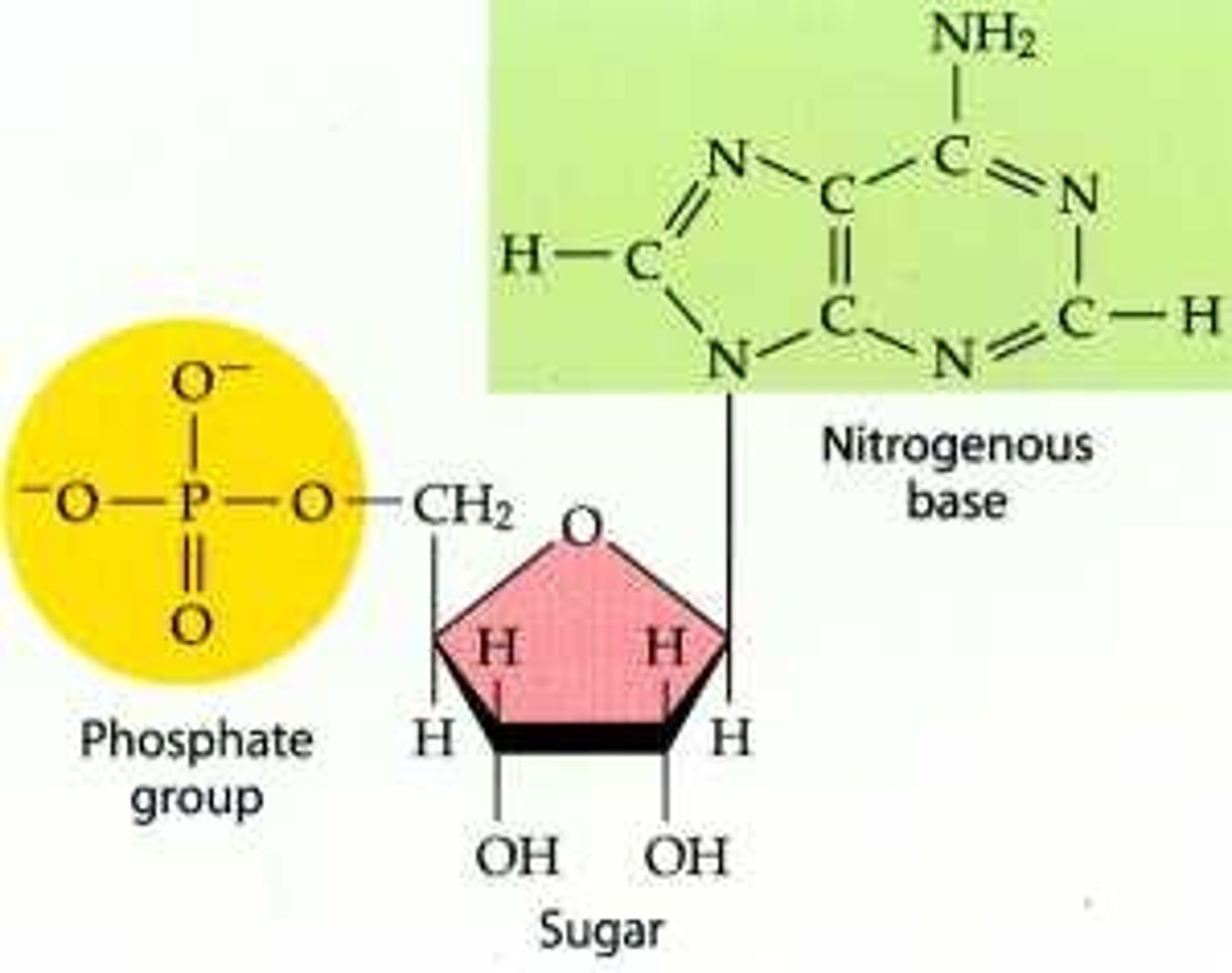
Nucleotides
Basic units of DNA molecule, composed of a phosphate, which is bonded to a 5-carbon sugar, and one of 4 DNA bases
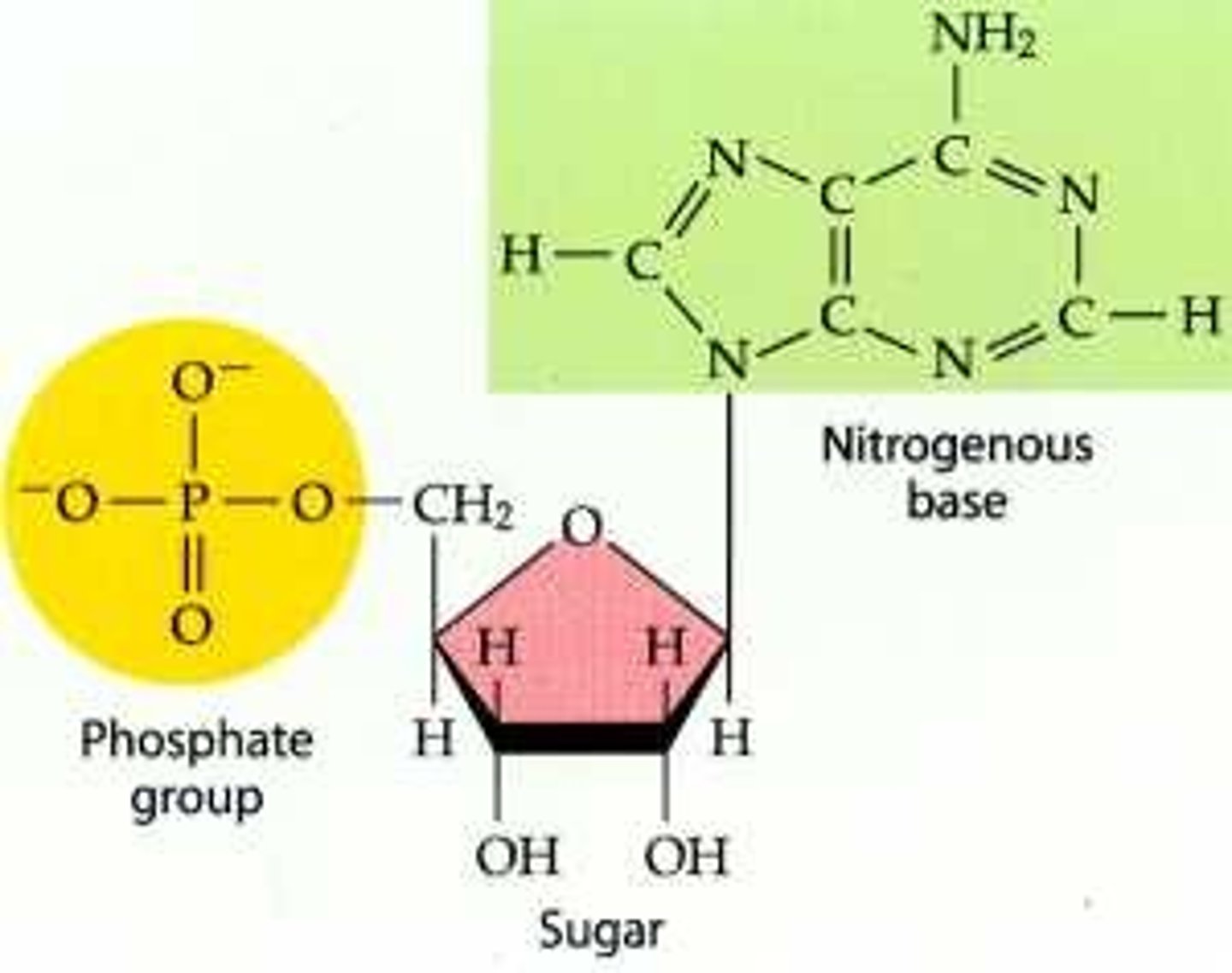
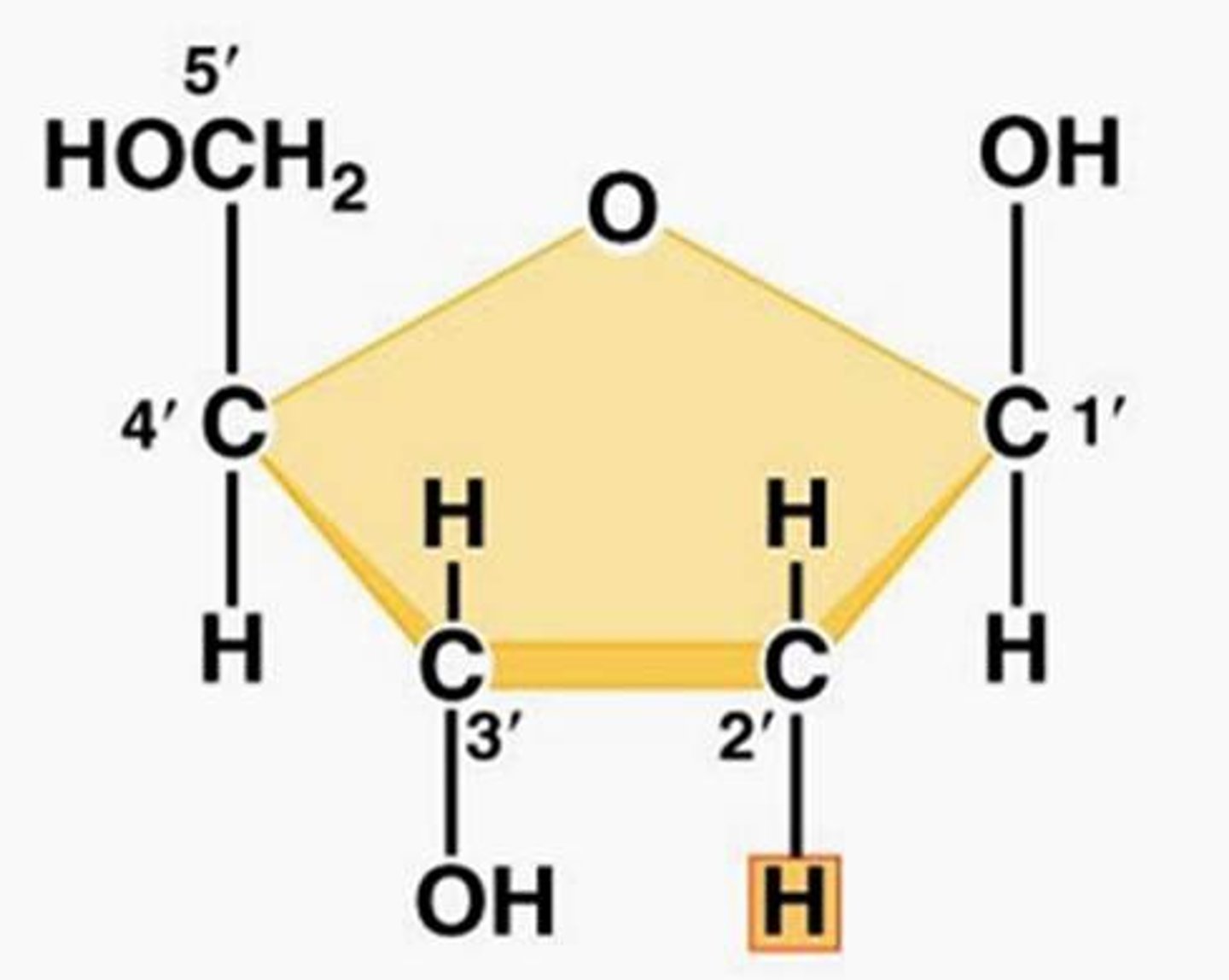
Ribonucleotides
-monomers of RNA
-sugar is ribose
-has an -OH group bonded to the 2' carbon
Deoxyribnucleotides
-monomers of DNA
-sugar is deoxyribose ("lacking oxygen")
-has H instead at 2' carbon
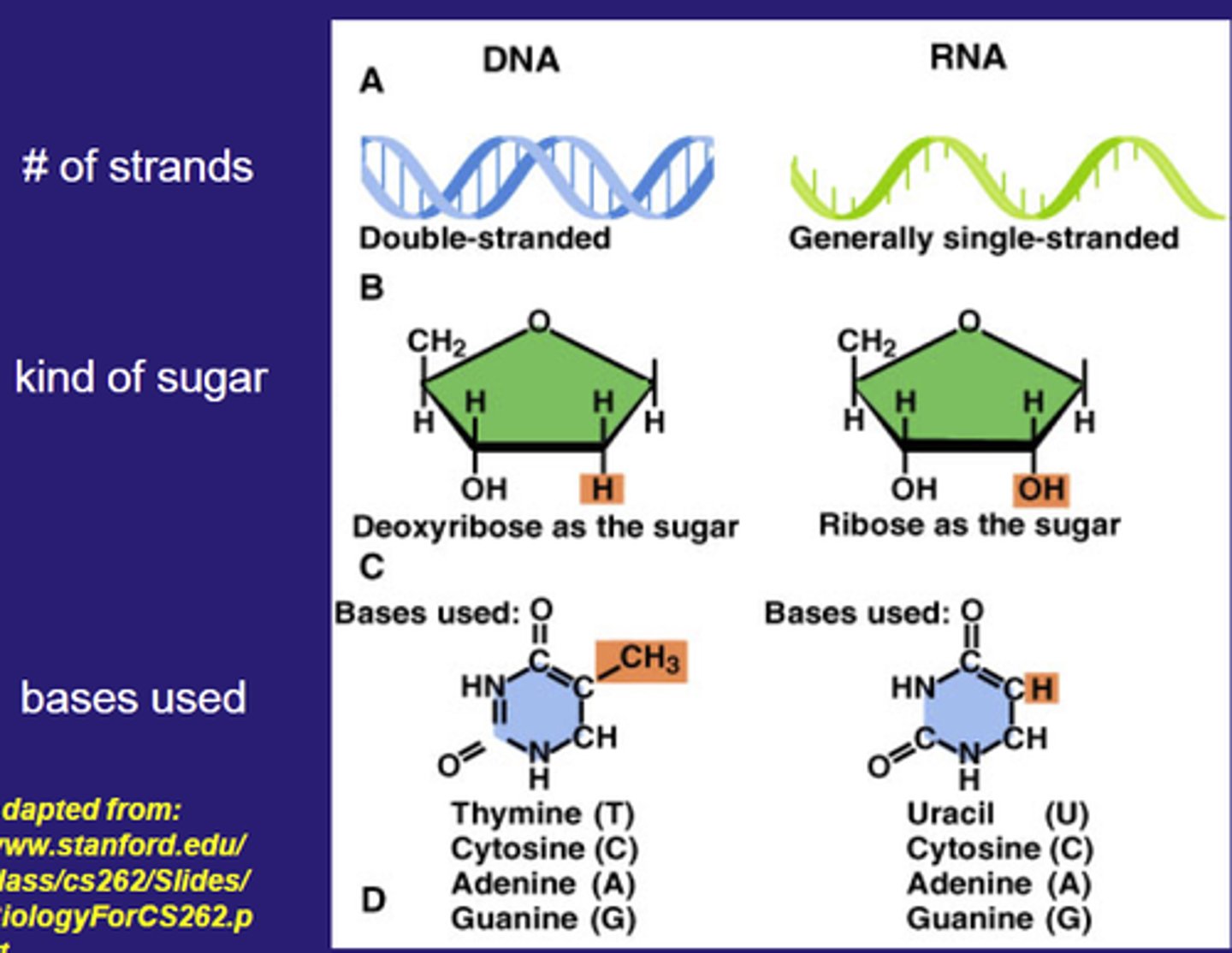
deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
-stores and transmits genetic information in modern cells
-A nucleic acid molecule
-usually a double-stranded helix
-each polynucleotide strand consists of nucleotide monomers with a deoxyribose sugar and the nitrogenous bases A T C G
-capable of being replicated and determining the inherited structure of a cell's proteins.
-has the information required for the organism's growth and reproduction
2 Groups of Nitrogenous Bases
1. Purines
-9 atoms (2 rings)
-Adenine (A), Guanine (G)
2. Pyrimidines
-6 atoms (1 ring)
-Cytosine (C), Uracil (U) in RNA, Thymine (T) in DNA
-For every A = amount of G, same with C=T (DNA) and C=U (RNA)
Could chemical evolution produce nucleotides?
-simulations of chemical evolution
-have not yet produced nucleotides
-sugars in nitrogenous bases are easily made
-minerals in deep-sea vents preferentially bind to ribose
-produces a high concentration of ribose
How do nucleic acids form?
-nucleotides polymerize via condensation reactions
Ribonucleic Acid (RNA)
-A type of nucleic acid consisting of nucleotide monomers with a ribose sugar and the nitrogenous bases adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and uracil (U)
-usually single-stranded
-functions in protein synthesis
-much more diverse in size, shape, and reactivity than DNA
-Highly versatile
-information-containing molecule
-capable of self-replication
-capable of catalyzing reactions: ribozymes
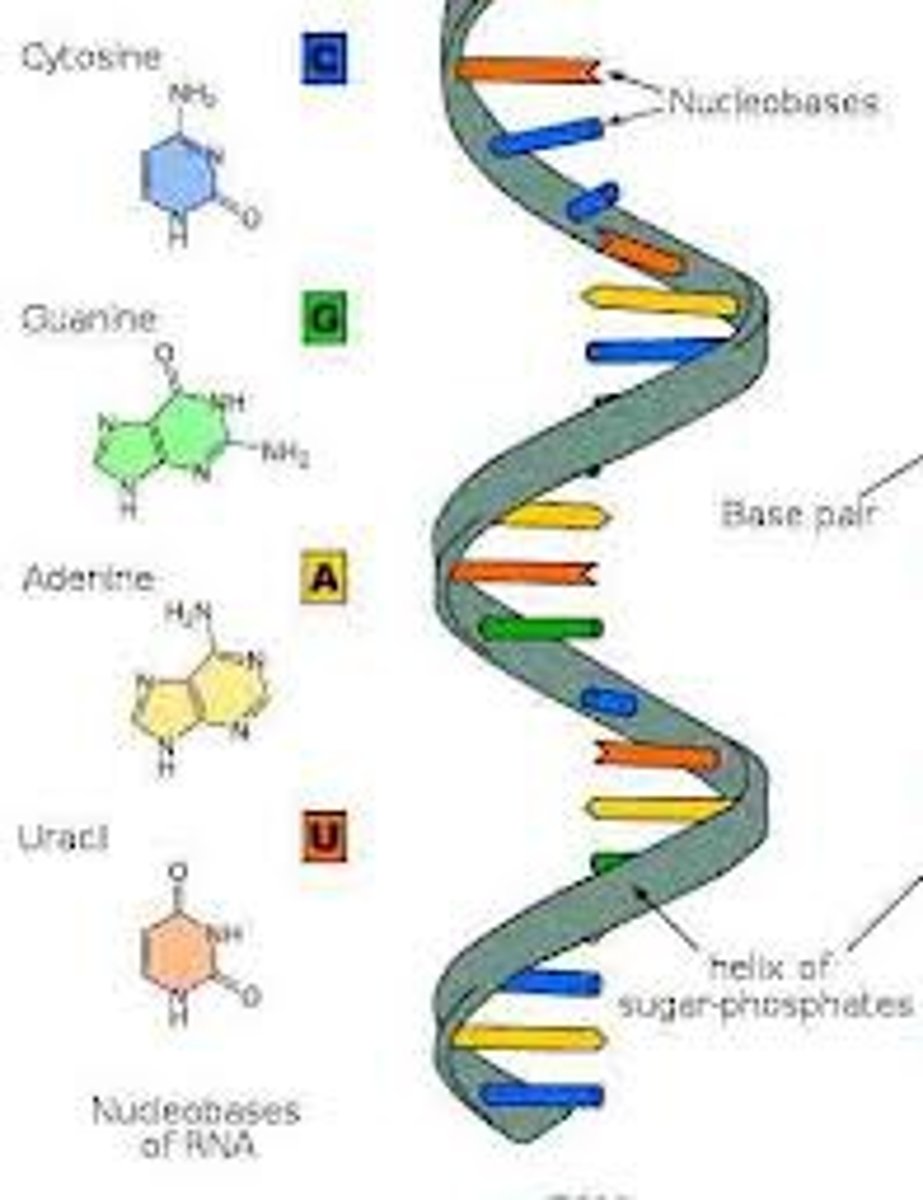
Purines
Adenine and Guanine
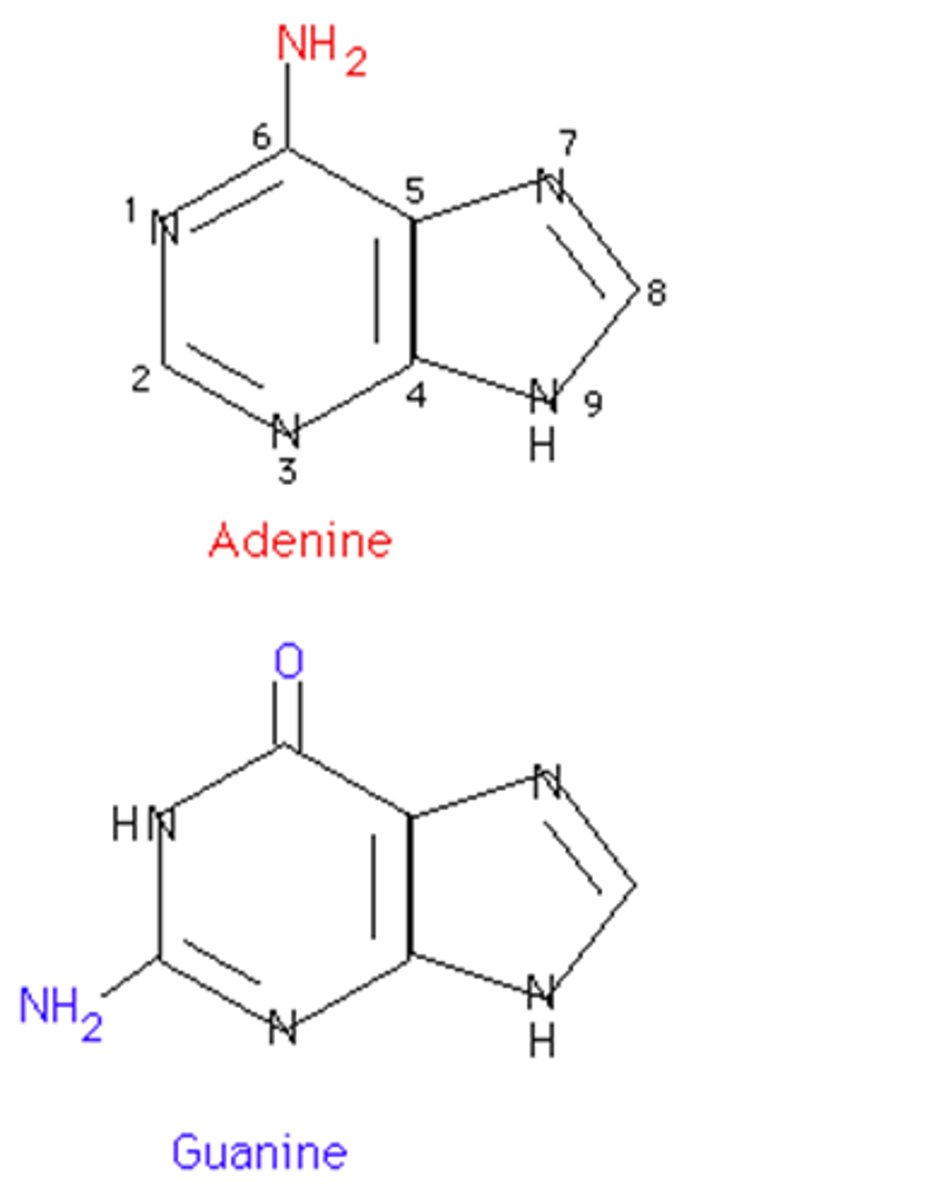
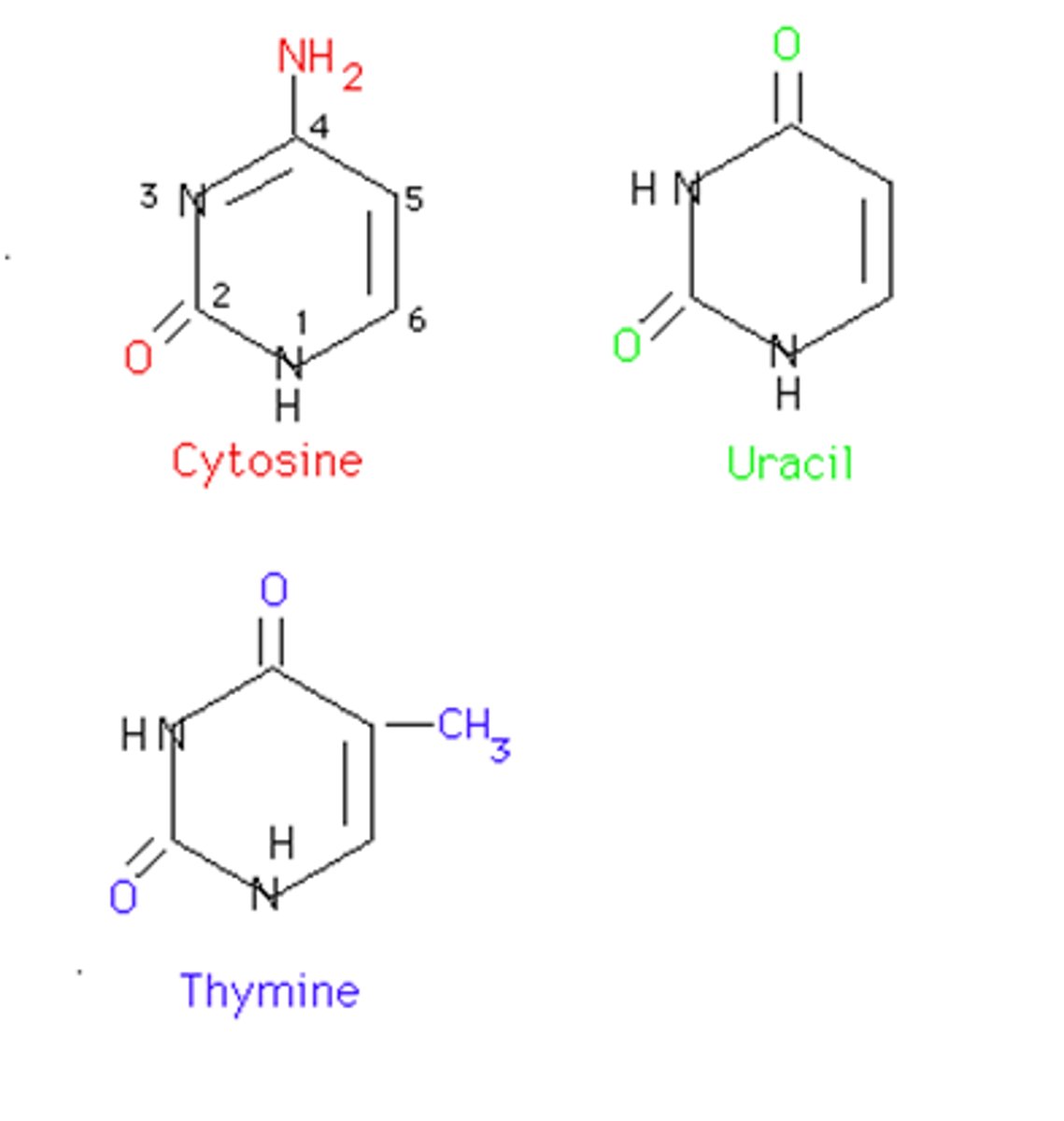
Pyrimidines
Cytosine and Thymine (in DNA) and Uracil (in RNA)
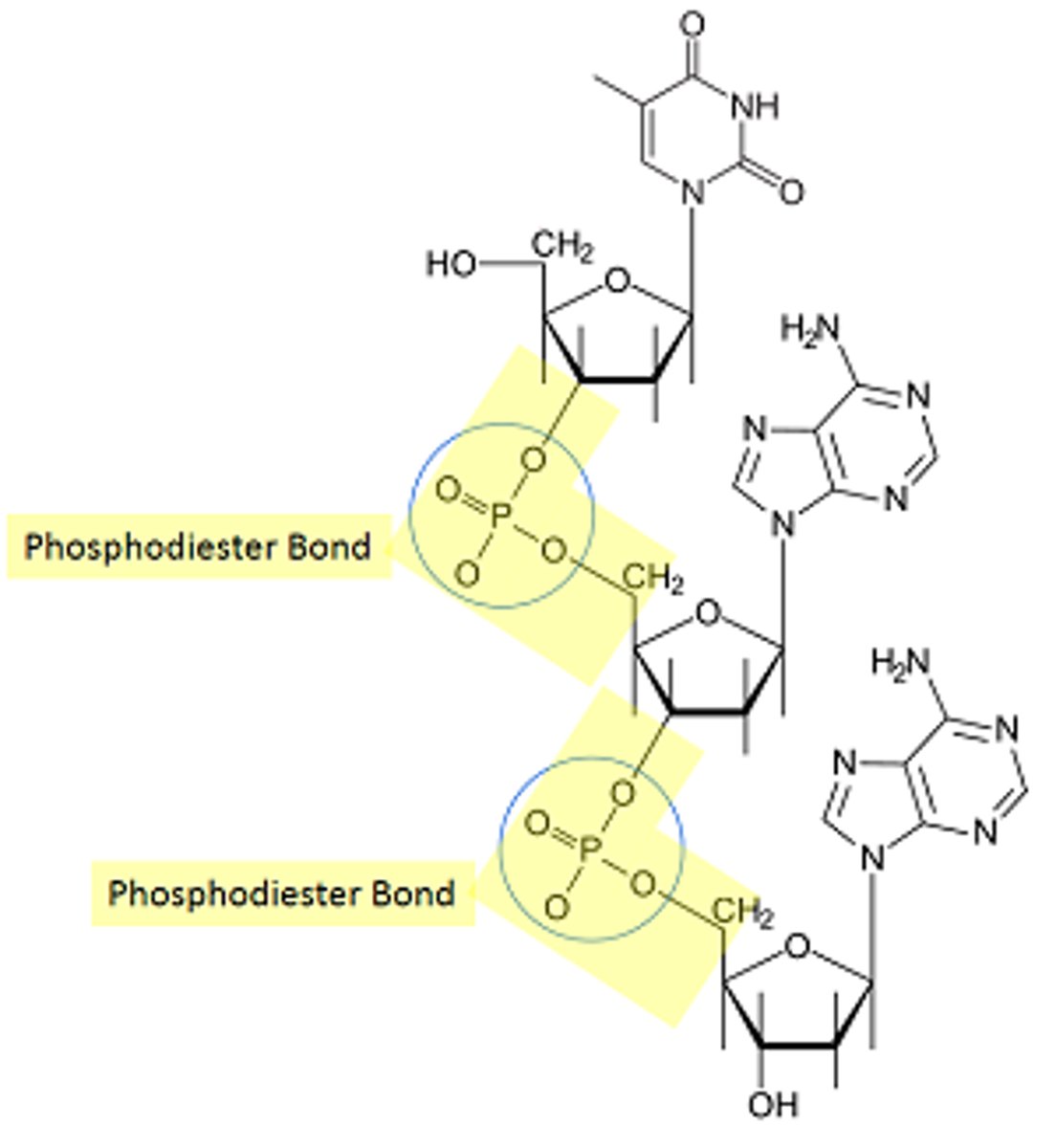
phosphodiester linkage
-"bonds with phosphorus"
-bond occurs with 5' carbon of phosphate group and -OH group on 3' carbon of another
What direction are DNA strands?
-5' > 3' direction
-Phosphate group (5') > Hydroxyl Group (3')
-Reflects the order that nucleotides are added to the growing molecule
Polymerization Requires an Energy Source
-polymerization is catalyzed by enzymes
-energy for polymerization comes from adding two extra phosphate groups to nucleotides
-negatively charged phosphate groups repel each other
-Linking them generates very high energy bonds
-Forms "activated nucleotides"
-Example: Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
X-ray crystallography
-a technique used to determine the three-dimensional helical structure of a protein
-Franklin and Wilkins
Antiparallel
The opposite arrangement of the sugar-phosphate backbones in a DNA double helix.
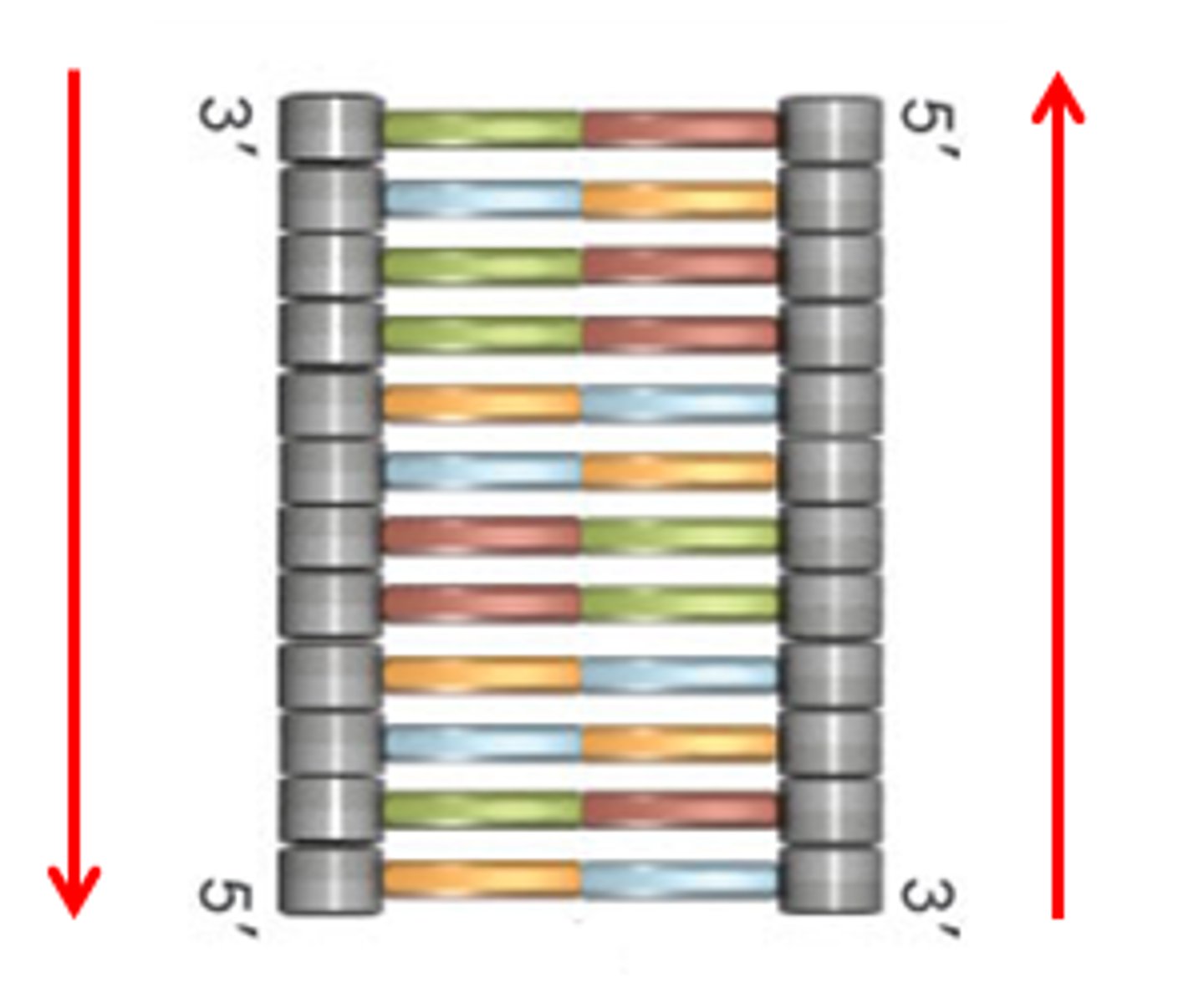
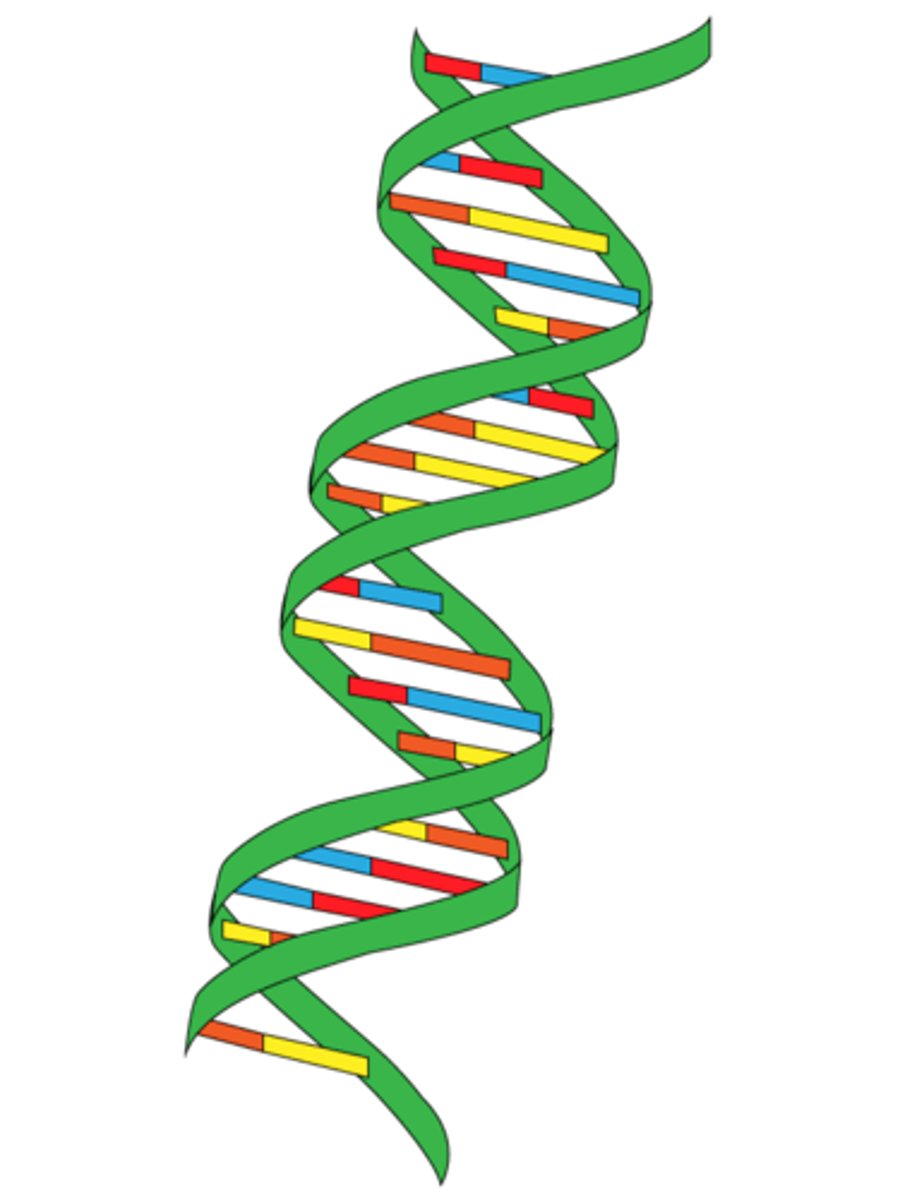
Double Helix
-The form of native DNA, referring to its two adjacent polynucleotide strands wound into a spiral shape.
-sugar-phosphate backbone faces exterior
-nitrogen base pairs face the interior
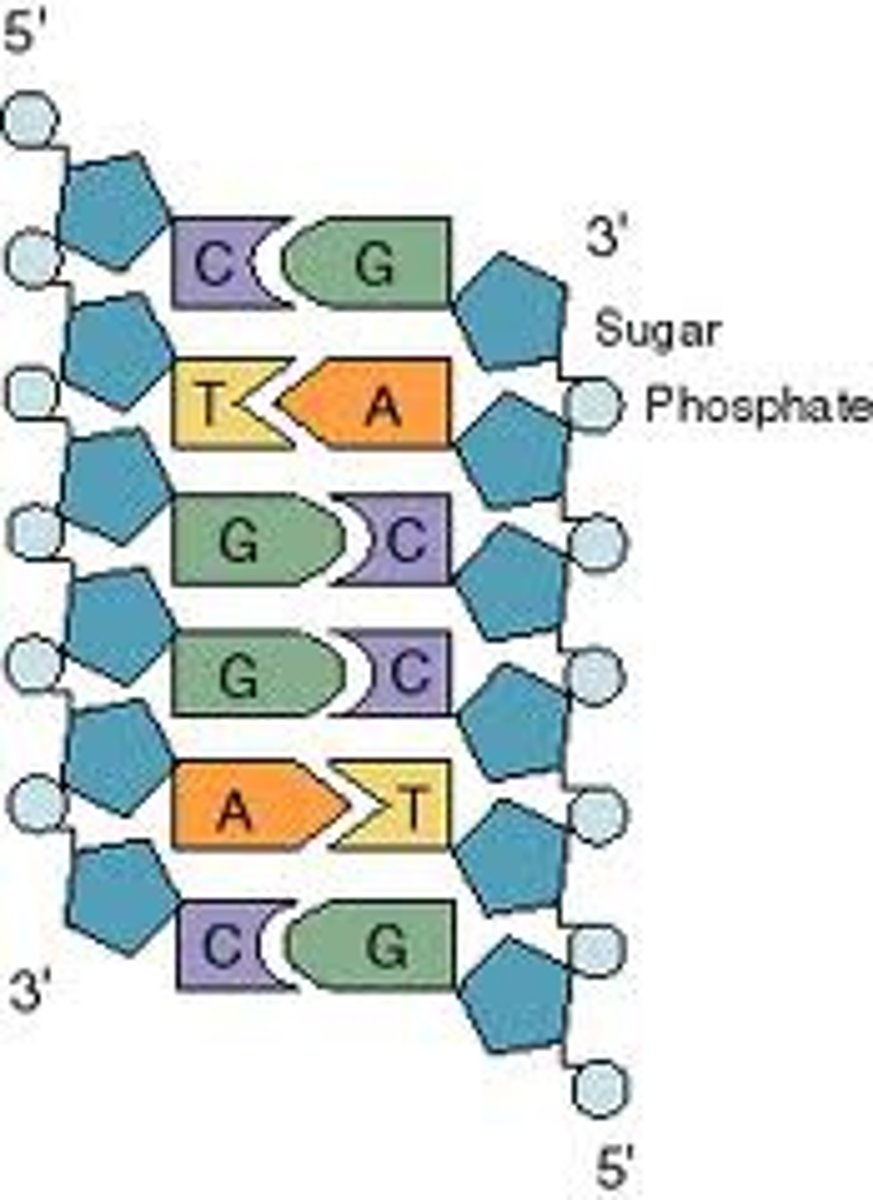
Complementary base pairing (Watson-Crick Paring)
Hydrogen bonding between particular pyrimidines and purines. Adenine & Thymine. Cytosine & Guanine.
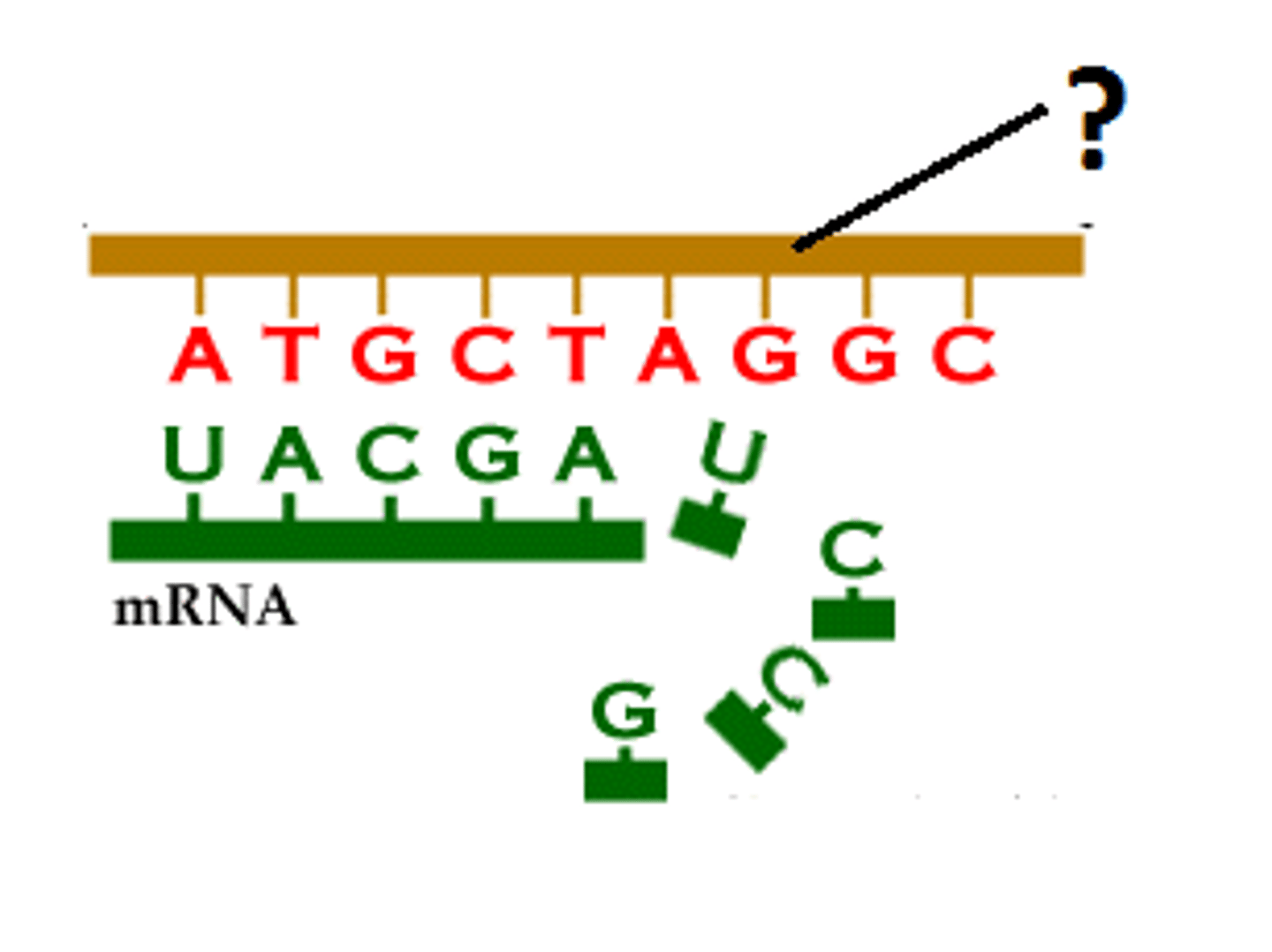
Template Strand
The DNA strand that provides the template for ordering the sequence of nucleotides
DNA grooves
1. Major Groove
2. Minor Groove
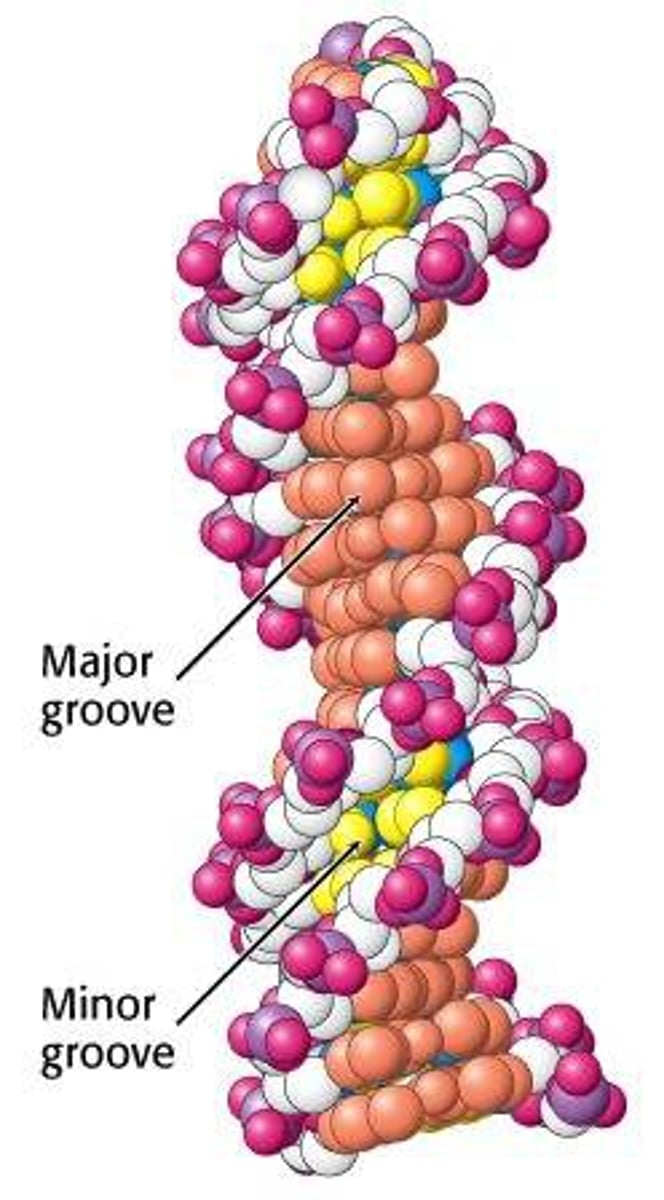
Additional Information about DNA
-one turn of helix = 10 base pairs
-hydrophobic interaction cause DNA to twist
-DNA hydrophillic overall
-negatively charged phosphate groups face out
What happens when DNA is too loose of tight?
-It forms supercoils
-wraps around proteins
Compacting DNA allows...
-discrete units for cell division
-helps DNA fit inside nucleus
-contributes to its function
DNA Replication has three steps:
Step 1: Two strands are separated by breaking the hydrogen bonds with heat or enzymes.
Step 2: Free deoxyribonucleotides hydrogen-bond complementary bases on the original strand of DNA (template strand).
-Phosphodiester linkages form to create new strand (complementary strand)
Step 3: Complementary base pairing allows each stand to be copied exactly
-produces two identical daughter molecules

Is DNA a stable structure?
-DNA is very stable
-It is resistant to chemical degradation
- Makes it a reliable store for genetic information
-Stable molecules such as DNA make poor catalysts
-DNA has never been observed to catalyze a reaction
-Biologists think first life form made of RNA
How does the structure of RNA differ from DNA?
1. RNA contains ribose instead of deoxyribose
-2' -OH group on ribose more reactive than -H
-RNA much less stable than DNA
2. RNA contains Uracil instead of Thymine